Содержание
- 2. Legislation Codex of the Republic of Kazakhstan “On people's health and the health care system” Law
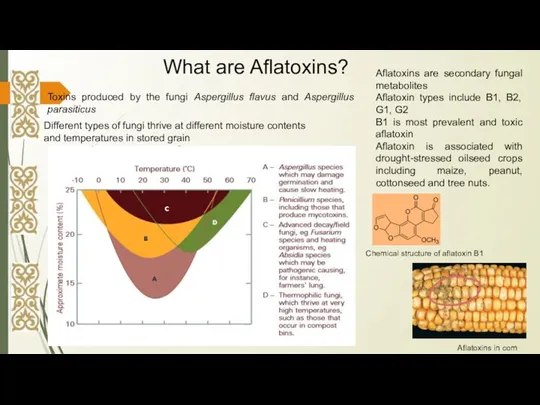
- 3. Toxins produced by the fungi Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus Different types of fungi thrive at
- 4. Influence of aflatoxins on human health Acute aflatoxicosis can be fatal. Presenting symptoms are determined by
- 5. Influence of aflatoxins on farm animals Poultry Highly sensitive Aflatoxin toxicity impairs uptake of essential nutrients
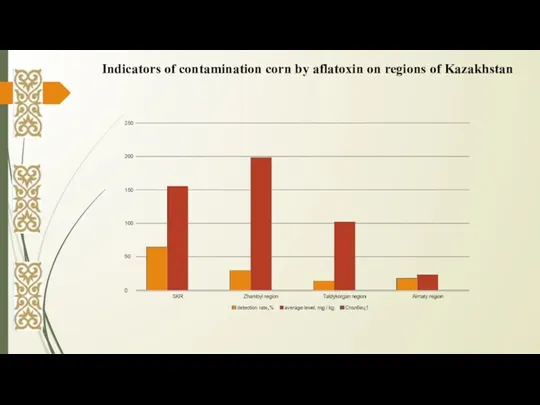
- 6. Indicators of contamination corn by aflatoxin on regions of Kazakhstan
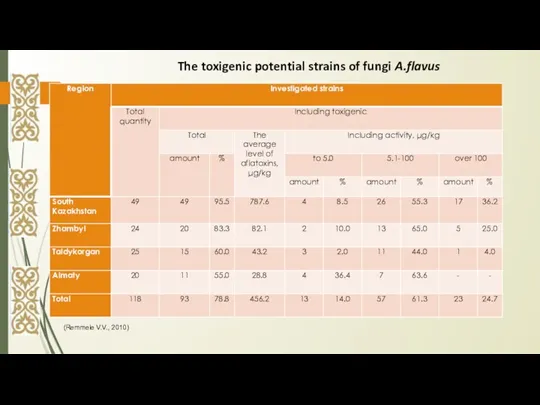
- 7. (Remmele V.V., 2010) The toxigenic potential strains of fungi A.flavus
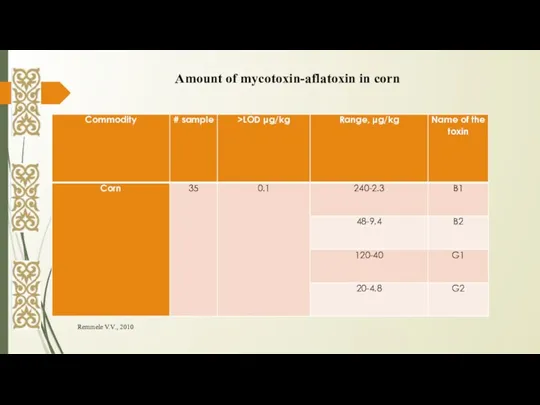
- 8. Remmele V.V., 2010 Amount of mycotoxin-aflatoxin in corn
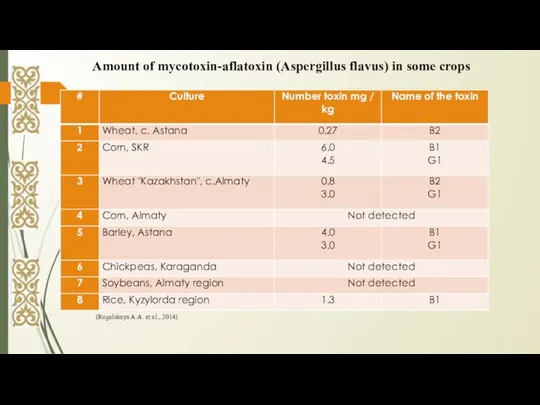
- 9. (Rogalskaya A.A. et al., 2014) Amount of mycotoxin-aflatoxin (Aspergillus flavus) in some crops
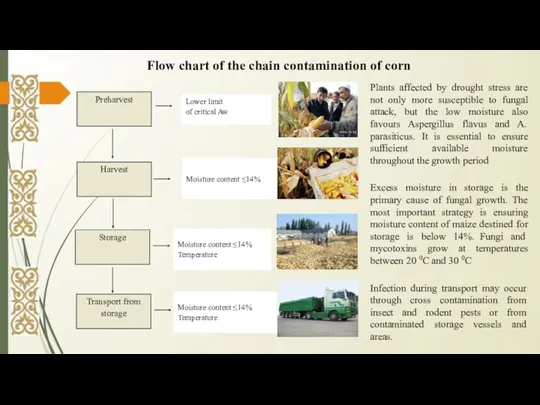
- 10. Flow chart of the chain contamination of corn Plants affected by drought stress are not only
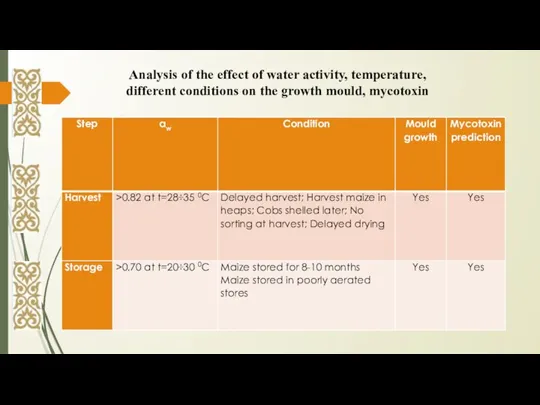
- 11. Analysis of the effect of water activity, temperature, different conditions on the growth mould, mycotoxin
- 12. Comparative analysis of content mycotoxins in maize (for human consumption) of legislations of EU and Customs
- 13. Conclusions the Republic of Kazakhstan is a zone of increased risk of contamination of corn by
- 15. Скачать презентацию





 Биология и распространение сурков
Биология и распространение сурков Селекция микроорганизмов. Биотехнология
Селекция микроорганизмов. Биотехнология Презентация по биологии Внутренняя среда организма. Кровь
Презентация по биологии Внутренняя среда организма. Кровь Учение об иммунитете
Учение об иммунитете Решение задач по генетике
Решение задач по генетике Основы систематики микроорганизмов
Основы систематики микроорганизмов Эндемики Австралии
Эндемики Австралии Рецепция (қабылдағыштар рөлі). Жүйке талшықтары, тұрлері, қозуды өткізу механизмі. Парабиоз
Рецепция (қабылдағыштар рөлі). Жүйке талшықтары, тұрлері, қозуды өткізу механизмі. Парабиоз слайды к уроку Курочка-ряба
слайды к уроку Курочка-ряба Процесс кровообращения. Вены большого круга кровообращения
Процесс кровообращения. Вены большого круга кровообращения Белки II. Уровни организации белков
Белки II. Уровни организации белков Corn
Corn Размножение и индивидуальное развитие организмов. Бесполое размножение
Размножение и индивидуальное развитие организмов. Бесполое размножение Презентация, Обобщающий урок по теме скелет.
Презентация, Обобщающий урок по теме скелет. Внешнее строение листа. Многообразие листьев
Внешнее строение листа. Многообразие листьев Исследовательский проект на тему: Мандариновое дерево
Исследовательский проект на тему: Мандариновое дерево Получение и применение моноклональных антител
Получение и применение моноклональных антител Электронный задачник. Часть 1. Содержание (Моногибридное скрещивание)
Электронный задачник. Часть 1. Содержание (Моногибридное скрещивание) Условия жизни на Земле Среды жизни на Земле и экологические факторы 9 класс По УМК И.Н. Пономаревой.
Условия жизни на Земле Среды жизни на Земле и экологические факторы 9 класс По УМК И.Н. Пономаревой. Догляд за руками
Догляд за руками Где живут белые медведи (окружающий мир, 1 класс)
Где живут белые медведи (окружающий мир, 1 класс) Скелет и соединения конечностей. Кости черепа человека
Скелет и соединения конечностей. Кости черепа человека Пищевые добавки. Классификация пищевых добавок
Пищевые добавки. Классификация пищевых добавок Изменения в жизни домашних животных весной. Труд людей весной (человек и мир, 1 класс)
Изменения в жизни домашних животных весной. Труд людей весной (человек и мир, 1 класс) Отдел: Покрытосеменные (Angiospermae), класс Двудольные (Dicotyledones)
Отдел: Покрытосеменные (Angiospermae), класс Двудольные (Dicotyledones) Айран дайындау технологиясы
Айран дайындау технологиясы Митоз. Митоздық цикл
Митоз. Митоздық цикл Эпителиальная ткань. Соединительная ткань. Лекция 3
Эпителиальная ткань. Соединительная ткань. Лекция 3