Содержание
- 2. What is positive selection?
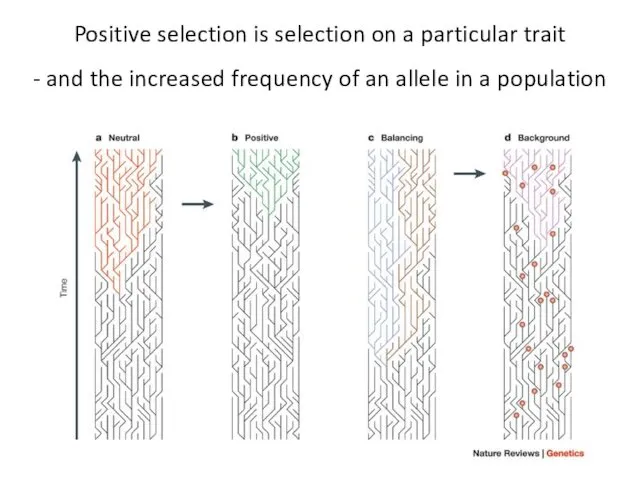
- 3. Positive selection is selection on a particular trait - and the increased frequency of an allele
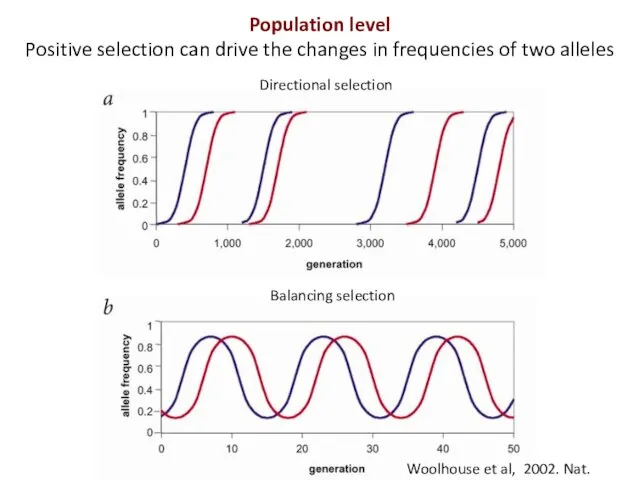
- 4. Woolhouse et al, 2002. Nat. Genet Directional selection Balancing selection Population level Positive selection can drive
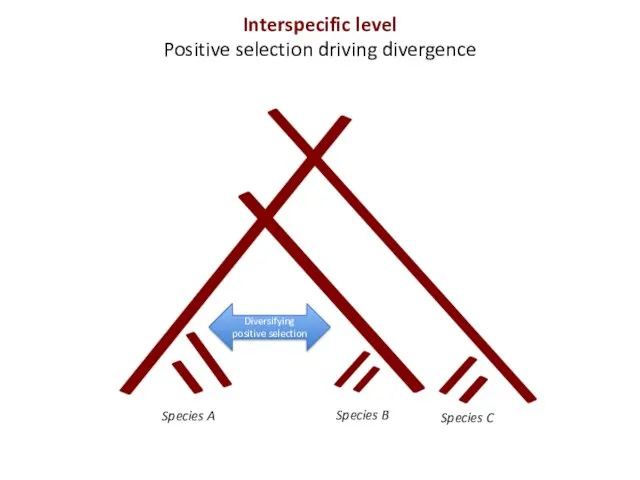
- 5. Species A Diversifying positive selection Interspecific level Positive selection driving divergence
- 6. Why is it interesting to identify traits which have undergone or are under positive selection? Function
- 7. How can we detect positive selection?
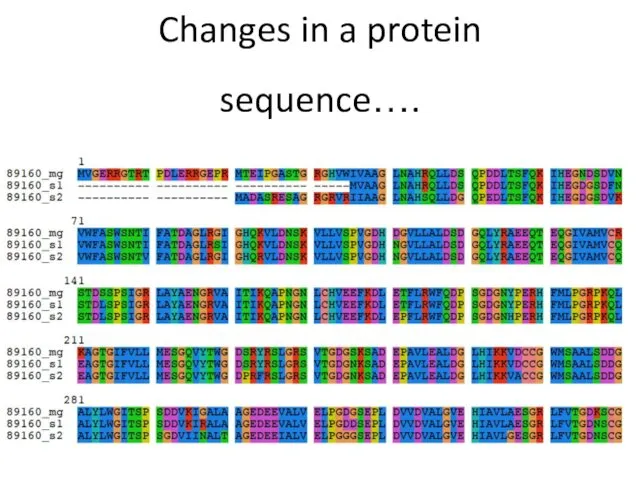
- 8. Changes in a protein sequence….
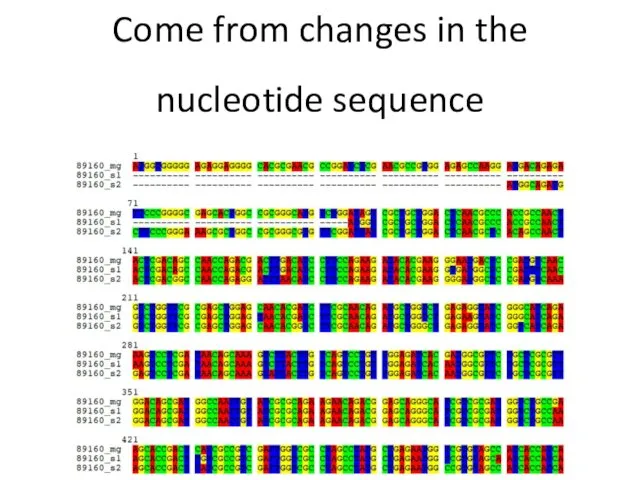
- 9. Come from changes in the nucleotide sequence
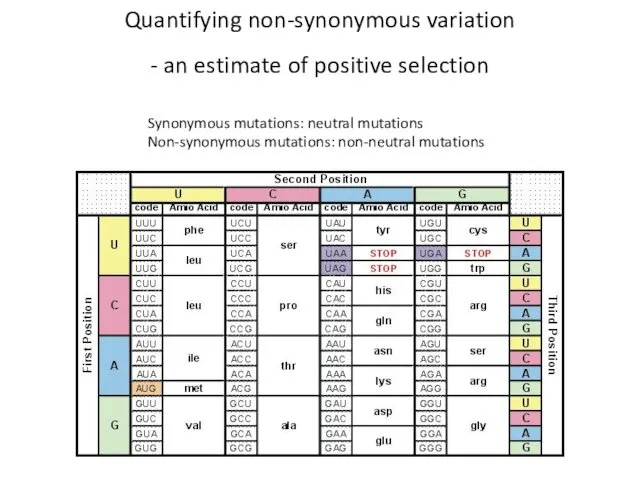
- 10. Quantifying non-synonymous variation - an estimate of positive selection Synonymous mutations: neutral mutations Non-synonymous mutations: non-neutral
- 11. Rate of synonymous mutations Rate of non-synonymous mutations To measure positive selection:
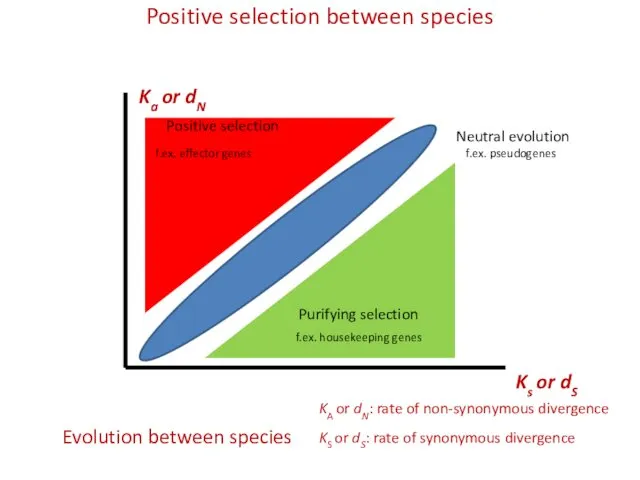
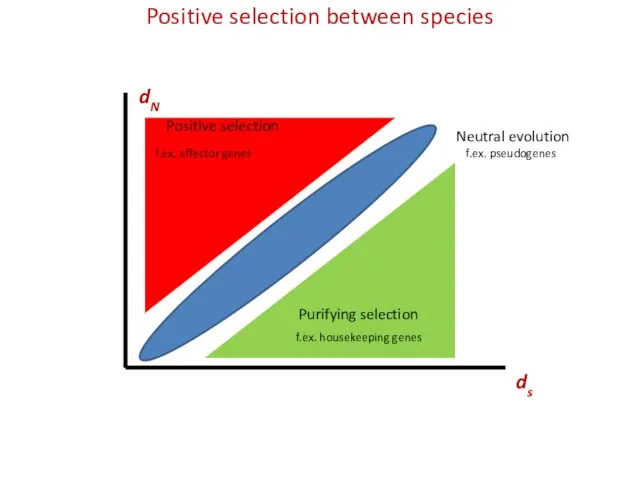
- 12. Positive selection between species Ks or dS Ka or dN
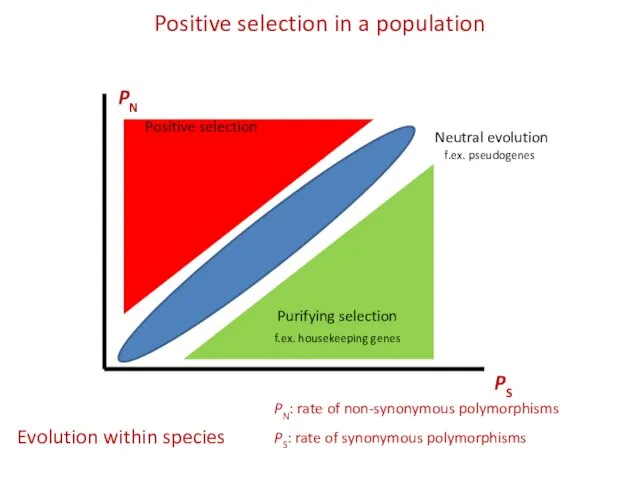
- 13. Positive selection in a population PS PN
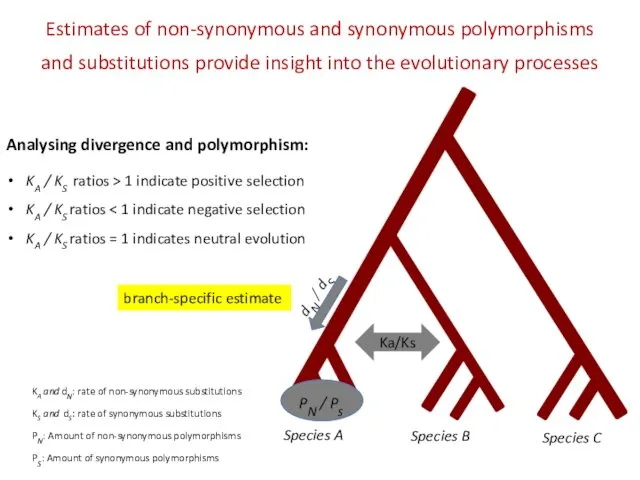
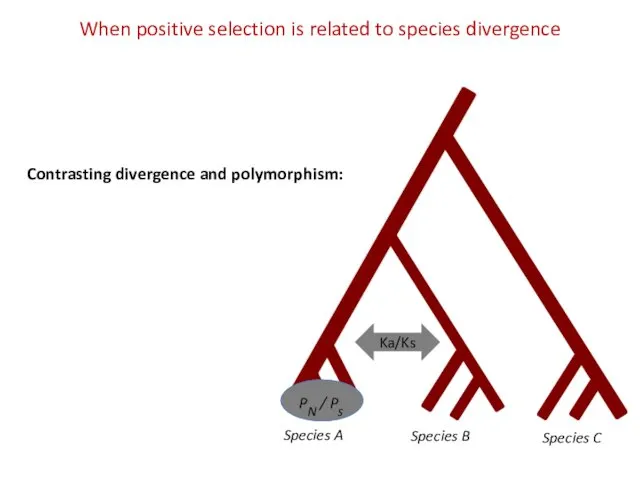
- 14. Species A Species B Species C PN / Ps Estimates of non-synonymous and synonymous polymorphisms and
- 15. Species A Species B Species C PN / Ps Estimates of non-synonymous and synonymous polymorphisms and
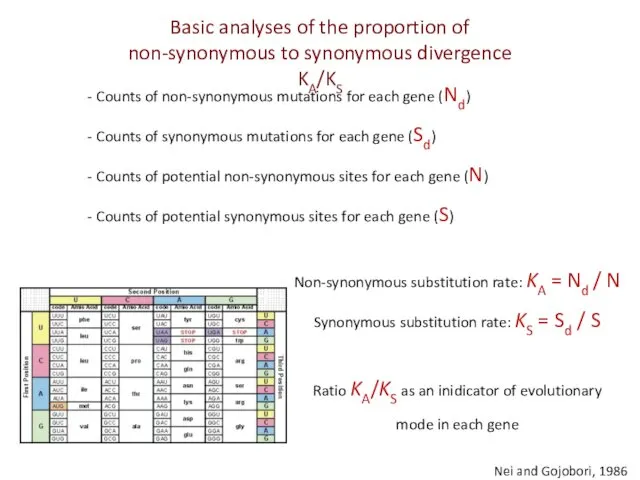
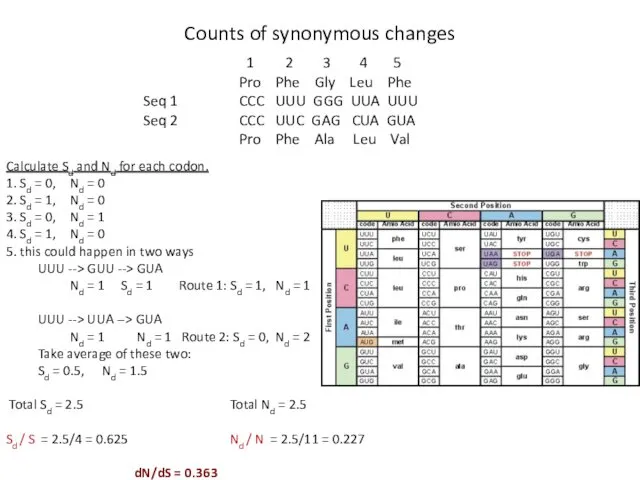
- 16. Nei and Gojobori, 1986 Counts of non-synonymous mutations for each gene (Nd) Counts of synonymous mutations
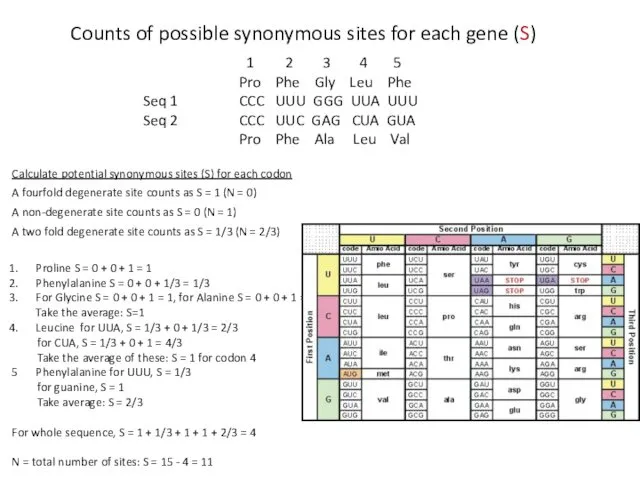
- 17. Calculate potential synonymous sites (S) for each codon A fourfold degenerate site counts as S =
- 18. Calculate Sd and Nd for each codon. 1. Sd = 0, Nd = 0 2. Sd
- 19. Positive selection between species ds dN
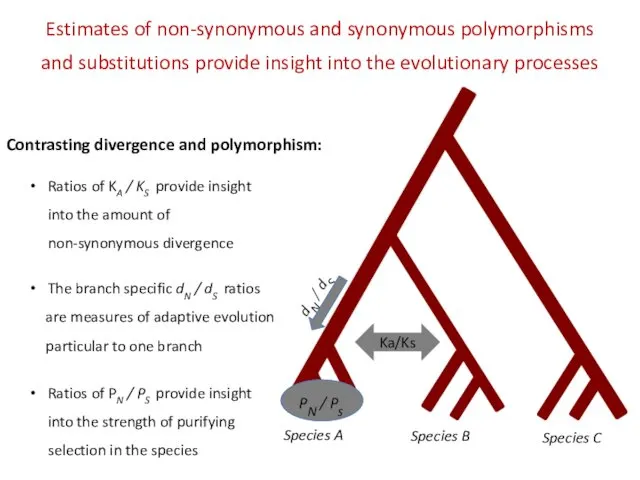
- 20. Species A Species B Species C PN / Ps When positive selection is related to species
- 21. McDonald Kreitman (MK) test to contrast within and between species variation
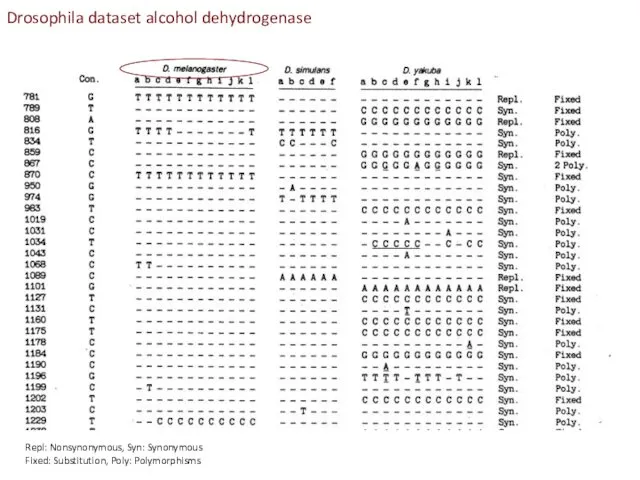
- 22. Repl: Nonsynonymous, Syn: Synonymous Fixed: Substitution, Poly: Polymorphisms Drosophila dataset alcohol dehydrogenase
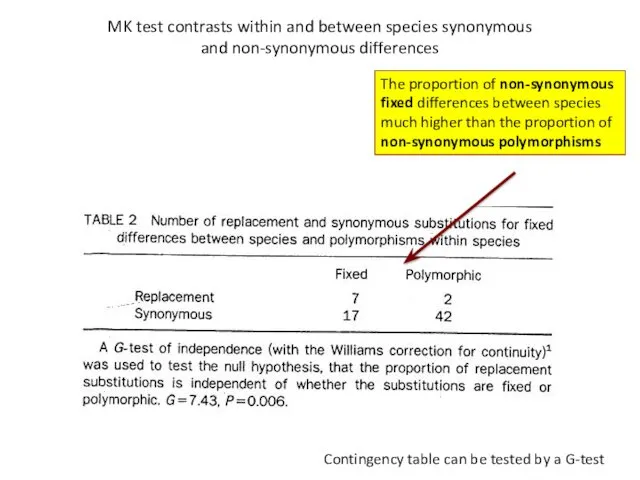
- 23. MK test contrasts within and between species synonymous and non-synonymous differences Contingency table can be tested
- 24. Conclusion from MK-test: Adh locus in Drosophila has accumulated adaptive mutations (been under positive selection) when
- 25. One problem with the “counting methods” Sometimes the signal of selection is not very strong
- 27. Скачать презентацию







 Рысь
Рысь Центры происхождения культурных растений по Н.И. Вавилову
Центры происхождения культурных растений по Н.И. Вавилову Мой питомец. Способы общения с людьми
Мой питомец. Способы общения с людьми Наследование групп крови человека
Наследование групп крови человека Органы пищеварения
Органы пищеварения Презентация теории восприятия
Презентация теории восприятия Биология - наука о жизни
Биология - наука о жизни презентация к педсовету по ФГОС2 Диск
презентация к педсовету по ФГОС2 Диск Анатомия глаза. Физиология. Методы исследования
Анатомия глаза. Физиология. Методы исследования Эти загадочные динозавры
Эти загадочные динозавры Пряно-вкусовые растения. Специи
Пряно-вкусовые растения. Специи Взаимодействие генов и их множественное действие
Взаимодействие генов и их множественное действие Микробиологическая лаборатория. Техника безопасности в микробиологической лаборатории. Световой микроскоп
Микробиологическая лаборатория. Техника безопасности в микробиологической лаборатории. Световой микроскоп Как распознать живое и неживое
Как распознать живое и неживое Посадка лука на перо
Посадка лука на перо Эукариотическая клетка
Эукариотическая клетка Макроеволюція
Макроеволюція Типы развития насекомых
Типы развития насекомых Корінь: основні функції (поглинання води та укріплення в ґрунті)
Корінь: основні функції (поглинання води та укріплення в ґрунті) Бактериялардың жіктелуі
Бактериялардың жіктелуі Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Книга памятников природе
Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Книга памятников природе Что такое хвоинки (для дошкольников)
Что такое хвоинки (для дошкольников) ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ДЛЯ ИНТЕРАКТИВНОЙ ДОСКИ. Пути и направления эволюции. 11 класс (В двух частях)
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ДЛЯ ИНТЕРАКТИВНОЙ ДОСКИ. Пути и направления эволюции. 11 класс (В двух частях) Урок – игра по теме Органы и системы органов животных
Урок – игра по теме Органы и системы органов животных Северо-Осетинский государственный заповедник
Северо-Осетинский государственный заповедник Мейоз. Механизм мейоза
Мейоз. Механизм мейоза Презентация к обобщающему уроку в 5 классе по теме Грибы
Презентация к обобщающему уроку в 5 классе по теме Грибы Квіти-первоцвіти
Квіти-первоцвіти