Слайд 6

Suffixes
(a) their origin: Romanic (-age, -ment, -tion), Native (-er, dom,
-ship), Greek (-ism, -ize), etc.;
(b) meaning: -er (the agent of the action), -ess (feminine gender), -ence/ance (abstract meaning), -ie and -let (diminutiveness), -age, -dom (collectivity), -an, -ese, -ian (appurtenance), etc.;
(c) part of speech they form: noun suffixes -er, -ness, -ment; adjective-forming suffixes -ish, -ful, -less, -y; verb-suffixes -en, -fy, etc.;
(d) productivity – productive suffixes are -er, -ly, -ness, -ie, -let, non-productive (-dom, -th) and semi-productive (-eer, -ward).







 Christmas
Christmas Эмоционально-художественные технологии в изучении английского языка
Эмоционально-художественные технологии в изучении английского языка Attractions of London
Attractions of London The Verb: Mood and Modality
The Verb: Mood and Modality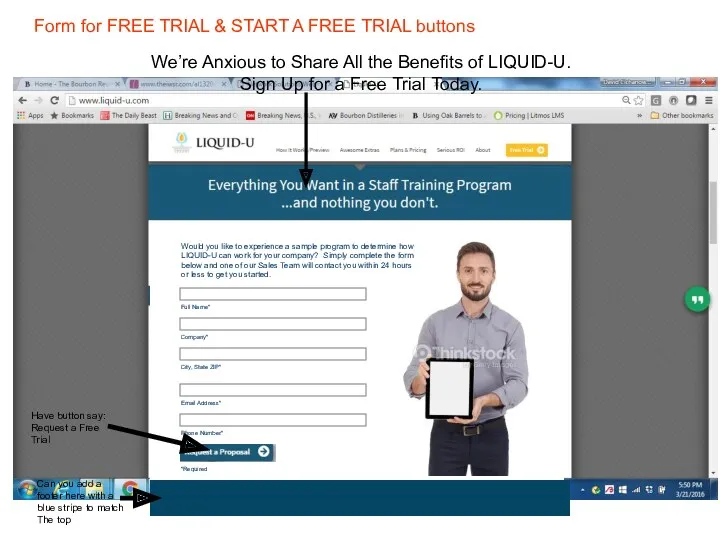 Website. Forms for free trial
Website. Forms for free trial Is the Internet the most important part of our life or not
Is the Internet the most important part of our life or not Writing an informal letter
Writing an informal letter Present simple passive voice
Present simple passive voice Irregular verbs
Irregular verbs 2018 FIFA World Cup
2018 FIFA World Cup История развития английского языка
История развития английского языка My school bag
My school bag Language of music as a means of communication
Language of music as a means of communication My favorite book
My favorite book Summer holidays (1)
Summer holidays (1) Моя семья. Spotlight (5 класс)
Моя семья. Spotlight (5 класс) International Public Law. Lecture 6
International Public Law. Lecture 6 How I learn English
How I learn English A tasty way to become healthy
A tasty way to become healthy Colours test
Colours test History of communications media. (Class 5)
History of communications media. (Class 5) On the topic of school
On the topic of school Portfolio
Portfolio Wild animals. English for kids
Wild animals. English for kids Sport in our life
Sport in our life Степени сравнения прилагательных
Степени сравнения прилагательных Spotlight 4. Module 4 (Unit 8). At the Zoo
Spotlight 4. Module 4 (Unit 8). At the Zoo Family (семья)
Family (семья)