Содержание
- 2. Key Words Opportunistic diseases Shigella Diarrhea - Bacillary dysentery Dysentery - Shiga toxin Urinary tract infections
- 3. septicemia, pneumonia, meningitis urinary tract infections Citrobacter Enterobacter Escherichia Hafnia Morganella Providencia Serratia Opportunistic diseases -Enterobacteriaceae
- 4. Enterobacteriaceae gastrointestinal diseases Escherichia coli Salmonella Shigella Yersinia entercolitica
- 5. Histocompatibility antigen (HLA) B27 Enterobacteriaceae Salmonella Shigella Yersinia Non-Enterobacteriaceae Campylobacter Chlamydia Reiter's syndrome
- 6. community acquired otherwise healthy people Klebsiella pneumoniae respiratory diseases prominent capsule urinary tract infection fecal contamination
- 7. E. coli fimbriae mannose Type 1 galactose glycolipids glycoproteins P
- 8. Enterobacteriaceae gram negative facultative anaerobic rods – oxidase negative (no cytochrome oxidase)
- 9. E. coli lactose positive not usually identified lactose positive sp. common, healthy intestine Shigella, Salmonella,Yersinia lactose
- 10. other sites identified biochemically Enterobacteriaceae
- 11. Serotypes reference laboratory antigens O (lipopolysaccharide) H (flagellar) K (capsular)
- 12. Diarrhea (watery feces) and Dysentery (blood in stools)
- 13. Caption: E. coli Escherichia coli
- 14. E. coli and Shigella genetically very similar separated for historical reasons overlap in pathogenesis Escherichia coli
- 15. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli Usually O157:H7 Flagella
- 16. Transmission – meat products or sewage-contaminated vegetables Hemorrhagic Bloody dysentery copious diarrhea few leukocytes afebrile hemolytic-uremic
- 17. Vero toxin “shiga-like toxin” Hemolysins Enterohemorrhagic E. coli
- 18. Enterotoxigenic E. coli diarrhea like cholera milder travellers diarrhea
- 19. Enterotoxigenic E. coli Heat labile toxin like choleragen Adenyl cyclase activated cyclic AMP secretion water/ions Heat
- 20. Enteropathogenic E. coli destruction of surface microvilli fever diarrhea vomiting nausea non-bloody stools (not generally seen
- 21. Enteroaggregative Brick-like bacterial aggregates - cell surfaces Mucus biofilm inhibits fluid absorption Diarrhea
- 22. Dysentery - resembles shigellosis Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC ) Gut lumen
- 23. Treatment -gastrointestinal disease fluid replacement antibiotics not used usually unless systemic e.g. hemolytic-uremia syndrome
- 24. Shigella Modified from Fig, Dennis Kunkel
- 25. Shigella S. flexneri, S. boydii, S. sonnei, S. dysenteriae bacillary dysentery shigellosis bloody feces intestinal pain
- 26. Shigellosis within 2-3 days epithelial cell damage Gut lumen
- 27. Shiga toxin enterotoxic cytotoxic inhibits protein synthesis lysing 28S rRNA
- 28. Shigellosis man only "reservoir" mostly young children fecal to oral contact children to adults transmitted by
- 29. Treating shigellosis manage dehydration patients respond to antibiotics disease duration diminished
- 30. Salmonella
- 31. Salmonella 2000 antigenic "types” genetically single species S. enterica disease category S. enteritidis many serotypes S.
- 32. Salmonellosis S. enteritidis the common salmonella infection poultry, eggs no human reservoir Gastroenteritis nausea vomiting non-bloody
- 33. Control of salmonellosis Monitoring of food in the US is limited microbiology is difficult Regulation is
- 34. Salmonellosis uncomplicated cases (the vast majority) antibiotic therapy not useful Gut lumen
- 36. Скачать презентацию
 Роль бактерий в природе и жизни человека
Роль бактерий в природе и жизни человека 28_L_Razmnozhenie_i_razvitie
28_L_Razmnozhenie_i_razvitie Строение клетки
Строение клетки Ближайшие родственники человека
Ближайшие родственники человека Биология – наука о жизни
Биология – наука о жизни Как ткани ткут и нити прядут
Как ткани ткут и нити прядут Введение в спланхнологию
Введение в спланхнологию Процессы жизнедеятельности прокариот
Процессы жизнедеятельности прокариот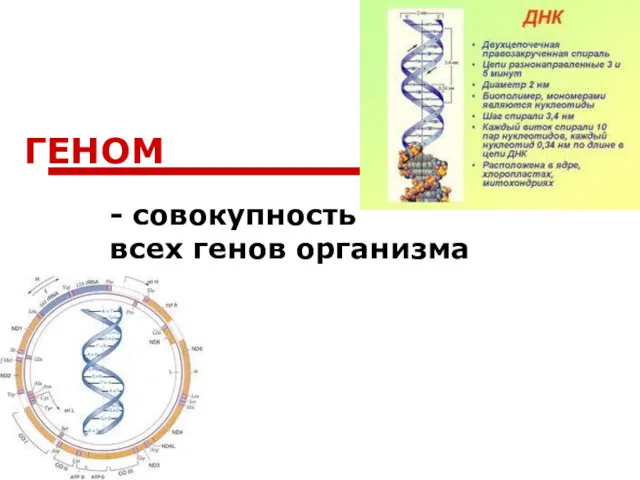 Геном - совокупность всех генов организма
Геном - совокупность всех генов организма Рептилії
Рептилії Насекомые. Отряд чешуекрылые
Насекомые. Отряд чешуекрылые Основы цитологии. Понятие о клетке
Основы цитологии. Понятие о клетке Методическая разработка урока по биологии Белки - природные высокомолекулярные вещества
Методическая разработка урока по биологии Белки - природные высокомолекулярные вещества Папоротники. Хвощи. Плауны
Папоротники. Хвощи. Плауны Развитие органического мира на Земле
Развитие органического мира на Земле История изучения клетки. Клеточная теория
История изучения клетки. Клеточная теория Звери и птицы весной
Звери и птицы весной Отряд голенастые
Отряд голенастые Функции тонкого и толстого кишечника. Роль печени
Функции тонкого и толстого кишечника. Роль печени УМК В.И. Сивоглазова 1 концентр. Базовый уровень
УМК В.И. Сивоглазова 1 концентр. Базовый уровень Отряды млекопитающих
Отряды млекопитающих Неклеточные формы жизни – вирусы
Неклеточные формы жизни – вирусы Болезни эмбрионов с/х птицы
Болезни эмбрионов с/х птицы Филогенетический ряд лошади
Филогенетический ряд лошади За всё надо платить
За всё надо платить Жылқы-малдың патшасы
Жылқы-малдың патшасы Тыныс алудың организм үшін маңызы. Тыныс алу кезеңдері. Тыныс алудың реттелуі
Тыныс алудың организм үшін маңызы. Тыныс алу кезеңдері. Тыныс алудың реттелуі Химия и обмен углеводов. Классификация
Химия и обмен углеводов. Классификация