Слайд 2Plan of lecture:
1 Ecological factors for plants.
2 Ecological groups of plants.
3 Life forms
of plants.
Слайд 3Basic literatures:
1 Еленевский А.Г., Соловьев М.П., Тихомиров В.Н. Ботаника: систематика высших, или
наземных, растений. 2 изд. - М.: Academіa, 2001. - 429 с.
2 Нестерова С.Г. Лабораторный практикум по систематике растений. - Алматы: Қазақ ун-ті, 2011. - 220 с.
3 Родман А.С. Ботаника. – М.: Колос, 2001. - 328 с.
Additional literatures:
1 Билич Г.Л., Крыжановский В.А. Биология. Т. 2: Ботаника. - М.: Оникс 21 век, 2002. - 543 с.
2 Ишмуратова М.Ю. Систематика и интродукция растений (курс лекций). - Караганда: РИО Болашак-Баспа, 2015. - 100 с.
3 Тусупбекова Г.Т. Основы естествознания. Ч. 1. Ботаника. – Астана: Фолиант, 2013. – 321 с.
Слайд 4Plant ecology- is a science about communication between plants and elements of environment.
All elements of environment are separated into 3 groups:
Need for plants;
dangerous;
Indifferent .
Need and dangerous element in general are called ecological factors.
Слайд 5Classification of ecological factor:
1. Abiotical factors – are factors of non-living nature:
а) climate
- light, worm, humidity, composition and moving of air;
б) edaphic (soil) – is different chemical and physical peculiarities of soils;
в) topographic – are factor of relief.
2. Biotic factors – are influences of living together organisms to each others.
а) influence one plant into neighbor plants;
б) influence animals into plants;
в) influence micro organisms into plants.
3. Anthropogenic factors – are different influence of human into plants.
Слайд 6Plasticity of plants species is vary in wide conditions. So, all plants can
be ranged into 3 groups:
Stenotope – with a small ecological diapasons. For example, trees of tropical forest.
2) Everytope – with a wide ecological diapasons. For examples, Pinus sylvestris.
3) Average plasticity – are the most species. They lie between stenotope and everytope species.
Слайд 7To influence of humidity it is determined the following groups of plants.
1. Xerophytes
– are plants growing in arid conditions with deficit of water in soil or air.
2. Mesophytes – are plants growing in conditions with enough amount of water.
3. Hygrophytes – are plants growing in the conditions with high level of humidity of soil or air.
4. Hydrophytes – are species growing in water conditions.
Слайд 8By influence to sun light it is usually separated the following groups:
1) Heliophytes;
2) Scioheliophytes;
3) Sciophytes.
Слайд 10Plants – semi-parasites: 1 – Viscum album, low part of plant with root
under cork; 2 – cross-cut of branch; 3 – Melampyrum arvense, which parasite on cereals
Слайд 11To depending from temperature it is separated 4 ecological groups:
Megaterm – hot-resistant plants;
Mesoterm – lnot hot resistant;
Microterm – growing in cold climate;
Gecistoterm – cold resistant plants.
Слайд 12Depending of soil chemical conditions are separated the following ecological groups of plants:
Acidophytes;
Basiophytes;
Neutrophytes.
Слайд 13Types of communication between plants:
1. Mutualism.
2. Commensalism.
3. Parasitism.
4. Concurention.
Слайд 14Scheme of life forms (according to A. Raunkier):
А – position of buds;
Б – perennial parts of stalk; 1 – hemocryptophytes; 2 – cryptophytes; 3 – terophytes; 4 - phanerophytes; 5 – chameophytes
 Класс Пресмыкающиеся. Особенности внешнего и внутреннего строения. Многообразие. Происхождение
Класс Пресмыкающиеся. Особенности внешнего и внутреннего строения. Многообразие. Происхождение Взгляды и гипотезы о происхождении жизни на Земле
Взгляды и гипотезы о происхождении жизни на Земле Физиология сна и сновидений
Физиология сна и сновидений Plant adaptations to habitats
Plant adaptations to habitats Тип Кишечнополостные. Гидра. на основе современных информационных технологий.
Тип Кишечнополостные. Гидра. на основе современных информационных технологий. Физиология бактерий
Физиология бактерий Дыхание растений
Дыхание растений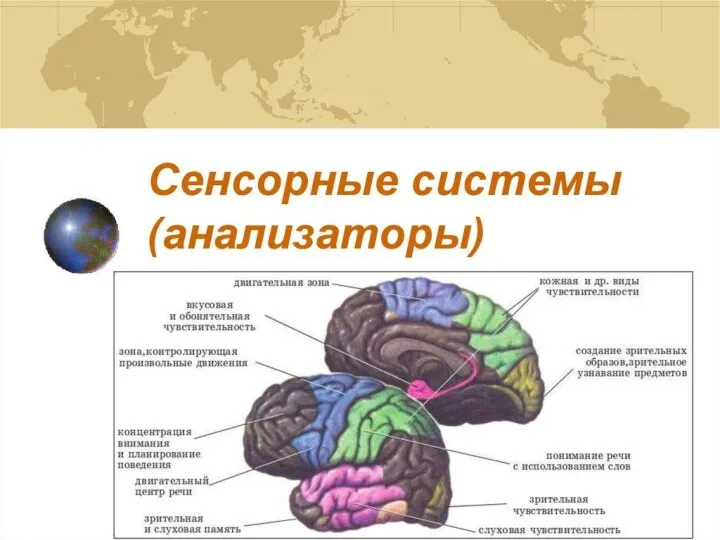 Сенсорные системы (анализаторы)
Сенсорные системы (анализаторы) Различия в строении клеток эукариот и прокариот
Различия в строении клеток эукариот и прокариот презентация по биологии 6 класс Координация и регуляция Диск
презентация по биологии 6 класс Координация и регуляция Диск Биоритмы. Физический биоритм
Биоритмы. Физический биоритм Урок-презентация. Плоды, их строение, значение, распространение в природе
Урок-презентация. Плоды, их строение, значение, распространение в природе Чому мігрують тварини
Чому мігрують тварини Основные направления эволюции биосферы
Основные направления эволюции биосферы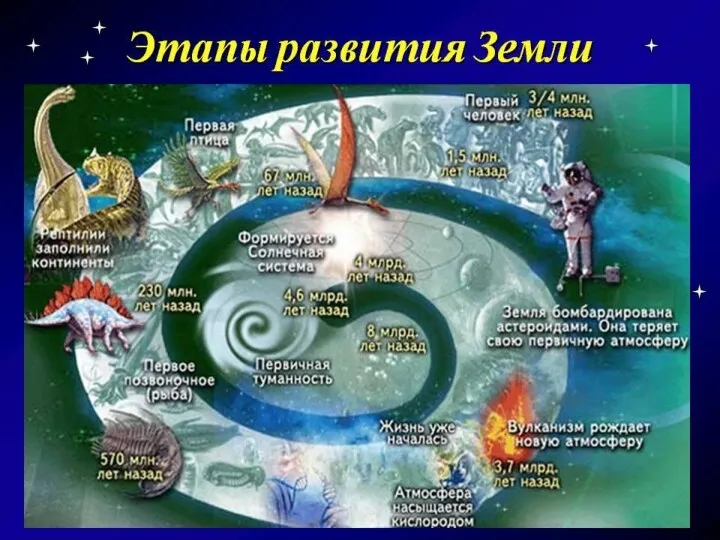 Этапы развития жизни на Земле
Этапы развития жизни на Земле Полевые сорняки
Полевые сорняки Половое размножение организмов. Мейоз. 9 класс
Половое размножение организмов. Мейоз. 9 класс Основы теории регулирования биологических систем
Основы теории регулирования биологических систем Память и внимание
Память и внимание Органы растений. Семя
Органы растений. Семя Животные. Хищники
Животные. Хищники Тіршіліктің пайда болуы туралы түсініктердің қалыптауы
Тіршіліктің пайда болуы туралы түсініктердің қалыптауы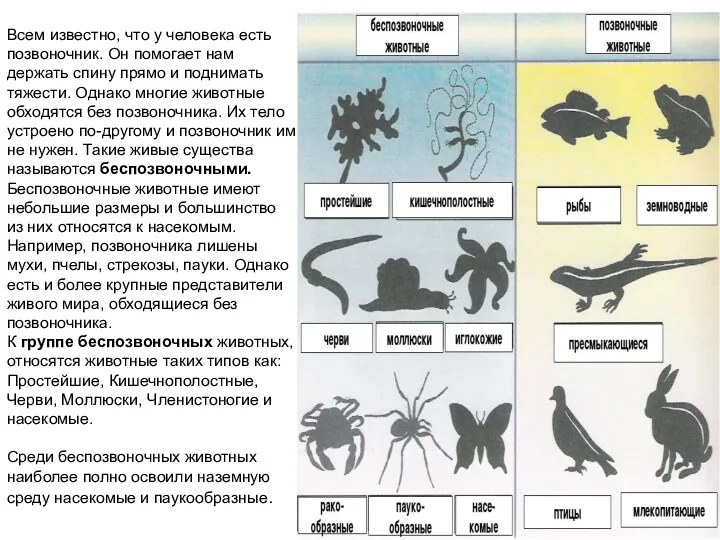 Наземные беспозвоночные
Наземные беспозвоночные Породы свиней
Породы свиней Рефлексы. Условные и безусловные рефлексы. 8 класс
Рефлексы. Условные и безусловные рефлексы. 8 класс Полимеразная цепная реакция
Полимеразная цепная реакция Классификация грибов
Классификация грибов Сказочный гербарий
Сказочный гербарий