Слайд 2

Genetic engineering: Changing the DNA in living organisms to create something
new.
This organisms are called Genetically Modified Organism (GMO)
Example:
Bacteria that produce human insulin
Genetically Modified organism are called transgenic organism; since genes are transferred from one organism to another.
Слайд 3

Some genetic engineering techniques are as follows:
1. Artificial selection
A. selective
breeding
B. hybridization
C. inbreeding
2. Cloning
3. Gene splicing
4. Gel electrophoresis: analyzing DNA
Слайд 4

1. artificial selection: breeders choose which organism to mate to produce
offspring with desired traits.
They cannot control what genes are passed.
When they get offspring with the desired traits, the maintain them.
Three types of artificial selection:
A. selective breeding
B. hybridization
C. inbreeding
Слайд 5

A. Selective breeding: when animals with desired characteristics are mated to
produce offspring with those desired traits.
Passing of important genes to next generation.
Example: Champion race horses, cows with tender meat, large juicy oranges on a tree.
Слайд 6

For example people breed dogs for specific purposes.
Dachshund were once bred
to hunt badgers and other burrowing animals.
They must be small to fit into the animals hole in the ground.
Слайд 7

Selective breeding occurs when you choose the best male and female
to breed.
This allows you to fine tune and control the traits
The offspring or babies will then have the best traits.
Then you continue to breed those organism with the best traits, those traits will be maintained.
Слайд 8

Examples of selective breeding:
Angus cows are bred to increase muscle mass
so that we get more meat,
Egg-Laying Hen-produces more eggs than the average hen
Слайд 9

B. Hybridizations: two individuals with unlike characteristics are crossed to produce
the best in both organisms.
Example: Luther Burbank created a disease resistant potato called the Burbank potato.
He crossed a disease resistant plant with one that had a large food producing capacity.
Result: disease resistant plant that makes a lot of potatoes.
Слайд 10

Other Examples of hybridization:
Liger: lion and tiger mix
Слайд 11
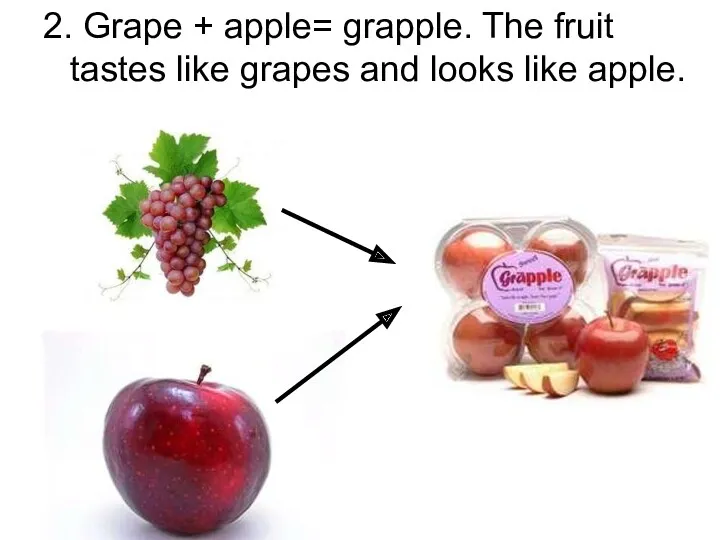
2. Grape + apple= grapple. The fruit tastes like grapes and
looks like apple.
Слайд 12

C. Inbreeding breeding of organism that genetically similar to maintain desired
traits.
Dogs breeds are kept pure this way.
Its how a Doberman remains a Doberman.
It keeps each breed unique from others.
Risk: since both have the same genes, the chance that a baby will get a recessive genetic disorder is high.
Risks: blindness, joint deformities.
Слайд 13

2. Cloning: creating an organism that is an exact genetic copy
of another.
Clone: group of cells or
organisms that are genetically
identical as a result of asexual
reproduction
They will have the same exact
DNA as the parent.
Слайд 14

How is cloning done?
A single cell is removed from a parent
organism.
An entire individual is grown from that cell.
Remember one cell has all the DNA needed to make an entire organism.
Each cell in the body has the same DNA, but cells vary because different genes are turned on in each cell.













 10 интересных фактов о животных
10 интересных фактов о животных Генетические основы селекции собак
Генетические основы селекции собак Распространение плодов и семян
Распространение плодов и семян Деление клеток
Деление клеток Классификация пестицидов
Классификация пестицидов Растительный мир уссурийской тайги
Растительный мир уссурийской тайги Происхождение и многообразие млекопитающих
Происхождение и многообразие млекопитающих Дослідження. Пророщування насіння
Дослідження. Пророщування насіння Основы вирусологии. Отличие вирусов от бактерий
Основы вирусологии. Отличие вирусов от бактерий Презентация Бактерии
Презентация Бактерии Різноманітність членистоногих
Різноманітність членистоногих Эстетическая, биологическая и культурная роль коллоидных систем в жизни человека
Эстетическая, биологическая и культурная роль коллоидных систем в жизни человека Клетка, как целостная живая система
Клетка, как целостная живая система Значение работ Менделя, Моргана и Кольцова для развития генетики
Значение работ Менделя, Моргана и Кольцова для развития генетики Хомячки
Хомячки Современные проблемы в воспроизводстве молочного скота и пути их решения
Современные проблемы в воспроизводстве молочного скота и пути их решения Микробиология ғылым ретінде. Микробиология пәні
Микробиология ғылым ретінде. Микробиология пәні Презентация к уроку на тему Стебель.
Презентация к уроку на тему Стебель. Урок-викторина Наш лесопарк Ход урока. Ход урока.
Урок-викторина Наш лесопарк Ход урока. Ход урока. Животные морей
Животные морей Увеличительные приборы
Увеличительные приборы Жизнь организмов в морях и океанах
Жизнь организмов в морях и океанах Государство Австралия. (2 класс)
Государство Австралия. (2 класс) Нуклеин қышқылдары
Нуклеин қышқылдары Осенние явления в жизни лиственных деревьев
Осенние явления в жизни лиственных деревьев Комнатные растения
Комнатные растения Обобщающий урок на тему: Дыхание. Заболевания органов дыханияֽ, их предупрежденияִ
Обобщающий урок на тему: Дыхание. Заболевания органов дыханияֽ, их предупрежденияִ Мышечные ткани
Мышечные ткани