Содержание
- 2. Resources (and sources for these slides) Richard C. Wydick, Plain English for Lawyers (5th ed. 2005)
- 3. Web resources Legalwriting.net Wayne Schiess’s Legal-Writing Blog: http://www.utexas.edu/law/faculty/wschiess/legalwriting/ Plain Language Association International (List of websites offering
- 4. Web resources, continued Michigan State Bar Association Plain language articles http://www.michbar.org/generalinfo/plainenglish/columns.cfm U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
- 5. Legal Writing in English - Unit One Lawyers spend half their time trying to understand what
- 6. Wydick’s view We lawyers do not write plain English. We use eight words to say what
- 7. A practicing lawyer’s view Lawyers in practice are generally judged by the final product they produce:
- 8. Ruth Bader Ginsburg Associate Justice U.S. Supreme Court Legal Writing in English - Unit One
- 9. Lawyers serve their clients best when their readers can quickly and firmly grasp their points. Readers
- 10. Ferret - “To ferret out . . .” *verb-based writing Legal Writing in English - Unit
- 11. Justice Ginsberg is saying Legal writing should be: Clear; Concise; Simple; and Well-ordered. “I see but
- 12. William Zinsser says Remember that what you write is often the only chance you’ll get to
- 13. Plain English for Lawyers The premise of this book is that good legal writing should not
- 14. Plain English for Lawyers Chapter 1 – Why Plain English? Chapter 2 – Omit surplus words
- 15. BE CONCISE Legal Writing in English - Unit One
- 16. Write concisely Write only what needs to be said. Eliminate the unnecessary. Cut clutter of all
- 17. Revise for brevity and clarity First, eliminate. Ask each word: What are you doing for me?
- 18. Example The landlord made a decision to delay replacement of the heating units. 12 words The
- 19. Example Smith’s case is an illustration of this point. 8 words Smith’s case is illustrative of
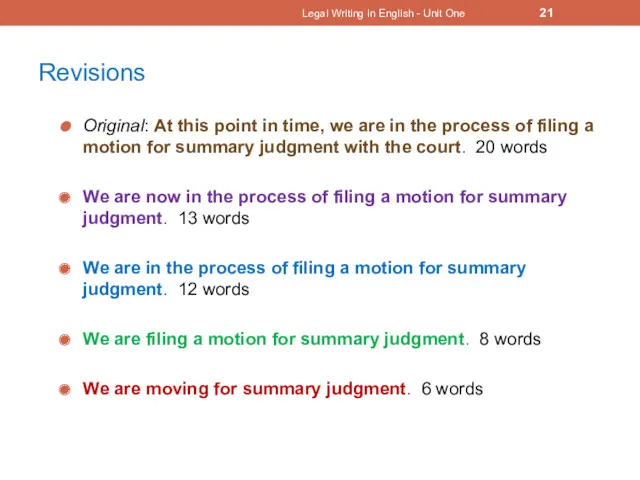
- 20. Revise this sentence At this point in time, we are in the process of filing a
- 21. Revisions Original: At this point in time, we are in the process of filing a motion
- 22. EXERCISES Paula LaRocque, The Book on Writing: The Ultimate Guide to Writing Well (2003) Legal Writing
- 23. Sentence 1 They are of the opinion that the agency needs to make changes in its
- 24. Sentence 1 revised They think the agency should change its proposal. Original: They are of the
- 25. Sentence 2 Prior to moving to Chicago, he lived in the city of Philadelphia. Legal Writing
- 26. Sentence 2 revised He lived in Philadelphia before moving to Chicago. Original: Prior to moving to
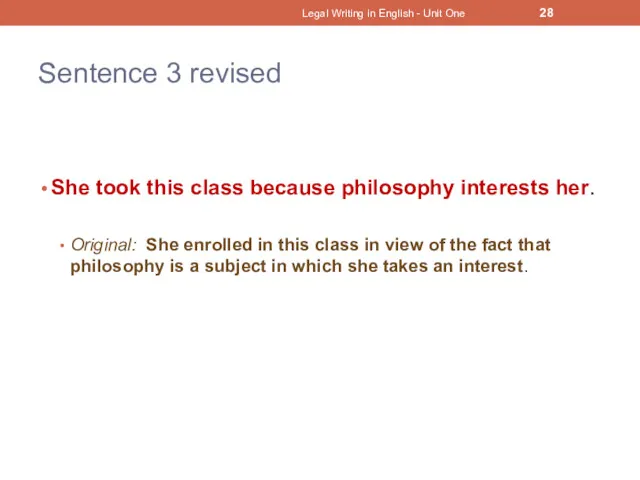
- 27. Sentence 3 She enrolled in this class in view of the fact that philosophy is a
- 28. Sentence 3 revised She took this class because philosophy interests her. Original: She enrolled in this
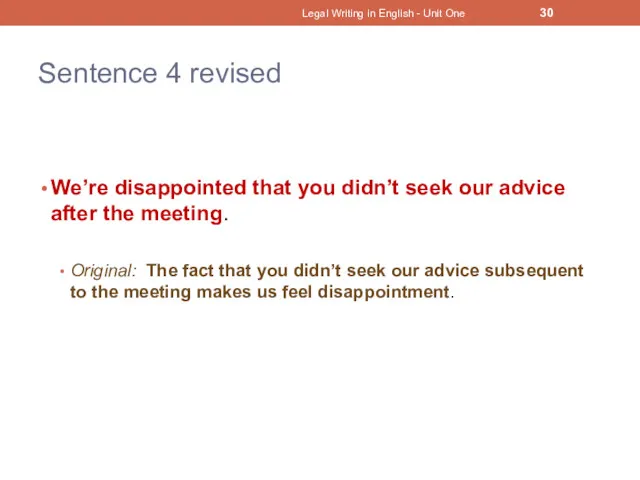
- 29. Sentence 4 The fact that you didn’t seek our advice subsequent to the meeting makes us
- 30. Sentence 4 revised We’re disappointed that you didn’t seek our advice after the meeting. Original: The
- 31. Sentence 5 There were three or four people on the committee who said that the companies
- 32. Sentence 5 revised Several committee members said the bidding companies should demonstrate the new equipment. Original:
- 33. Sentence 6 Some residents of the suburb of Oakwood have a tendency to consider the neighborhood
- 34. Sentence 6 revised Some Oakwood residents consider it a bedroom community. Original: Some residents of the
- 35. Sentence 7 There were 108 accidents in the targeted area during the crackdown, down from 145
- 36. Sentence 7 revised During the crackdown, the number of accidents in the targeted area fell to
- 37. Sentence 8 Military officers need to have knowledge and an understanding of their troops. Legal Writing
- 38. Sentence 8 revised Military officers should know and understand their troops. Original: Military officers need to
- 39. Sentence 9 As per our telephone conversation, enclosed please find information on a new blocking device
- 40. Sentence 9 revised Here’s information on a blocking device that can keep hackers out of your
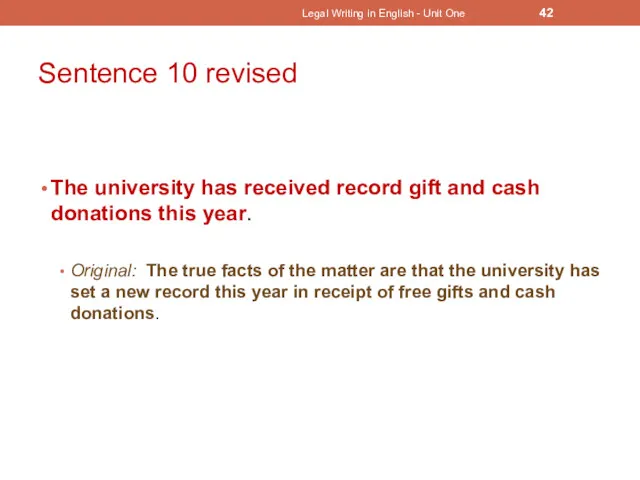
- 41. Sentence 10 The true facts of the matter are that the university has set a new
- 42. Sentence 10 revised The university has received record gift and cash donations this year. Original: The
- 43. Summary – Avoid redundancies Legal Writing in English - Unit One
- 44. Summary – Avoid “filler” phrases Legal Writing in English - Unit One
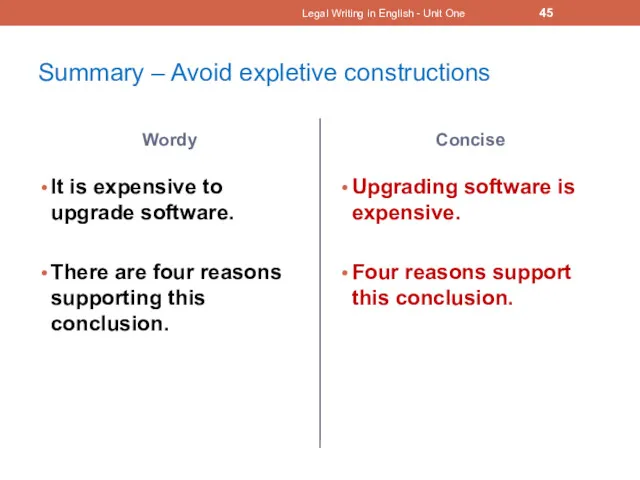
- 45. Summary – Avoid expletive constructions Wordy It is expensive to upgrade software. There are four reasons
- 46. Summary – Use one-word modifiers and possessives Wordy The dog that had rabies The order of
- 47. In future classes, more ways to be concise . . . Favor the active voice Avoid
- 49. Скачать презентацию

































 Past tenses. Simple. Continuous. Formation. Function
Past tenses. Simple. Continuous. Formation. Function Lesson plans: components/ headings. Planning and preparing young learner lessons
Lesson plans: components/ headings. Planning and preparing young learner lessons I have a horrible headache
I have a horrible headache Present Simple
Present Simple Great Britain
Great Britain The Gerund Герундий 9 класс
The Gerund Герундий 9 класс Grammar. Future Tenses
Grammar. Future Tenses Old English Phonetic System
Old English Phonetic System Важно правильно говорить
Важно правильно говорить Scorpions
Scorpions An Introduction to EAP – Academic Skills in English. Lesson 1
An Introduction to EAP – Academic Skills in English. Lesson 1 Transport. Транспорт
Transport. Транспорт Crime and the law Vocabulary
Crime and the law Vocabulary My family. Family members
My family. Family members The structure and level of scientific knowledge. The methodology of science
The structure and level of scientific knowledge. The methodology of science Some facts about Britain
Some facts about Britain The present simple tense (5 класс)
The present simple tense (5 класс) Oral part of the Unified State Exam
Oral part of the Unified State Exam Do you want to become tomorrow's leade
Do you want to become tomorrow's leade Present perfect
Present perfect Leading teams
Leading teams Teaching young learners listening and speaking skills
Teaching young learners listening and speaking skills Travelling. Новые слова
Travelling. Новые слова Spotlight 3. Module 7 (Unit 13). A Day Off
Spotlight 3. Module 7 (Unit 13). A Day Off Russian winter festivals guide
Russian winter festivals guide Making One‘s Family Profile
Making One‘s Family Profile Day 2. Effective teaching and learning
Day 2. Effective teaching and learning Present Simple and Present Continuous
Present Simple and Present Continuous