Слайд 2

Introduction to Cell
By Arnat Balabiyev
PhD student
Arizona State University
Слайд 3

1.0 Unity and diversity of cells
Слайд 4

What defines “Life”?
Are highly organized
Homeostasis
Reproduce themselves
Grow and develop
Use the energy from
environment and transform it
Respond to stimuli
Adaptation to environment
Слайд 5
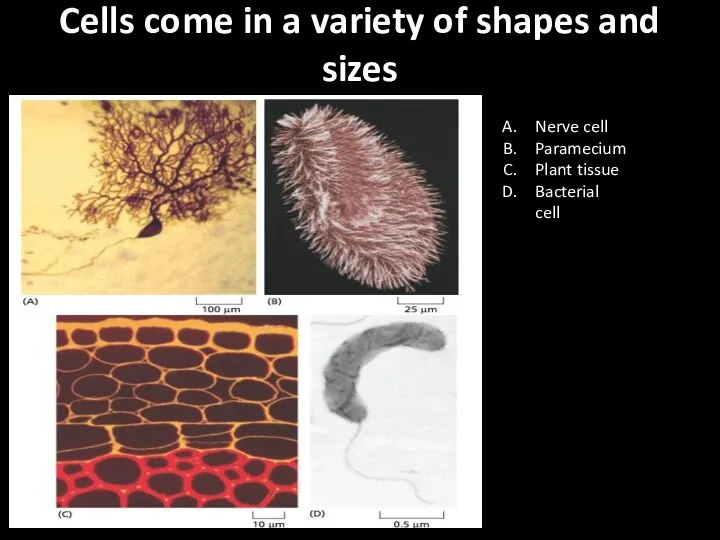
Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes
Nerve cell
Paramecium
Plant
tissue
Bacterial cell
Слайд 6
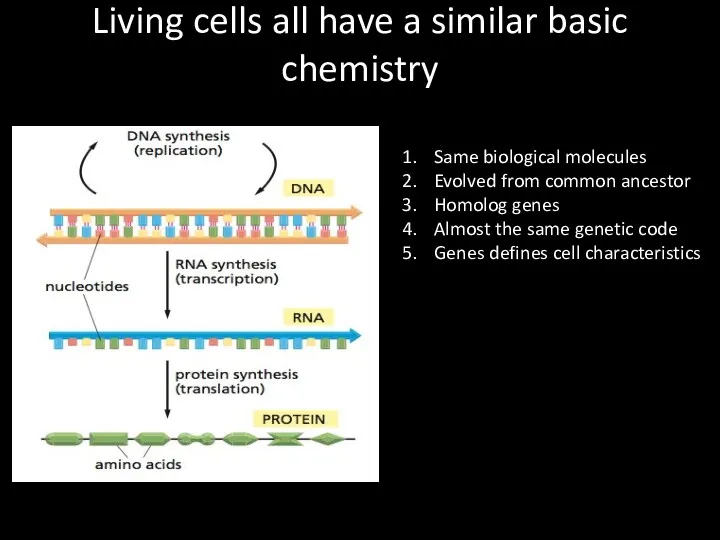
Living cells all have a similar basic chemistry
Same biological molecules
Evolved
from common ancestor
Homolog genes
Almost the same genetic code
Genes defines cell characteristics
Слайд 7

Prokaryotic cell
Have simplest structure
No organelles
No nucleus, just naked DNA
“Pro”- before, “karyo”-nucleus
Different
sizes and shapes
Ex: domain bacteria and archea
Слайд 8
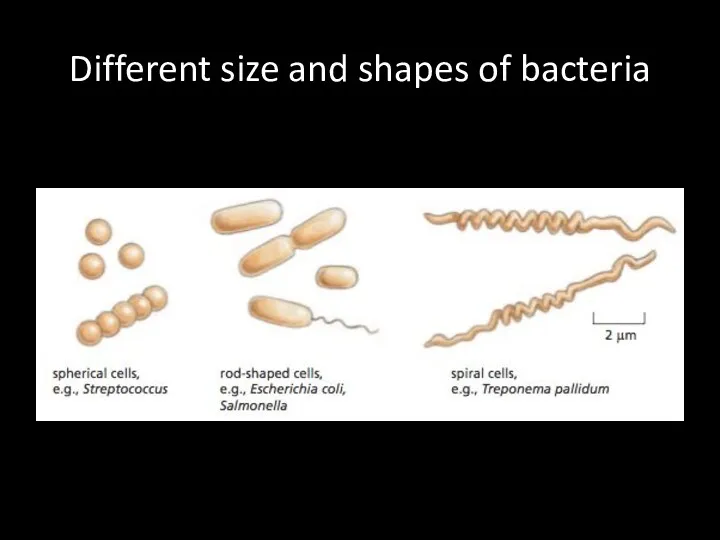
Different size and shapes of bacteria
Слайд 9

Some other features of bacteria
Have cell wall- may differ upon peptidoglycan
content: gram positive and negative
E. coli can divide every 20 minutes
8 billion in 11 hours: WOW!!!!
N=N0 x 2t/G: number of cells at time “t”
N0: # of cells at time 0
G: population doubling time
Слайд 10

Prokaryotes are the most diverse and numerous cells on Earth
Can be
single celled and form clusters, chains
Can live in numerous environments: hot, salty, soil and etc..
Can be photosynthetic
Can be aerobic or anaerobic
E.coli serve as a model organism to study molecular biology
Слайд 11
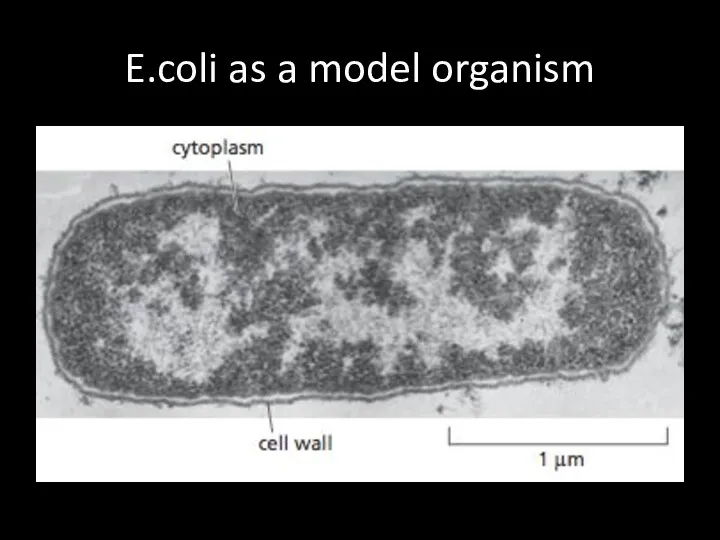
E.coli as a model organism
Слайд 12
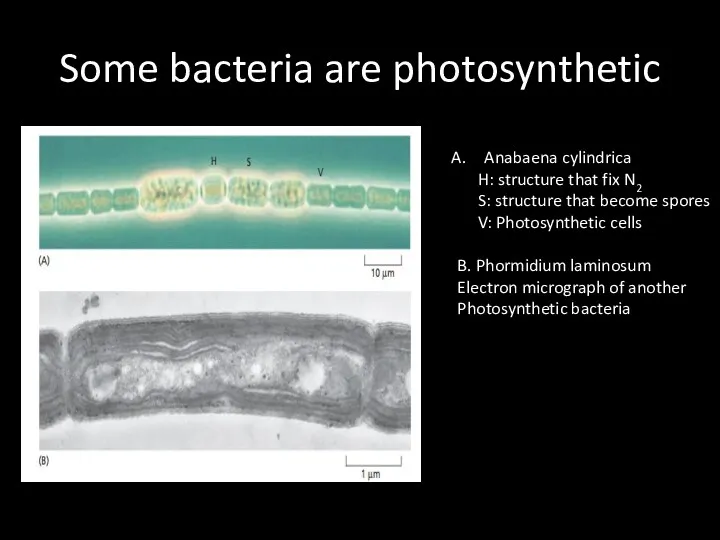
Some bacteria are photosynthetic
Anabaena cylindrica
H: structure that fix N2
S:
structure that become spores
V: Photosynthetic cells
B. Phormidium laminosum
Electron micrograph of another
Photosynthetic bacteria
Слайд 13
Слайд 14

The eukaryotic cells
Bigger in size
Elaborate lots of forms: unicellular and multicellular
Have nucleus and other membrane bound organelles
Слайд 15

The nucleus is the information store of the cell
Слайд 16
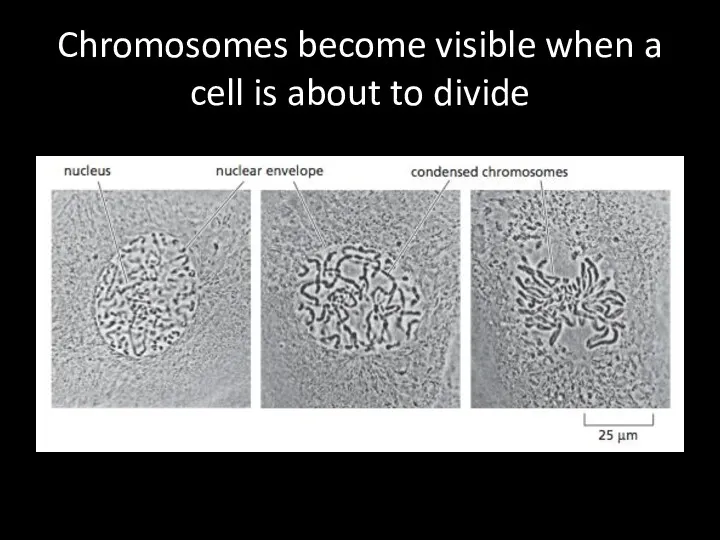
Chromosomes become visible when a cell is about to divide
Слайд 17

Mitochondria generate usable energy from food to power the cell
Слайд 18
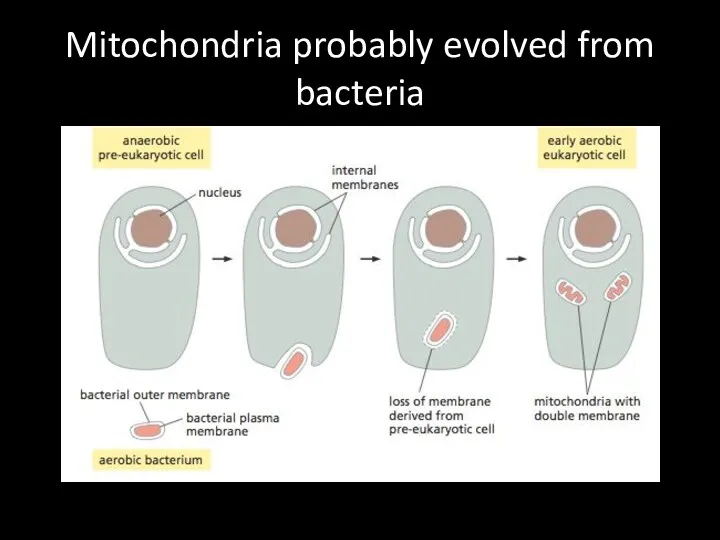
Mitochondria probably evolved from bacteria
Слайд 19
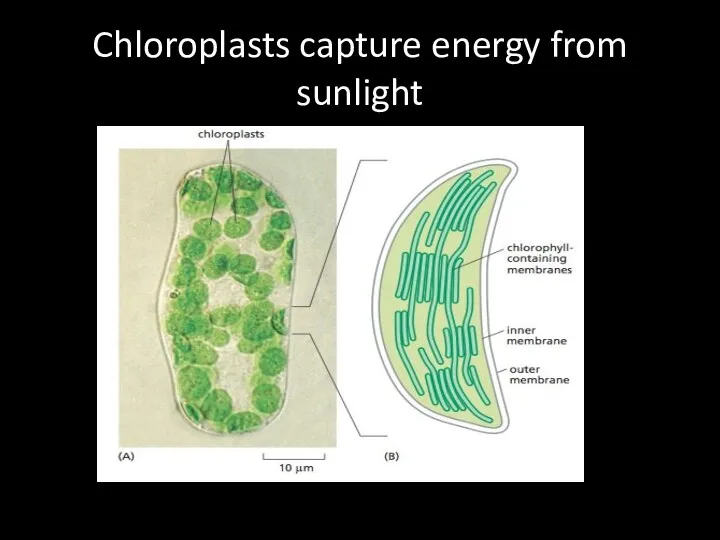
Chloroplasts capture energy from sunlight
Слайд 20
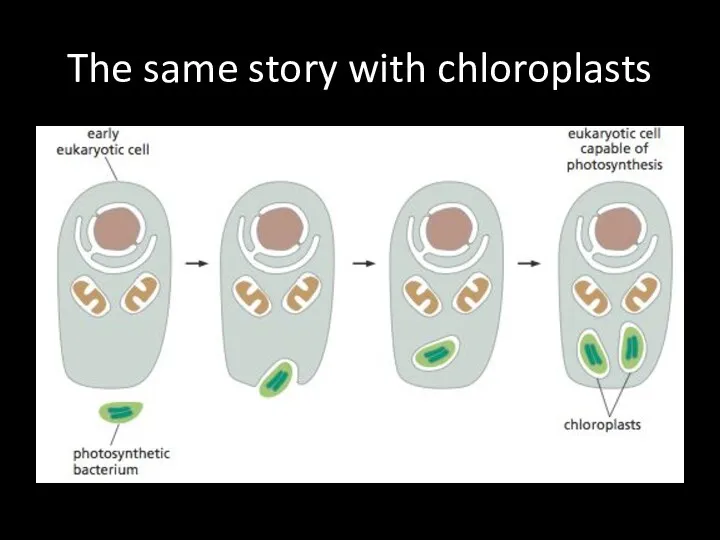
The same story with chloroplasts
Слайд 21
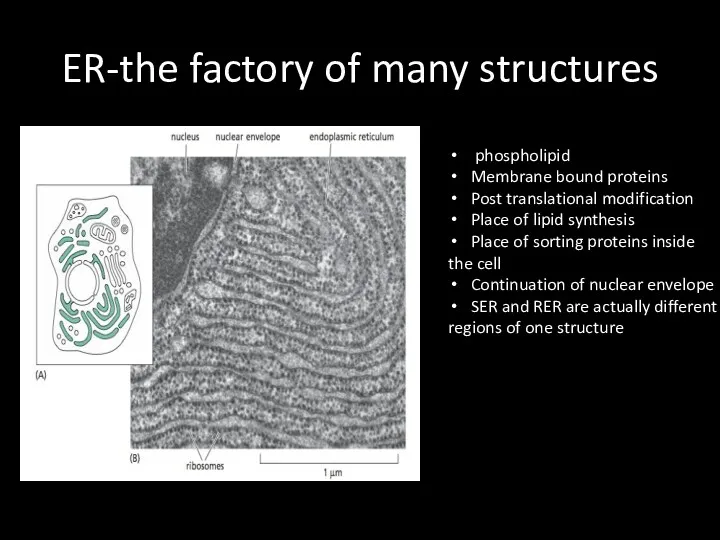
ER-the factory of many structures
phospholipid
Membrane bound proteins
Post translational modification
Place
of lipid synthesis
Place of sorting proteins inside
the cell
Continuation of nuclear envelope
SER and RER are actually different
regions of one structure
Слайд 22
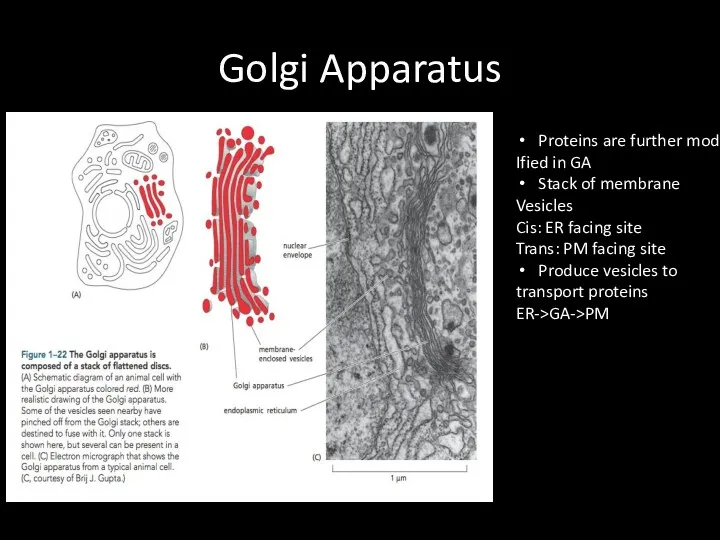
Golgi Apparatus
Proteins are further mod
Ified in GA
Stack of membrane
Vesicles
Cis: ER
facing site
Trans: PM facing site
Produce vesicles to
transport proteins
ER->GA->PM
Слайд 23
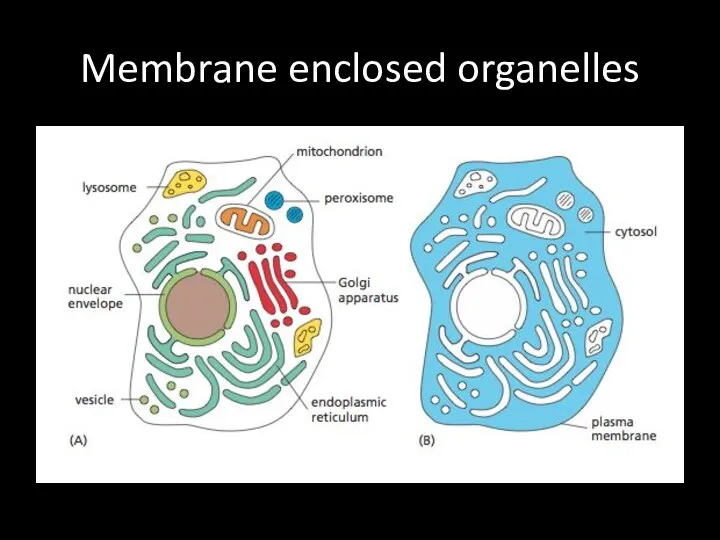
Membrane enclosed organelles
Слайд 24
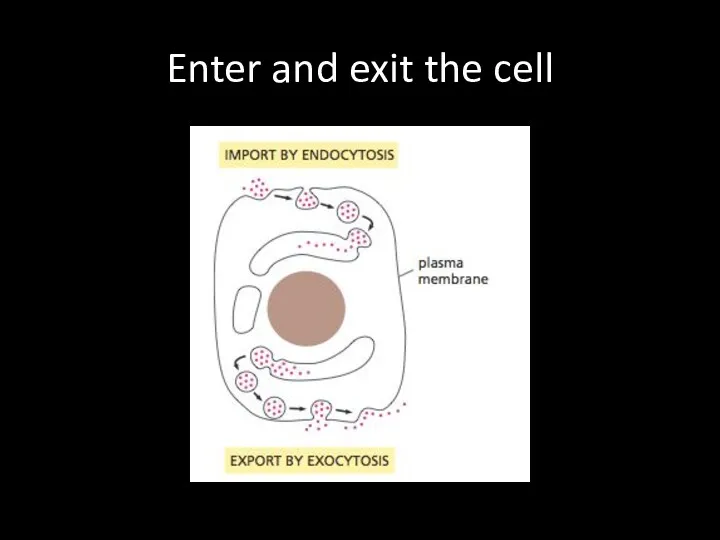
Слайд 25
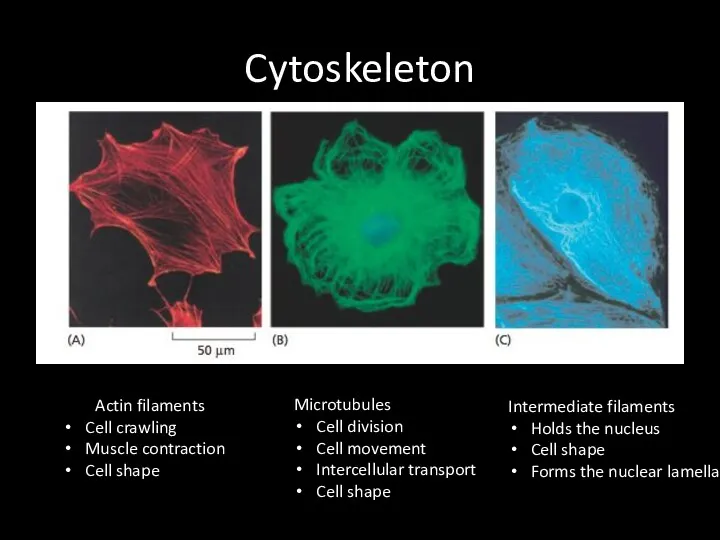
Cytoskeleton
Actin filaments
Cell crawling
Muscle contraction
Cell shape
Microtubules
Cell division
Cell movement
Intercellular transport
Cell shape
Intermediate filaments
Holds
the nucleus
Cell shape
Forms the nuclear lamella
Слайд 26
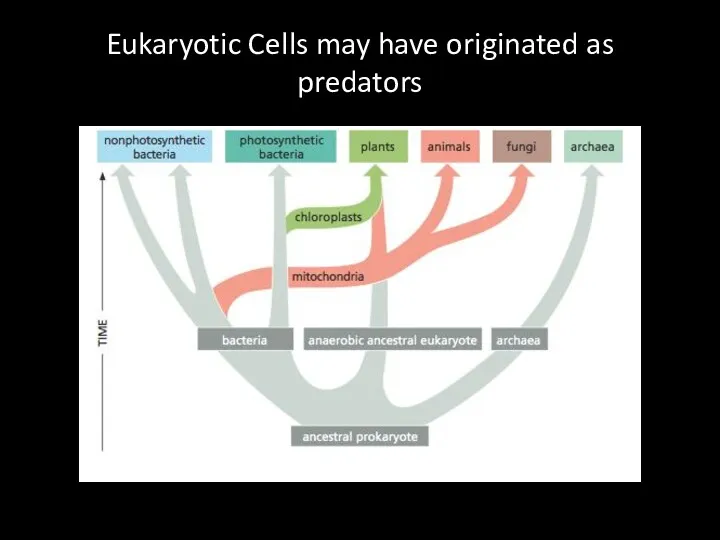
Eukaryotic Cells may have originated as predators
Слайд 27

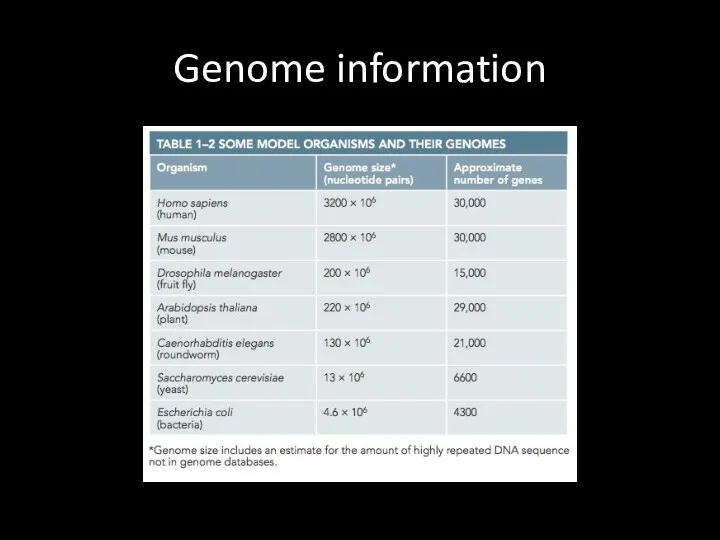
Model organisms
E.coli
Simple structure (small genome size)
Easy to grow (37C)
in agar media
20 min doubling time
Many conserved genes
Easy to manipulate
Слайд 28
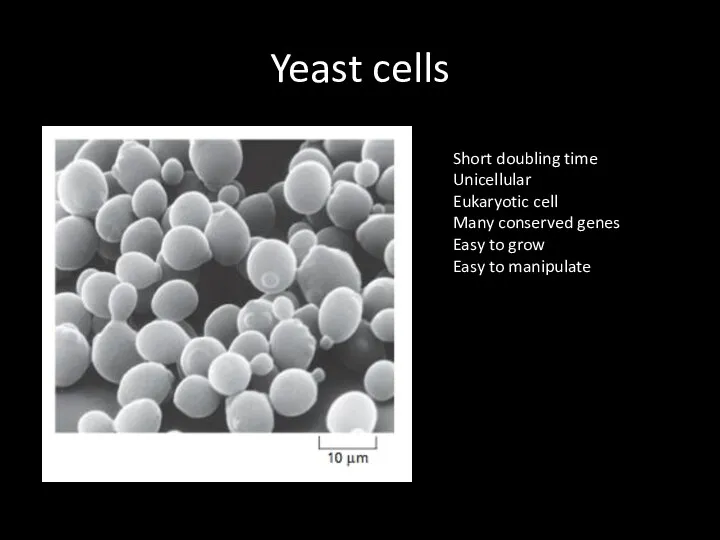
Yeast cells
Short doubling time
Unicellular
Eukaryotic cell
Many conserved genes
Easy to grow
Easy to manipulate
Слайд 29
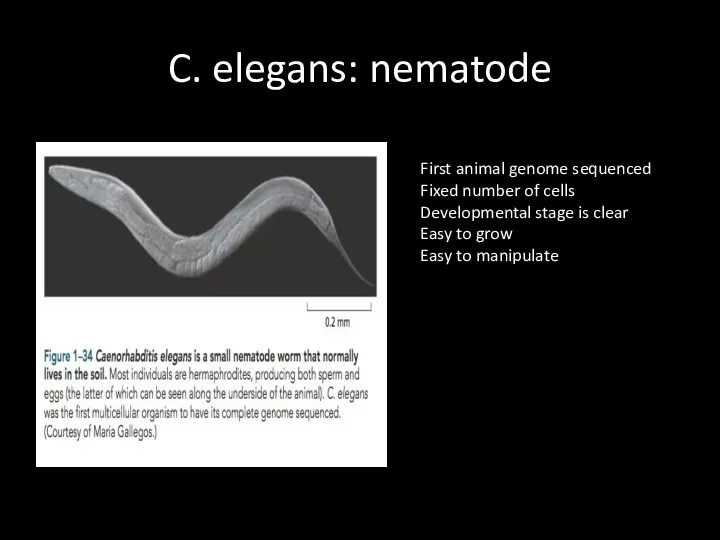
C. elegans: nematode
First animal genome sequenced
Fixed number of cells
Developmental stage is
clear
Easy to grow
Easy to manipulate
Слайд 30

Arabidopsis
Fast growing plant
Easy to grow and maintain
Good model organism to study
plants
Слайд 31

Drosophila melanogaster
Great model to study animals
Insects are the most numerous
Conserved genes
Easy
to grow
Great for genetical analysis
Слайд 32

Zebra fish
First developmental stages are transparent
Good model to study vertebrate development
Easy
to grow
Слайд 33
Mouse model
Easy to breed. Many conserved genes with human genome. Easy
to manipulate
Слайд 34
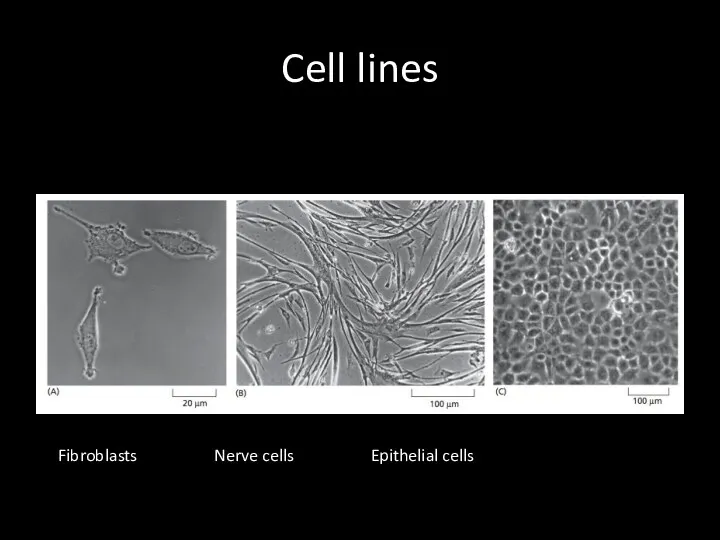
Cell lines
Fibroblasts Nerve cells Epithelial cells
Слайд 35


































 Загадочный мир океана
Загадочный мир океана Что такое биоинформатика? Банк SwissProt
Что такое биоинформатика? Банк SwissProt Продление рода. Органы размножения
Продление рода. Органы размножения Популяционные волны
Популяционные волны Органы чувств. Анализаторы
Органы чувств. Анализаторы 5 Natural Ways To Get Rid of House Crickets
5 Natural Ways To Get Rid of House Crickets Самые редкие и необычные породы кошек
Самые редкие и необычные породы кошек Интересные факты о животном мире
Интересные факты о животном мире Всероссийская проверочная работа по окружающему миру. Опыты (4 класс)
Всероссийская проверочная работа по окружающему миру. Опыты (4 класс) Санитарлық-көрсеткіш микроағзалар. Стерилдеу мен залалсыздандыру
Санитарлық-көрсеткіш микроағзалар. Стерилдеу мен залалсыздандыру Отряд Непарнокопытные
Отряд Непарнокопытные 4 стихии зарождения жизни
4 стихии зарождения жизни Методическая разработка урока-игры по биологии в 10 классе по теме: Путешествие по эукариотической клетке
Методическая разработка урока-игры по биологии в 10 классе по теме: Путешествие по эукариотической клетке Растения и животные леса
Растения и животные леса Микробиота тела человека. Роль микроорганизмов в возникновении инфекций. Способы передачи инфекций
Микробиота тела человека. Роль микроорганизмов в возникновении инфекций. Способы передачи инфекций α-Aminoacids, peptides, proteins
α-Aminoacids, peptides, proteins Многообразие органического мира. Принципы систематики
Многообразие органического мира. Принципы систематики Животные живого уголка
Животные живого уголка Профилактика вредных привычек.Давайте жить! Давайте жизнью дорожить!
Профилактика вредных привычек.Давайте жить! Давайте жизнью дорожить! Что такое метаболизм и как его измерить
Что такое метаболизм и как его измерить оплодотворение
оплодотворение Pielea, organ tactil, termic, dureros și de presiune. (Lectie 11)
Pielea, organ tactil, termic, dureros și de presiune. (Lectie 11) Древнейшие люди
Древнейшие люди Развитие кожи в эмбриогенезе
Развитие кожи в эмбриогенезе Обмен веществ и энергии. Фотосинтез
Обмен веществ и энергии. Фотосинтез Тип Губки
Тип Губки Птичий переполох (игра)
Птичий переполох (игра) Самые опасные насекомые в мире
Самые опасные насекомые в мире