Содержание
- 2. Where does the word “lexicology come from”? Give the definition of lexicology. What are the main
- 3. What is the principal difference between a phoneme and a morpheme? What are LANGUAGE UNIVERSALS? What
- 4. What is semasiology? What type of meaning does semasiology deal with? Is semasiology the same notion
- 5. What school of approach to meaning do Saussure’s disciples represent? What is meaning according to them?
- 6. Do morpheme possess grammatical meaning? Do they possess lexical meaning? Give an example of connotational meaning
- 7. Who does the most complete classification of the meaning change belong to? In what book is
- 8. What kind of similarity do we single out concerning metaphors? What kind of contiguity is metonymy
- 9. What are monosemantic words? What does the word “polysemy” mean? What problem is of primary importance
- 10. Give the definition of homonyms. Why is the English language rich in homonyms? How is the
- 11. What is synonymy? Among which parts of speech can synonyms be found? Give the examples of
- 12. What are allomorphs? What two classes do English words fall into according to their structure? Give
- 13. Which parts of speech are formed with the help of suffixation? Prefixation? How can prefixes be
- 14. What are the suffixes from the point of view of the character of the lexico-grammatical base
- 15. In a converted pair how do we know which word is derived from which? Which scholars
- 16. What does the term “native” mean referring to the English word-stock? What is the proportion between
- 17. What languages gave the greatest amount of borrowings at an early stage of its development? What
- 19. Скачать презентацию
















 Игра Jeopardy
Игра Jeopardy Changing times, changing styles
Changing times, changing styles Theoretical English Grammar: Basic Concepts
Theoretical English Grammar: Basic Concepts Сонеты Уильяма Шекспира
Сонеты Уильяма Шекспира Prepositions of time
Prepositions of time English alphabet
English alphabet Decorate a Leprechaun's House
Decorate a Leprechaun's House The Present Perfect
The Present Perfect Reported speech. Косвенная речь. Тест
Reported speech. Косвенная речь. Тест Разница между словами. Words difference
Разница между словами. Words difference Food
Food Animals. Животные
Animals. Животные Report to the Apple Inc
Report to the Apple Inc Do or make game. Teacher switcher
Do or make game. Teacher switcher The causative form have/get something done
The causative form have/get something done What kind of talent would you like to have and why
What kind of talent would you like to have and why English - speaking countries
English - speaking countries How’s the weather?
How’s the weather? International Justice International Security
International Justice International Security The present perfect tense
The present perfect tense How to write a personal letter
How to write a personal letter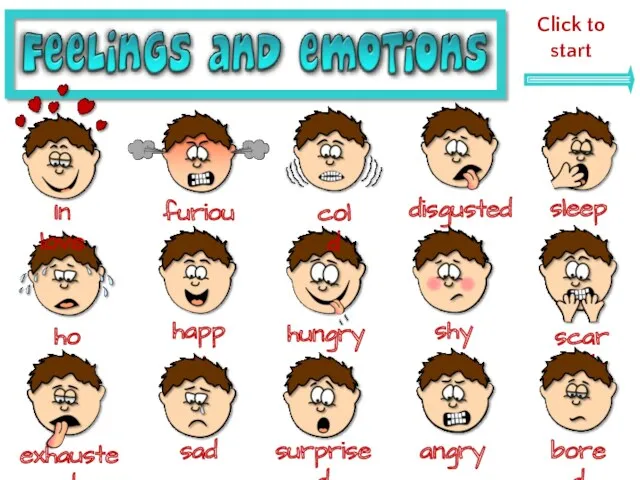 Feelings and emotions
Feelings and emotions Present Continuous
Present Continuous Facts about Australia
Facts about Australia Choose the correct answer. Food game
Choose the correct answer. Food game Salty dough products
Salty dough products Conditional clauses. Type 3. Game
Conditional clauses. Type 3. Game The world of travelling
The world of travelling