Содержание
- 2. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting Definitions Composting = aerobic biological decomposition of the biodegradable
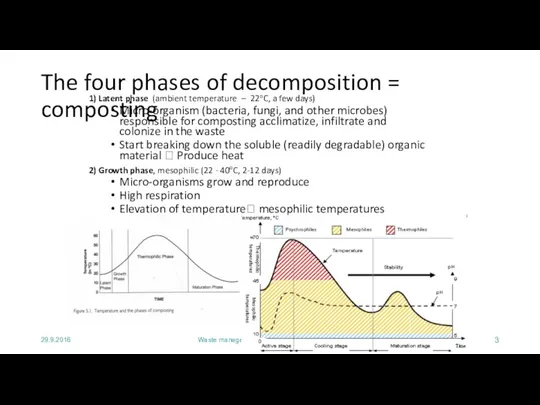
- 3. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting The four phases of decomposition = composting 1) Latent
- 4. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting The five phases of decomposition = composting 3) Thermophilic
- 5. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting Factors affecting the decomposition in the compost Temperature Depends
- 6. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting Factors affecting the decomposition in the compost Particle size
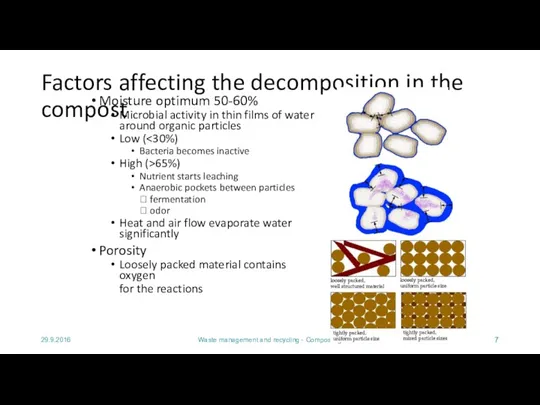
- 7. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting Factors affecting the decomposition in the compost Moisture optimum
- 8. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting Factors affecting the decomposition in the compost Composition of
- 9. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting Materials and elements in composting Often Dry = high
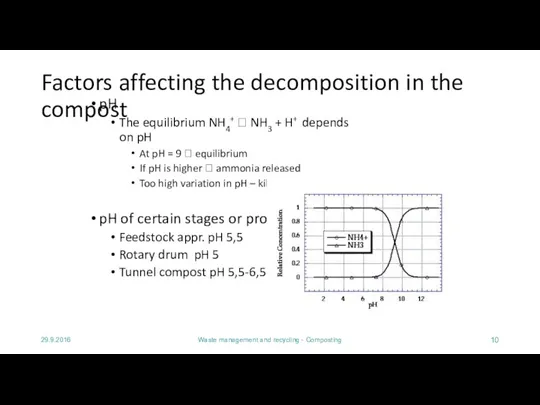
- 10. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting Factors affecting the decomposition in the compost pH The
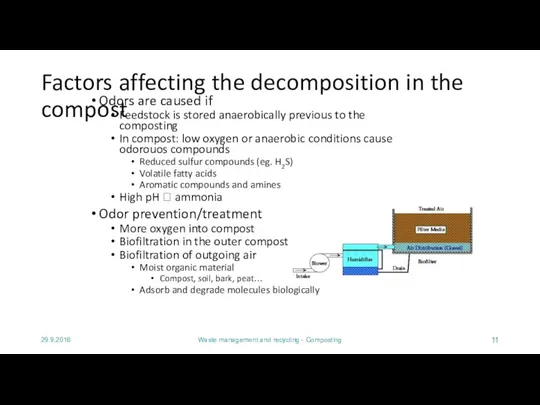
- 11. 29.9.2016 Waste management and recycling - Composting Factors affecting the decomposition in the compost Odors are
- 13. Скачать презентацию






 Белки. Переваривание и всасывание
Белки. Переваривание и всасывание Органи і системи органів тварин
Органи і системи органів тварин Ас қорытудың маңызы
Ас қорытудың маңызы Внутренняя среда организма. Значение крови и её состав
Внутренняя среда организма. Значение крови и её состав Молекулярная структура гена. Структура геномов вирусов, про - и эукариот. Регуляция экспрессии генов
Молекулярная структура гена. Структура геномов вирусов, про - и эукариот. Регуляция экспрессии генов Физиология мышечного сокращения. Строение, свойства и функции мышечной ткани
Физиология мышечного сокращения. Строение, свойства и функции мышечной ткани Цветок. Плод. Семя
Цветок. Плод. Семя Строение нервной системы. Спинной мозг. Спинномозговые сплетения
Строение нервной системы. Спинной мозг. Спинномозговые сплетения Собачий клещ (Ixodes ricinus)
Собачий клещ (Ixodes ricinus) Тракененская порода лошадей
Тракененская порода лошадей Тест по теме Селекция
Тест по теме Селекция История развития биологии
История развития биологии Ferment. Ferment substrata
Ferment. Ferment substrata Физиология энергетического обмена и температурного гомеостазиса
Физиология энергетического обмена и температурного гомеостазиса Биогеохимические циклы
Биогеохимические циклы Человек и домашние животные
Человек и домашние животные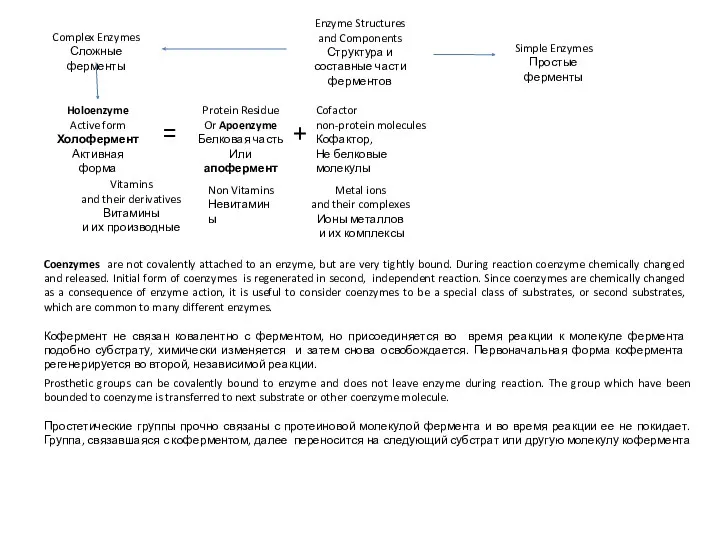 Структура и составные части ферментов. Тема 2.1
Структура и составные части ферментов. Тема 2.1 ОЖЖ-дегі тежелу механизмдері. ОЖЖ-дегі тежелудің координациялық механизмдері
ОЖЖ-дегі тежелу механизмдері. ОЖЖ-дегі тежелудің координациялық механизмдері Улюблена домашня тварина
Улюблена домашня тварина Плауны. Хвощи. Папоротники
Плауны. Хвощи. Папоротники Животные Ярославской области, занесенные в Красную книгу
Животные Ярославской области, занесенные в Красную книгу Видоизменения побегов
Видоизменения побегов Индивидуальное развитие организмов (онтогенез)
Индивидуальное развитие организмов (онтогенез) Генетика. Наследственность
Генетика. Наследственность Государство Австралия. (2 класс)
Государство Австралия. (2 класс) Нервная система животных. Рефлекс. Инстинкт
Нервная система животных. Рефлекс. Инстинкт Викторина В мире животных
Викторина В мире животных Anaerobic Gram-Positive Spore-Forming Bacilli
Anaerobic Gram-Positive Spore-Forming Bacilli