Содержание
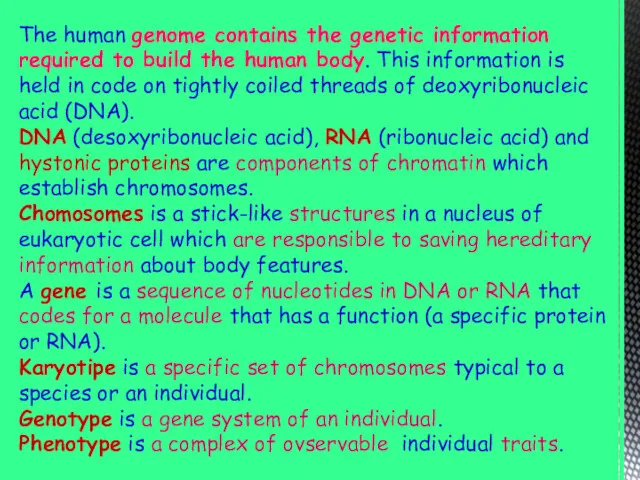
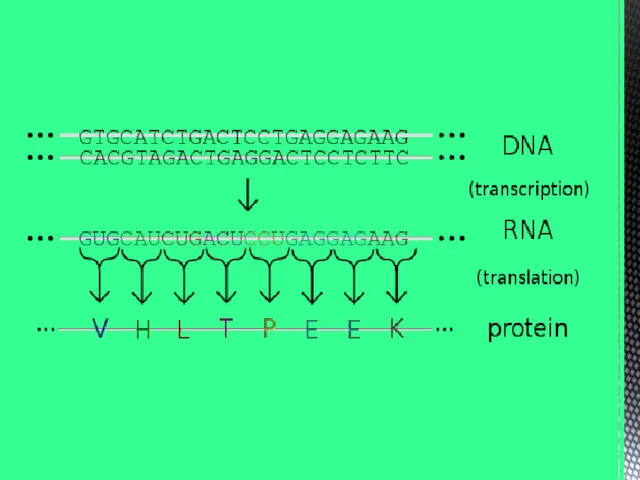
- 2. The human genome contains the genetic information required to build the human body. This information is
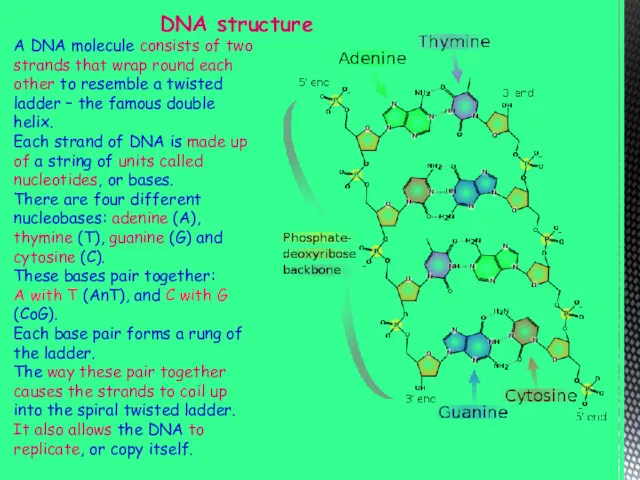
- 3. DNA structure A DNA molecule consists of two strands that wrap round each other to resemble
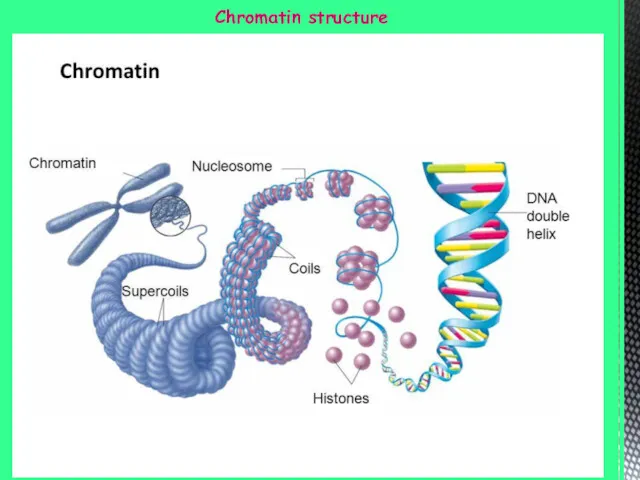
- 4. Chromatin structure
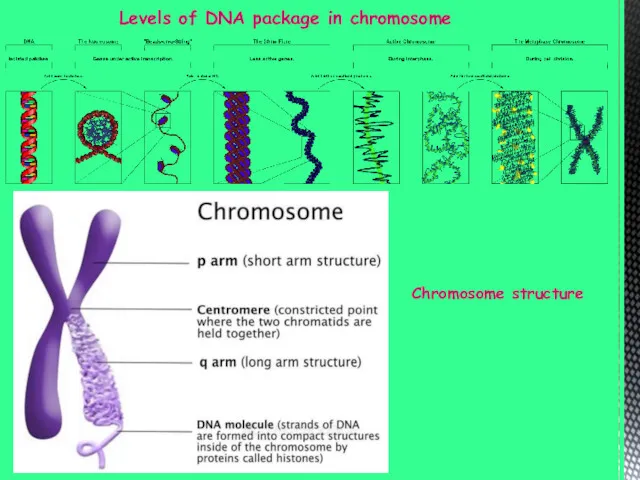
- 5. Levels of DNA package in chromosome Chromosome structure
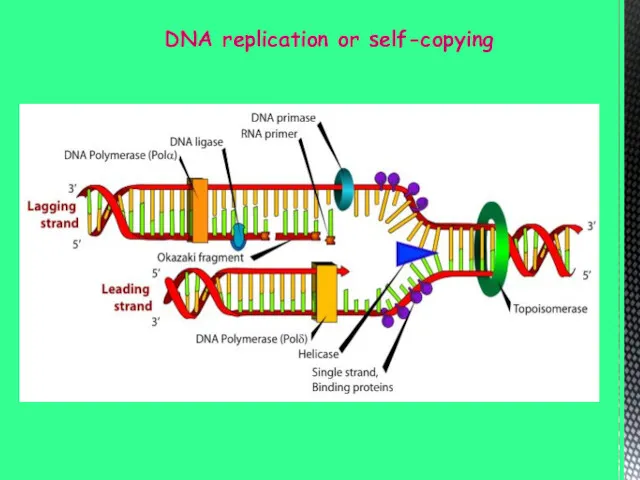
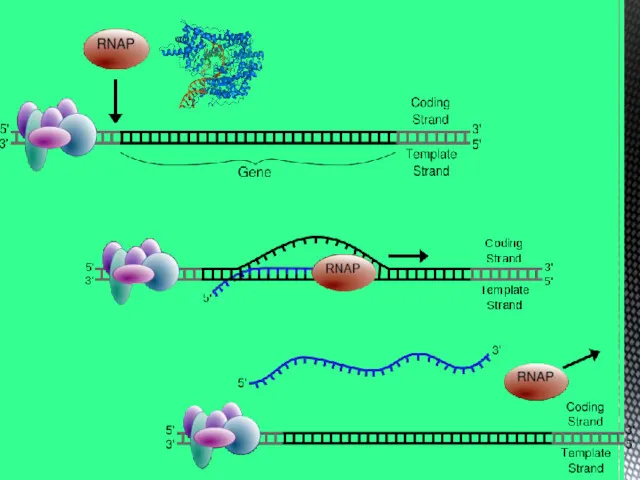
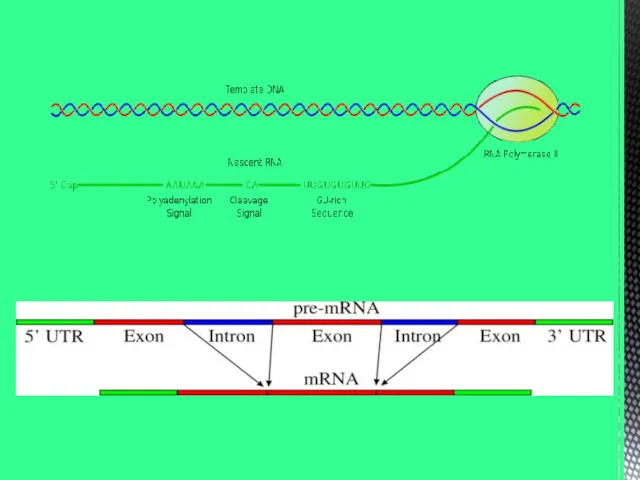
- 6. DNA replication or self-copying
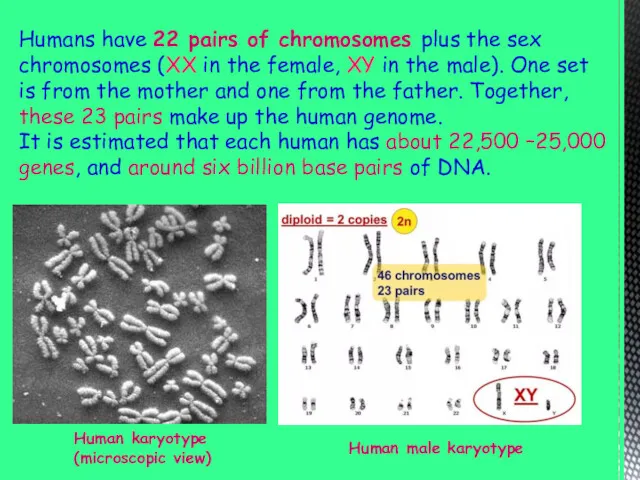
- 7. Humans have 22 pairs of chromosomes plus the sex chromosomes (XX in the female, XY in
- 8. Chromosomes, Chromatids, Chromatin, etc. (20) https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=5&v=s9HPNwXd9fk Proteins carry out the work of a cell. They are
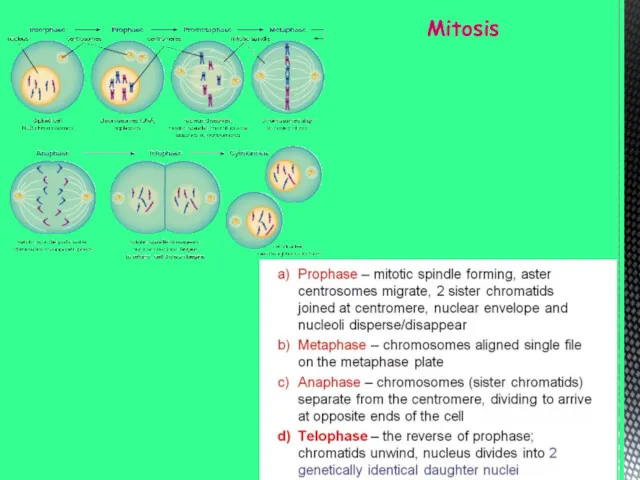
- 9. Mitosis
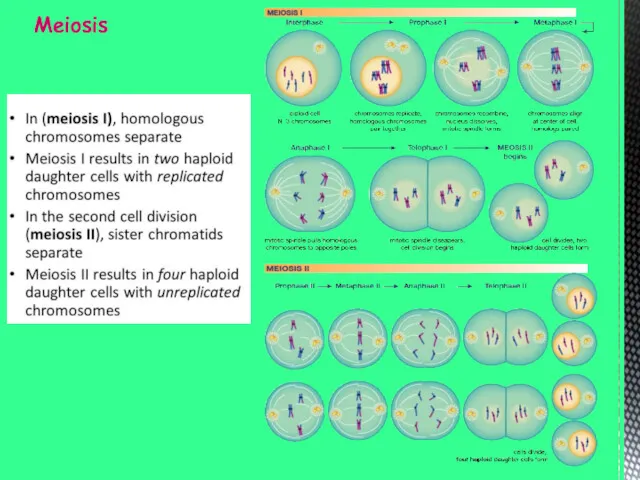
- 10. Meiosis
- 11. Mitosis, Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction (19) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kaSIjIzAtYA Phases of Meiosis (27) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ijLc52LmFQg
- 12. The lection time is over
- 17. Скачать презентацию



 Traditional Russian kitchen
Traditional Russian kitchen Pronoun. Personal Pronouns
Pronoun. Personal Pronouns Ways to express future tense. My summer holidays plans
Ways to express future tense. My summer holidays plans 10 great days this summer
10 great days this summer Настоящее совершенное
Настоящее совершенное Parrot Peter picked a pack of pickled peppers
Parrot Peter picked a pack of pickled peppers Appearance. Well - dressed, elegant
Appearance. Well - dressed, elegant Present continuous (progressive). Настоящее продолженное время
Present continuous (progressive). Настоящее продолженное время Let’s repeat relative clauses
Let’s repeat relative clauses How to write case-briefs
How to write case-briefs Singular and plural nouns
Singular and plural nouns Discourse analysis of the concept of ethics of care in the works of N. Noddings and its application in English teaching
Discourse analysis of the concept of ethics of care in the works of N. Noddings and its application in English teaching Opinion Essays. Требования к сочинению
Opinion Essays. Требования к сочинению French fries, recipe at home
French fries, recipe at home Etiquette in England
Etiquette in England My home
My home My favourite sportsman Sergey Vladimirovich Shubenkov
My favourite sportsman Sergey Vladimirovich Shubenkov Instructions for presentation
Instructions for presentation Prepositions
Prepositions Have a look at some beautiful places in my country and complete the conditional sentences with the right verb tense
Have a look at some beautiful places in my country and complete the conditional sentences with the right verb tense Biosphere reserve Askania-Nova
Biosphere reserve Askania-Nova Shops and shopping
Shops and shopping Business culture of Turkey
Business culture of Turkey Medical education in different countries
Medical education in different countries Ilia Efimovich Repin
Ilia Efimovich Repin Customs and traditions of celebrating Christmas in different countries
Customs and traditions of celebrating Christmas in different countries Verbals – non-finite forms of the Verb
Verbals – non-finite forms of the Verb Present simple
Present simple