Содержание
- 2. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Cell walls are made of chitin (complex polysaccharide) Body is called the
- 3. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Grow best in warm, moist environments Mycology is the study of fungi
- 4. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Important decomposers & recyclers of nutrients in the environment Most are multicellular,
- 6. Spores and More Spores Fungi are prolific spore producers Spores can be sexual, asexual, or both
- 7. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Fungi include puffballs, yeasts, mushrooms, toadstools, rusts, smuts, ringworm, and molds The
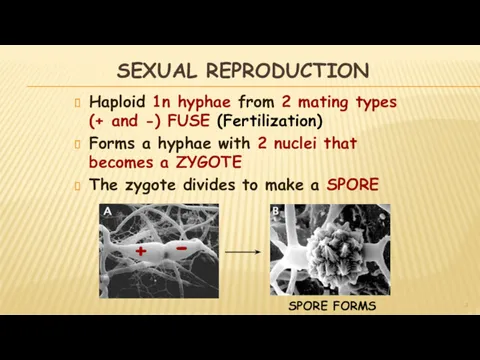
- 8. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Haploid 1n hyphae from 2 mating types (+ and -) FUSE (Fertilization) Forms a
- 9. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Fruiting Bodies are modified hyphae that make asexual spores An upright stalk called the
- 10. IT’S ALL ABOUT THE SPORES! Fungi are classified by their REPRODUCTIVE STRUCTURES and SPORES The reproductive
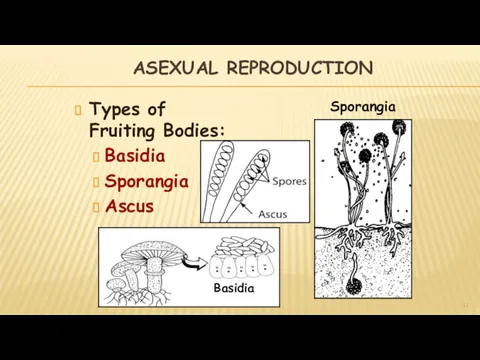
- 11. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Types of Fruiting Bodies: Basidia Sporangia Ascus Basidia Sporangia
- 12. Each spore that germinates can be the start of a hypha and a mycelium. Stalked reproductive
- 13. Classification by Nutrition Saprobes Decomposers Molds, mushrooms, etc. Parasites Harm host Rusts and smuts (attack plants)
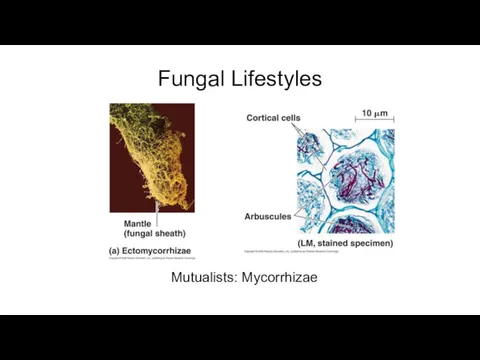
- 14. Fungal Lifestyles Mutualists: Mycorrhizae
- 15. Fungal Lifestyles Parasites
- 16. Fungal Lifestyles Predators
- 17. Fungal Lifestyles Mutualists: Lichens Photo Credit: Field Biology Student, 360 Overlook 2005
- 18. Fungal Lifestyles Saprobes = Decomposers
- 19. MAJOR GROUPS OF FUNGI Basidiomycota – Club Fungi Zygomycota – Bread Molds Chytridiomycota – Chytrids AM
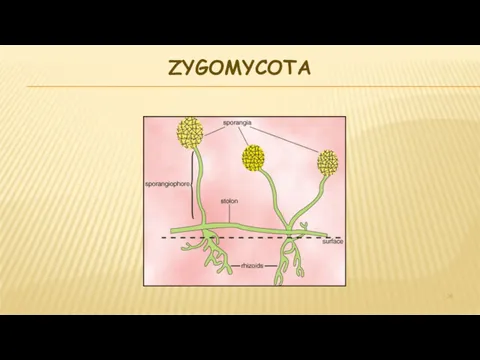
- 20. ZYGOMYCOTA
- 21. ZYGOMYCOTA Called the sporangium fungi Commonly called molds Also includes blights Hyphae have no cross walls
- 22. ZYGOMYCOTA Asexual reproductive structure called sporangium atop sporangiospores make spores Rhizoids anchor the mold & release
- 23. USES FOR BASIDIOMYCOTA Some are used as food (mushrooms) Others damage crops (rusts & smuts) Corn
- 24. ASCOMYCOTA
- 25. CHARACTERISTICS Called Sac fungi Includes Cup fungi, morels, truffles, yeasts, and mildew May be plant parasites
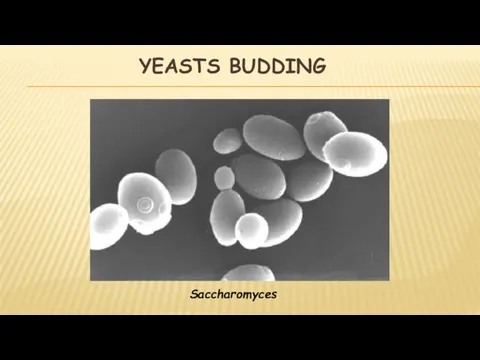
- 26. YEASTS BUDDING Saccharomyces
- 27. USES OF ASCOMYCETES Truffles and morels are good examples of edible ascomycetes Penicillium mold makes the
- 28. BASIDIOMYCOTA Called Club fungi Includes: Mushrooms Toadstools Bracket & Shelf fungi Puffballs Stinkhorns Rusts and smuts
- 29. USES FOR BASIDIOMYCOTA Some are used as food (mushrooms) Others damage crops (rusts & smuts) Corn
- 31. Скачать презентацию























 Однодольные растения. Liliopsida, Monocotyledones, Monocotyledoneae
Однодольные растения. Liliopsida, Monocotyledones, Monocotyledoneae Рефлекторная деятельность ЦНС
Рефлекторная деятельность ЦНС Ұлпаның және ағзаның электростимуляциясы
Ұлпаның және ағзаның электростимуляциясы Биологическая продукция, скорость накопления биомассы в экосистеме
Биологическая продукция, скорость накопления биомассы в экосистеме Общая характеристика пищеварительной системы. Пищеварение в полости рта. Лекция 25
Общая характеристика пищеварительной системы. Пищеварение в полости рта. Лекция 25 Тест по биологии (8 класс) по теме Биосоциальная сущность человека для системы тестирования PROClass
Тест по биологии (8 класс) по теме Биосоциальная сущность человека для системы тестирования PROClass Влияние факторов внешней среды на онтогенез
Влияние факторов внешней среды на онтогенез Роль генетичних особливостей спортсмена у культуризмі
Роль генетичних особливостей спортсмена у культуризмі Гормональний стан самиці в продовж вагітності
Гормональний стан самиці в продовж вагітності Подготовка учащихся к государственной итоговой аттестации по биологии
Подготовка учащихся к государственной итоговой аттестации по биологии Бактерії
Бактерії Распространение плодов и семян
Распространение плодов и семян Malysham_o_pchelakh_i_mede
Malysham_o_pchelakh_i_mede Структура и химический состав бактериальной клетки
Структура и химический состав бактериальной клетки Моё домашнее животное - хомяк
Моё домашнее животное - хомяк Лекарственные растения
Лекарственные растения Инструктивные карточки по биологии для 5 класса.
Инструктивные карточки по биологии для 5 класса. Игра четвёртый лишний
Игра четвёртый лишний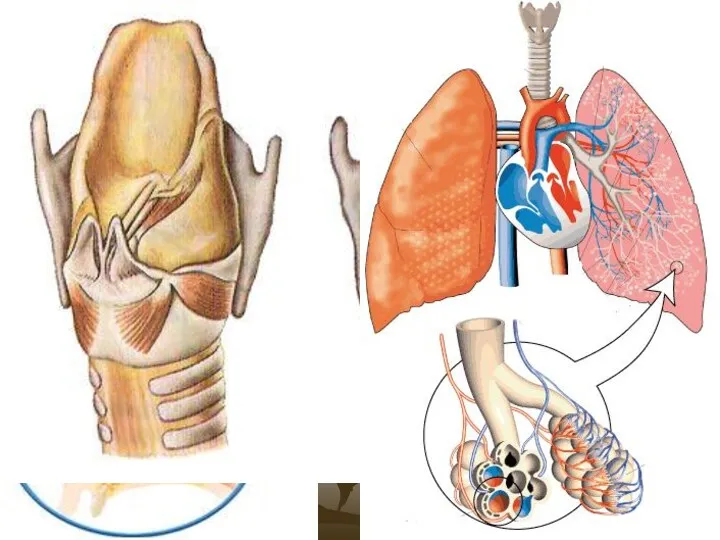 Строение легких. Легочное и тканевое дыхание
Строение легких. Легочное и тканевое дыхание Строение нервной системы
Строение нервной системы Тип Членистоногие
Тип Членистоногие Происхождение и эволюция человека
Происхождение и эволюция человека Физиология микроорганизмов. (Лекция 3)
Физиология микроорганизмов. (Лекция 3) Значение генетики
Значение генетики Метапредметная игра, посвященная 100-летию юннатского движения в России
Метапредметная игра, посвященная 100-летию юннатского движения в России Отряд Двукрылые
Отряд Двукрылые Семейство Бобовые
Семейство Бобовые Транспорт веществ через биологические мембраны. (Лекция 12)
Транспорт веществ через биологические мембраны. (Лекция 12)