Содержание
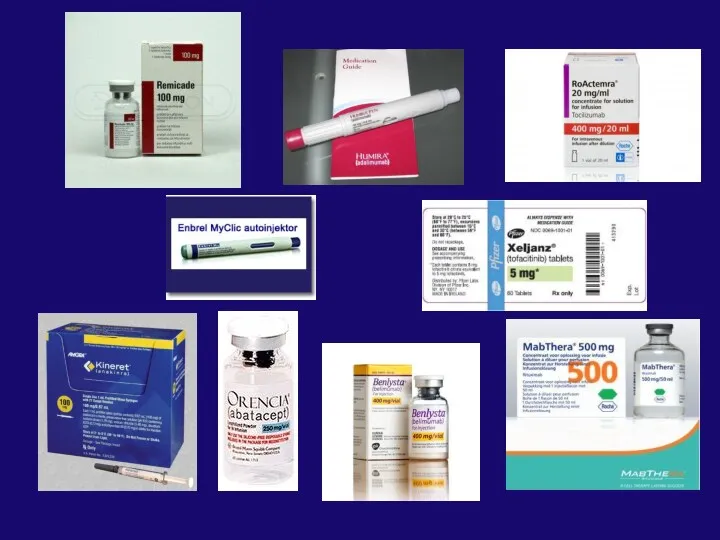
- 3. List of diseases treated with biologic drugs Rheumatoid arthritis Juvenile arthritis Psoriatic arthritis Ankylosing spondylitis Psoriasis
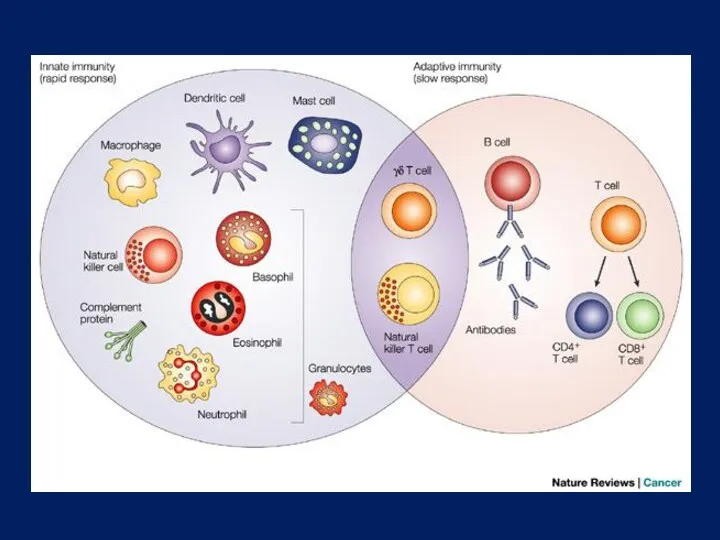
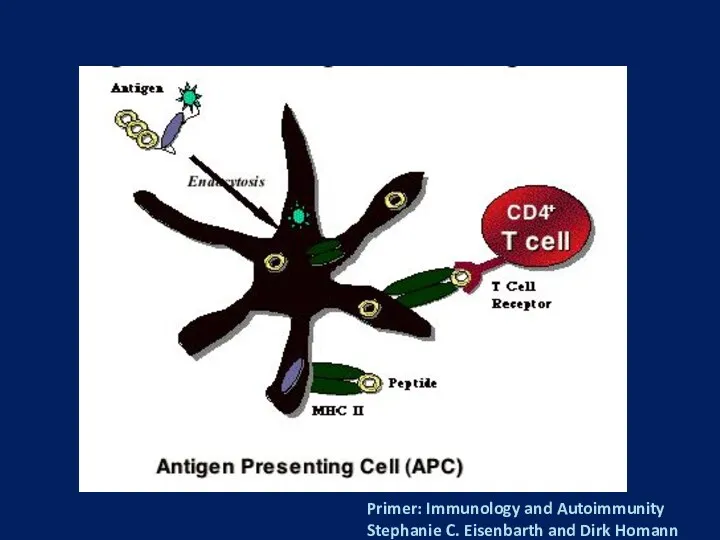
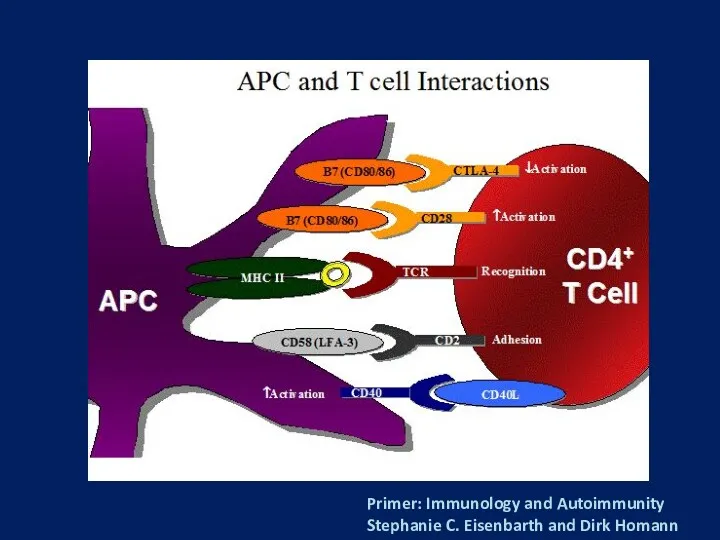
- 5. Primer: Immunology and Autoimmunity Stephanie C. Eisenbarth and Dirk Homann
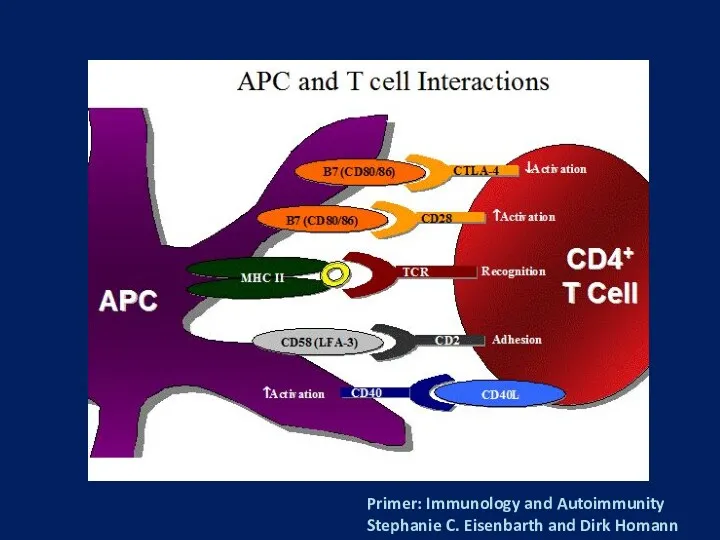
- 6. Primer: Immunology and Autoimmunity Stephanie C. Eisenbarth and Dirk Homann
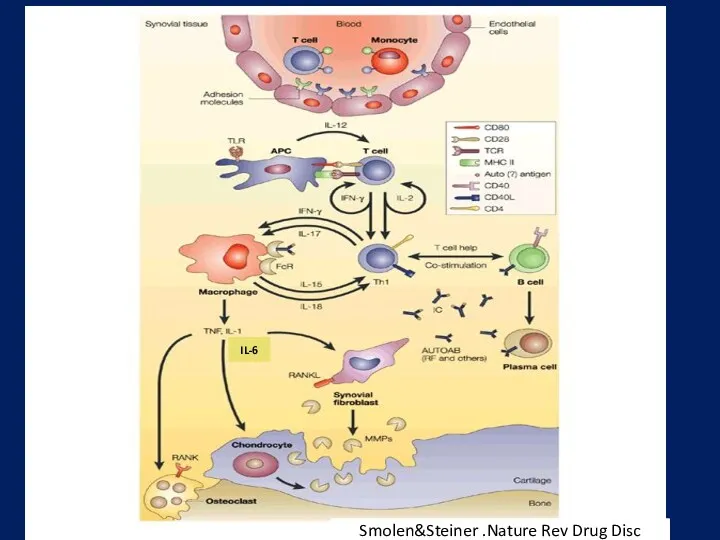
- 7. Smolen&Steiner .Nature Rev Drug Disc IL-6
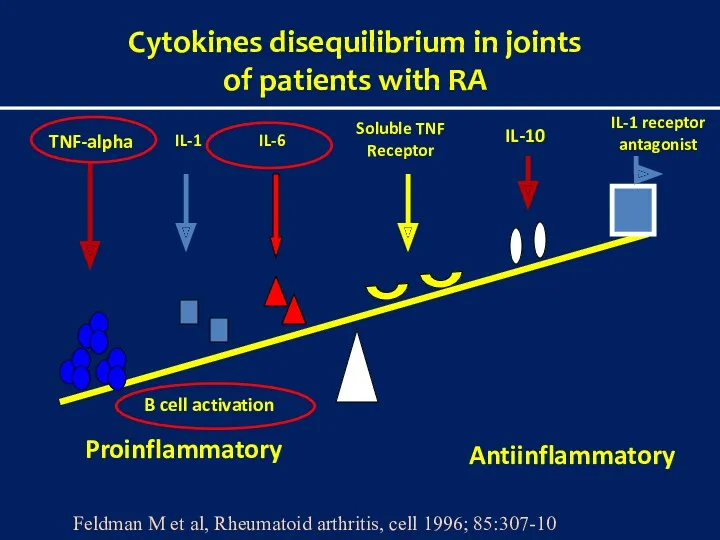
- 8. Cytokines disequilibrium in joints of patients with RA Proinflammatory Antiinflammatory TNF-alpha IL-1 Soluble TNF Receptor IL-1
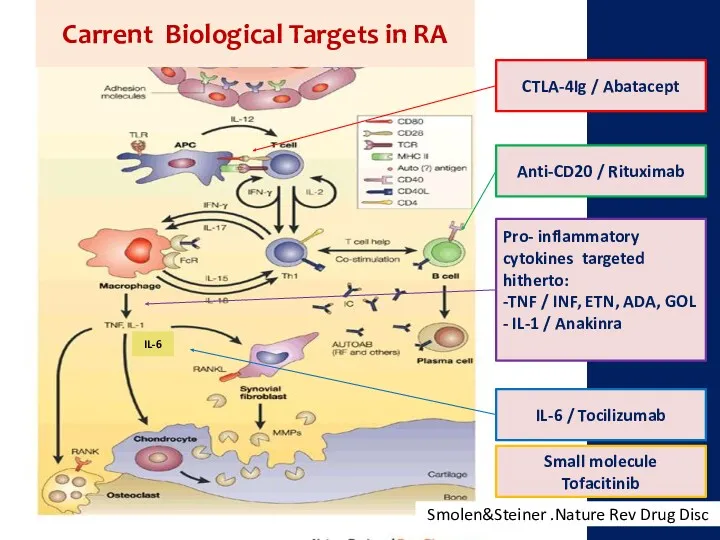
- 10. IL-6 CTLA-4Ig / Abatacept Anti-CD20 / Rituximab Pro- inflammatory cytokines targeted hitherto: -TNF / INF, ETN,
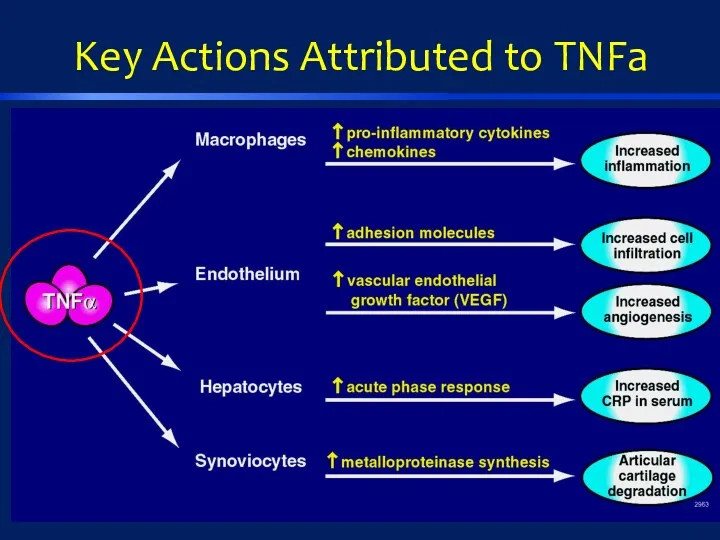
- 12. Key Actions Attributed to TNFa
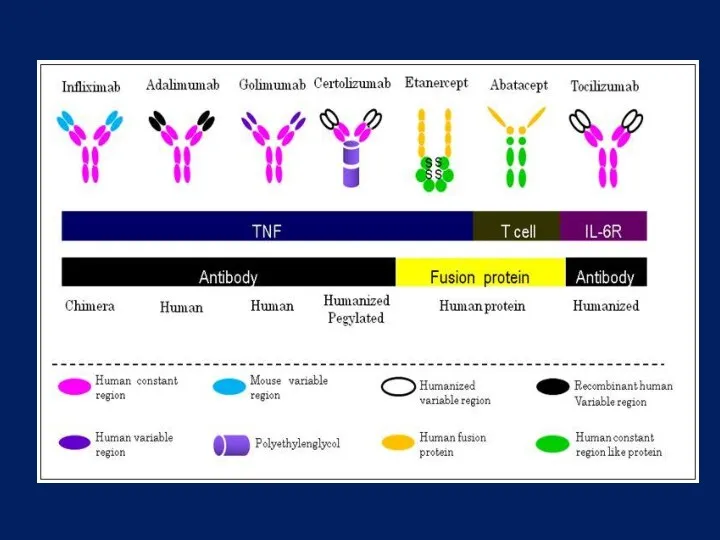
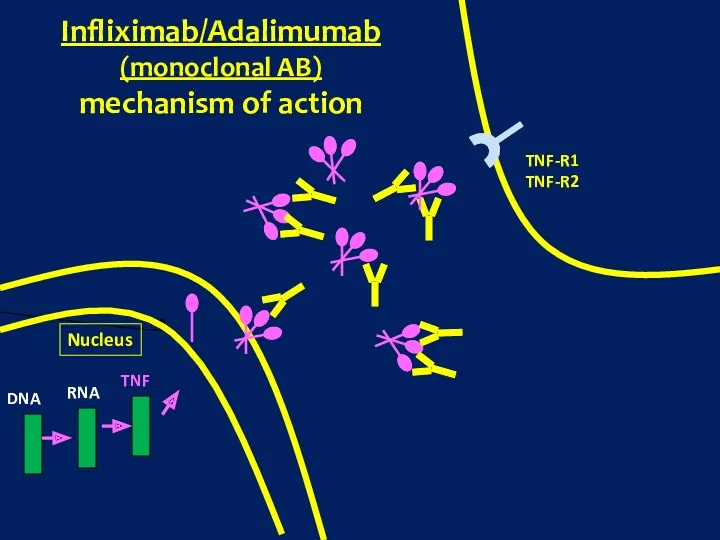
- 13. Nucleus DNA RNA TNF TNF-R1 TNF-R2 Infliximab/Adalimumab (monoclonal AB) mechanism of action
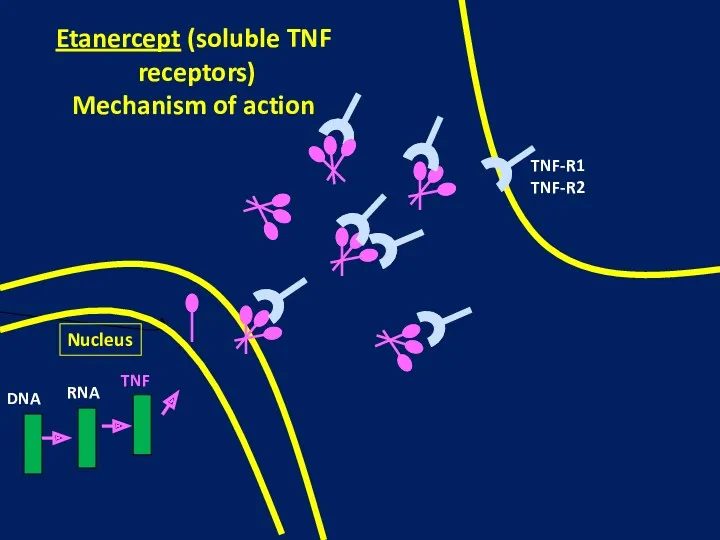
- 14. Nucleus DNA RNA TNF TNF-R1 TNF-R2 Etanercept (soluble TNF receptors) Mechanism of action
- 15. Anti TNF side effects Anaphylaxis Local site irritation Rash Chest pain Shortness of breath Infections- All+TB,
- 16. Relative contraindications to the use of TNF inhibitors SLE, Lupus overlap s-me Multiple sclerosis, optic neuritis,
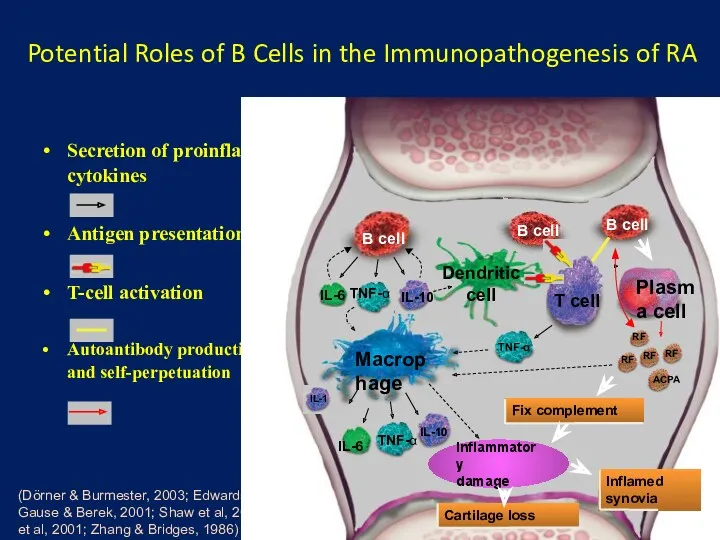
- 17. Potential Roles of B Cells in the Immunopathogenesis of RA
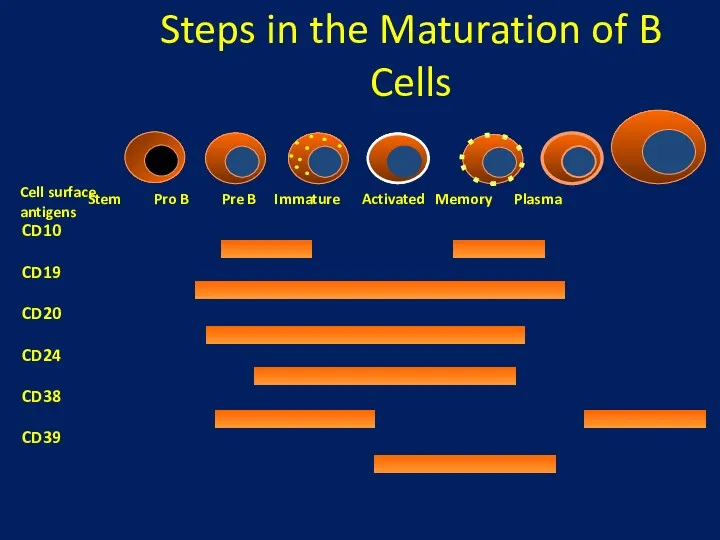
- 18. Steps in the Maturation of B Cells
- 19. Rituximab Rituximab is a genetically engineered anti-CD20 therapeutic monoclonal antibody that selectively depletes CD20+ B cells
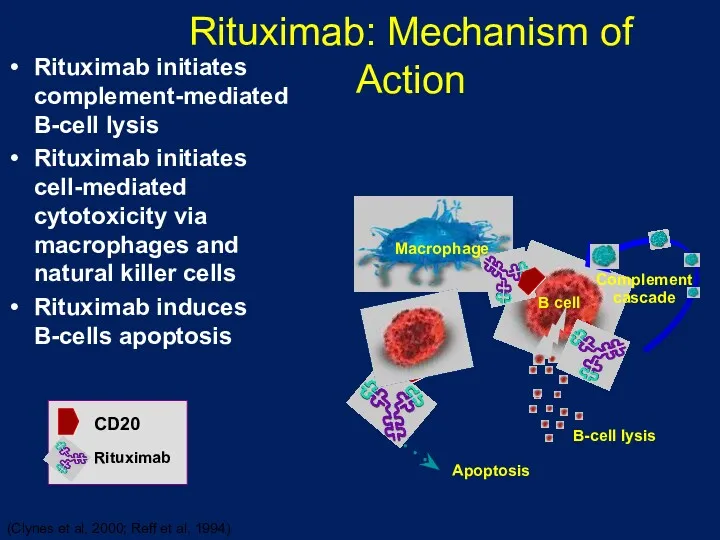
- 20. Rituximab: Mechanism of Action Rituximab initiates complement-mediated B-cell lysis Rituximab initiates cell-mediated cytotoxicity via macrophages and
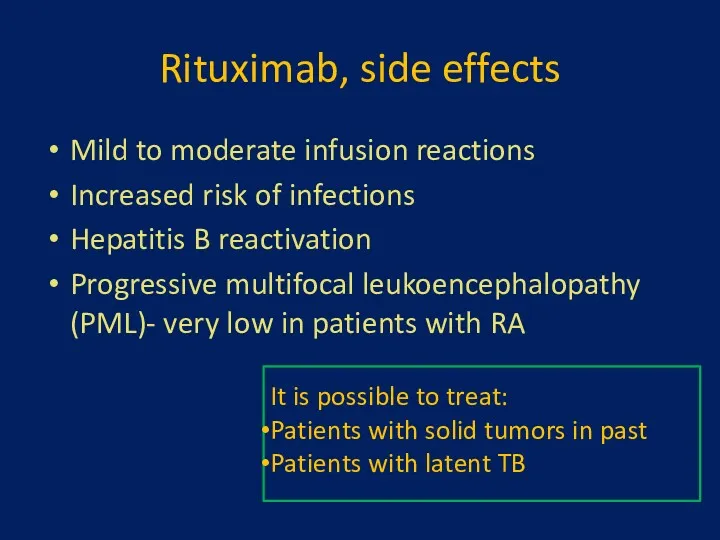
- 21. Rituximab, side effects Mild to moderate infusion reactions Increased risk of infections Hepatitis B reactivation Progressive
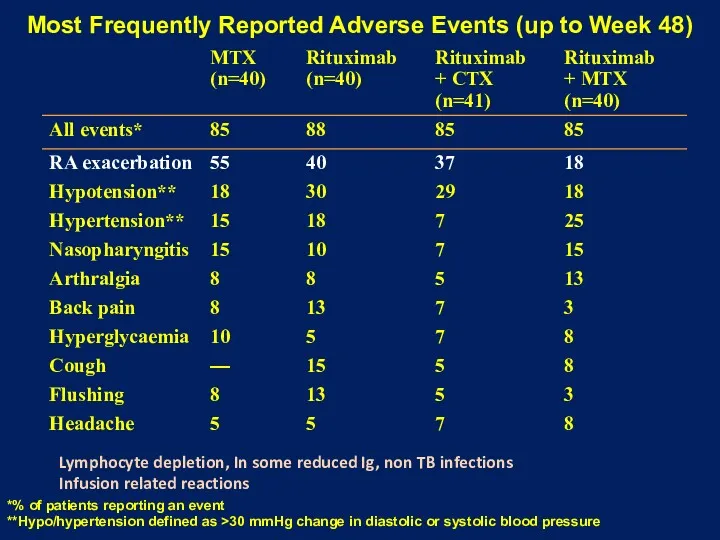
- 22. Most Frequently Reported Adverse Events (up to Week 48) *% of patients reporting an event **Hypo/hypertension
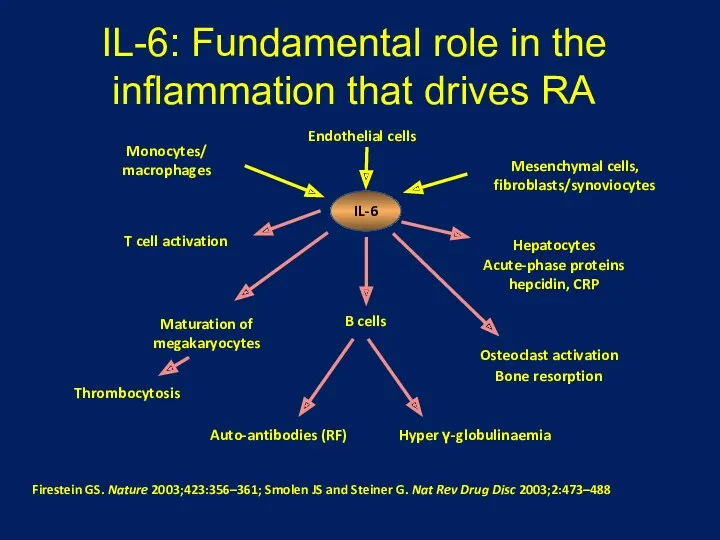
- 23. IL-6: Fundamental role in the inflammation that drives RA Firestein GS. Nature 2003;423:356–361; Smolen JS and
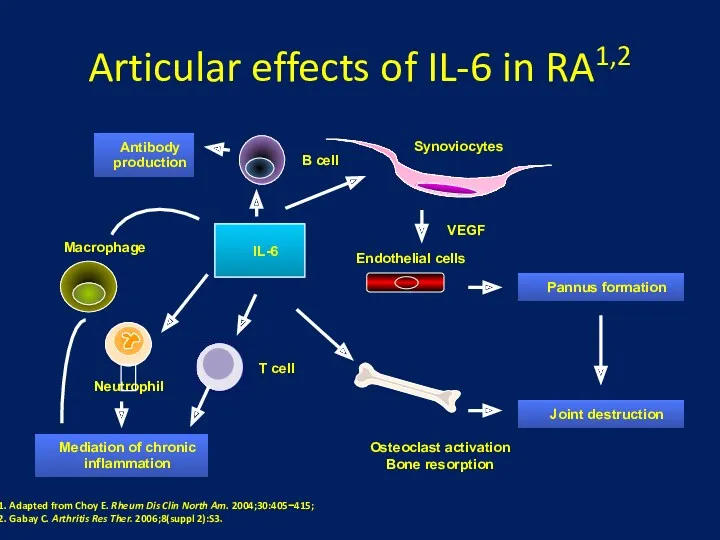
- 24. Articular effects of IL-6 in RA1,2 Synoviocytes Osteoclast activation Bone resorption Endothelial cells VEGF Pannus formation
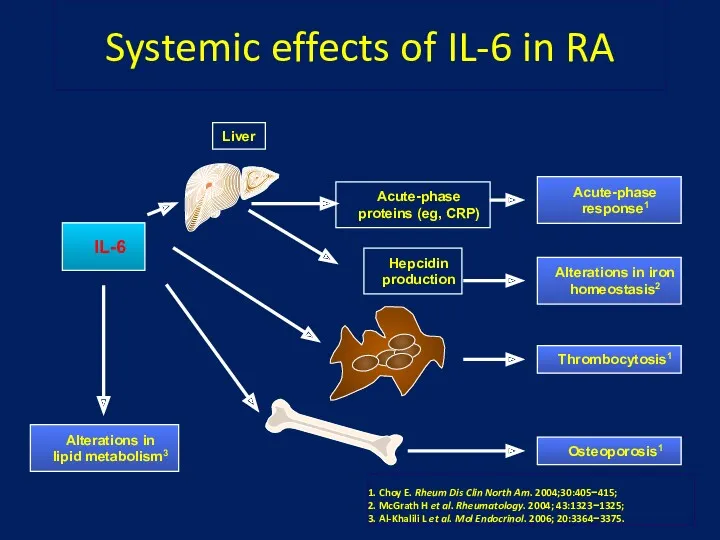
- 25. Systemic effects of IL-6 in RA IL-6 Acute-phase response1 Alterations in iron homeostasis2 Liver Acute-phase proteins
- 27. Primer: Immunology and Autoimmunity Stephanie C. Eisenbarth and Dirk Homann
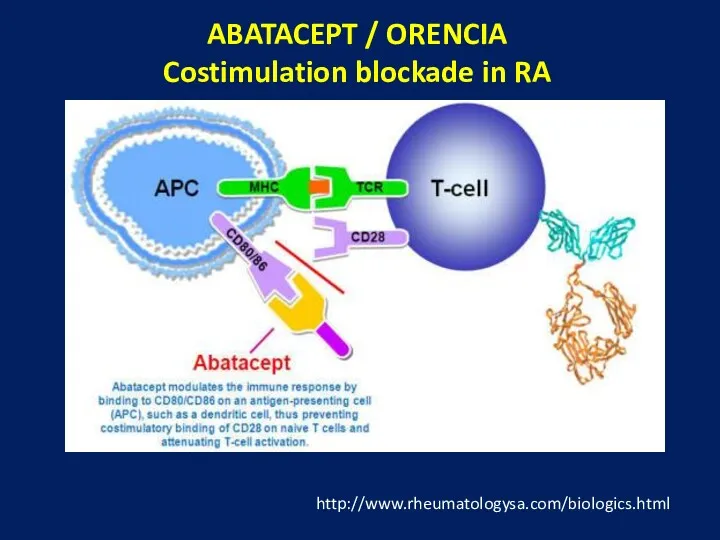
- 28. ABATACEPT / ORENCIA Costimulation blockade in RA http://www.rheumatologysa.com/biologics.html
- 29. XELJANZ (Tofacitinib): a new class of oral RA therapy that targets inflammation from inside the cell
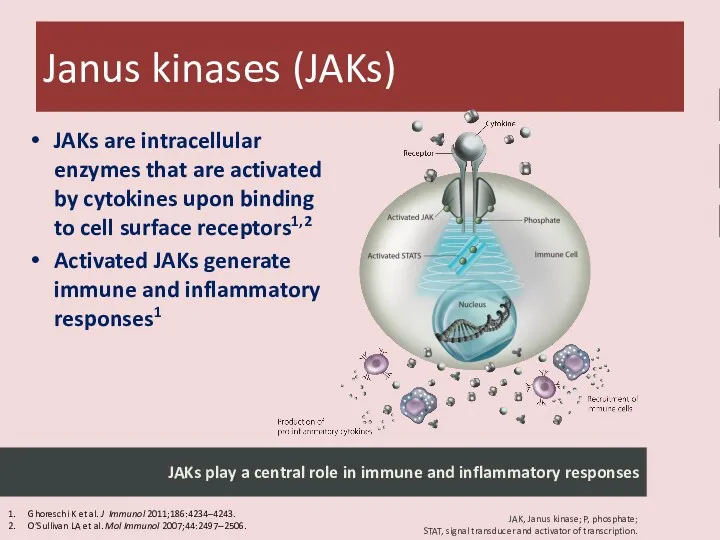
- 30. JAKs are intracellular enzymes that are activated by cytokines upon binding to cell surface receptors1,2 Activated
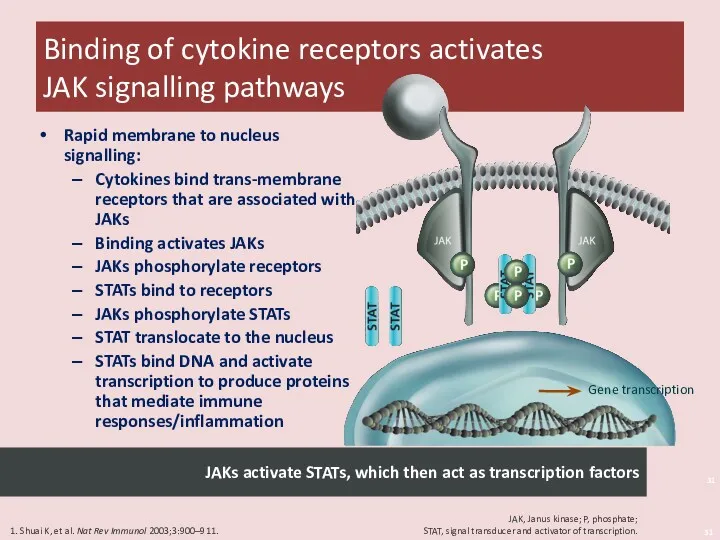
- 31. Binding of cytokine receptors activates JAK signalling pathways Shuai 2003/p 900/col 1/para 1 & p 901/Fig
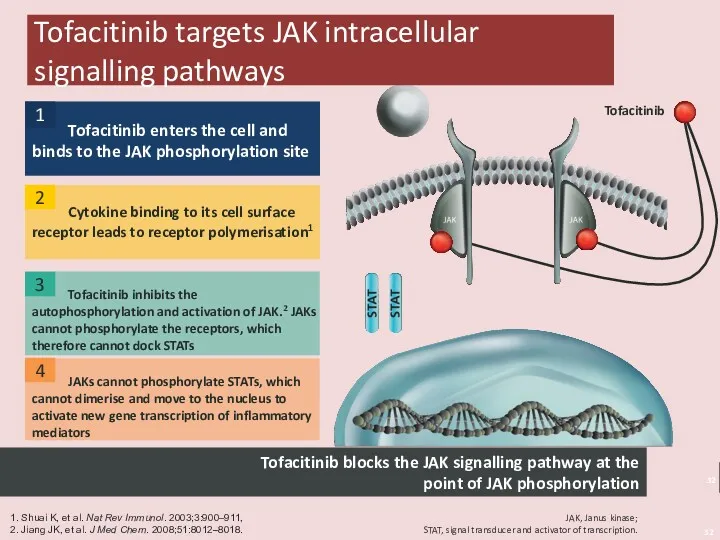
- 32. Tofacitinib targets JAK intracellular signalling pathways Tofacitinib inhibits the autophosphorylation and activation of JAK.2 JAKs cannot
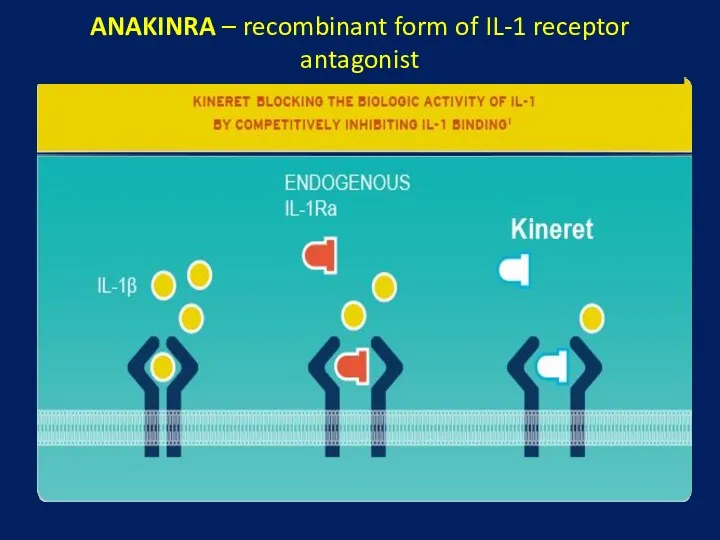
- 33. ANAKINRA – recombinant form of IL-1 receptor antagonist
- 34. Anakinra indications Auto- inflammatory syndromes, periodic fevers Systemic onset juvenile inflammatory arthritis Adult-onset Still’s disease Familial
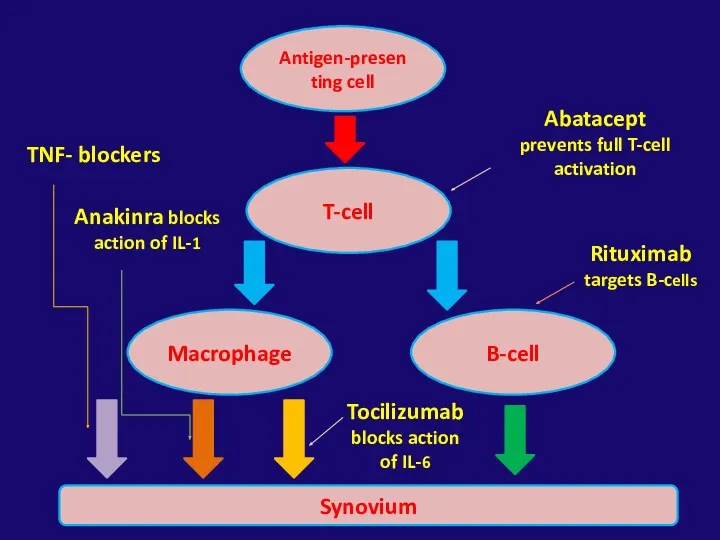
- 35. Antigen-presenting cell T-cell B-cell Macrophage Synovium TNF- blockers Anakinra blocks action of IL-1 Tocilizumab blocks action
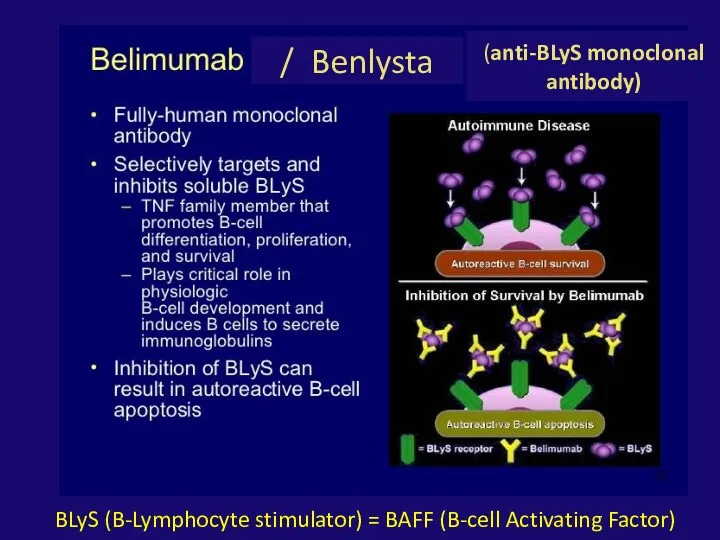
- 36. / Benlysta BLyS (B-Lymphocyte stimulator) = BAFF (B-cell Activating Factor) (anti-BLyS monoclonal antibody)
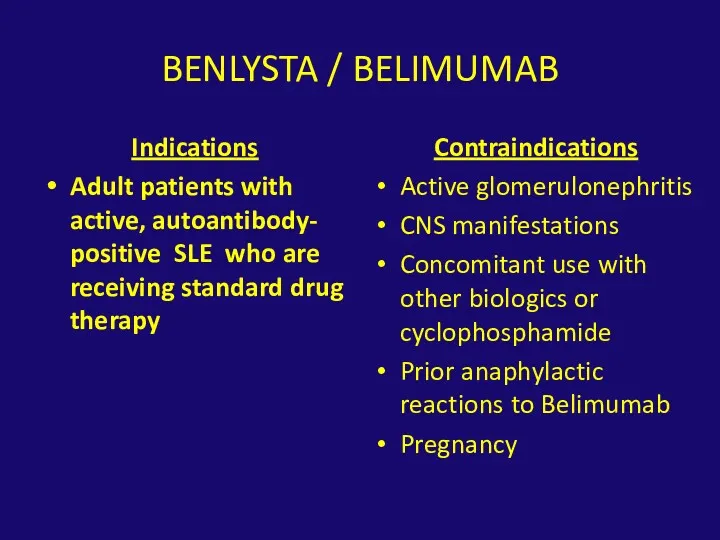
- 37. BENLYSTA / BELIMUMAB Indications Adult patients with active, autoantibody- positive SLE who are receiving standard drug
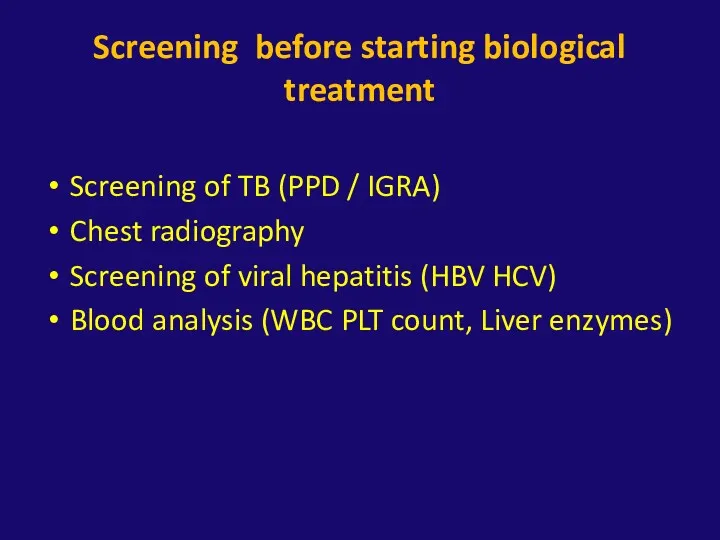
- 38. Screening before starting biological treatment Screening of TB (PPD / IGRA) Chest radiography Screening of viral
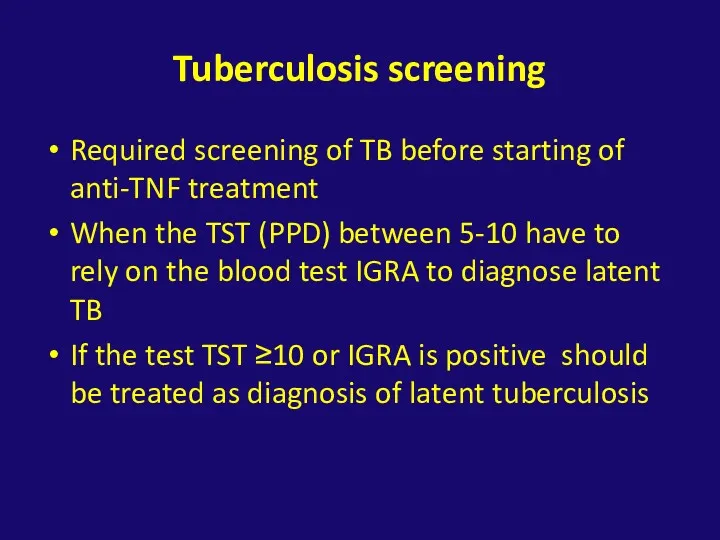
- 39. Tuberculosis screening Required screening of TB before starting of anti-TNF treatment When the TST (PPD) between
- 42. Скачать презентацию








 Роль лишайников в почвообразовании
Роль лишайников в почвообразовании Кровь и остальные компоненты внутренней среды организма
Кровь и остальные компоненты внутренней среды организма Строение центральной нервной системы человека. Подготовка к ОГЭ и ЕГЭ
Строение центральной нервной системы человека. Подготовка к ОГЭ и ЕГЭ Зимующие птицы Тульской области
Зимующие птицы Тульской области Тениоз Цистицеркоз
Тениоз Цистицеркоз Третий закон Грегора Менделя
Третий закон Грегора Менделя Сцепленное с полом наследование
Сцепленное с полом наследование Мутациялық өзгерістер
Мутациялық өзгерістер Строение цветка
Строение цветка Птицы от А до Я
Птицы от А до Я Вестники весны
Вестники весны Мимические мышцы
Мимические мышцы Проблема безпритульних тварин
Проблема безпритульних тварин Видозміни листка (газообмін, випаровування води, фотосинтез),
Видозміни листка (газообмін, випаровування води, фотосинтез), Презентация Экологическая игра Моя планета-человеческий дом
Презентация Экологическая игра Моя планета-человеческий дом Презентация по теме: Экосистема
Презентация по теме: Экосистема Железы внутренней секреции
Железы внутренней секреции Биологический метод исследования. Определение патогенности и вирулентности микроорганизмов
Биологический метод исследования. Определение патогенности и вирулентности микроорганизмов Развитие низших хордовых. Амфибии
Развитие низших хордовых. Амфибии Животные степей
Животные степей Развитие эмбриологии в XVI—XVIII и начале XIX века. (Лекция 10)
Развитие эмбриологии в XVI—XVIII и начале XIX века. (Лекция 10) Обмен веществ - основа существования клетки
Обмен веществ - основа существования клетки Этапы эволюции человека
Этапы эволюции человека Презентация Многообразие насекомых
Презентация Многообразие насекомых Мышцы головы животных. Мультимедийный проект
Мышцы головы животных. Мультимедийный проект Dinoflagellates
Dinoflagellates Жизненный цикл и деление клетки митоз амитоз
Жизненный цикл и деление клетки митоз амитоз Вегетативная нервная система
Вегетативная нервная система