Слайд 2

Content :
Anatomy of brest
Hormonal change in breast during pregnancy
Structural changes in
breast during pregnancy
Слайд 3

Anatomy of Normal Adult breast
The breast are bilateral glandular structures which
are considered as accessory reproductive organs as they are concerned with lactation following the childbirth.
Breast usually extends from second to sixth rib in midclavicular line
It lies in subcutaneous tissue over fascia covering pectorals major or even beyond to lie over serratus anterior and external oblique muscles
There is areola placed in the center of the breast and it is pigmented and is about 2.5cm in diameter and it contains sebaceous glands and few involuntary muscles.
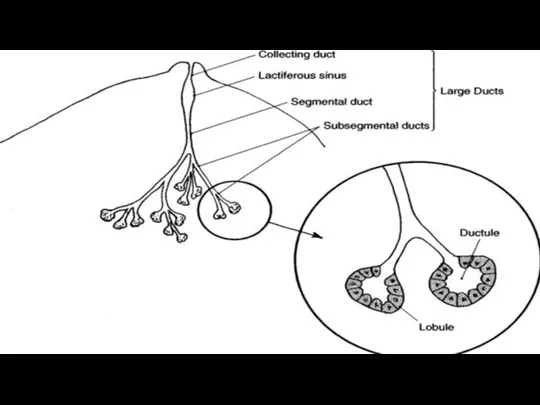
The muscular projection covered by pigmented skin is called Nipple which has a vascular supply and due to its unstriped muscles it is erectile and it accomodates the opening of 15-20 lactiferous ducts
Слайд 4

Now talking about the breast tisssue, it is composed of nearly
16-20 lobes , the lobes consists of glandular tissue which secretes milk and the milk is drained into the duct system which opens at nipple.
Between the lobes there is fibrofatty tissues which are responsible for the softness of the breast.
Слайд 5

Слайд 6

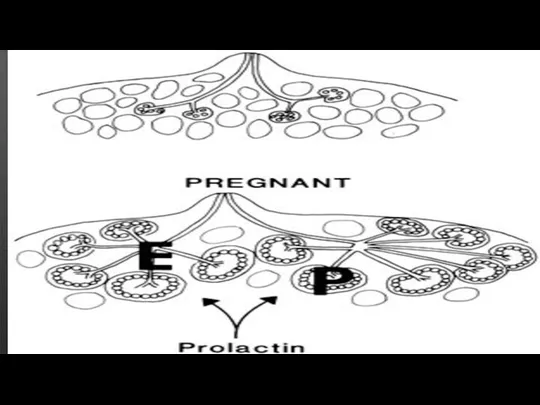
Physiological effects of hormones on breast during normal pregnancy
During pregnancy there
is stimulation of anterior pituitary gland due to which there is more release of its hormones out of which high concentration of Growth hormone , glucocorticoids and oestrogen which stimulate the breast duct to proliferate during pregnancy .
Progesterone and prolactin stimulate the alveolar growth.
From 3-4 months of pregnancy until the first 30 hours after delivery the breast secrete a thick , protein rich fluid called Colostrum which is stimulated by prolactin and placental lactogen.
During pregnancy high levels of oestrogen and progesterone prevent alveolar transcription of alpha-lactalbumin which is a protein contained in milk and thus preventing full lactation.
Слайд 7

After delivery there is sudden increase in decrease in progesterone and
oestrogen levels which in fact allows the prolactin to act directly on the alveolar cells to stimulate the synthsis of milk.
Also when the baby is suckling it directly sends impulses to hypothalamus which stimulate release of prolactin and oxytocin.
Here oxytocin causes the contraction of myoepithelial cells which surrounds lobules to contract and milk is ejected into the ducts
After the 5th day of delivery the milk production is full which is approximately 500-1000 ml in 24 hours and as a result it demands additional 500kcal intake per day of that mother.
Слайд 8

Structural changes of breast in normal pregnancy
A woman’s breast structure changes
during pregnancy to prepare the breast for breastfeeding the baby. The normal changes include :
tenderness of nipple and breast
Changes in colour and size of nipples and areola.
There is significant increase in breast size over the course of pregnancy.
There is pronounced appearance of MONTOGOMERY’S tubercles which are also known as bumps on areola.
Слайд 9
Слайд 10
Слайд 11

A woman’s breast usually grows 1 to 2 cup size more
during the pregnancy due to the proliferation the lobules which causes hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium.
Once when full lactation begins the breast swell significantly and there will be sensation of achy pain and breast may be felt as lumpy and heavy also known as engorgement
Size of mother breasts totally depends on how much the child nurses of her mother’s breast.
After 8-12 weeks of delivery the woman’s breast will reduce in size but will remain usually 1 cup size larger than prior to her pregnancy
The breast size changes may be related to the sex of the infant, as mothers of female infants have greater changes in breast size than mothers of male infant.










 Future simple tense. Будущее простое время
Future simple tense. Будущее простое время Books in our lives
Books in our lives Welcome to Great Britain
Welcome to Great Britain Speaking phrases
Speaking phrases Now I know… Итоговый урок в 3 классе
Now I know… Итоговый урок в 3 классе Amazing creatures
Amazing creatures Holidays in Russia
Holidays in Russia 5 Form (второй иностр. язык)
5 Form (второй иностр. язык) Canada. Geography
Canada. Geography Prefix and sufix
Prefix and sufix How many are there?
How many are there? Икт во внеурочной деятельности по английскому языку в начальной школе
Икт во внеурочной деятельности по английскому языку в начальной школе Tell me about each person in the photos with “is” and “are”
Tell me about each person in the photos with “is” and “are” Game rules
Game rules My best friend
My best friend Sports scene
Sports scene Spotlight 4. Module 2 (Unit 4). A Working Day
Spotlight 4. Module 2 (Unit 4). A Working Day Мастер-класс по грамортному написанию мотивационного письма для успешной подачи заявки на международную программу
Мастер-класс по грамортному написанию мотивационного письма для успешной подачи заявки на международную программу Disposal of radioactive waste
Disposal of radioactive waste Family
Family Закрытый и открытый слоги. Чтение буквы Aa в открытом слоге. Урок английского языка во 2 классе
Закрытый и открытый слоги. Чтение буквы Aa в открытом слоге. Урок английского языка во 2 классе Reported speech. Part 1
Reported speech. Part 1 A – an - some
A – an - some Days of the week. Дни Недели
Days of the week. Дни Недели Easter
Easter Personal Information. Basic 3
Personal Information. Basic 3 Collocations do vs make
Collocations do vs make The rainforests of the sea
The rainforests of the sea