Содержание
- 2. Source of chemical mutagens are food, air and water. Effect of radiation is localized, while chemical
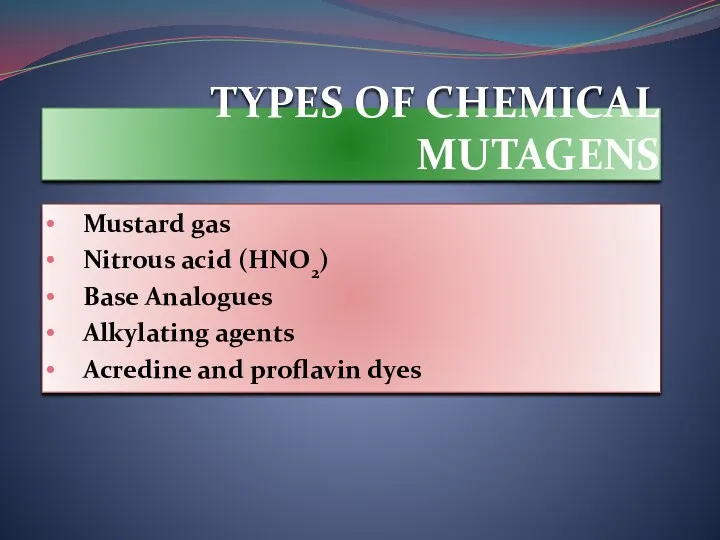
- 3. TYPES OF CHEMICAL MUTAGENS Mustard gas Nitrous acid (HNO2) Base Analogues Alkylating agents Acredine and proflavin
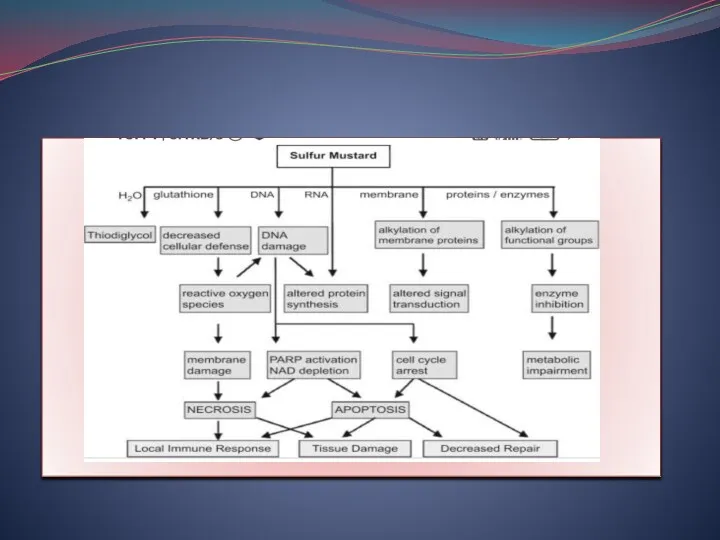
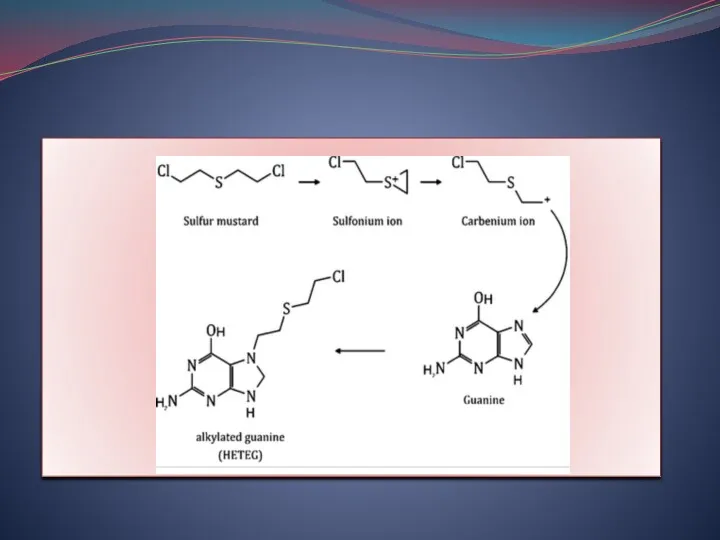
- 4. Mustard gas Mustard gas causes genetic damage in all systems in which it was tested. It
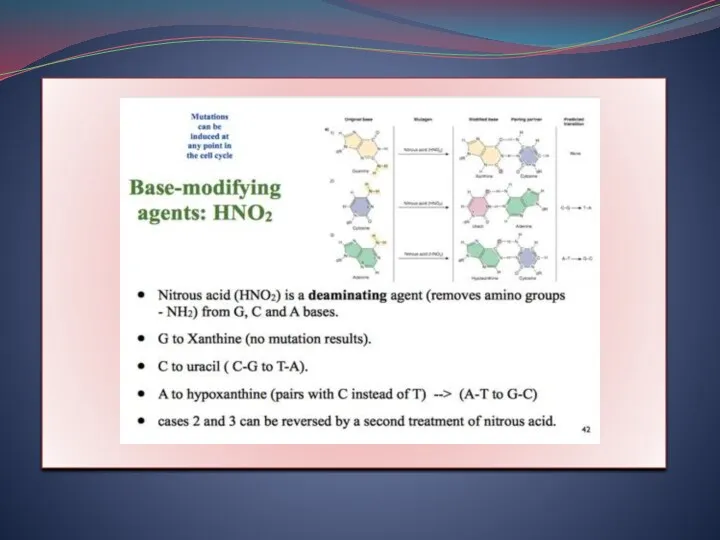
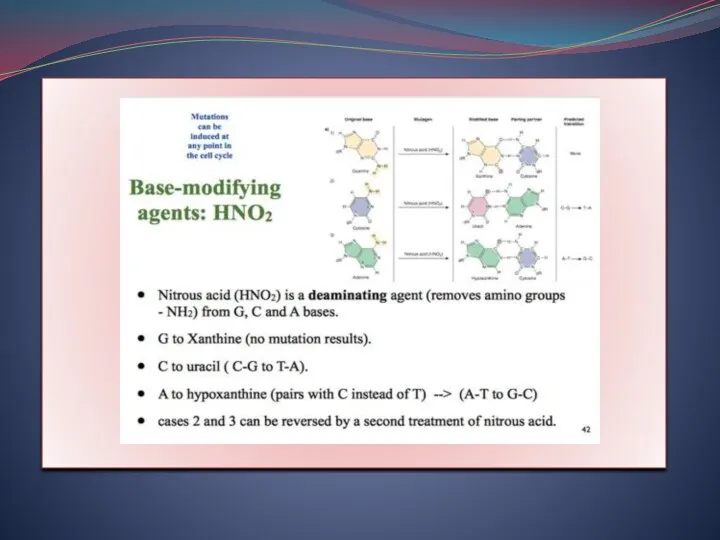
- 7. Adenine ---deamination--? Hypoxanthine Guanine ---deamination---? Xanthine Cytosine ---deamination---? Uracil In first DNA replication, Tautomer of adenine
- 8. It is unusual pairing which is called as forbidden pairing so a wrong type of DNA
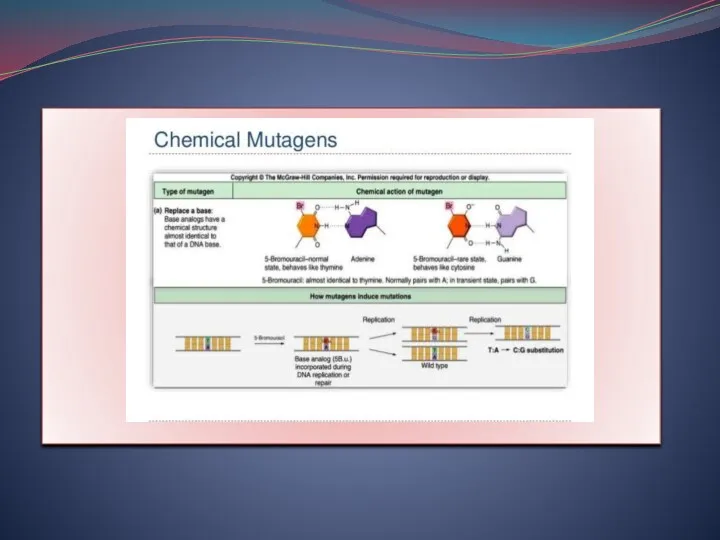
- 11. Base Analogues Those chemicals which are same as nitrogenous base in function. They are called base
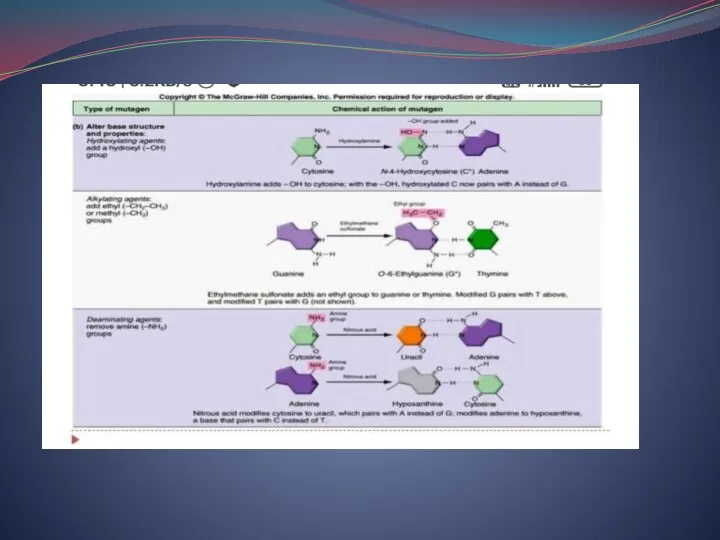
- 13. Alkylating agents EMS ? Ethyl methane sulphonate MMS ? Methyl methane sulphonate These chemicals causes depurination
- 15. Acredine and proflavin dyes They causes loss or addition of one or rarely more than one
- 19. Mostly mutations are harmful. Sometimes they are lethal which leads to death of organisms. But sometimes
- 21. Скачать презентацию










 Фотосинтез
Фотосинтез Общая характеристика царства Растения
Общая характеристика царства Растения Высшая нервная деятельность человека
Высшая нервная деятельность человека Пищеварение в ротовой полости
Пищеварение в ротовой полости Личностно-ориентированная технология на уроках биологии
Личностно-ориентированная технология на уроках биологии Нервная система
Нервная система Вид. Критерии вида
Вид. Критерии вида Внутрішнє середовище організму. Кров, її склад та функції
Внутрішнє середовище організму. Кров, її склад та функції Размножение многоклеточных животных
Размножение многоклеточных животных Презентация к уроку биологии по теме Классификация животных. Влияние человека на животных - 7 класс, линия Пономарёвой.
Презентация к уроку биологии по теме Классификация животных. Влияние человека на животных - 7 класс, линия Пономарёвой. Лес - наше богатство
Лес - наше богатство Органы чувств
Органы чувств Родина бобові Fabaceae Lindl
Родина бобові Fabaceae Lindl Невидимые нити в весеннем лесу
Невидимые нити в весеннем лесу Витаминные, ферментные, антиферментные препараты. Понятие о биологически активных добавках к пище
Витаминные, ферментные, антиферментные препараты. Понятие о биологически активных добавках к пище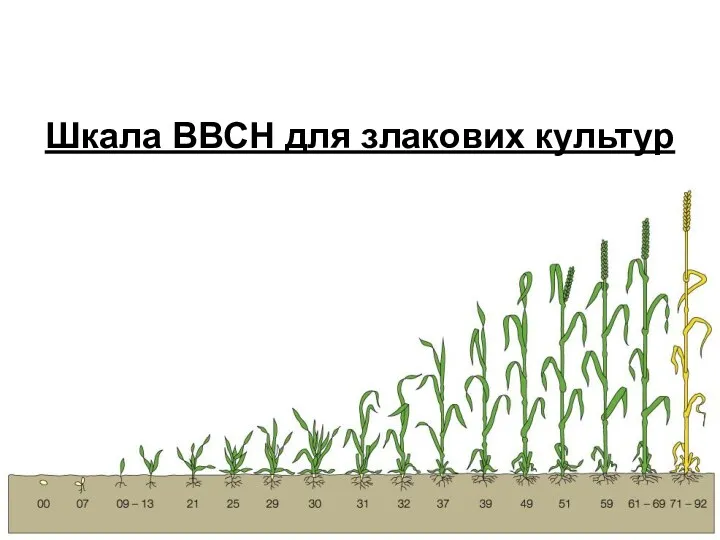 Шкала ВВСН для злакових культур. Етапи розвитку злаків
Шкала ВВСН для злакових культур. Етапи розвитку злаків Презентация к уроку по биологии 8 класс по теме Глаз как орган зрения и оптическая система Урок по биологии в 8 классе Глаз как орган зрения и оптическая система
Презентация к уроку по биологии 8 класс по теме Глаз как орган зрения и оптическая система Урок по биологии в 8 классе Глаз как орган зрения и оптическая система Голоса птиц
Голоса птиц Фармакогнозия. Краткая история фармакогностических исследований. Развитие европейской фармакогнозии
Фармакогнозия. Краткая история фармакогностических исследований. Развитие европейской фармакогнозии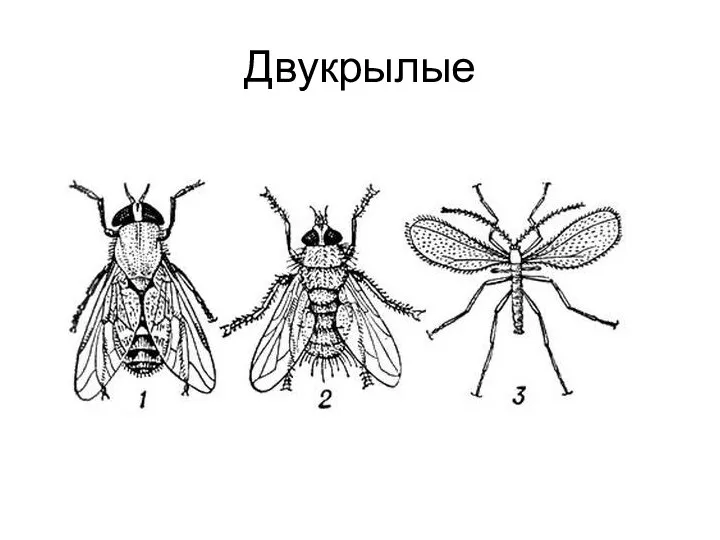 Насекомые
Насекомые Презентация по биологии 8 класс темы Внутренняя среда организма
Презентация по биологии 8 класс темы Внутренняя среда организма Ленточные черви (Cestoda) – паразиты человека и животных
Ленточные черви (Cestoda) – паразиты человека и животных Гены, геномы и хромосомы
Гены, геномы и хромосомы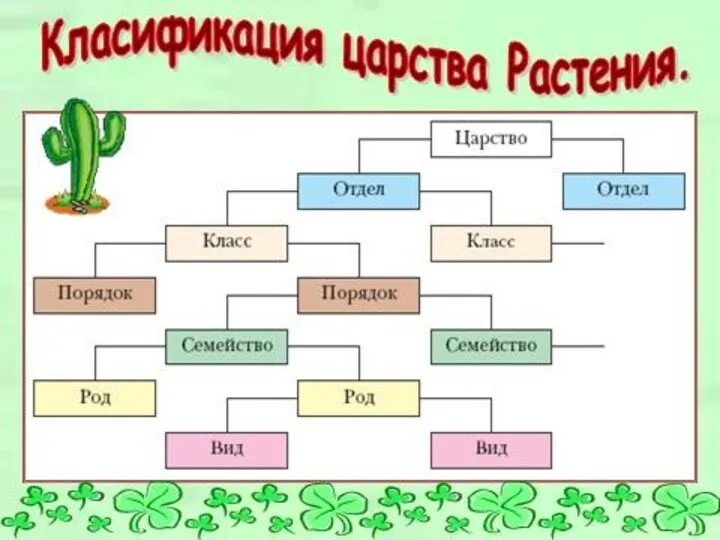 Классификация царства Растения
Классификация царства Растения Борьба за существование и естественный отбор
Борьба за существование и естественный отбор Весеннее пробуждение растений
Весеннее пробуждение растений Интерактивный плакат по теме Эволюция скелетных систем
Интерактивный плакат по теме Эволюция скелетных систем Глюкоза. Строение. Физические и химические свойства
Глюкоза. Строение. Физические и химические свойства