Содержание
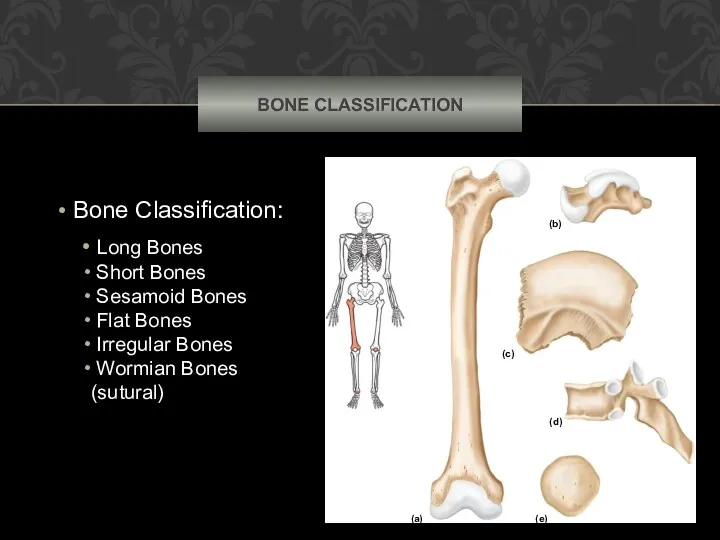
- 2. BONE CLASSIFICATION Bone Classification: Long Bones Short Bones Sesamoid Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Wormian Bones
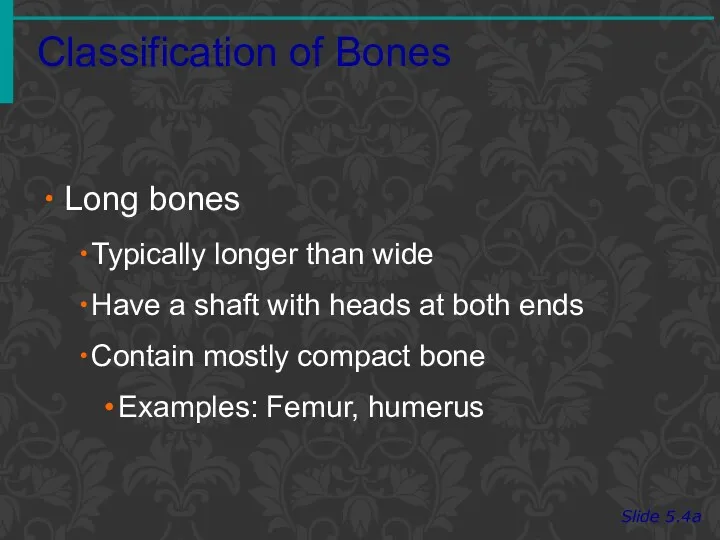
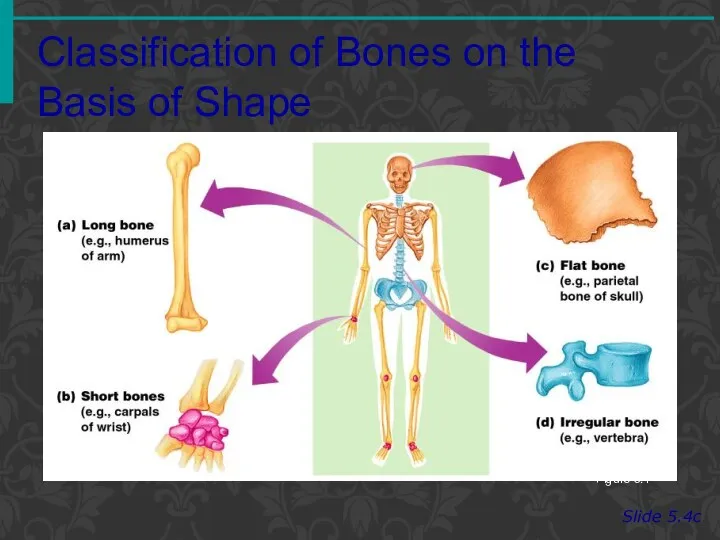
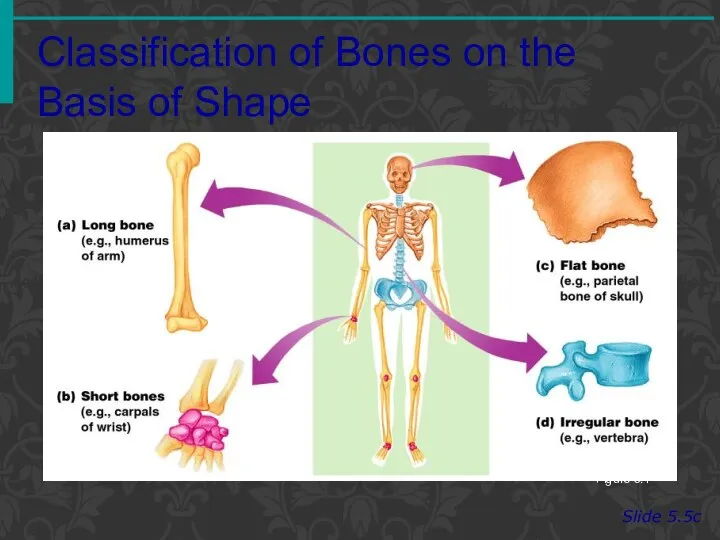
- 3. Classification of Bones Slide 5.4a Long bones Typically longer than wide Have a shaft with heads
- 4. Classification of Bones Slide 5.4b Short bones Generally cube-shape Contain mostly spongy bone Examples: Carpals, tarsals
- 5. Classification of Bones on the Basis of Shape Slide 5.4c Figure 5.1
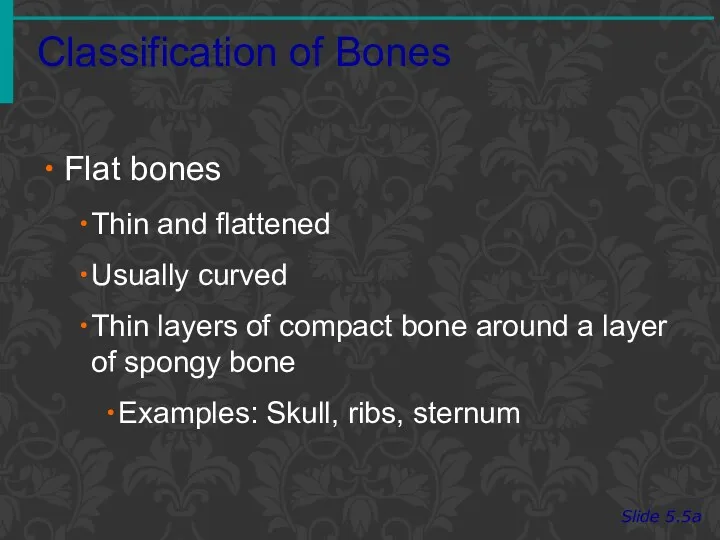
- 6. Classification of Bones Slide 5.5a Flat bones Thin and flattened Usually curved Thin layers of compact
- 7. Classification of Bones Slide 5.5b Irregular bones Irregular shape Do not fit into other bone classification
- 8. Classification of Bones on the Basis of Shape Slide 5.5c Figure 5.1
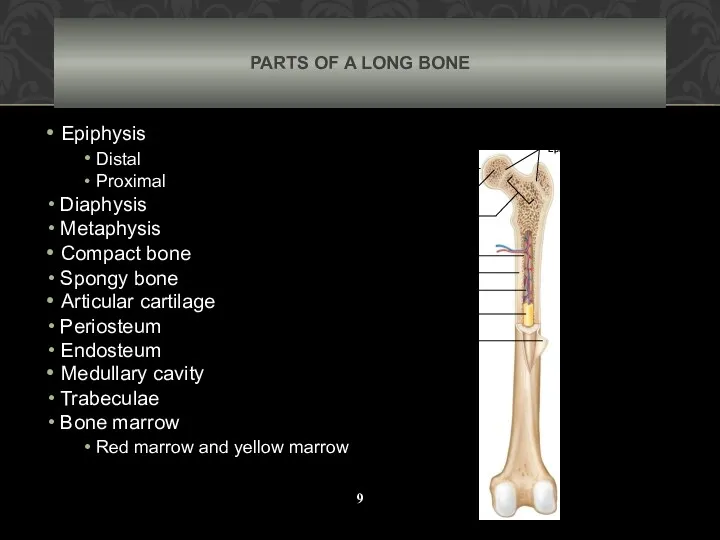
- 9. PARTS OF A LONG BONE Epiphysis Distal Proximal Diaphysis Metaphysis Compact bone Spongy bone Articular cartilage
- 10. MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE Bone cells are called osteocytes in a lacuna Osteocytes transport nutrients and wastes by
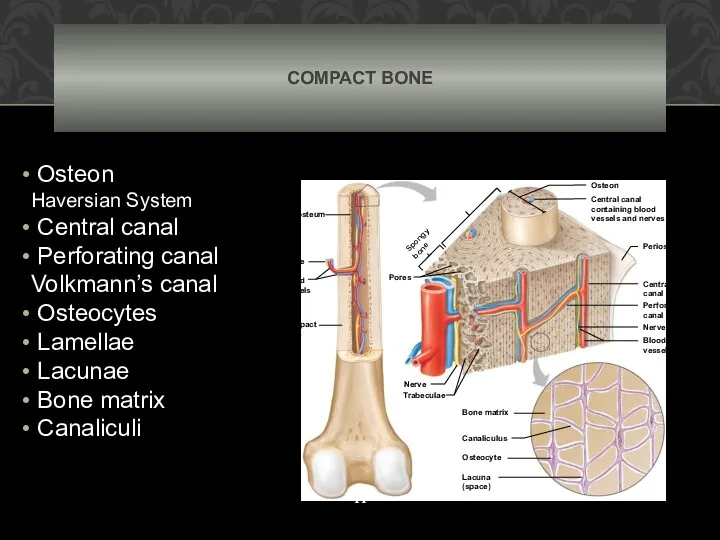
- 11. COMPACT BONE Osteon Haversian System Central canal Perforating canal Volkmann’s canal Osteocytes Lamellae Lacunae Bone matrix
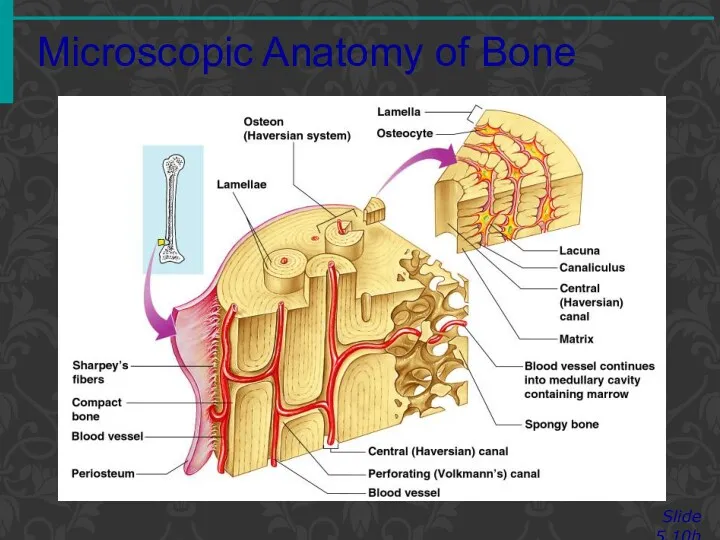
- 12. Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Slide 5.10b Figure 5.3
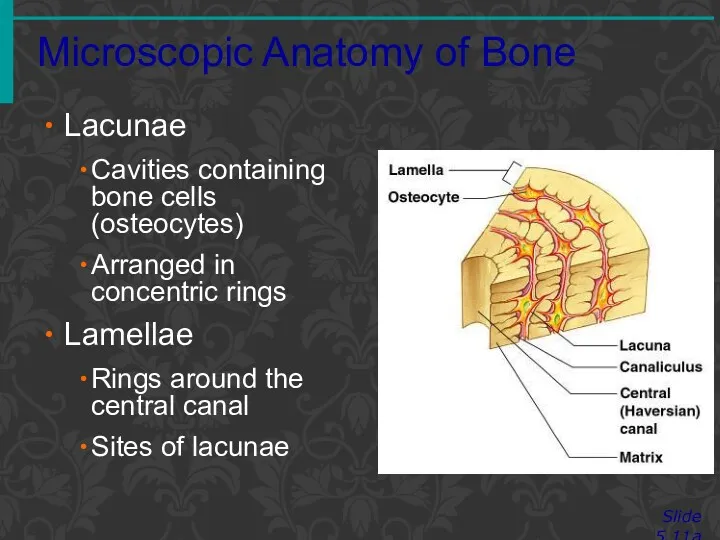
- 13. Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Slide 5.11a Lacunae Cavities containing bone cells (osteocytes) Arranged in concentric rings
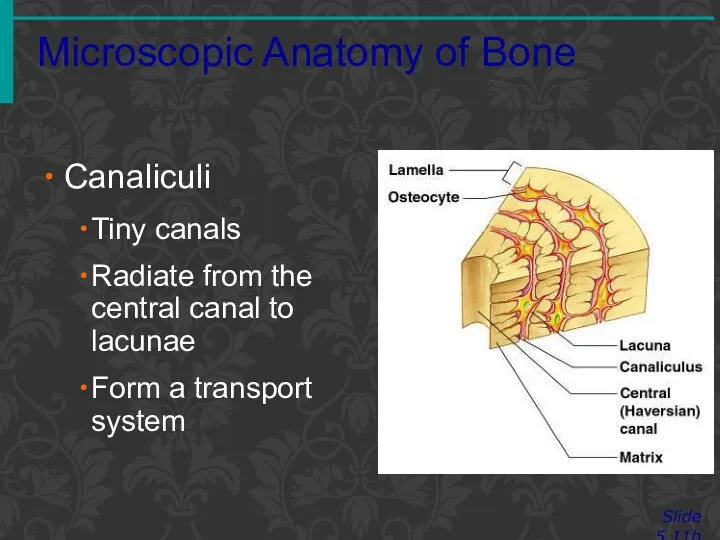
- 14. Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Slide 5.11b Canaliculi Tiny canals Radiate from the central canal to lacunae
- 15. BONE DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH Parts of the skeletal system begin to develop during the first few
- 16. INTRAMEMBRANOUS BONES Intramembranous Bones These bones originate within sheetlike layers of connective tissues They are the
- 17. ENDOCHONDRAL BONES Endochondral Bones Bones begin as hyaline cartilage Form models for future bones These are
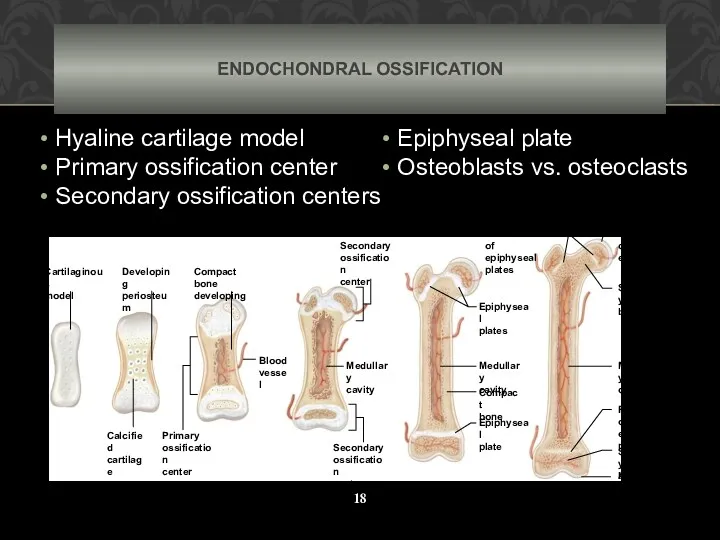
- 18. ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION Hyaline cartilage model Primary ossification center Secondary ossification centers Epiphyseal plate Osteoblasts vs. osteoclasts
- 19. BONE FUNCTION Bones shape, support, and protect body structures
- 20. SUPPORT, PROTECTION, AND MOVEMENT Support, Movement & Protection Gives shape to head, etc. Supports body’s weight
- 21. BLOOD CELL FORMATION Blood Cell Formation Also known as hematopoiesis Occurs in the red bone marrow
- 22. INORGANIC SALT STORAGE Inorganic Salt Storage Calcium Phosphate Magnesium Sodium Potassium
- 23. SKELETAL ORGANIZATION The actual number of bones in the human skeleton varies from person to person
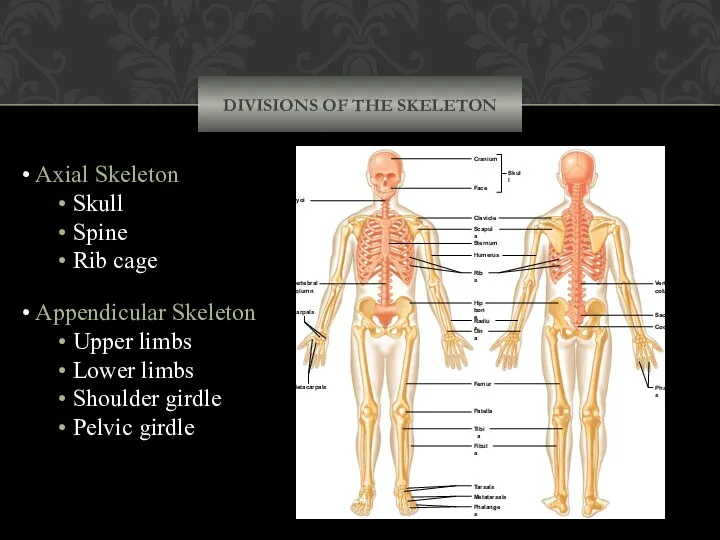
- 24. DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETON Axial Skeleton Skull Spine Rib cage Appendicular Skeleton Upper limbs Lower limbs
- 25. SKULL Is composed of the cranium (brain case) and the facial bones
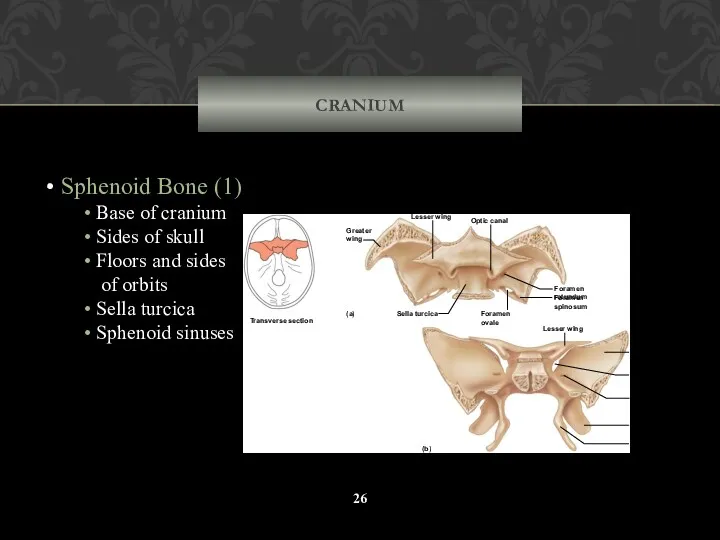
- 26. CRANIUM Sphenoid Bone (1) Base of cranium Sides of skull Floors and sides of orbits Sella
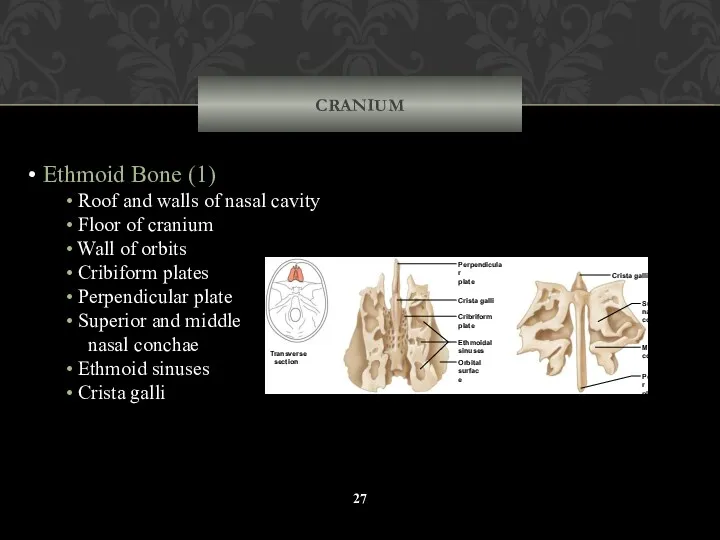
- 27. CRANIUM Ethmoid Bone (1) Roof and walls of nasal cavity Floor of cranium Wall of orbits
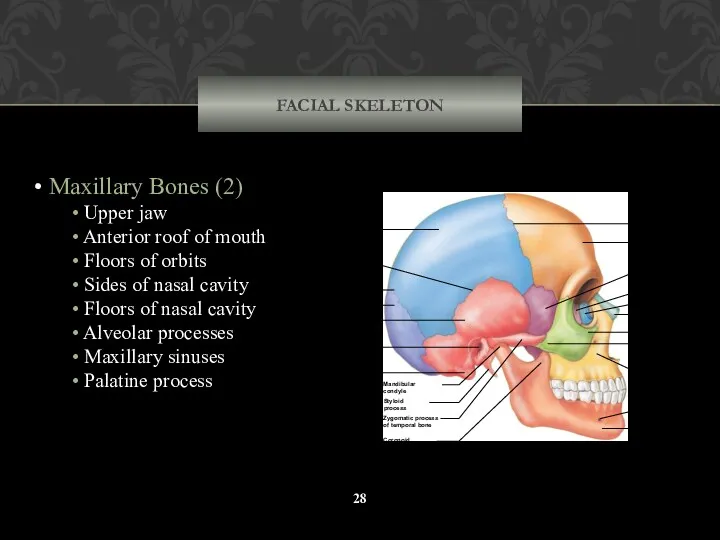
- 28. FACIAL SKELETON Maxillary Bones (2) Upper jaw Anterior roof of mouth Floors of orbits Sides of
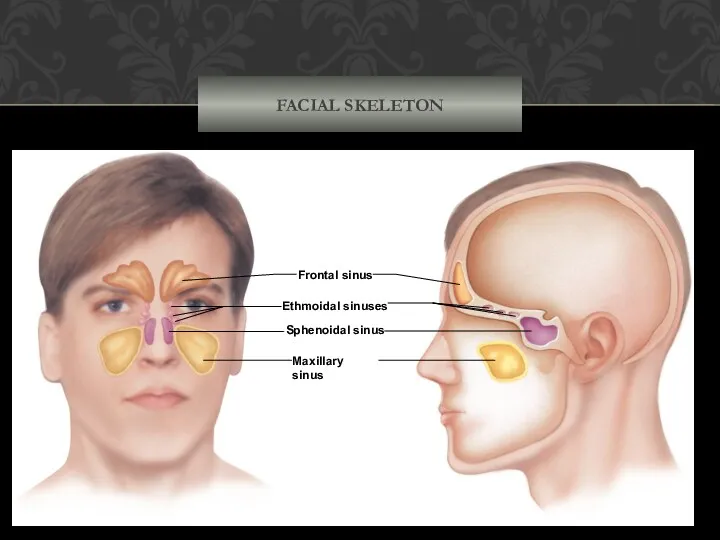
- 29. FACIAL SKELETON Frontal sinus Ethmoidal sinuses Sphenoidal sinus Maxillary sinus
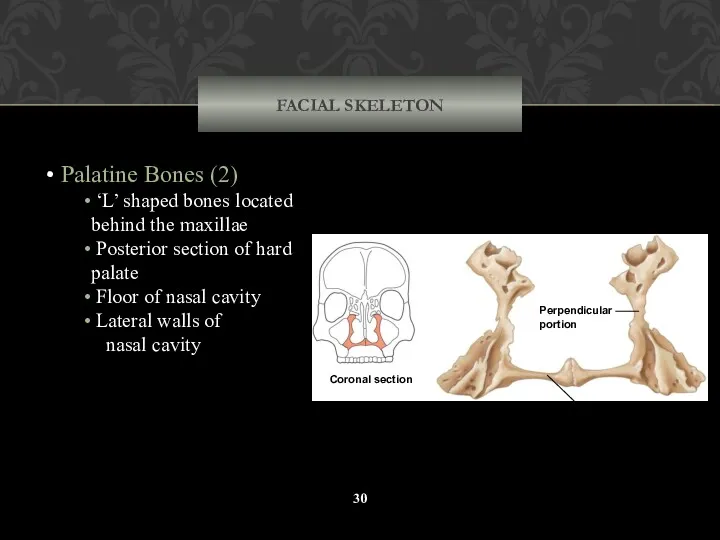
- 30. FACIAL SKELETON Palatine Bones (2) ‘L’ shaped bones located behind the maxillae Posterior section of hard
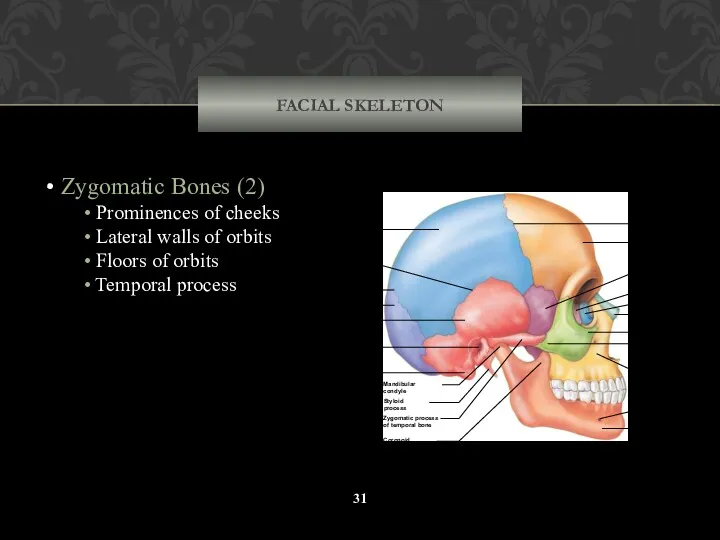
- 31. FACIAL SKELETON Zygomatic Bones (2) Prominences of cheeks Lateral walls of orbits Floors of orbits Temporal
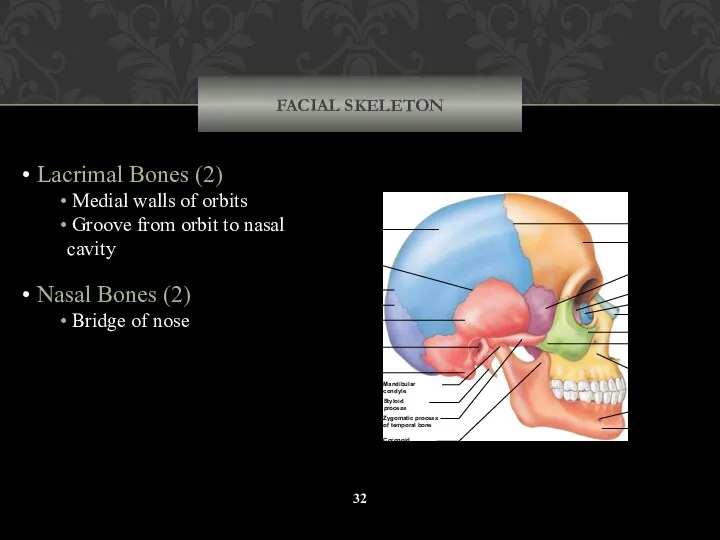
- 32. FACIAL SKELETON Lacrimal Bones (2) Medial walls of orbits Groove from orbit to nasal cavity Nasal
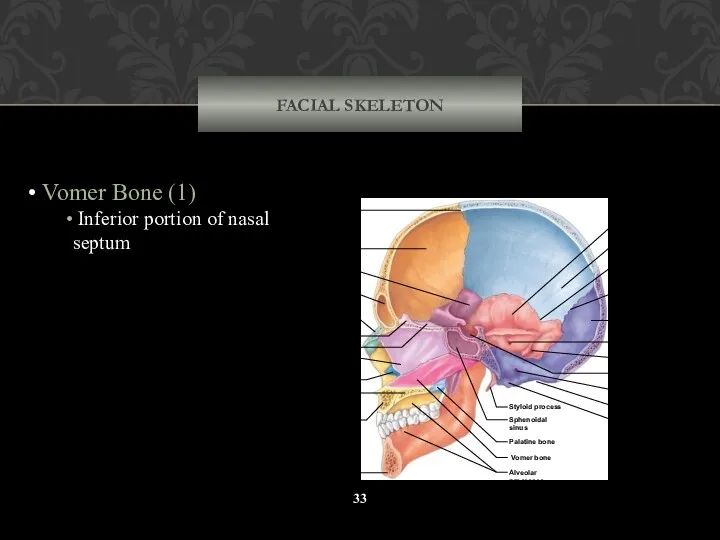
- 33. FACIAL SKELETON Vomer Bone (1) Inferior portion of nasal septum Coronal suture Frontal bone Nasal bone
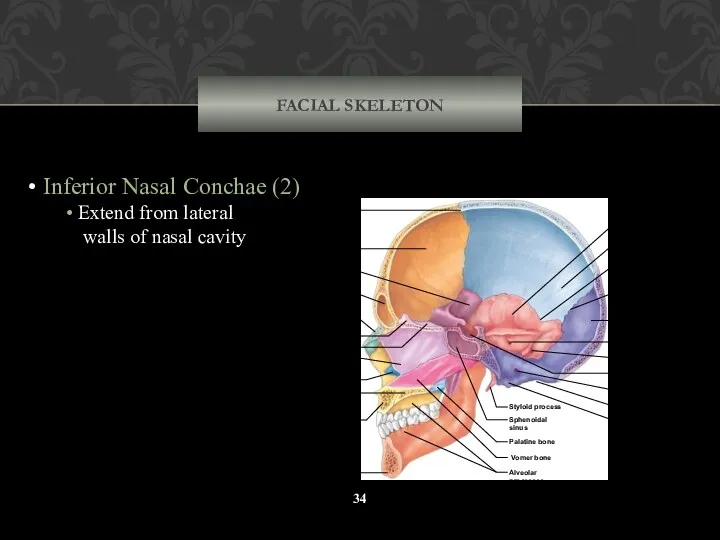
- 34. FACIAL SKELETON Inferior Nasal Conchae (2) Extend from lateral walls of nasal cavity Coronal suture Frontal
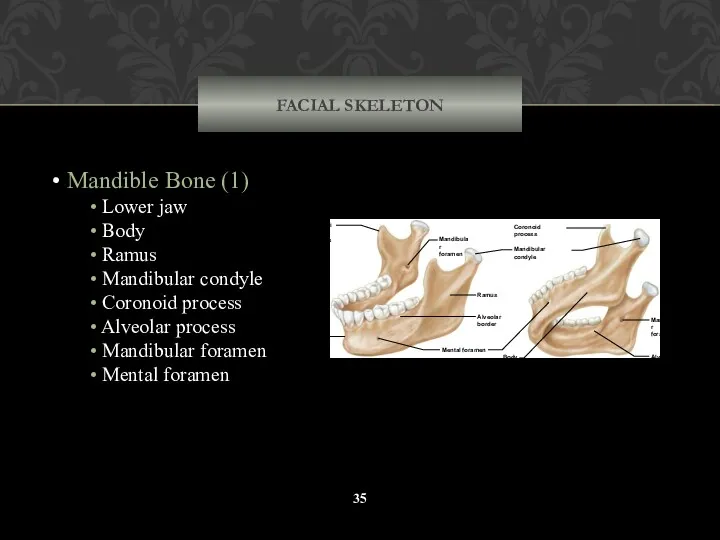
- 35. FACIAL SKELETON Mandible Bone (1) Lower jaw Body Ramus Mandibular condyle Coronoid process Alveolar process Mandibular
- 36. VERTEBRAL COLUMN The vertebral column, or spinal column, consists of many vertebrae separated by cartilaginous intervertebral
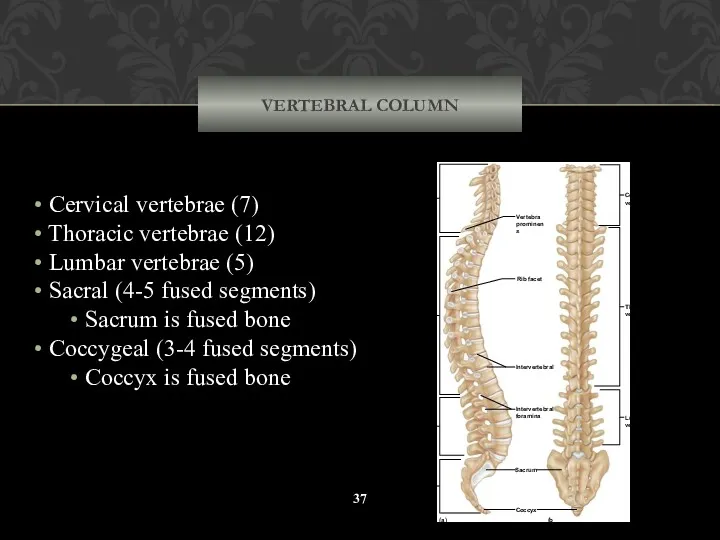
- 37. VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cervical vertebrae (7) Thoracic vertebrae (12) Lumbar vertebrae (5) Sacral (4-5 fused segments) Sacrum
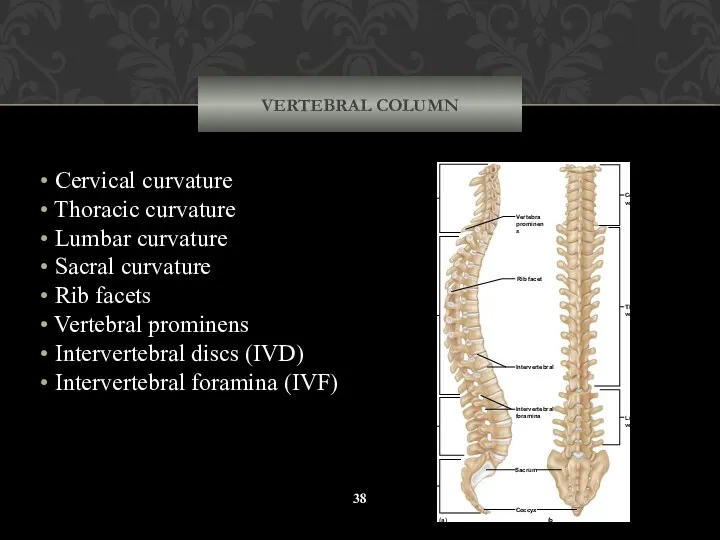
- 38. VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cervical curvature Thoracic curvature Lumbar curvature Sacral curvature Rib facets Vertebral prominens Intervertebral discs
- 39. TYPICAL VERTEBRAE Includes the following parts: Vertebral body Pedicles Lamina Spinous process Transverse processes Vertebral foramen
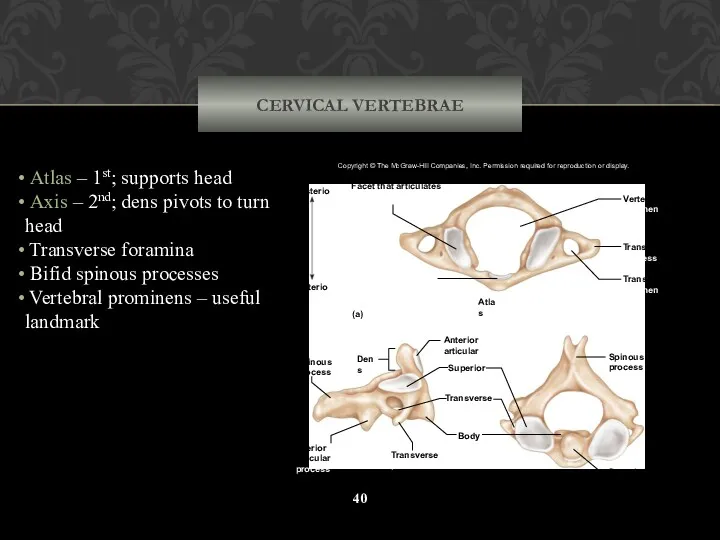
- 40. CERVICAL VERTEBRAE Atlas – 1st; supports head Axis – 2nd; dens pivots to turn head Transverse
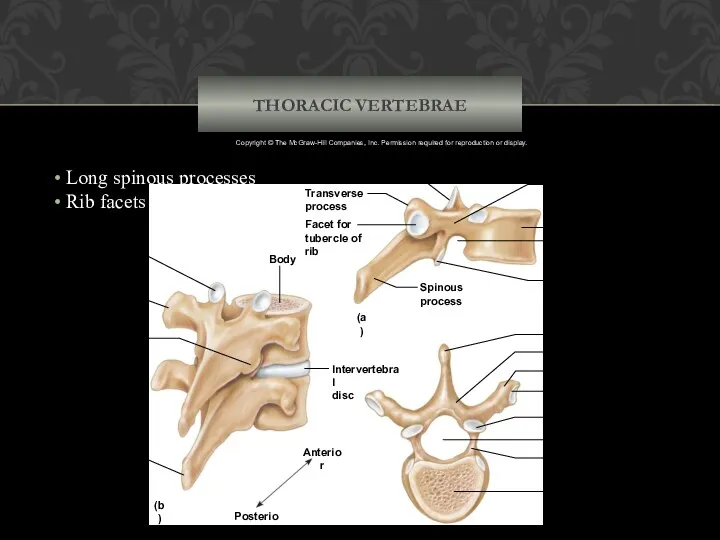
- 41. THORACIC VERTEBRAE Body Superior articular process Spinous process Transverse process Inferior articular process Intervertebral disc Anterior
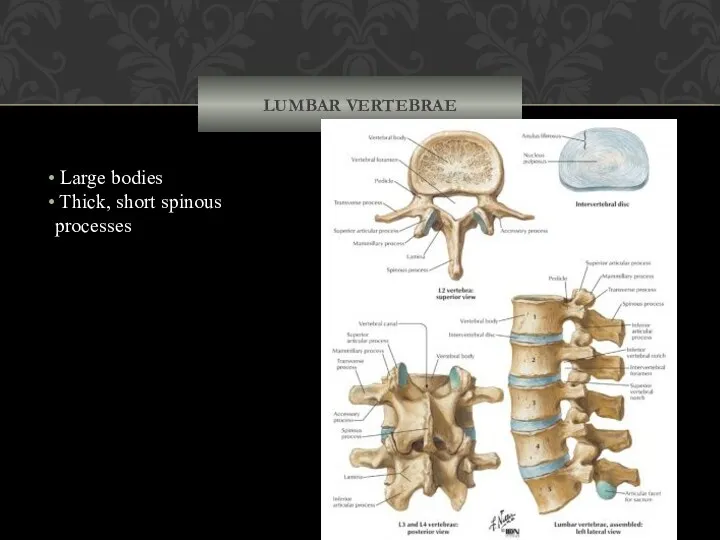
- 42. LUMBAR VERTEBRAE Large bodies Thick, short spinous processes (c) Lumbar vertebra Lamina Pedicle Body Vertebral foramen
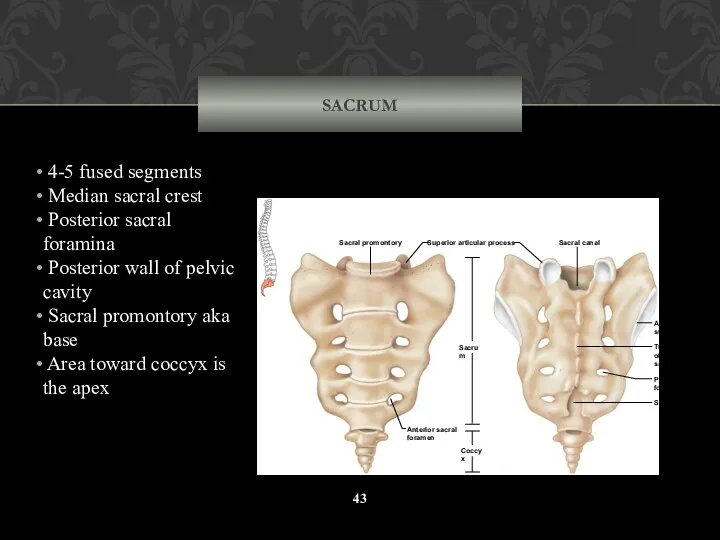
- 43. SACRUM 4-5 fused segments Median sacral crest Posterior sacral foramina Posterior wall of pelvic cavity Sacral
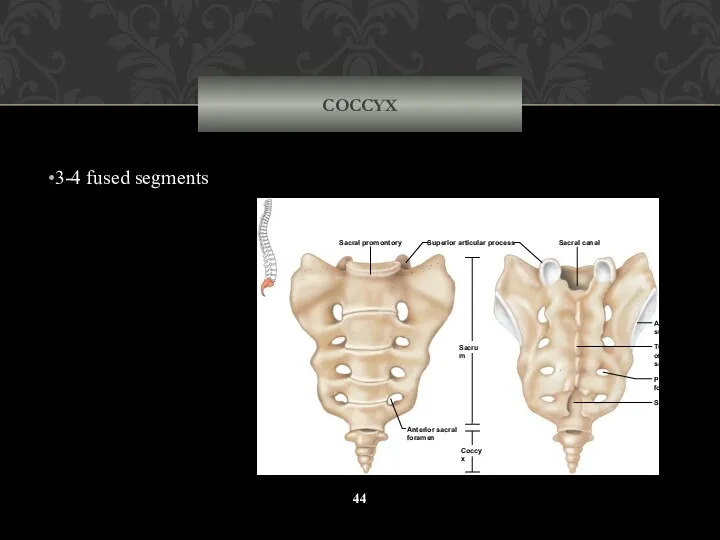
- 44. COCCYX 3-4 fused segments Sacral canal Tubercle of median sacral crest Auricular surface Posterior sacral foramen
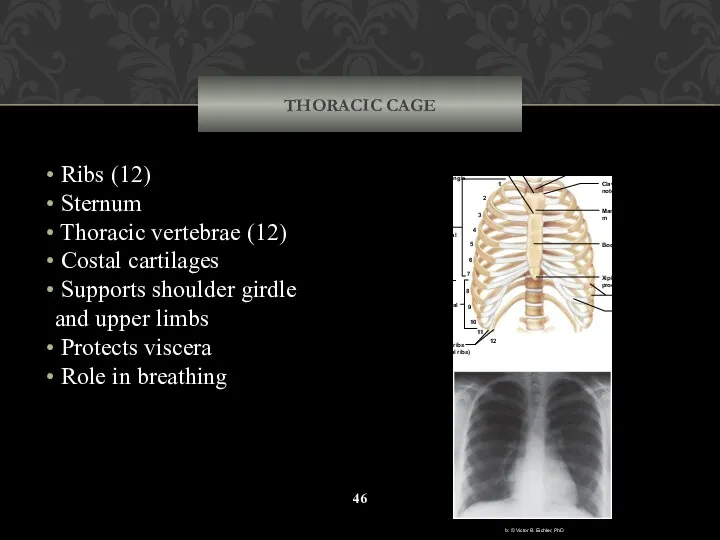
- 45. THORACIC CAGE The thoracic cage includes the ribs, the thoracic vertebrae, the sternum, and the costal
- 46. THORACIC CAGE Ribs (12) Sternum Thoracic vertebrae (12) Costal cartilages Supports shoulder girdle and upper limbs
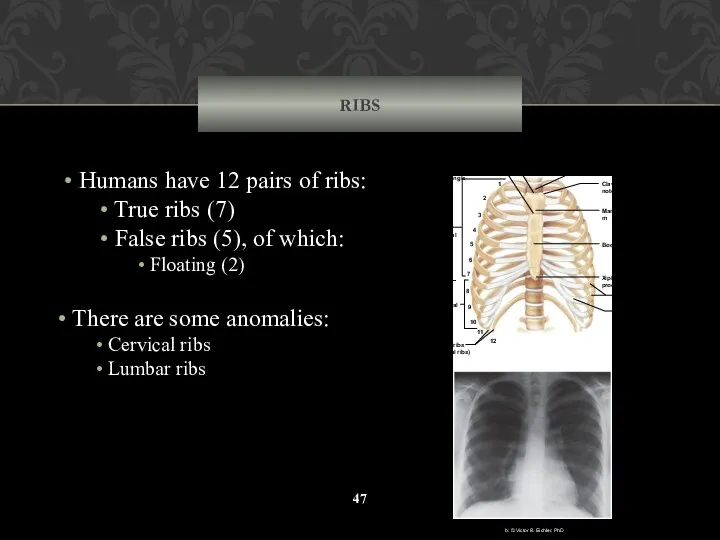
- 47. RIBS Humans have 12 pairs of ribs: True ribs (7) False ribs (5), of which: Floating
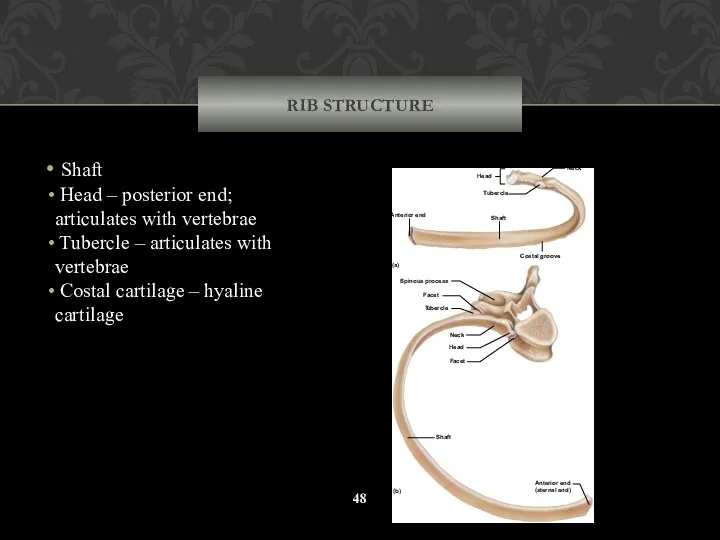
- 48. RIB STRUCTURE Shaft Head – posterior end; articulates with vertebrae Tubercle – articulates with vertebrae Costal
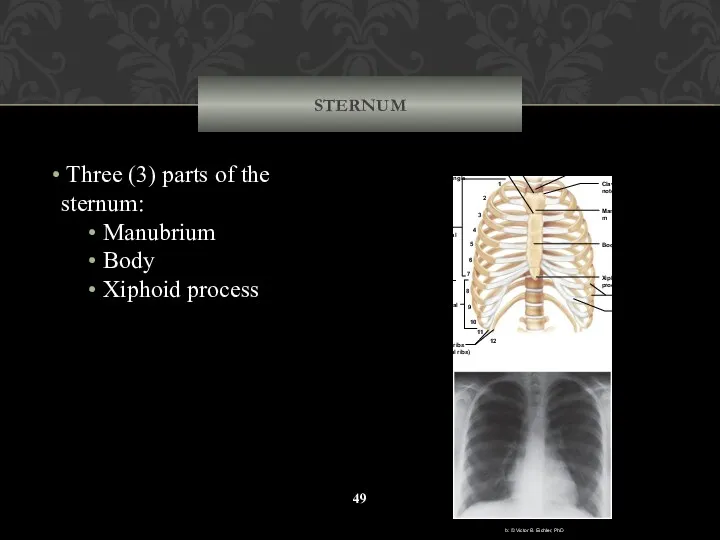
- 49. STERNUM Three (3) parts of the sternum: Manubrium Body Xiphoid process 1 2 3 4 5
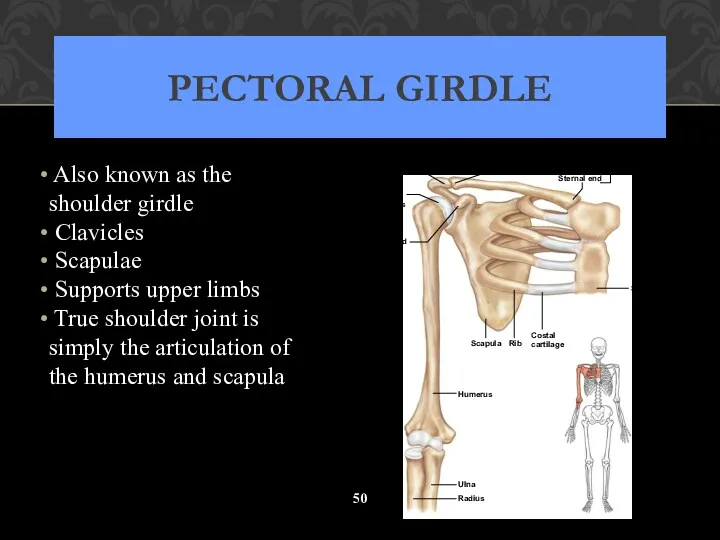
- 50. PECTORAL GIRDLE Also known as the shoulder girdle Clavicles Scapulae Supports upper limbs True shoulder joint
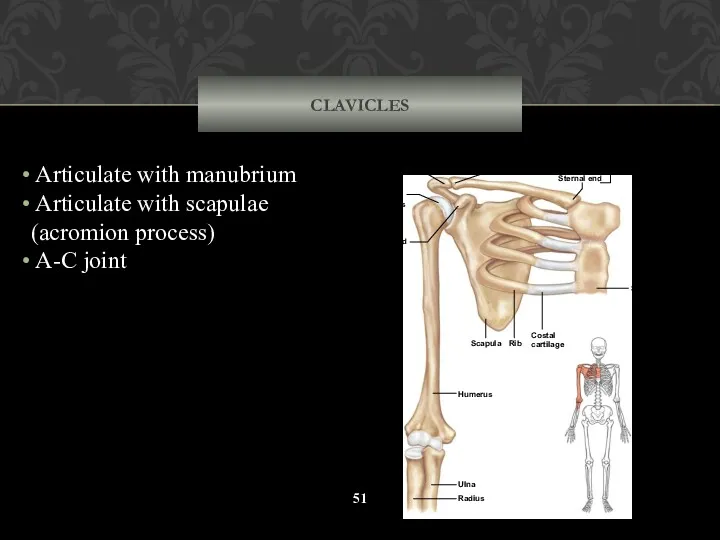
- 51. CLAVICLES Articulate with manubrium Articulate with scapulae (acromion process) A-C joint Sternum Costal cartilage Rib Scapula
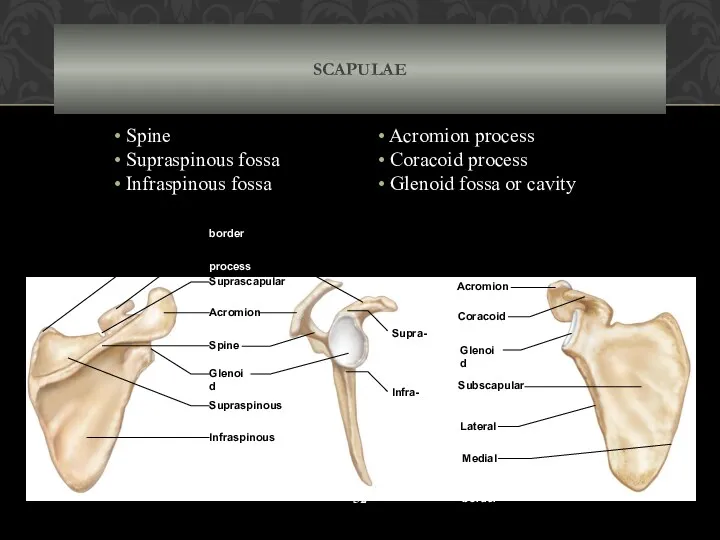
- 52. Acromion process Coracoid process Spine Glenoid cavity Suprascapular notch Superior border Supra- glenoid tubercle Infra- glenoid
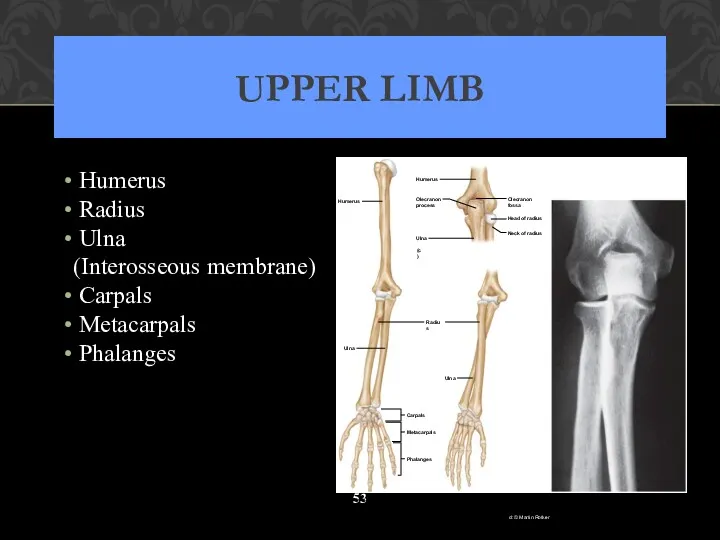
- 53. UPPER LIMB Humerus Radius Ulna (Interosseous membrane) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Olecranon process Head of radius Neck
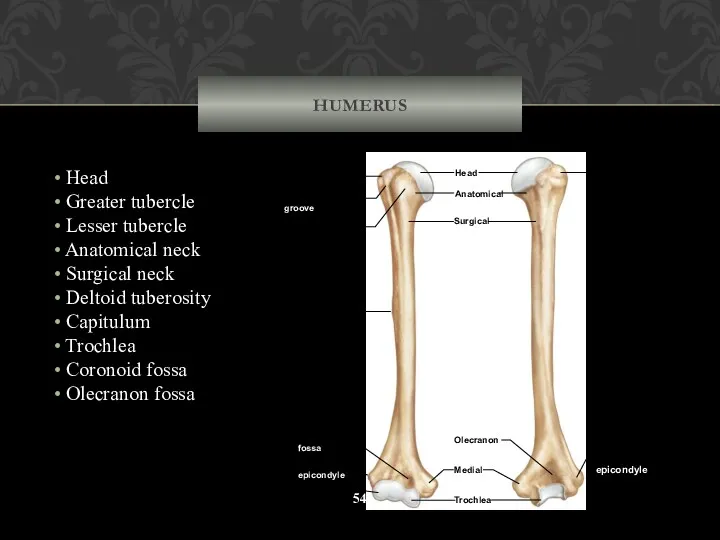
- 54. HUMERUS Head Greater tubercle Lesser tubercle Anatomical neck Surgical neck Deltoid tuberosity Capitulum Trochlea Coronoid fossa
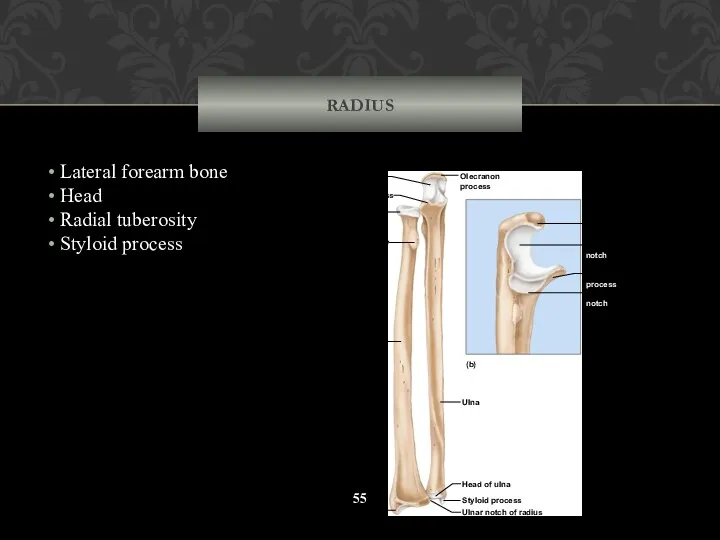
- 55. RADIUS Lateral forearm bone Head Radial tuberosity Styloid process Styloid process Ulnar notch of radius Styloid
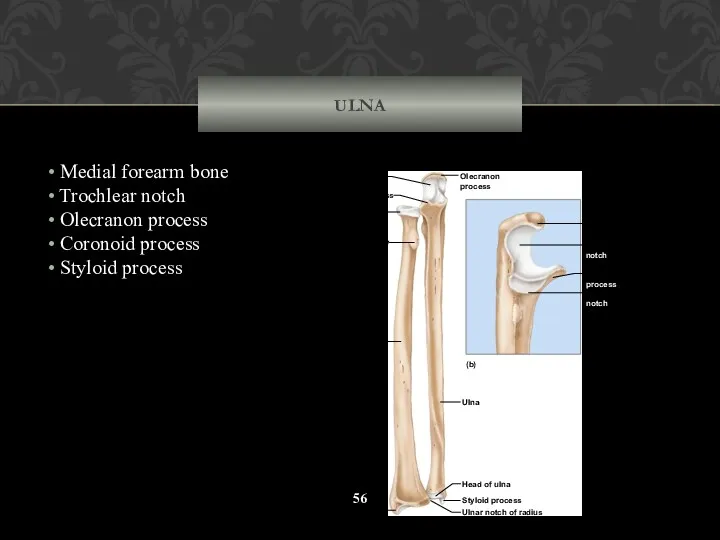
- 56. ULNA Medial forearm bone Trochlear notch Olecranon process Coronoid process Styloid process Styloid process Ulnar notch
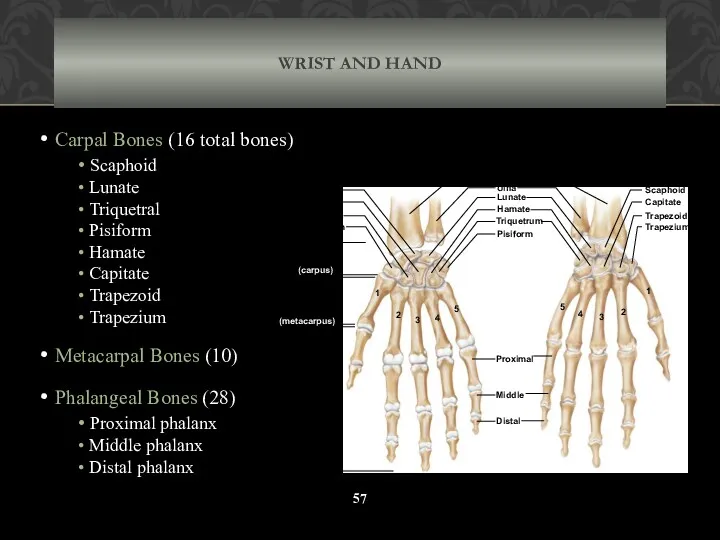
- 57. WRIST AND HAND Carpal Bones (16 total bones) Scaphoid Lunate Triquetral Pisiform Hamate Capitate Trapezoid Trapezium
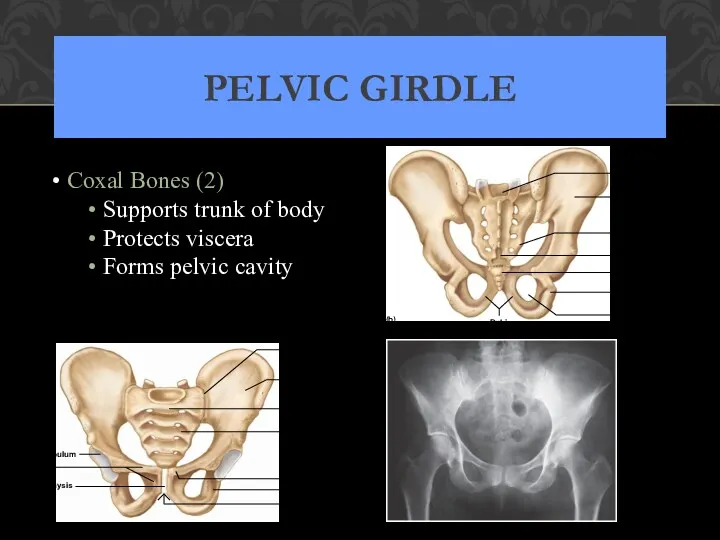
- 58. PELVIC GIRDLE Coxal Bones (2) Supports trunk of body Protects viscera Forms pelvic cavity Sacrum Sacral
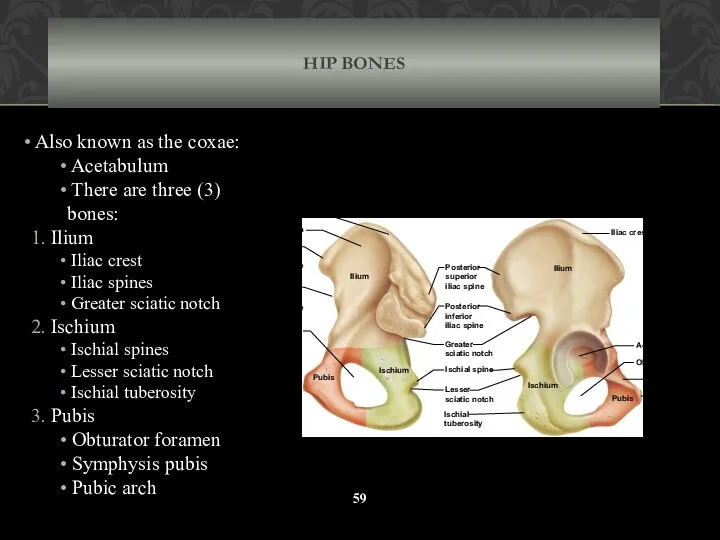
- 59. HIP BONES Also known as the coxae: Acetabulum There are three (3) bones: 1. Ilium Iliac
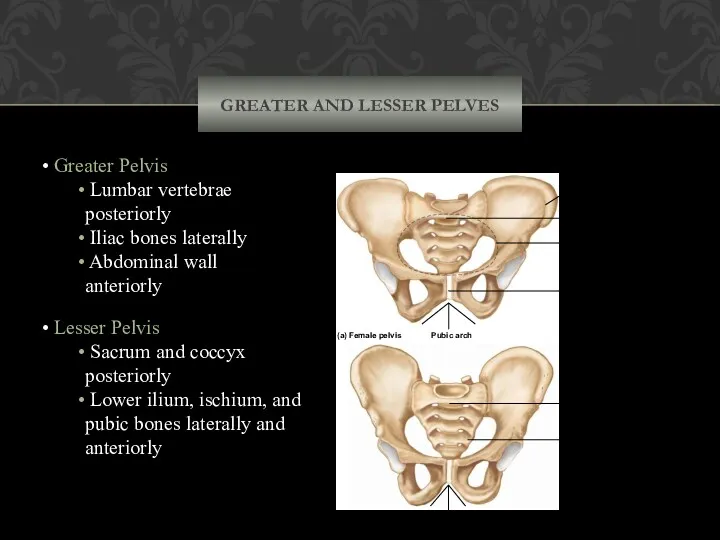
- 60. GREATER AND LESSER PELVES Greater Pelvis Lumbar vertebrae posteriorly Iliac bones laterally Abdominal wall anteriorly Lesser
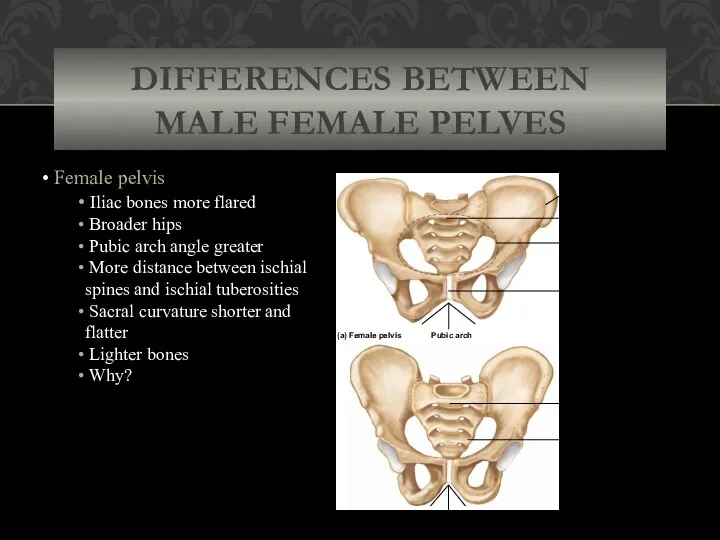
- 61. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MALE FEMALE PELVES Female pelvis Iliac bones more flared Broader hips Pubic arch angle
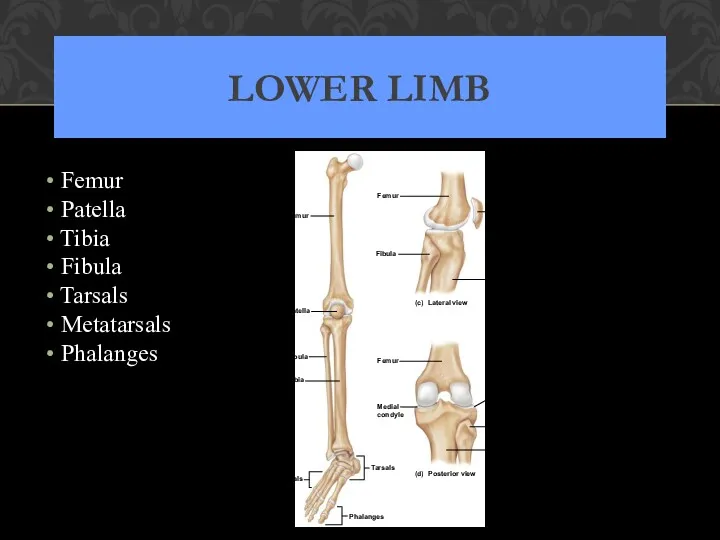
- 62. LOWER LIMB Femur Patella Tibia Fibula Tarsals Metatarsals Phalanges Metatarsals Fibula Tibia T ibia Patella Femur
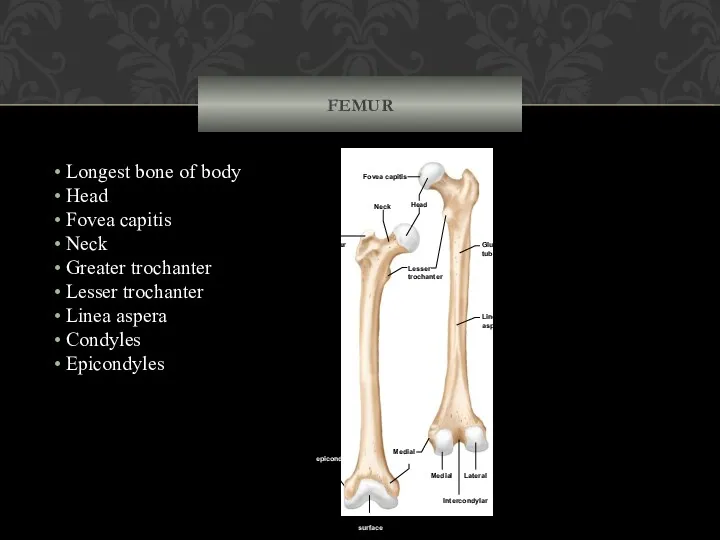
- 63. FEMUR Longest bone of body Head Fovea capitis Neck Greater trochanter Lesser trochanter Linea aspera Condyles
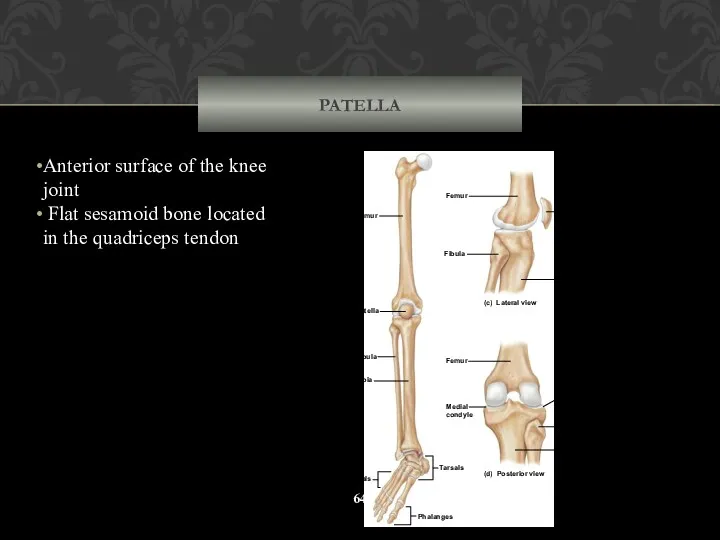
- 64. PATELLA Anterior surface of the knee joint Flat sesamoid bone located in the quadriceps tendon Metatarsals
- 65. TIBIA Medial to fibula Condyles Tibial tuberosity Makes the medial malleolus Tibia Fibula Medial malleolus Tibial
- 66. FIBULA Lateral to tibia Long, slender Head Makes the lateral malleolus Non-weight bearing Tibia Fibula Medial
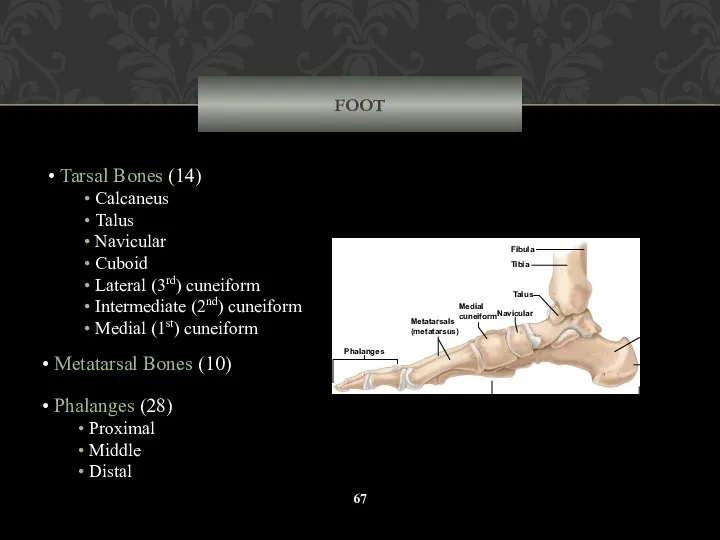
- 67. FOOT Tarsal Bones (14) Calcaneus Talus Navicular Cuboid Lateral (3rd) cuneiform Intermediate (2nd) cuneiform Medial (1st)
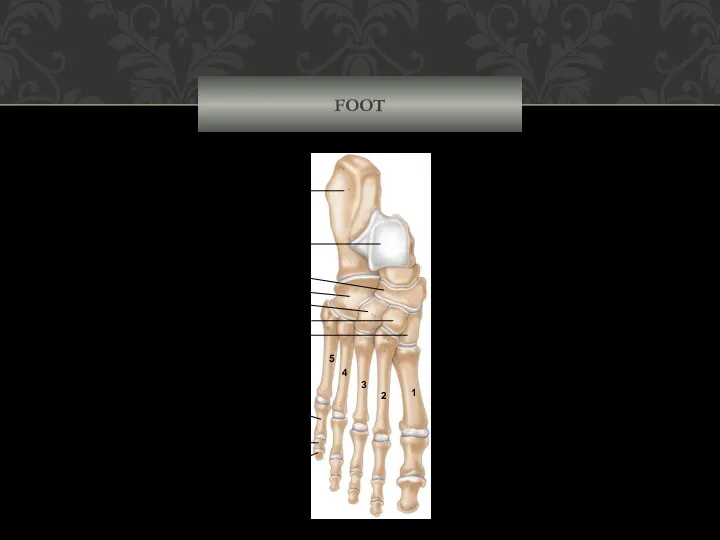
- 68. FOOT Calcaneus Talus Navicular Cuboid Lateral cuneiform Intermediate cuneiform Medial cuneiform Proximal phalanx Middle phalanx Distal
- 69. LIFESPAN CHANGES Decrease in height at about age 30 Calcium levels fall Bones become brittle Osteoclasts
- 70. Joints Slide 5.43 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Articulations of bones
- 71. Functional Classification of Joints Slide 5.44 Synarthroses – immovable joints Amphiarthroses – slightly moveable joints Diarthroses
- 72. Structural Classification of Joints Slide 5.45 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
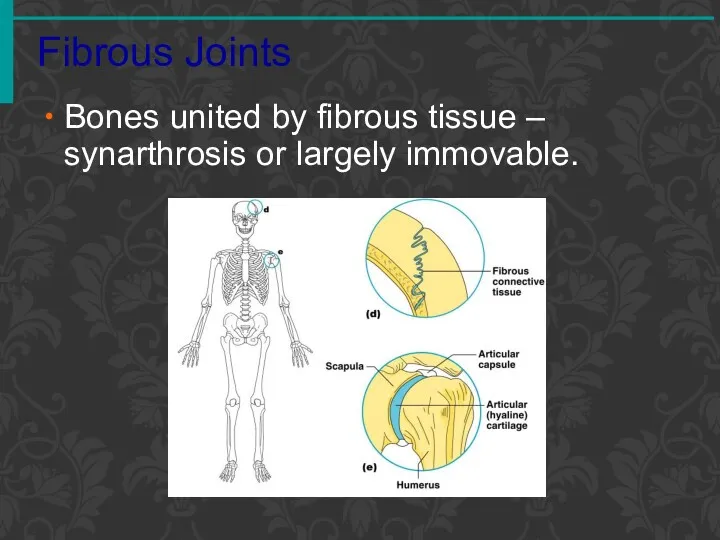
- 73. Fibrous Joints Bones united by fibrous tissue – synarthrosis or largely immovable.
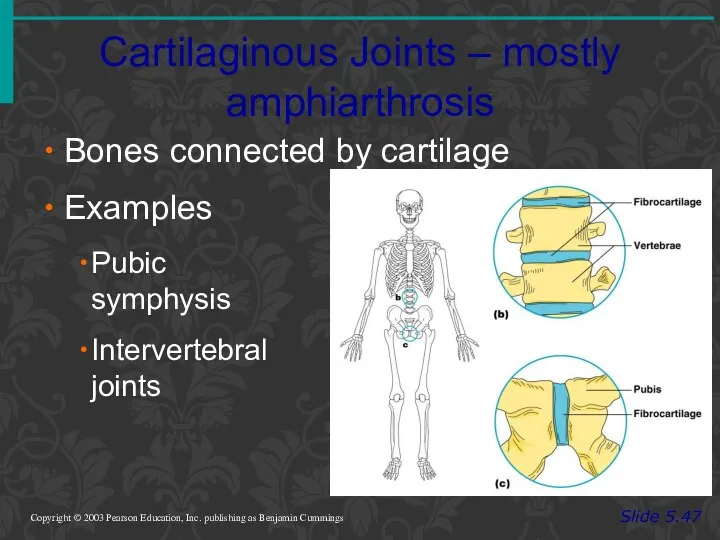
- 74. Cartilaginous Joints – mostly amphiarthrosis Slide 5.47 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin
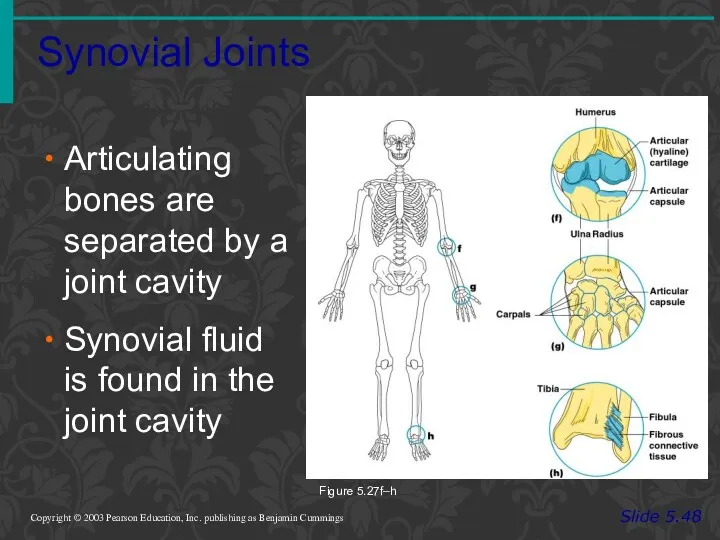
- 75. Synovial Joints Slide 5.48 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Articulating bones
- 76. Features of Synovial Joints- Diarthroses Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) covers the ends of bones Joint surfaces
- 77. Structures Associated with the Synovial Joint Slide 5.50 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as
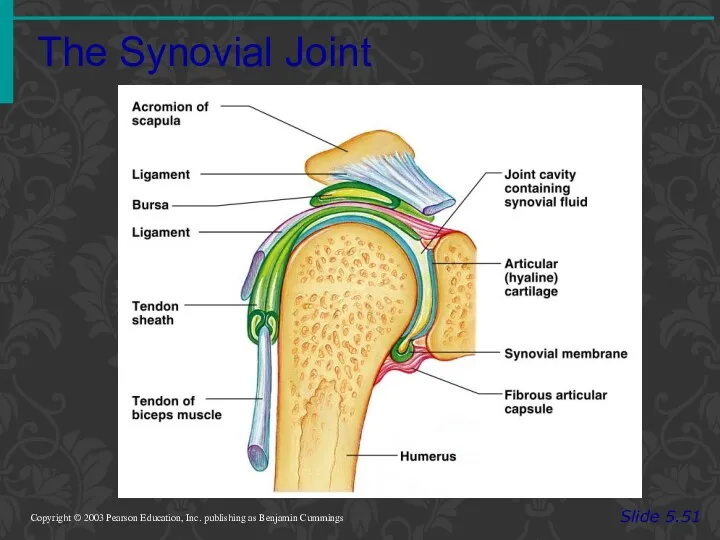
- 78. The Synovial Joint Slide 5.51 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure
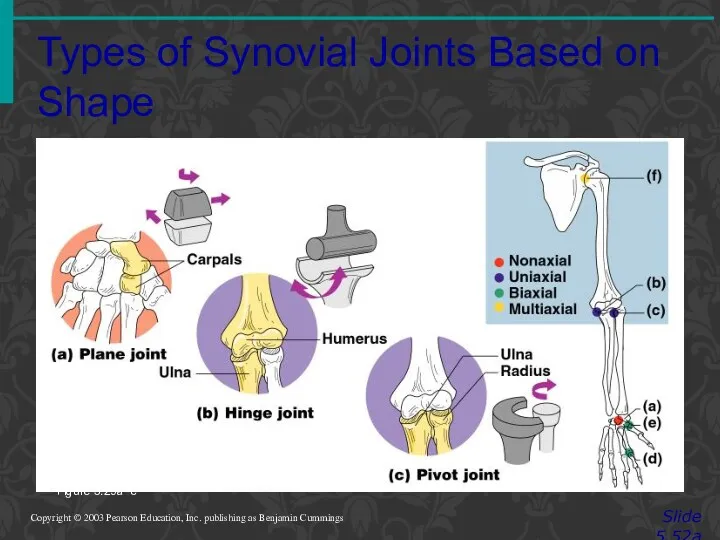
- 79. Types of Synovial Joints Based on Shape Slide 5.52a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing
- 81. Скачать презентацию





















 Болезни и вредители цитрусовых
Болезни и вредители цитрусовых Рыба речная: Окунь
Рыба речная: Окунь Витамины – понятие о гиповитаминозах, гипервитаминозах, авитаминозах
Витамины – понятие о гиповитаминозах, гипервитаминозах, авитаминозах Мышечные цепи. Взаимосвязи миофасциальной сети
Мышечные цепи. Взаимосвязи миофасциальной сети Вода. Роль воды в жизни человека
Вода. Роль воды в жизни человека Строение. Функции. Значение кожи
Строение. Функции. Значение кожи Тип Хордовые класс Млекопитающие
Тип Хордовые класс Млекопитающие Профилактика употреблениия ПАВ через преподавание биологии
Профилактика употреблениия ПАВ через преподавание биологии Простейшие
Простейшие Наружные и внутренние мужские и женские половые органы
Наружные и внутренние мужские и женские половые органы Процессы жизнеобеспечения в организме человека. Эндокринные железы (железы внутренней секреции)
Процессы жизнеобеспечения в организме человека. Эндокринные железы (железы внутренней секреции) Применение проектной технологии на уроках биологии и во внеурочной деятельности
Применение проектной технологии на уроках биологии и во внеурочной деятельности Ядовитые змеи мира
Ядовитые змеи мира Пластичность клеток разных тканей
Пластичность клеток разных тканей الزواحف
الزواحف Домашние животные. Кошки
Домашние животные. Кошки Биоритмы. Характеристика хронологических типов человека
Биоритмы. Характеристика хронологических типов человека Рост и развитие волос
Рост и развитие волос Биотехнология түсініктері, даму тарихы, негізгі әдістері
Биотехнология түсініктері, даму тарихы, негізгі әдістері Суринам ұн жемірі
Суринам ұн жемірі Використання тваринами знарядь праці
Використання тваринами знарядь праці Гүл, оның құрылысы мен маңызы
Гүл, оның құрылысы мен маңызы Морские животные. Тип мягкотелые
Морские животные. Тип мягкотелые Экология и природопользование. Экосистемы
Экология и природопользование. Экосистемы Передвижение веществ в организме растения
Передвижение веществ в организме растения Транспорт веществ в организме. 6 класс
Транспорт веществ в организме. 6 класс Класс Пресмыкающиеся, или Рептилии
Класс Пресмыкающиеся, или Рептилии Методы иммуноанализа с применением различных меток
Методы иммуноанализа с применением различных меток