Содержание
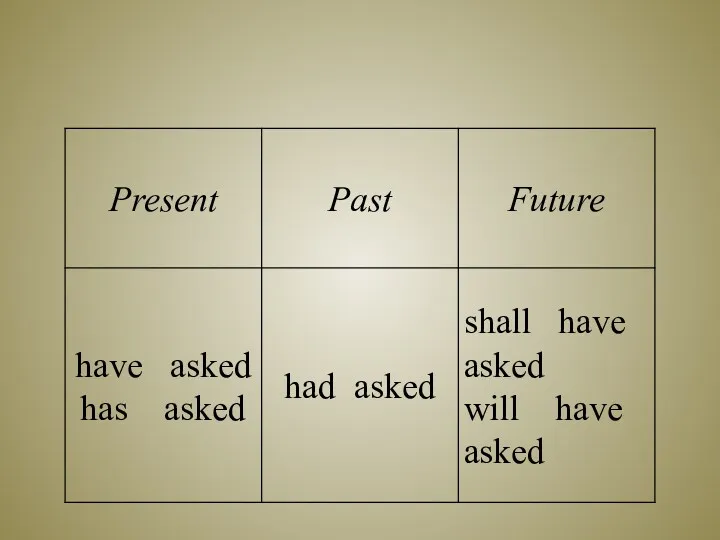
- 2. Present Perfect Tense (Active) Времена группы Perfect (Present, Past, Future) выражают действие, которое уже совершилось к
- 3. Запомните : 1. Причастие прошедшего времени (Past Participle) от стандартных глаголов совпадает по форме с глаголами
- 5. Present Perfect Tense The Present Perfect Tense употребляется для обозначения действия, которое только что (недавно) закончилось
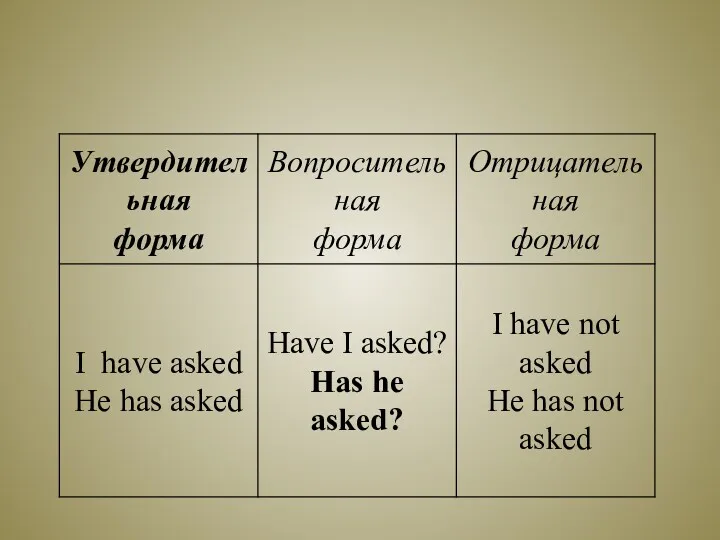
- 7. Обратите внимание ! а) При образовании вопросительной формы вспомогательный глагол to have ставится перед подлежащим. б)
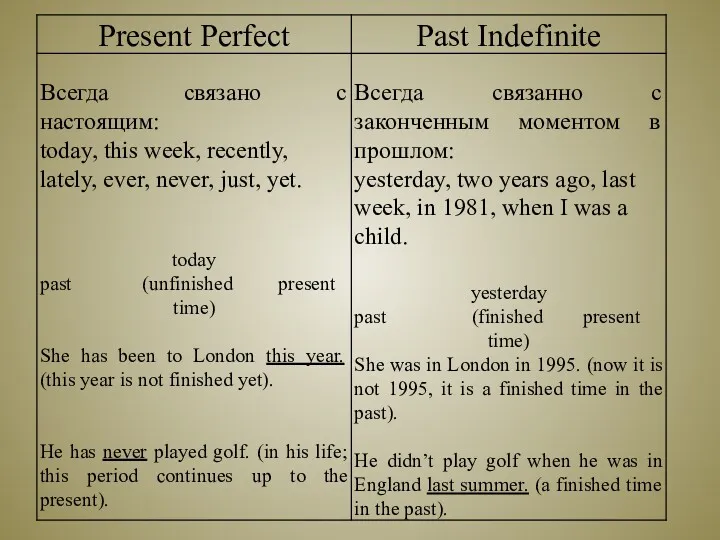
- 8. Запомните основные случаи употребления Present Perfect Tense: Действие совершилось, и результат его связан с настоящим; время
- 9. Обратите внимание: наречия неопределенного времени ставятся между вспомогательным и смысловым глаголами, наречие yet – в конце
- 10. 3. Действие совершилось, а указанный период времени не истек. В предложениях используются обстоятельства типа: this week
- 11. 4. Действие началось в прошлом и продолжается в момент речи. В предложениях употреблены предлоги since –
- 12. Запомните! Предлог for употребляется, когда речь идет о периоде времени: for two days – два дня
- 13. предлог since употребляется, когда обозначается начало периода времени: since Monday – с понедельника; since childhood –
- 14. 5. После превосходной степени прилагательных. What a boring film! It is the most boring film I’ve
- 15. 6. С выражениями: This is the first (the second) time ... It is the first (the
- 17. Use Present Perfect or Present Simple: 1. Helen (to be) sick since last week. She (to
- 18. Use Present Perfect or Present Simple: 1. Helen (to be) sick since last week. She (to
- 19. Past Perfect Tense
- 20. Past Perfect Tense употребляется для выражения действия, совершившегося к определенному моменту в прошлом. Этот момент может
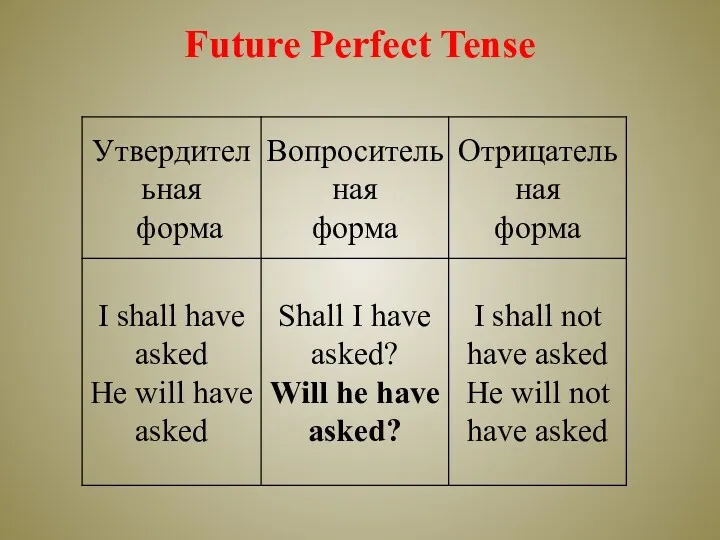
- 21. Future Perfect Tense
- 22. Внимание: а) при образовании вопросительной формы перед подлежащим ставится только первый вспомогательный глагол; б) при образовании
- 23. Future Perfect Tense употребляется для выражения действия, которое завершится к определенному моменту в будущем. Этот момент
- 24. Помните! В придаточных предложениях времени и условия будущее время не употребляется. We shall have finished the
- 25. Analyze the use of the Perfect Forms. Translate the sentences into Russian. 1. I was sure
- 26. Open the brackets using a) Past Perfect: 1. She hoped I (to pay) for the tickets.
- 27. Open the brackets using b) Future Perfect: 1. When the father returns from his round the
- 28. Use "had" or "will have". 1. When we came to the station the train ... left.
- 30. Скачать презентацию























 Intellectual development, education of well-rounded person
Intellectual development, education of well-rounded person State of Poland
State of Poland Современные мультимедийные технологии на уроках английского языка на начальном и среднем этапе обучения
Современные мультимедийные технологии на уроках английского языка на начальном и среднем этапе обучения My house
My house Правила чтения гласных букв под ударением. Aa, Ee, Ii, Oo, Uu, Yy
Правила чтения гласных букв под ударением. Aa, Ee, Ii, Oo, Uu, Yy What's on the desk
What's on the desk Prepositions of place on; in front of; in; on the left; on the right; between; under; behind
Prepositions of place on; in front of; in; on the left; on the right; between; under; behind Complex object (v + object + (to) infinitive). Сложное дополнение
Complex object (v + object + (to) infinitive). Сложное дополнение What was in Fashion in the Past
What was in Fashion in the Past Writing skills
Writing skills My family is my wealth
My family is my wealth Викторина по английскому языку
Викторина по английскому языку Oil and Gas – Black Gold
Oil and Gas – Black Gold Грамматическая конструкция may must
Грамматическая конструкция may must Describing pictures in English class
Describing pictures in English class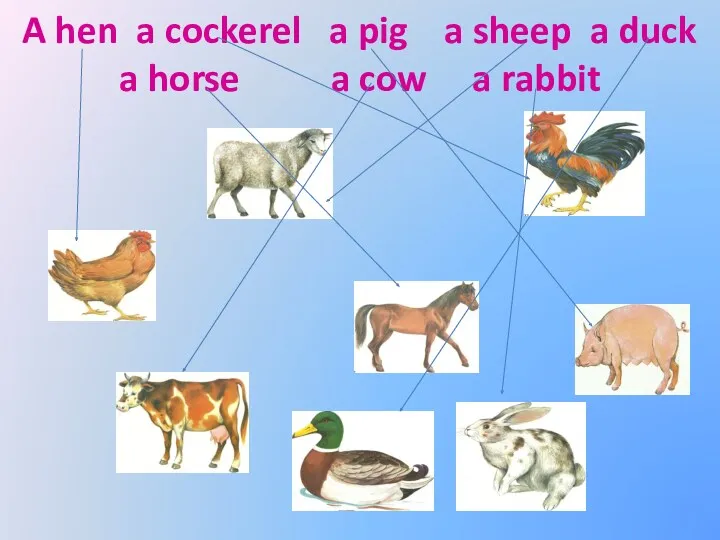 Animals. On a farm. In the zoo. In the forest
Animals. On a farm. In the zoo. In the forest Things to do
Things to do Professions
Professions Moscow is the capital of Russia
Moscow is the capital of Russia Цифры на английском языке
Цифры на английском языке Морфологический уровень языка. Понятие грамматической категории. Типология частей речи
Морфологический уровень языка. Понятие грамматической категории. Типология частей речи Numbers 1-1000
Numbers 1-1000 Basic vocabulary. Game
Basic vocabulary. Game What is a sportsman
What is a sportsman Untranslatables
Untranslatables Heroes. Grammar game (Pr. simple and be)
Heroes. Grammar game (Pr. simple and be) Do or does? game
Do or does? game The Plurals. Exceptions.
The Plurals. Exceptions.