Morphological characteristics
Time distinctions (Indefinite and Continuous forms express actions simultaneous to
that one of the main verb, Perfect and Perfect continuous – prior actions)
Aspect distinctions (Indefinite Infinitives express states or facts simultaneous to the one of the main verb, Continuous Infinitives show processes, simultaneous to the one of the main verb, Perfect Infinitives express actions completed by the time expressed by the main verb)
Voice (We use the active infinitive if we are focusing on the agent (the person who does the action). We use the passive infinitive when we want to focus on the receiver (the person who experiences the action), or when we do not want to mention the agent (the person who does the action)
The Infinitive











 Australian music
Australian music Давайте вспомним, что мы узнали в прошлом году. Повторение
Давайте вспомним, что мы узнали в прошлом году. Повторение Clownfish
Clownfish Does Russia have the same ecological problems as the rest of the world
Does Russia have the same ecological problems as the rest of the world Minions race simple teacher switcher
Minions race simple teacher switcher Prepositions of time in, on, at
Prepositions of time in, on, at Halloween
Halloween Ordinal numbers
Ordinal numbers English Language Day
English Language Day Различие глаголов Do и Make в английском языке
Различие глаголов Do и Make в английском языке School rules
School rules Организация обучения чтению на уроке английского языка по методике Jolly Phonics
Организация обучения чтению на уроке английского языка по методике Jolly Phonics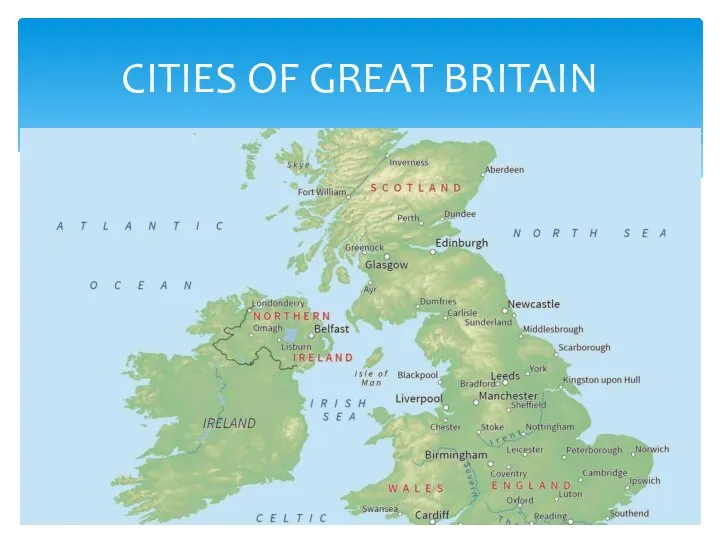 Cities Of Great Britain
Cities Of Great Britain Vitus Jonassen Berring and his discoveries
Vitus Jonassen Berring and his discoveries My mobile phone Samsung Galaxy J1 mini
My mobile phone Samsung Galaxy J1 mini My house
My house Irregular Verbs. Same forms
Irregular Verbs. Same forms Gerunds and infinitives
Gerunds and infinitives Perfect Tenses
Perfect Tenses The capital of Ukraine is Kyiv
The capital of Ukraine is Kyiv Global environmental problems and solutions
Global environmental problems and solutions Why do we study English
Why do we study English English grammar
English grammar What is a cell
What is a cell Why i love me school
Why i love me school Opposites. Game
Opposites. Game Английский марафон
Английский марафон ABC book
ABC book