Содержание
- 2. Chapter 1 What Is Organizational Behavior? 1-
- 3. 1- After studying this chapter you should be able to: Demonstrate the importance of interpersonal skills
- 4. 1- The Importance of Interpersonal Skills Good people skills are important Good places to work have
- 5. 1- The Field of Organizational Behavior Organizational behavior studies the influence that individuals, groups, and structure
- 6. 1- Focal Points of OB Jobs Work Absenteeism Employment turnover Productivity Human performance Management Copyright ©2016
- 7. 1- Complementing Intuition with Systematic Study Intuition: your “gut feeling” explanation of behavior Systematic study improves
- 8. 1- Systematic Study Examines relationships Attempts to attribute causes and effects Bases conclusions on scientific evidence:
- 9. 1- Evidence-Based Management Evidence-based management: Bases decisions on the best available scientific evidence Complements systematic study
- 10. 1- Big Data Big data: the extensive use of statistical compilation and analysis Identify persistent and
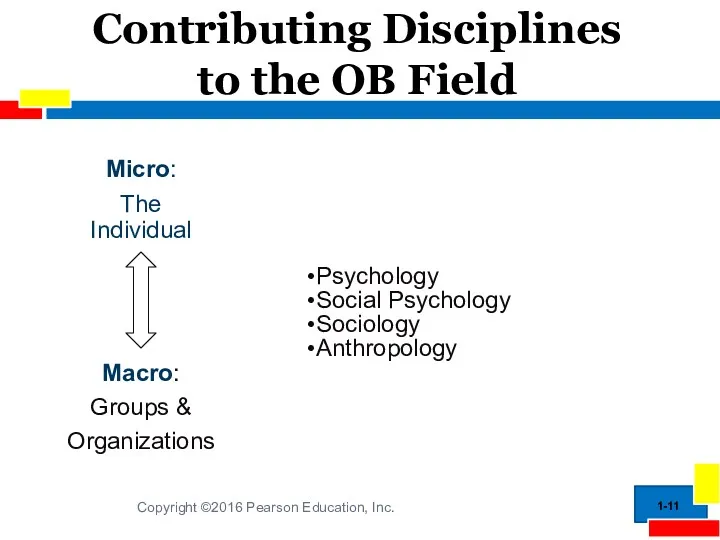
- 11. Contributing Disciplines to the OB Field 1- Psychology Social Psychology Sociology Anthropology Macro: Groups & Organizations
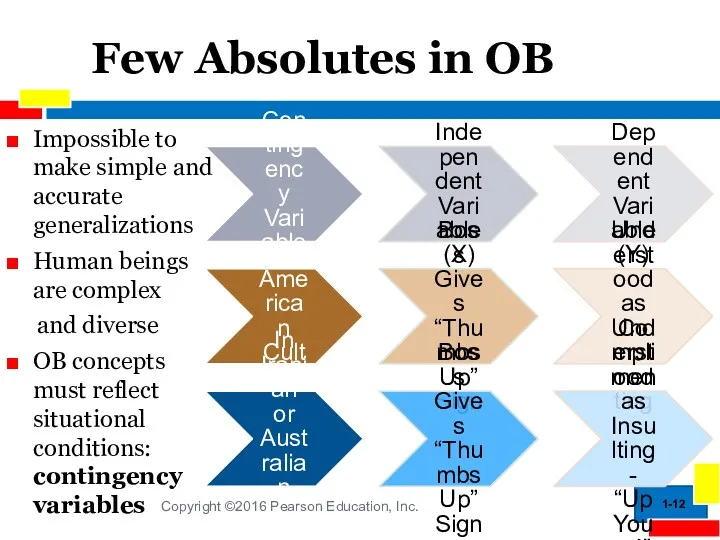
- 12. 1- Few Absolutes in OB Impossible to make simple and accurate generalizations Human beings are complex
- 13. 1- Challenges and Opportunities for OB Responding to economic pressures Responding to globalization Managing workplace diversity
- 14. 1- Responding to Economic Pressures Effective management can be just as hard, if not harder, in
- 15. 1- Responding to Globalization Increased foreign assignments Working with people from different cultures Overseeing movement of
- 16. Managing Workforce Diversity Workforce diversity: organizations are becoming a more heterogeneous mix of people in terms
- 17. 1- Improving Customer Service and People Skills The majority of employees in developed nations work in
- 18. 1- Working in Networked Organizations Managers must adapt their skills and communication styles to succeed in
- 19. 1- Enhancing Employee Well-Being at Work The line between work and non-work has blurred and managers
- 20. 1- Creating a Positive Work Environment Positive organizational scholarship: how organizations develop human strengths, foster vitality
- 21. 1- Improving Ethical Behavior Managers facing ethical dilemmas or ethical choices are required to identify right
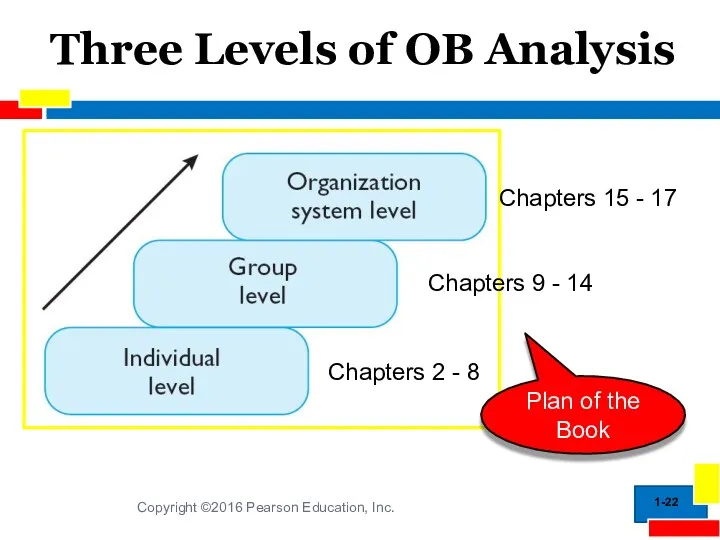
- 22. Three Levels of OB Analysis 1- Chapters 2 - 8 Chapters 9 - 14 Chapters 15
- 23. 1- Implications for Managers Don’t rely on generalizations Use metrics and situational variables rather than “hunches”
- 24. 1- Keep in Mind… OB’s goal is to understand and predict human behavior in organizations Fundamental
- 25. 1- Summary Demonstrated the importance of interpersonal skills in the workplace. Defined Organizational Behavior (OB). Showed
- 27. Скачать презентацию




















 Zero article
Zero article I like…/ I don’t like…
I like…/ I don’t like… Tag-Questions Разделительные Вопросы. Правила образования тэгов
Tag-Questions Разделительные Вопросы. Правила образования тэгов Deinococcus radiodurans
Deinococcus radiodurans Тренажёр к устной части ОГЭ. Topic 8. Choosing a profession
Тренажёр к устной части ОГЭ. Topic 8. Choosing a profession Степени сравнения прилагательных. Имя прилагательное
Степени сравнения прилагательных. Имя прилагательное Викторина по английскому языку для младших школьников
Викторина по английскому языку для младших школьников My Working Day
My Working Day 2018 FIFA World Cup
2018 FIFA World Cup Past Tenses
Past Tenses Reported speech
Reported speech Astana – capital of the Kazakhstan
Astana – capital of the Kazakhstan Speaking 8 year 2016
Speaking 8 year 2016 What’s the weather like today?
What’s the weather like today? Present Simple & Present Continuous in comparison
Present Simple & Present Continuous in comparison Условные предложения. Conditionals
Условные предложения. Conditionals Abstract
Abstract Past Tenses
Past Tenses What’s the weather like
What’s the weather like The mousetrap. Articles
The mousetrap. Articles Foodoo 22
Foodoo 22 Merry Christmas
Merry Christmas Let’s cook!
Let’s cook! My friends
My friends How are you feeling today
How are you feeling today Eco-Mind
Eco-Mind Passive Voice Present Simple
Passive Voice Present Simple Differences in British and American English
Differences in British and American English