Слайд 2

Слайд 3

Слайд 4

Слайд 5

Слайд 6

Слайд 7

Слайд 8

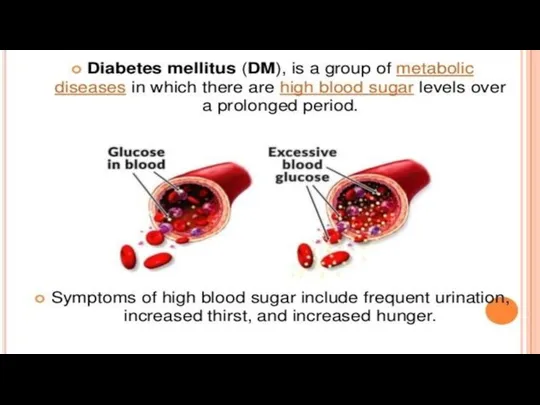
ADRENOGENITAL SYNDROME
Adrenogenital syndrome, also known as congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH),
is caused by an inherited enzyme deficiency in the adrenal cortex that leads to altered levels of adrenal cortical hormones. Adrenal cortical hormones include mineralocorticoids ( ie, aldosterone), glucocorticoids (Ie, cortisol), and sex steroids ( ie, testosterone and estrogen). The syndrome occurs when an enzyme deficiency leads to decreased adrenal synthesis of glucocorticoid, which impairs feedback inhibition on the pituitary
Слайд 9

RESULT
As a result, the pituitary secretes increased levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone
(ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands to enlarge and produce more intermediate substrates. These intermediate substrates are shunted toward functioning arms of the hormone synthesis pathways, where increased levels of other hormones are produced (either mineralocorticoids or androgens, depending on the enzyme deficiency). Altered levels of mineralocorticoids and sex hormones lead to electrolyte abnormalities, problems with sexual differentiation, and other signs and symptoms, depending on the deficient enzyme and extent of the deficiency.
Слайд 10

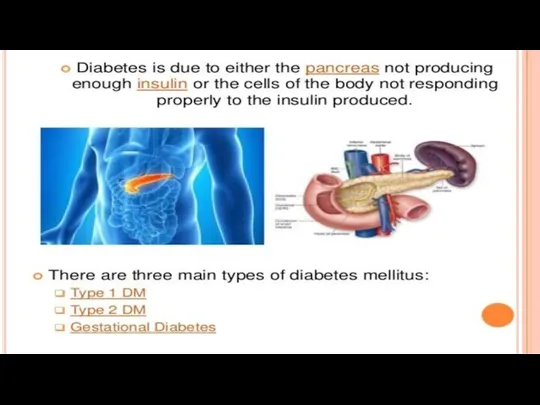
TREATMENT AND DIAGNOSIS
Treatment with relatively small doses of cortisone is effective
in suppressing the excessive secretion of adrenal androgen without causing abnormal metabolic or toxic effects. The minimum maintenance dose of intramuscular or oral cortisone must be determined in each case, following the urinary 17-ketosteroids and the rates of somatic growth and development as guides. In individuals of either sex who have reached a level of somatic development comparable to that of puberty (i.e., a bone age of 11 years or greater) suppression of the adrenal hyperactivity with cortisone results promptly in normal adolescent sexual development corresponding to the sex of the patient.
Слайд 11
Слайд 12
Слайд 13
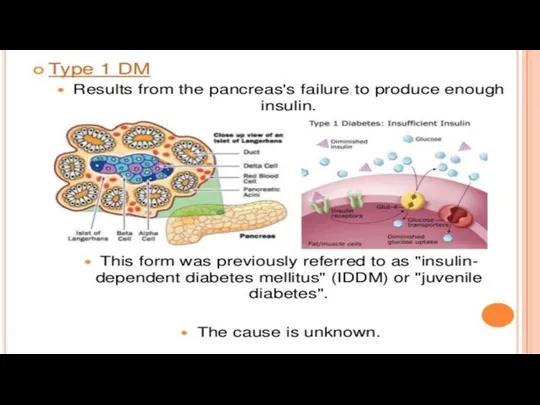
Слайд 14

Слайд 15

TREATMENT
Treatment of diabetes with insulin
Insulin remains the mainstay of treatment for patients with type 1 diabetes. Insulin
is also an important therapy for type 2 diabetes when blood glucose levels cannot be controlled by diet, weight loss, exercise, and oral medications.














 Электрофорез в полиакриламидном геле
Электрофорез в полиакриламидном геле Понятие о биосфере
Понятие о биосфере Жизнь ёлки до и после Нового года
Жизнь ёлки до и после Нового года Раздражители, применяемые при дрессировки собак
Раздражители, применяемые при дрессировки собак Клинико-генеалогический метод исследования в медицинской генетики человека
Клинико-генеалогический метод исследования в медицинской генетики человека Берёза
Берёза Половое и бесполое размножение Покрытосеменных
Половое и бесполое размножение Покрытосеменных Влияние почвогрунта на выгонку лилейника буро – желтого к определенной дате
Влияние почвогрунта на выгонку лилейника буро – желтого к определенной дате тема Кораллы и Моллюски
тема Кораллы и Моллюски Муравьи
Муравьи Основные группы рыб, их многообразие и роль в экосистеме
Основные группы рыб, их многообразие и роль в экосистеме Размножение споровых растений
Размножение споровых растений Тип кишечнополостные (пресноводная гидра)
Тип кишечнополостные (пресноводная гидра) Lecture B6: DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation
Lecture B6: DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation Деление клетки – основа размножения, роста и развития организмов
Деление клетки – основа размножения, роста и развития организмов Нераздельный органический мир
Нераздельный органический мир Різноманітність тварин у природі. Звірі. Урок №46. Я досліджую світ
Різноманітність тварин у природі. Звірі. Урок №46. Я досліджую світ Снежный барс
Снежный барс Презентации к уроку по теме: Иммунитет
Презентации к уроку по теме: Иммунитет Природный комплекс. Природные зоны
Природный комплекс. Природные зоны Адаптация теориясы
Адаптация теориясы 20231023_rasteniya_v_interere_doma
20231023_rasteniya_v_interere_doma Презентация по экологии по теме Зеленые друзья для 5-7 кл.
Презентация по экологии по теме Зеленые друзья для 5-7 кл.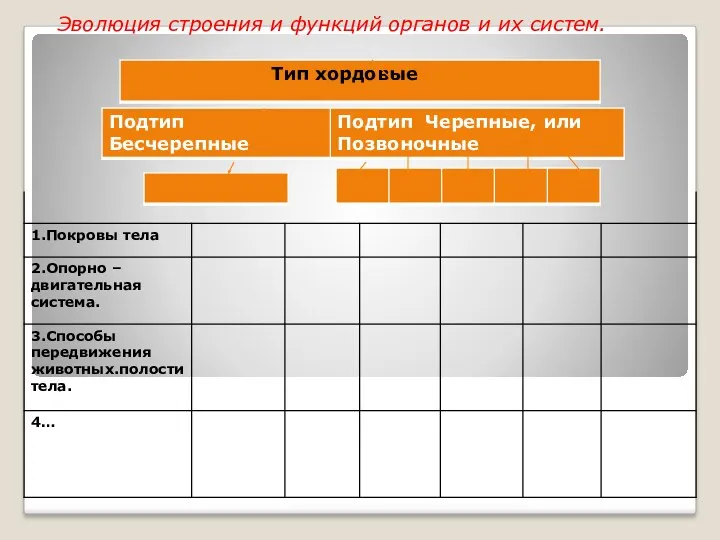 Эволюция строения и функций органов и их систем. Тип хордовые
Эволюция строения и функций органов и их систем. Тип хордовые Нервная система. Спинной мозг. Рефлектроная дуга
Нервная система. Спинной мозг. Рефлектроная дуга Строение цветка. Соцветия
Строение цветка. Соцветия Презентация по биологии Систематика животных
Презентация по биологии Систематика животных Движение
Движение