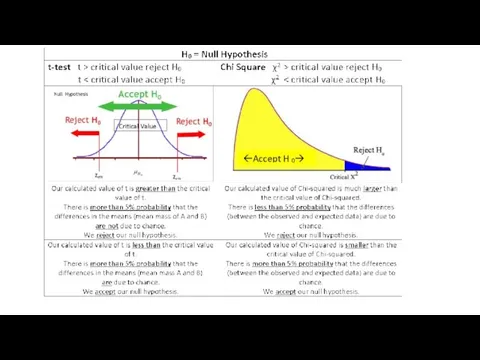
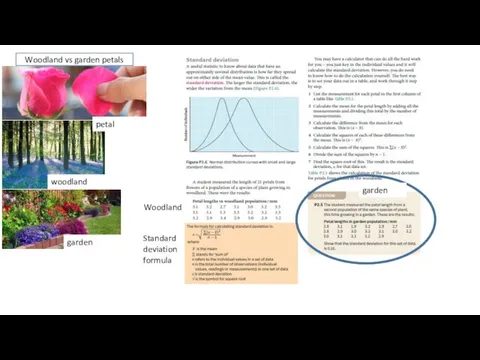
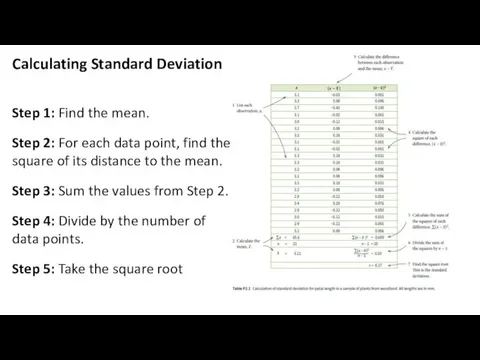
Alternative Hypothesis vs Null Hypothesis
Our calculated value of Chi-squared is
much larger than the critical value of Chi-squared.
There is less than 5% probability that the differences (between the observed and expected data) are due to chance.
We reject our null hypothesis.
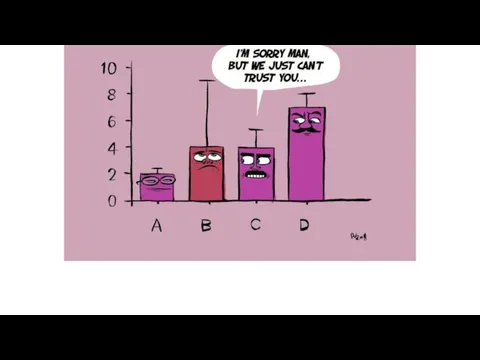
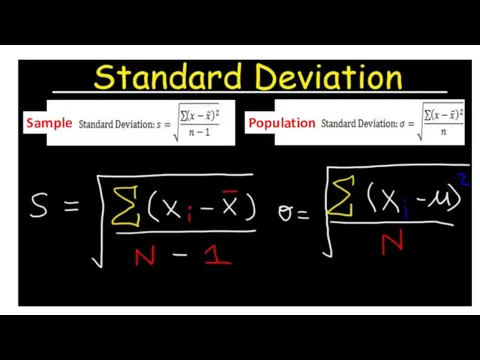
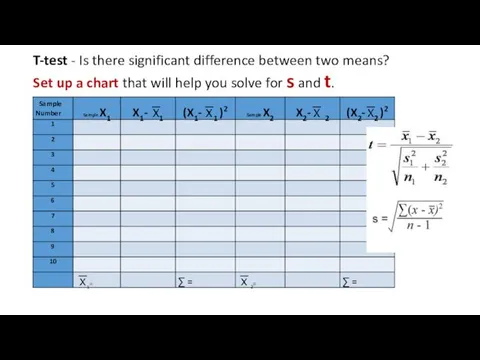
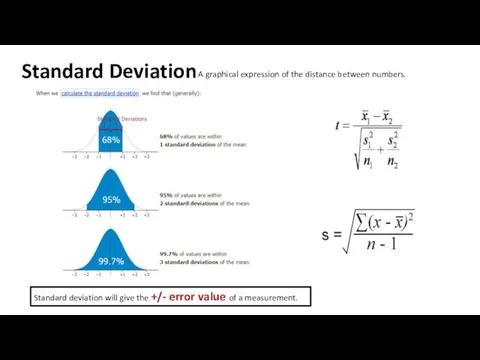
Our calculated value of t is less than the critical value of t.
There is more than 5% probability that the differences in the means (mean of A and the mean of B) are due to chance.
We accept our null hypothesis.
Acceptance or Rejection of the of the Null Hypothesis







 Генетика: основные термины и понятия
Генетика: основные термины и понятия Хомяк джунгарский
Хомяк джунгарский Промышленное культивирование микроорганизмов
Промышленное культивирование микроорганизмов Фізіологія ендокринної системи
Фізіологія ендокринної системи ПРИСПОСОБИТЕЛЬНЫЕ ОСОБЕННОСТИ СТРОЕНИЯ,ОКРАСКИ ТЕЛА И ПОВЕДЕНИЯ ЖИВОТНЫХ.
ПРИСПОСОБИТЕЛЬНЫЕ ОСОБЕННОСТИ СТРОЕНИЯ,ОКРАСКИ ТЕЛА И ПОВЕДЕНИЯ ЖИВОТНЫХ. Meristem and cover tissues. Constant tissues: transport, mechanic
Meristem and cover tissues. Constant tissues: transport, mechanic Учение о тканях
Учение о тканях Плауны. Хвощи. Папоротники
Плауны. Хвощи. Папоротники Тип хордовые. Подтип черепные. Класс земноводные (амфибии
Тип хордовые. Подтип черепные. Класс земноводные (амфибии Биогенные элементы. Классификация. Топография биогенных элементов в организме человека
Биогенные элементы. Классификация. Топография биогенных элементов в организме человека Энергетический и пластический обмен
Энергетический и пластический обмен Спинной мозг
Спинной мозг Мочеполовой аппарат
Мочеполовой аппарат Урок-игротека Животные
Урок-игротека Животные Тұқымқуалаудың хромосомадан тыс факторлары: плазмидалар, транспозондар, isтіркестер. Бактериялар мен вирустардың генетикасы
Тұқымқуалаудың хромосомадан тыс факторлары: плазмидалар, транспозондар, isтіркестер. Бактериялар мен вирустардың генетикасы Посевные качества семян
Посевные качества семян Обобщение по теме Царство Грибы
Обобщение по теме Царство Грибы Что нужно знать, чтобы вырастить различные виды растений?
Что нужно знать, чтобы вырастить различные виды растений? Задачи по генетике: дигибридное скрещивание
Задачи по генетике: дигибридное скрещивание Рефлексы
Рефлексы Иммуноферментный анализ (ИФА). Иммуноблоттинг
Иммуноферментный анализ (ИФА). Иммуноблоттинг Половое размножение животных
Половое размножение животных Белки. Переваривание и всасывание
Белки. Переваривание и всасывание Основы цитологии. Понятие о клетке
Основы цитологии. Понятие о клетке Общие свойства сенсорных систем. Болевая сенсорная система
Общие свойства сенсорных систем. Болевая сенсорная система Игра Что? Где? Когда?
Игра Что? Где? Когда? Дидактическая игра Самые умные
Дидактическая игра Самые умные Большой год 2019 областной фотоконкурс
Большой год 2019 областной фотоконкурс