Содержание
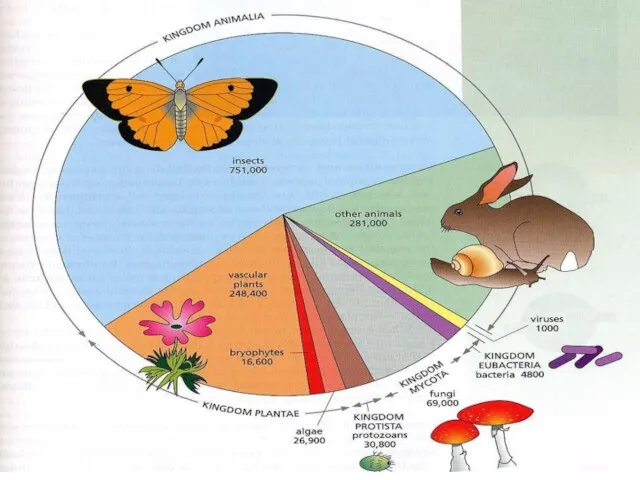
- 2. There are 13 billion known species of organisms This is only 5% of all organisms that
- 3. What is Classification? Classification is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities
- 4. Benefits of Classifying Accurately & uniformly names organisms Prevents misnomers such as starfish & jellyfish that
- 5. Confusion in Using Different Languages for Names copyright cmassengale
- 6. Latin Names are Understood by all Taxonomists copyright cmassengale
- 7. Early Taxonomists 2000 years ago, Aristotle was the first taxonomist Aristotle divided organisms into plants &
- 8. Early Taxonomists John Ray, a botanist, was the first to use Latin for naming His names
- 9. Carolus Linnaeus 1707 – 1778 18th century taxonomist Classified organisms by their structure Developed naming system
- 10. Carolus Linnaeus Called the “Father of Taxonomy” Developed the modern system of naming known as binomial
- 11. Standardized Naming Binomial nomenclature used Genus species Latin or Greek Italicized in print Capitalize genus, but
- 12. Binomial Nomenclature Which TWO are more closely related? copyright cmassengale
- 13. Rules for Naming Organisms The International Code for Binomial Nomenclature contains the rules for naming organisms
- 14. Classification Groups Taxon ( taxa-plural) is a category into which related organisms are placed There is
- 15. Hierarchy-Taxonomic Groups Domain Kingdom Phylum (Division – used for plants) Class Order Family Genus Species BROADEST
- 16. Dumb King Phillip Came Over For Gooseberry Soup! copyright cmassengale
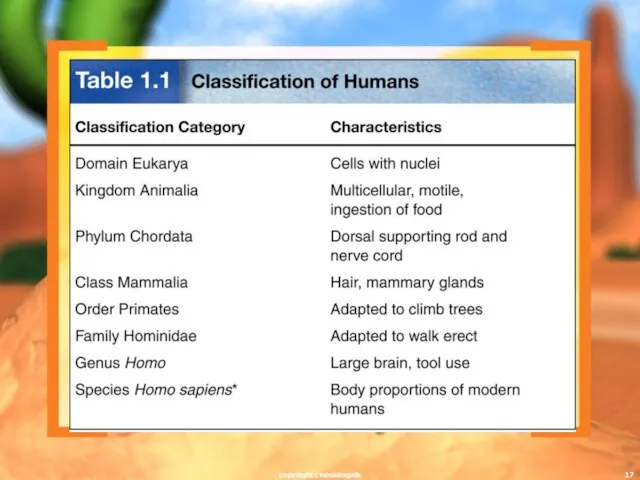
- 17. copyright cmassengale
- 18. Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound
- 19. ARCHAEA Kingdom - ARCHAEBACTERIA Probably the 1st cells to evolve Live in HARSH environments Found in:
- 20. ARCHAEAN copyright cmassengale
- 21. BACTERIA Kingdom - EUBACTERIA Some may cause DISEASE Found in ALL HABITATS except harsh ones Important
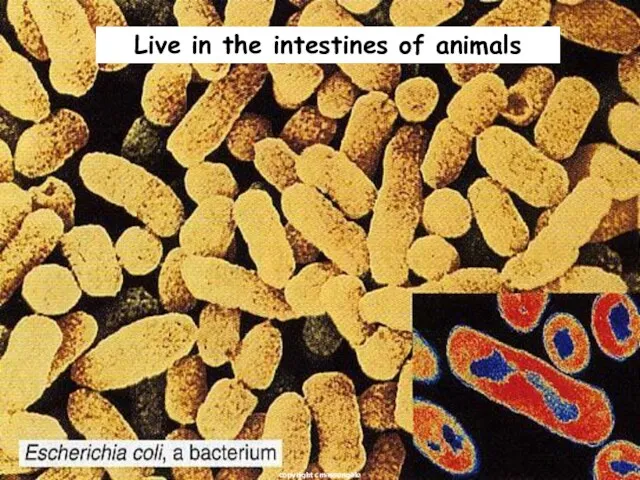
- 22. Live in the intestines of animals copyright cmassengale
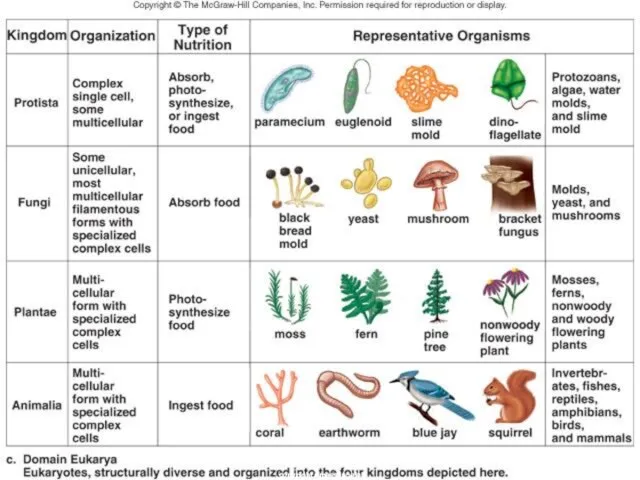
- 23. Domain Eukarya is Divided into Kingdoms Protista (protozoans, algae…) Fungi (mushrooms, yeasts …) Plantae (multicellular plants)
- 24. Protista Most are unicellular Some are multicellular Some are autotrophic, while others are heterotrophic Aquatic copyright
- 25. Fungi Multicellular, except yeast Absorptive heterotrophs (digest food outside their body & then absorb it) Cell
- 26. Plantae Multicellular Autotrophic Absorb sunlight to make glucose – Photosynthesis Cell walls made of cellulose copyright
- 27. Animalia Multicellular Ingestive heterotrophs (consume food & digest it inside their bodies) Feed on plants or
- 28. copyright cmassengale
- 29. Taxons Most genera contain a number of similar species The genus Homo is an exception (only
- 30. copyright cmassengale
- 31. Basis for Modern Taxonomy Homologous structures (same structure, different function) Similar embryo development Molecular Similarity in
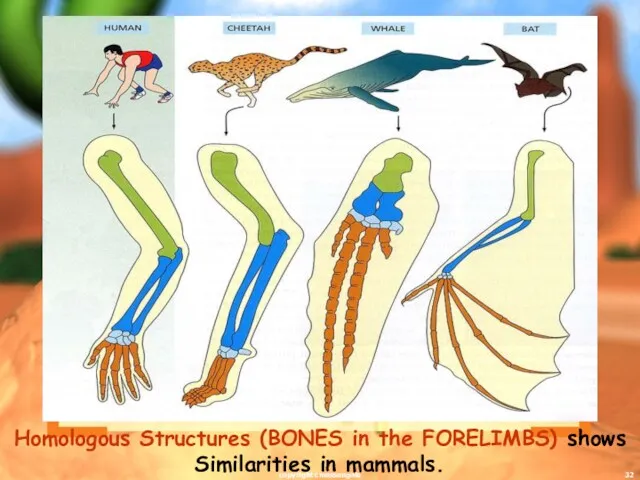
- 32. Homologous Structures (BONES in the FORELIMBS) shows Similarities in mammals. copyright cmassengale
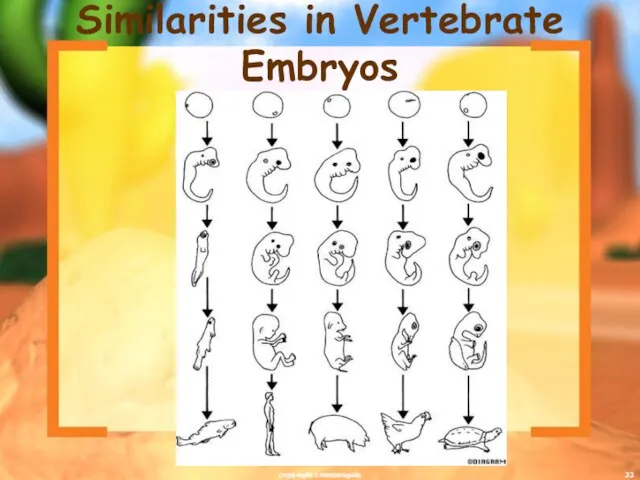
- 33. Similarities in Vertebrate Embryos copyright cmassengale
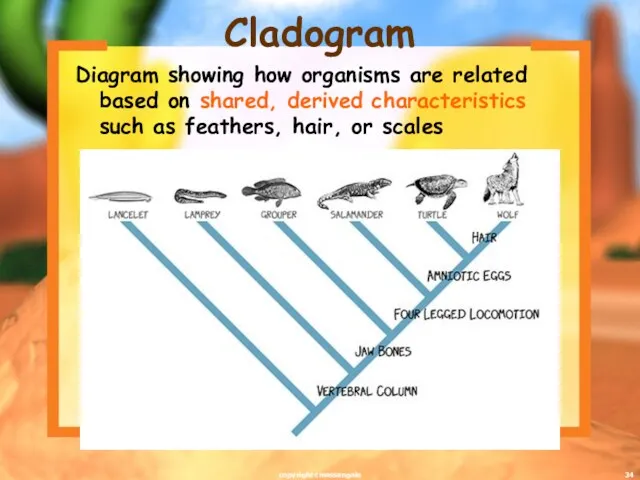
- 34. Cladogram Diagram showing how organisms are related based on shared, derived characteristics such as feathers, hair,
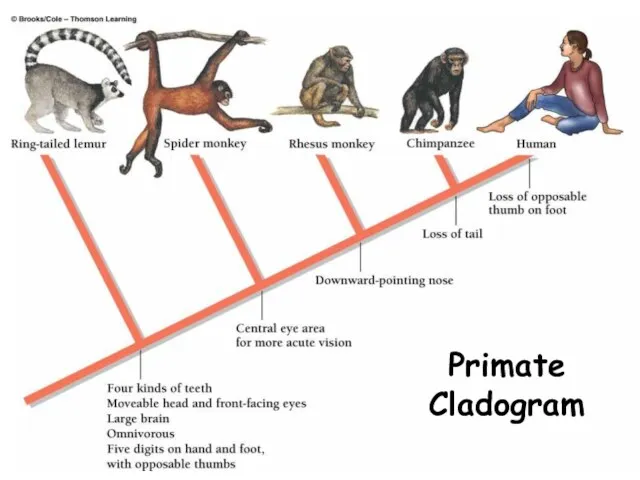
- 35. Primate Cladogram copyright cmassengale
- 36. Dichotomous Keying Used to identify organisms Characteristics given in pairs Read both characteristics and either go
- 37. Example of Dichotomous Key 1a Tentacles present – Go to 2 1b Tentacles absent – Go
- 39. Скачать презентацию



























 Эволюция черепа, жаберного и челюстного аппарата позвоночных
Эволюция черепа, жаберного и челюстного аппарата позвоночных Особенности пищеварения у собак и котов. Питательные и биологически активные вещества
Особенности пищеварения у собак и котов. Питательные и биологически активные вещества Растениеводство. Системы земледелия
Растениеводство. Системы земледелия Биологические и хозяйственные особенности кур
Биологические и хозяйственные особенности кур Формирование целостной картины мира. Играем на лугу. Луг и его обитатели
Формирование целостной картины мира. Играем на лугу. Луг и его обитатели Копитні ссавці
Копитні ссавці Задания ЕГЭ по теме Клетка
Задания ЕГЭ по теме Клетка Применение активных дрожжей в кормлений животных
Применение активных дрожжей в кормлений животных Влияние света на проращивание семян (часть 1)
Влияние света на проращивание семян (часть 1) Ошущение. Возникновение ощущений
Ошущение. Возникновение ощущений Тип Членистоногие, класс Паукообразные
Тип Членистоногие, класс Паукообразные Птицы Африки
Птицы Африки Стрес та його чинники. Адаптація людини до стресу
Стрес та його чинники. Адаптація людини до стресу Биология – наука о живой природе
Биология – наука о живой природе Презентация по теме Проектная деятельность
Презентация по теме Проектная деятельность Взаимодействие микроорганизмов с человеком и животными
Взаимодействие микроорганизмов с человеком и животными Молекулярні механізми скорочення м’язового волокна
Молекулярні механізми скорочення м’язового волокна Ядовитые растения
Ядовитые растения Факторы среды, влияющие на размножение и формирование пола у животных. (Лекция 3)
Факторы среды, влияющие на размножение и формирование пола у животных. (Лекция 3) Красная книга Таштагольского района
Красная книга Таштагольского района Фенологические наблюдения за природой
Фенологические наблюдения за природой Анатомия ЦНС. Задний мозг. Варолиев мост
Анатомия ЦНС. Задний мозг. Варолиев мост Экология человека
Экология человека Строение и жизнедеятельность бактерий
Строение и жизнедеятельность бактерий Молекулярно-биологические методы диагностики
Молекулярно-биологические методы диагностики Всё о мёде, способы фальсификации
Всё о мёде, способы фальсификации Электрофорез белков в полиакриламидном геле и вестерн-блоттинг
Электрофорез белков в полиакриламидном геле и вестерн-блоттинг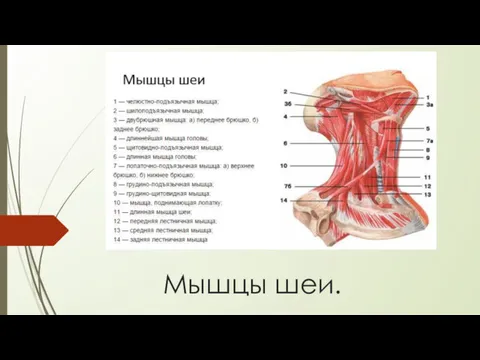 Мышцы шеи
Мышцы шеи