niche - is the functional role that it plays within an
ecosystem. The niche (better refined as the 'ecological niche') is determined by the abiotic factors (non-living). New populations develop around new niches – usually due to an adaptation that allows survival.
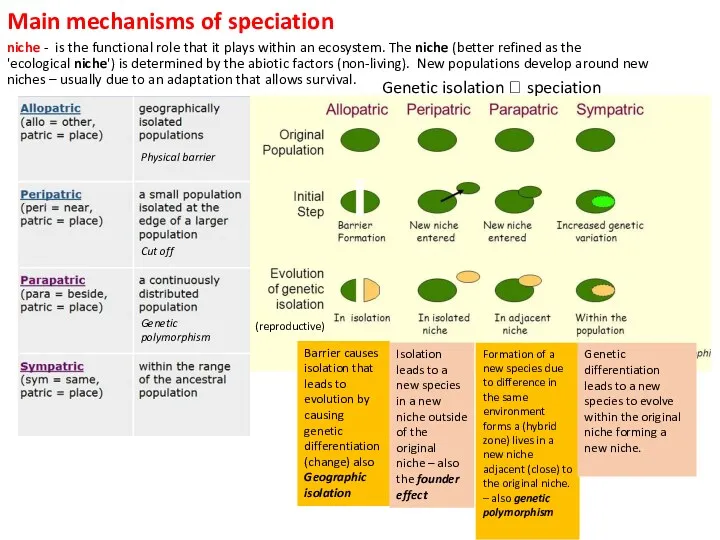
Genetic isolation ? speciation
Barrier causes isolation that leads to evolution by causing genetic differentiation(change) also
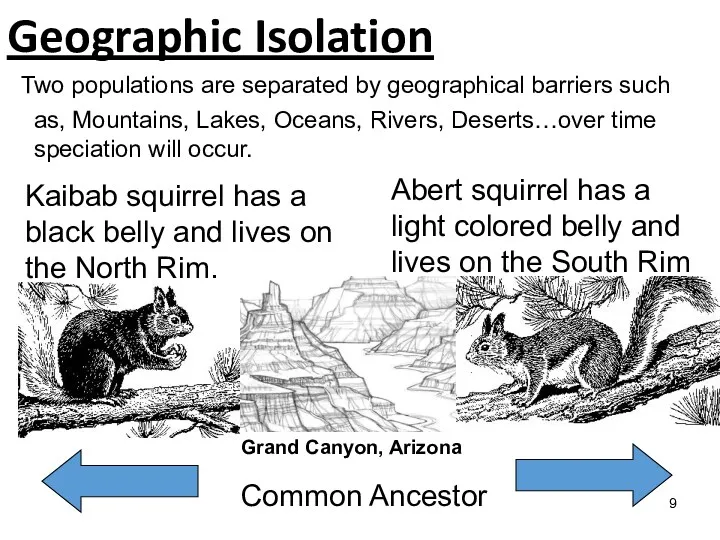
Geographic isolation
Formation of a new species due to difference in the same environment forms a (hybrid zone) lives in a new niche adjacent (close) to the original niche. – also genetic polymorphism
Isolation leads to a new species in a new niche outside of the original niche – also the founder effect
Genetic differentiation leads to a new species to evolve within the original niche forming a new niche.
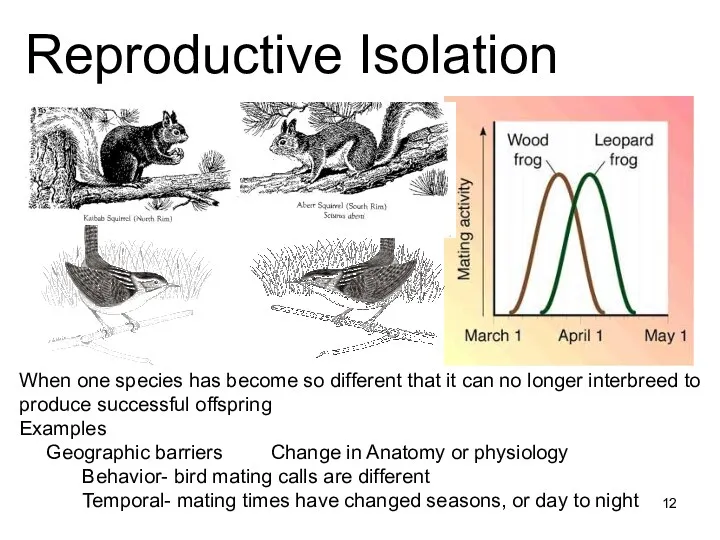
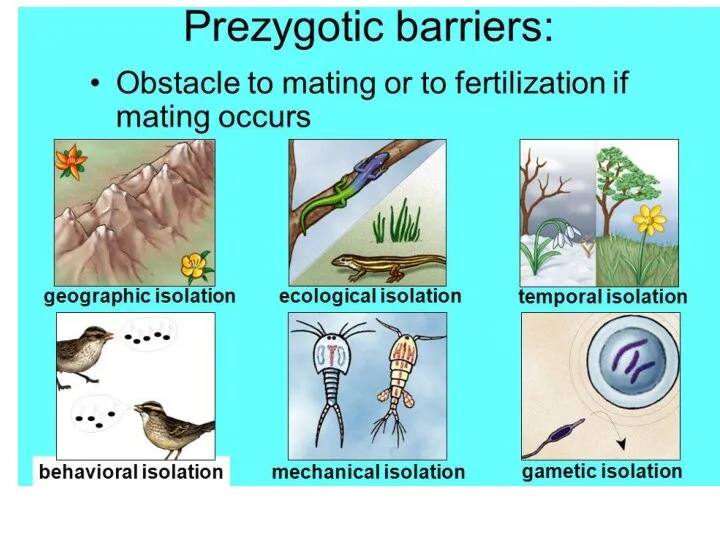
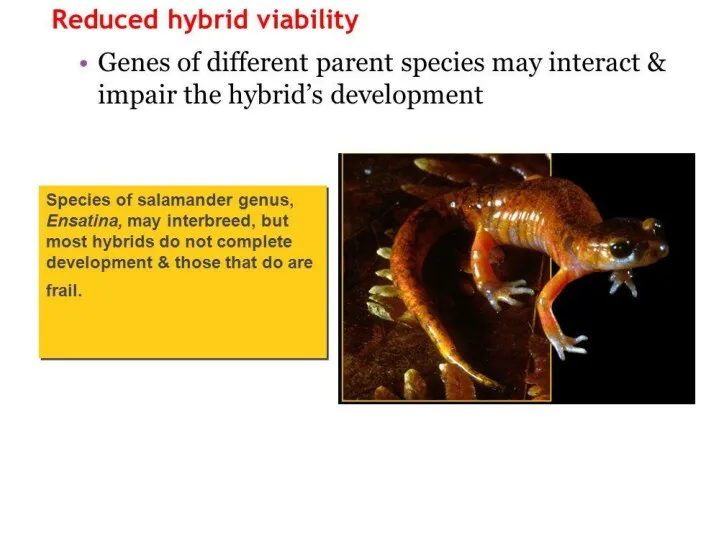
(reproductive)
Cut off
Physical barrier
Genetic polymorphism
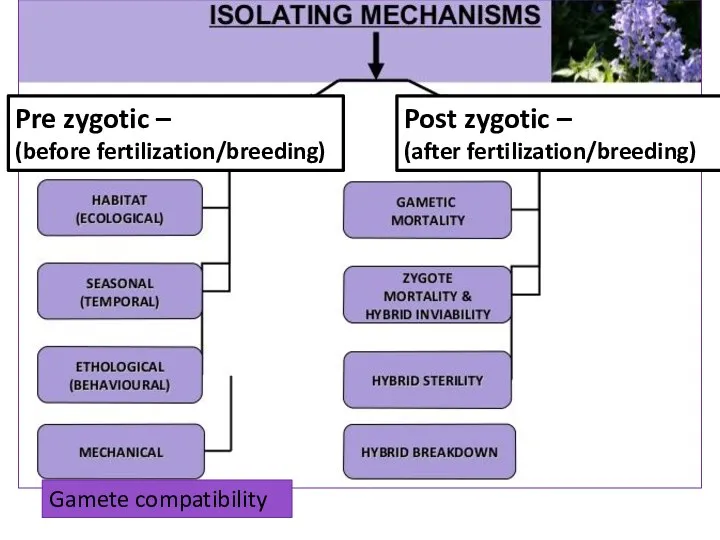
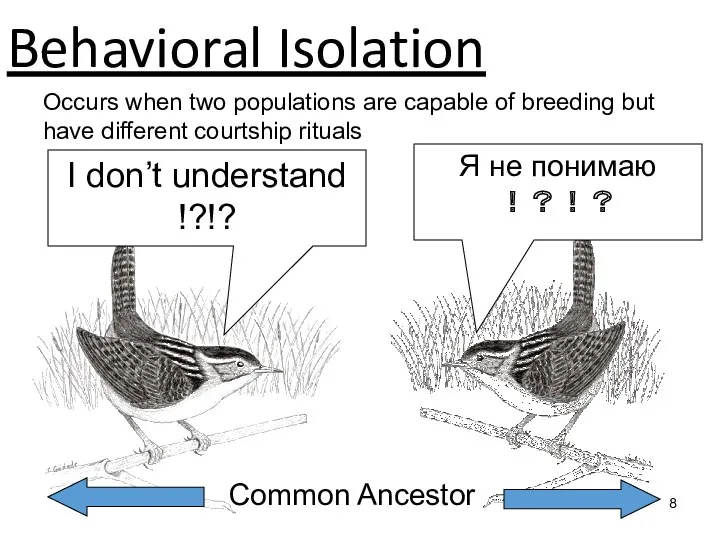
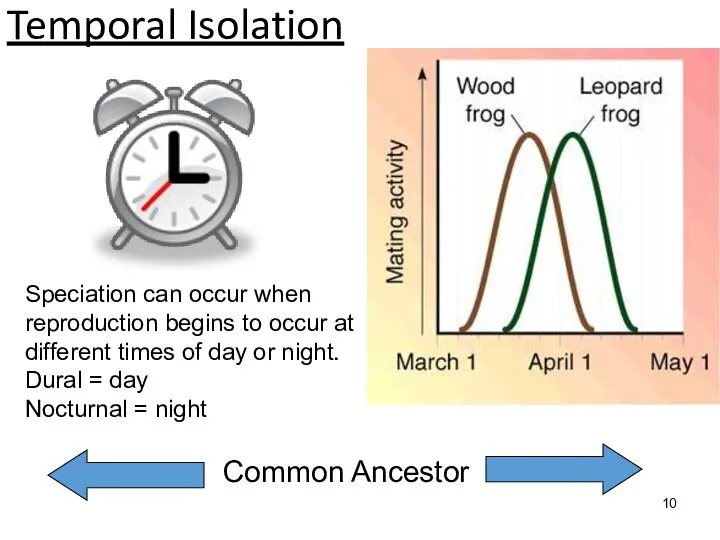
Main mechanisms of speciation





 Класс ракообразные
Класс ракообразные Введение в генетику микроорганизмов
Введение в генетику микроорганизмов Опорно-двигательная система человека. Скелет туловища
Опорно-двигательная система человека. Скелет туловища Эволюция опорно- двигательной системы у животных
Эволюция опорно- двигательной системы у животных Теломерлер. Теломеразалық белсенділік
Теломерлер. Теломеразалық белсенділік Теория существования прокариот
Теория существования прокариот Законы Менделя
Законы Менделя Ученик и мобильный телефон.
Ученик и мобильный телефон. урок исследование Видоизмененные побеги
урок исследование Видоизмененные побеги Макроэволюция: направления и пути эволюции
Макроэволюция: направления и пути эволюции презентация к обобщающему уроку биологии по теме Пресмыкающиеся к учебнику константинов в.м. и др.
презентация к обобщающему уроку биологии по теме Пресмыкающиеся к учебнику константинов в.м. и др.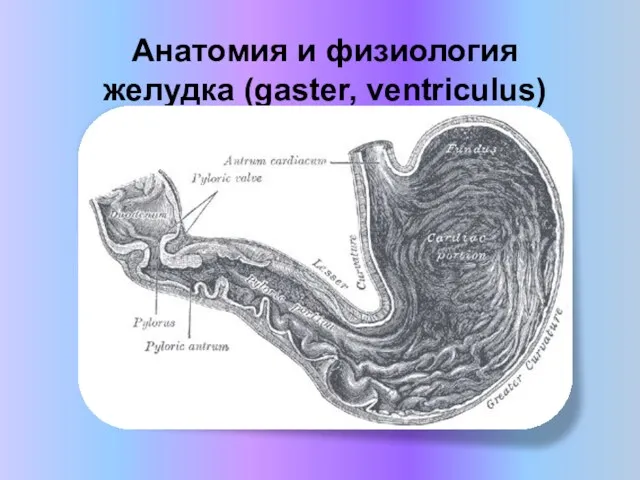 Анатомия и физиология желудка
Анатомия и физиология желудка Семейство Бобовые или Мотыльковые
Семейство Бобовые или Мотыльковые Амфибилер
Амфибилер Царство Грибов. 5 класс
Царство Грибов. 5 класс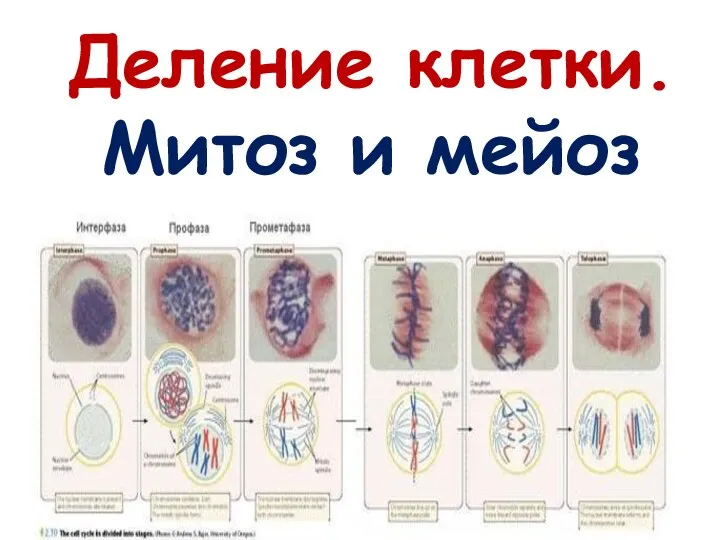 Деление клетки. Митоз и мейоз
Деление клетки. Митоз и мейоз Брюхоногие моллюски
Брюхоногие моллюски Основные понятия пластической анатомии
Основные понятия пластической анатомии Красные водоросли
Красные водоросли Акция Каждой пичужке кормушка
Акция Каждой пичужке кормушка Модификационная изменчивость.
Модификационная изменчивость. Эмбриональное развитие организмов
Эмбриональное развитие организмов Изготовление и рассматривание микропрепарата кожицы лука
Изготовление и рассматривание микропрепарата кожицы лука Собака домашняя
Собака домашняя Презентация Отряд Блохи
Презентация Отряд Блохи Поле чудес. В мире животных
Поле чудес. В мире животных Электрические свойства тканей организма. (Лекция 6)
Электрические свойства тканей организма. (Лекция 6) Этапы развития науки генетики
Этапы развития науки генетики