Содержание
- 2. 1. Definition of a contract. Process of contract making. 2. Types of contracts. 3. Structure of
- 3. A contract is an agreement giving rise to obligations which are enforced or recognized by law.
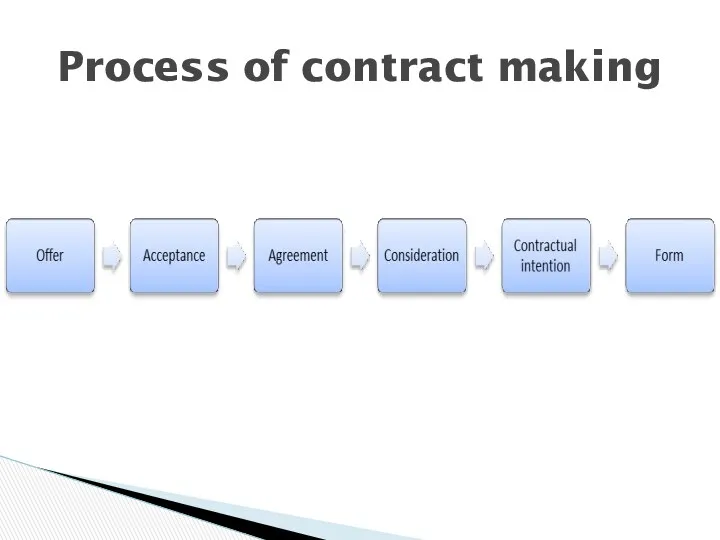
- 4. Process of contract making
- 5. A. OFFER An offer is an expression of willingness to contract on specified terms, made with
- 6. An acceptance is a final and unqualified expression of assent to ALL the terms of an
- 7. Features of Acceptance:
- 8. Consideration is promise by one party to a contract that constitutes the price for which the
- 9. Contractual intention means that the parties must intend their agreement to be legally binding. D. CONTRACTUAL
- 10. Contracts can be formal and informal; oral or in writing. Note: There are statutory exceptions to
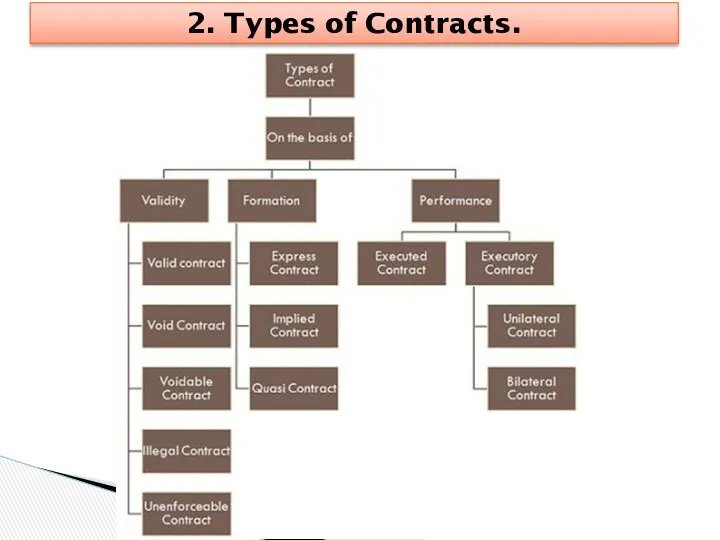
- 11. 2. Types of Contracts.
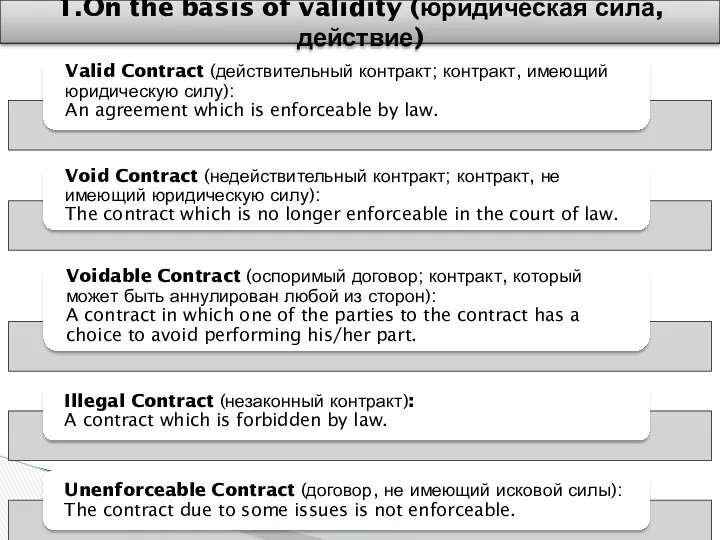
- 12. 1.On the basis of validity (юридическая сила, действие)
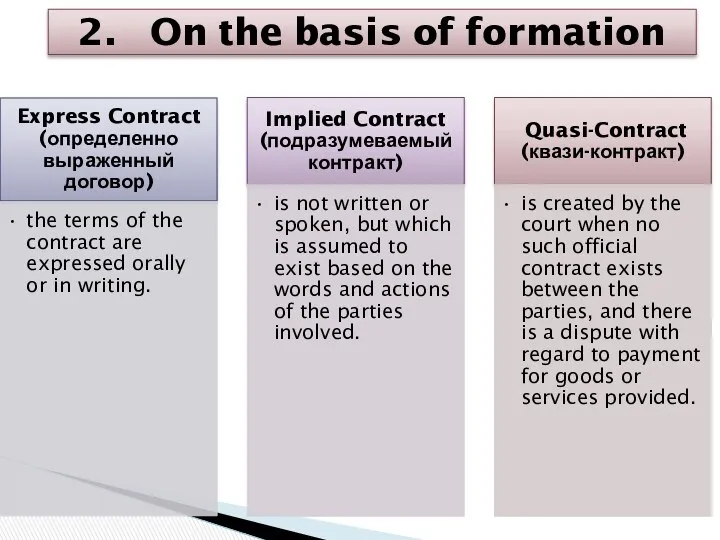
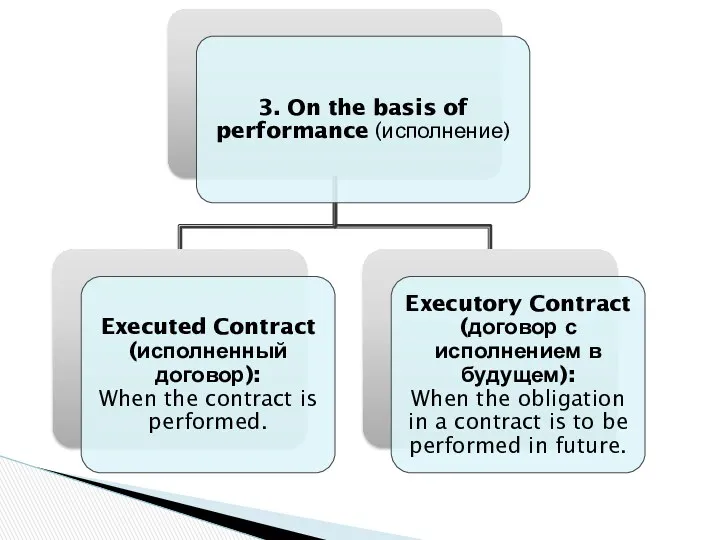
- 13. 2. On the basis of formation
- 16. SELF-TEST QUESTIONS 1. An implied contract a. must be in writing b. is one in which
- 17. 3. STRUCTURE OF A CONTRACT
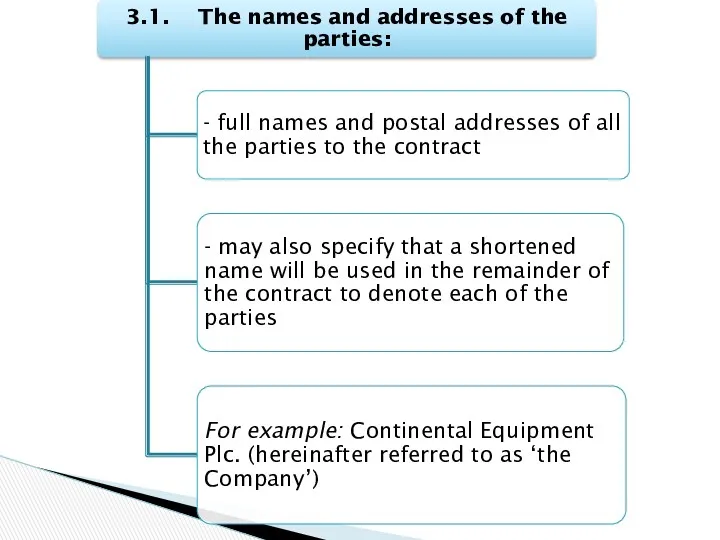
- 19. Recitals provide the reader with a general idea about - the purpose of the contract, -
- 20. 3.3. Definitions
- 22. 3.4. Subject
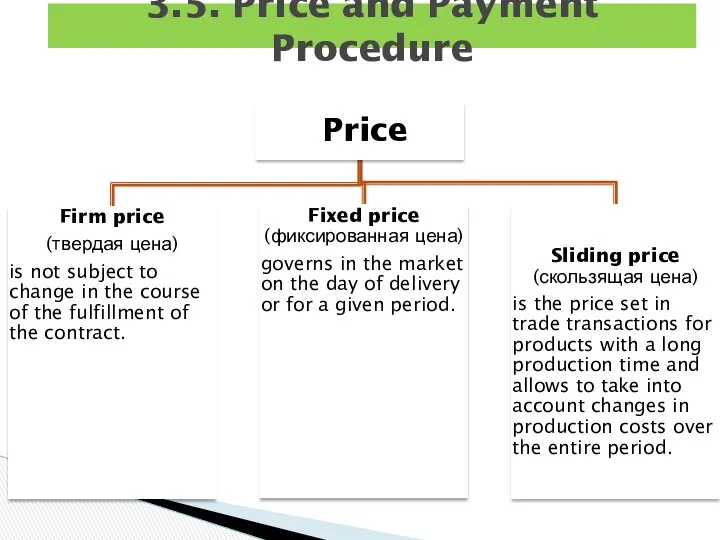
- 23. 3.5. Price and Payment Procedure
- 25. Example:
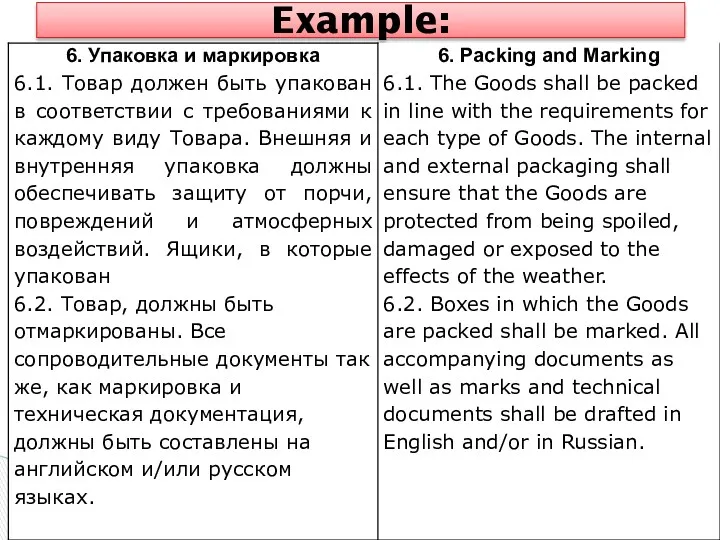
- 26. 3.6. Packing and Marking
- 27. Example:
- 28. 3.7. Delivery Terms
- 29. СРТ - «Carriage Paid to / Перевозка оплачена до» CIP - «Carriage and Insurance Paid to
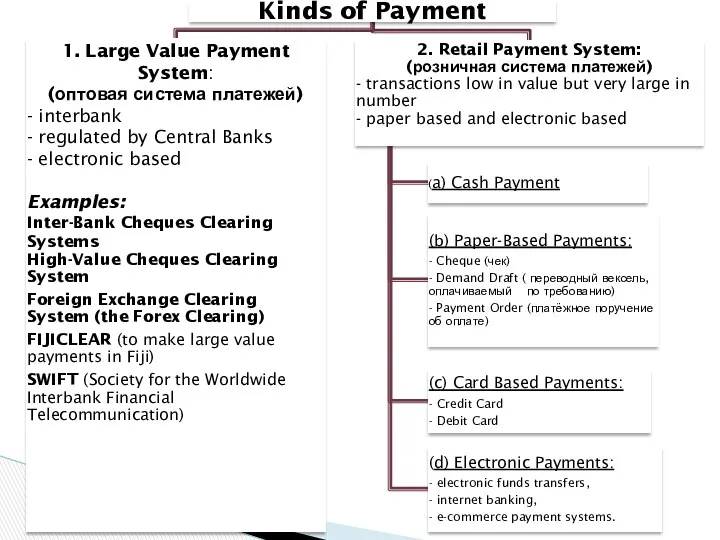
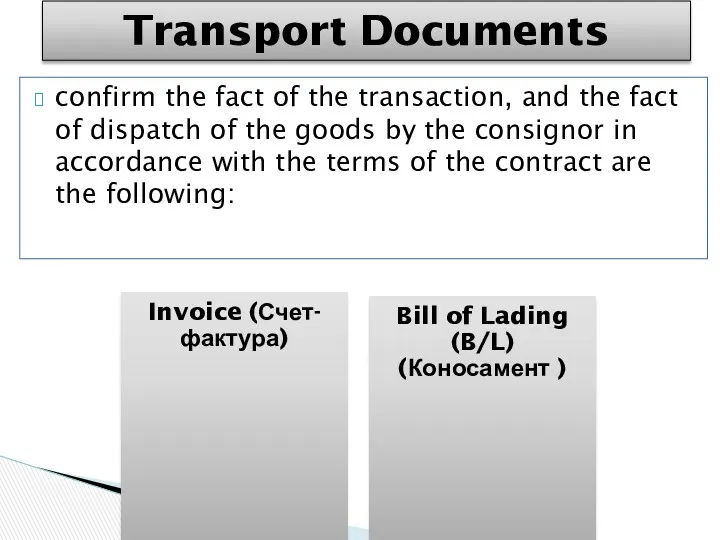
- 30. confirm the fact of the transaction, and the fact of dispatch of the goods by the
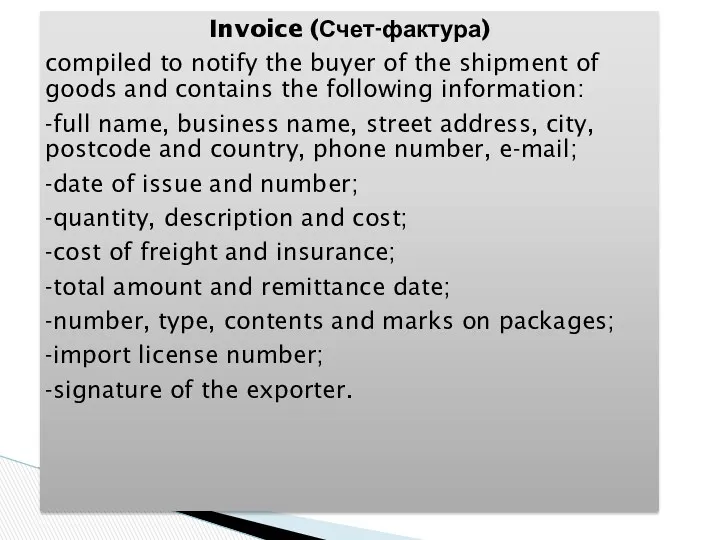
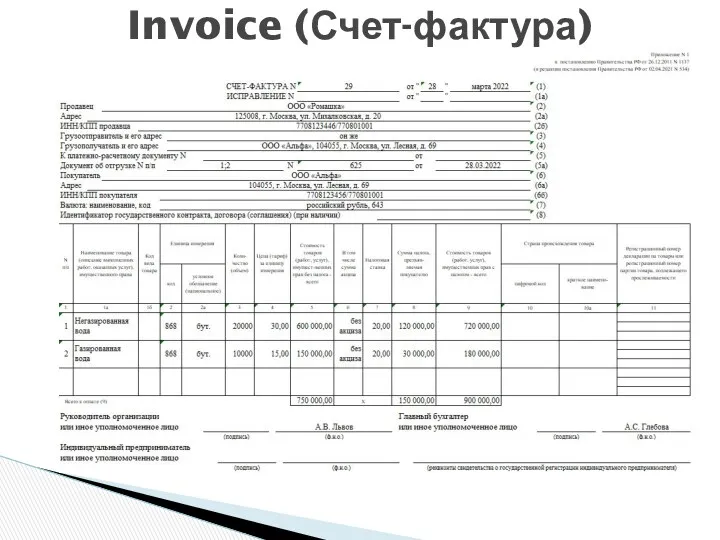
- 32. Invoice (Счет-фактура)
- 34. Bill of Lading (B/L) (Коносамент )
- 35. Example:
- 36. The idea of insurance is to obtain indemnity in case of damage or loss. Insurance is
- 37. Example:
- 38. 3.9. Force Majeure
- 39. Example:
- 40. Sanctions are commercial and financial penalties. Example: In the event of delay in delivery of the
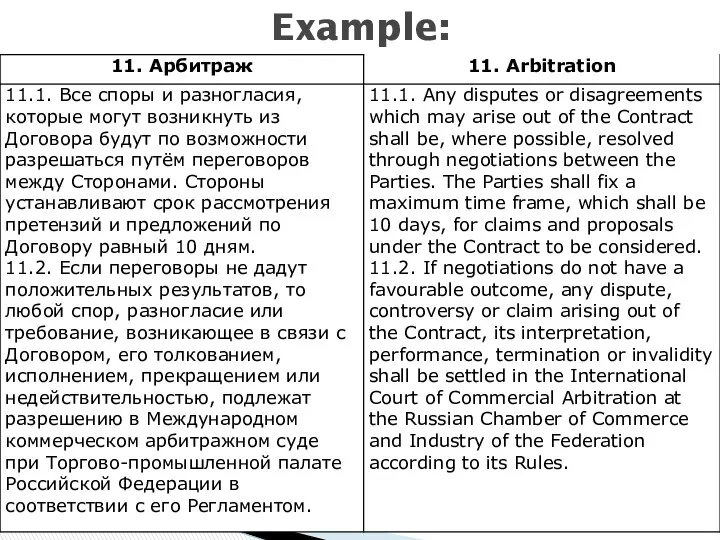
- 41. Arbitration is the hearing and settling of a dispute by a third party agreed to by
- 42. Example:
- 43. 12. Other conditions 13. Judicial addresses of the Sides 14. Signatures of the seller and the
- 45. Скачать презентацию





























 Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal Civil Rights Movement
Civil Rights Movement You are going to give a talk about travelling
You are going to give a talk about travelling Special question. Grade 2
Special question. Grade 2 Spotlight 2. Unit 6. My Favourite Food
Spotlight 2. Unit 6. My Favourite Food I would have... if I were... by helgabel
I would have... if I were... by helgabel Английский язык. Занятие 8
Английский язык. Занятие 8 The Title of my project is Welcome to Russia!
The Title of my project is Welcome to Russia! Fast food
Fast food Space programm of Russia
Space programm of Russia My name is Alina
My name is Alina The Weather
The Weather Locations and directions
Locations and directions Present Tenses
Present Tenses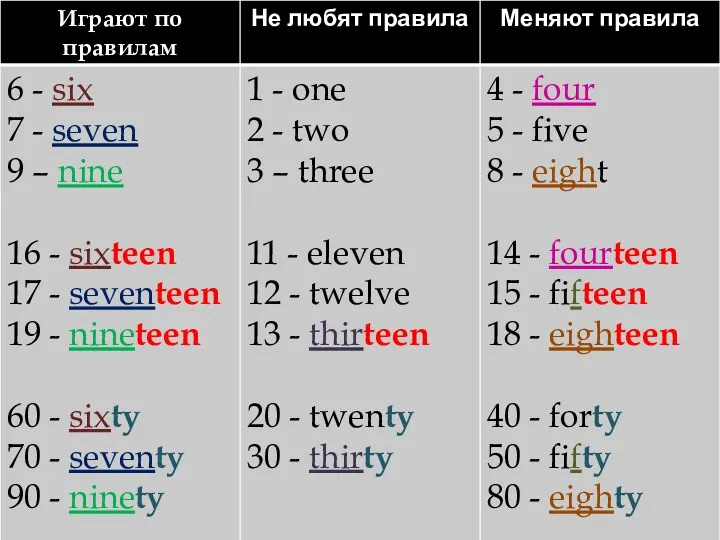 Numerals
Numerals Личное письмо. Подготовка к ЕГЭ по английскому языку
Личное письмо. Подготовка к ЕГЭ по английскому языку Indefinite article. Неопределенный артикль
Indefinite article. Неопределенный артикль Conditionals - сложноподчиненные предложения
Conditionals - сложноподчиненные предложения What are animal prosthetics
What are animal prosthetics Сочинительные союзы
Сочинительные союзы Простое настоящее время
Простое настоящее время Puzata Hata (Ukraine)
Puzata Hata (Ukraine) Tigers
Tigers Chromium ore enrichment (beneficiation) technology
Chromium ore enrichment (beneficiation) technology Great Britain. (Часть 1)
Great Britain. (Часть 1) English in the World of Work. Английский в мире труда
English in the World of Work. Английский в мире труда Глагол have got, has got
Глагол have got, has got The Gerund
The Gerund