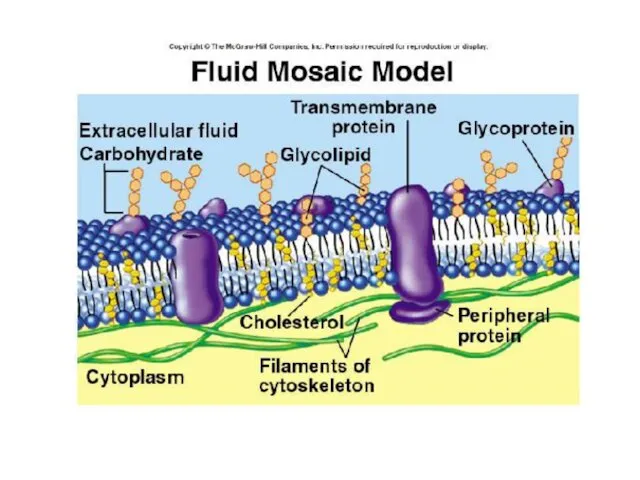
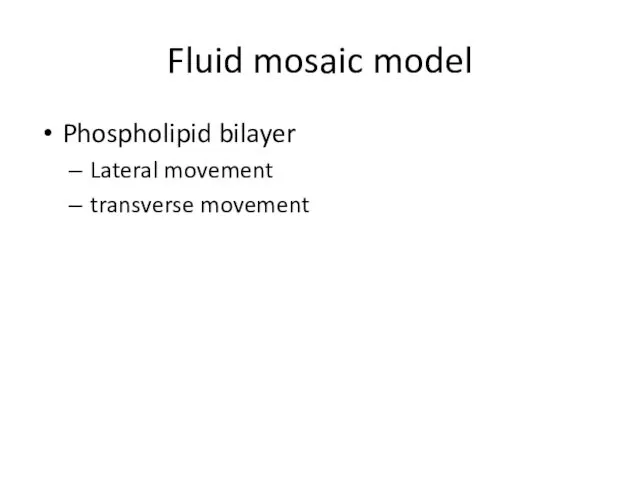
Phospholipid molecules in the plasma membrane have two parts
Hydrophilic heads interact
with water molecules to provide passage
Hydrophobic tails interact with each other, forming a barrier to hydrophilic molecules
The matched pairs thus allow regulation of liquid and solids into and out of the individual cell
Cholestrol - Stabilizes the membrane by providing rigidity
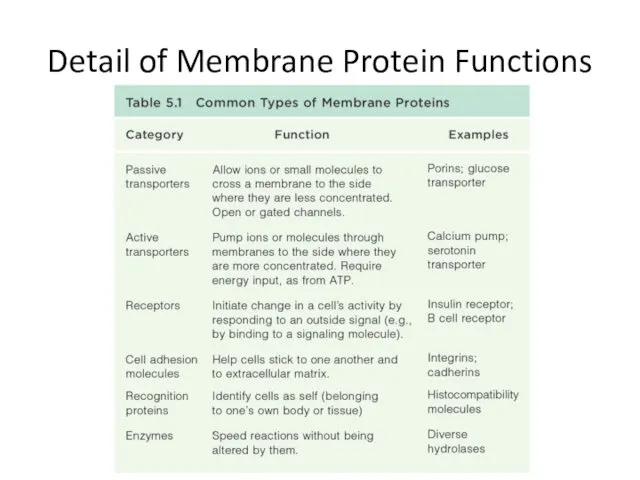
Channel and Carrier Proteins: Selective transport of ions and polar molecules across the membrane.
Glycoproteins (Proteins combined with carbohydrates) on cell surface.
Plasma Membrane




 Естественный отбор – главная движущая сила эволюции
Естественный отбор – главная движущая сила эволюции Понятие об организме. Основные части организма
Понятие об организме. Основные части организма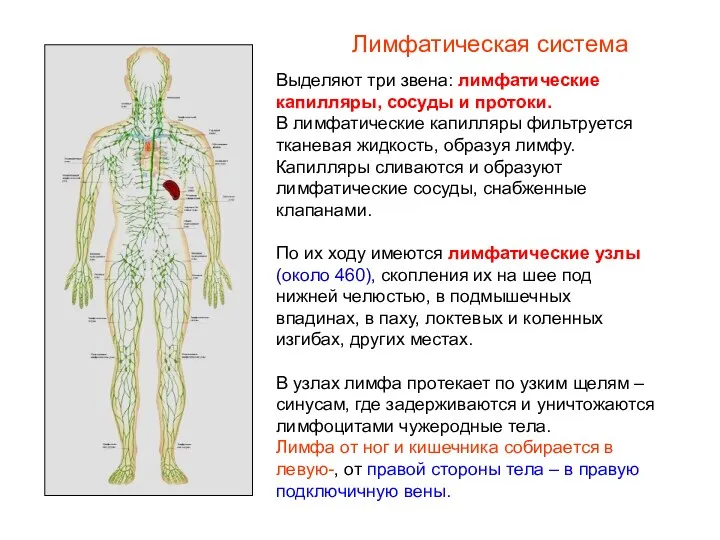 Лимфатическая система в организме человека
Лимфатическая система в организме человека 10 редких лесных животных России
10 редких лесных животных России Презентации к урокам
Презентации к урокам Хоботные
Хоботные Видовое разнообразие беспозвоночных животных Рязанской области
Видовое разнообразие беспозвоночных животных Рязанской области Разнообразие рептилий
Разнообразие рептилий Різноманітність членистоногих
Різноманітність членистоногих Дидактическая игра Волейбол по теме ГИДРА
Дидактическая игра Волейбол по теме ГИДРА Полевые сорняки
Полевые сорняки Медоносная пчела. Пчеловодство
Медоносная пчела. Пчеловодство Работоспособность сердца
Работоспособность сердца Среда обитания
Среда обитания Виды корней и типы корневых систем растений
Виды корней и типы корневых систем растений Систематика
Систематика Происхождение человека и становление общества
Происхождение человека и становление общества The respiratory system
The respiratory system Общая характеристика обмена веществ
Общая характеристика обмена веществ Определение аскорбиновой кислоты во фруктах и соках
Определение аскорбиновой кислоты во фруктах и соках Доказательства и основные этапы антропогенеза
Доказательства и основные этапы антропогенеза И.П. Павлов — основоположник физиологической школы
И.П. Павлов — основоположник физиологической школы Многообразие голосеменных растений и особенности их строения
Многообразие голосеменных растений и особенности их строения Ткани. Соединительная ткань
Ткани. Соединительная ткань Растения водоёмов
Растения водоёмов Вид. Критерии вида
Вид. Критерии вида Рослини - хижаки
Рослини - хижаки Химические средства защиты растений
Химические средства защиты растений