Содержание
- 2. Terminology Add revision of lipids forming micelles…. And other stuff…pictures videos
- 3. Equipment
- 4. Introduction In the DNA isolation procedure, cell walls (plants) and cell membranes are broken down by
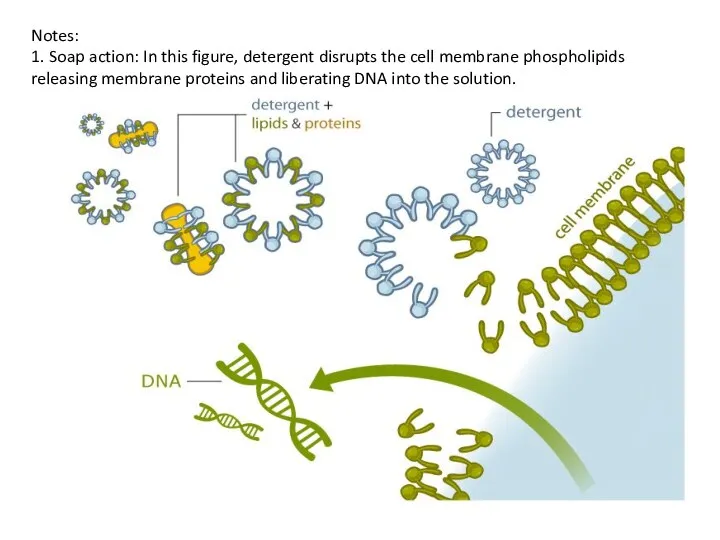
- 5. Notes: 1. Soap action: In this figure, detergent disrupts the cell membrane phospholipids releasing membrane proteins
- 6. water alcohol DNA coming out of water solution into the alcohol layer 2. DNA is highly
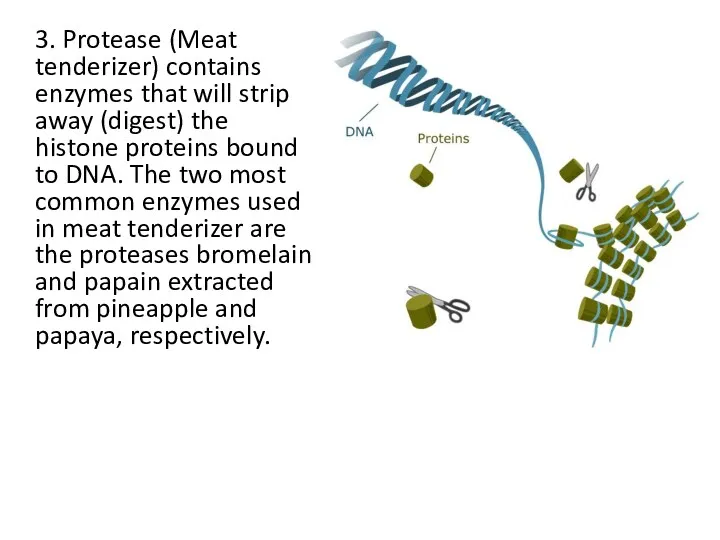
- 7. 3. Protease (Meat tenderizer) contains enzymes that will strip away (digest) the histone proteins bound to
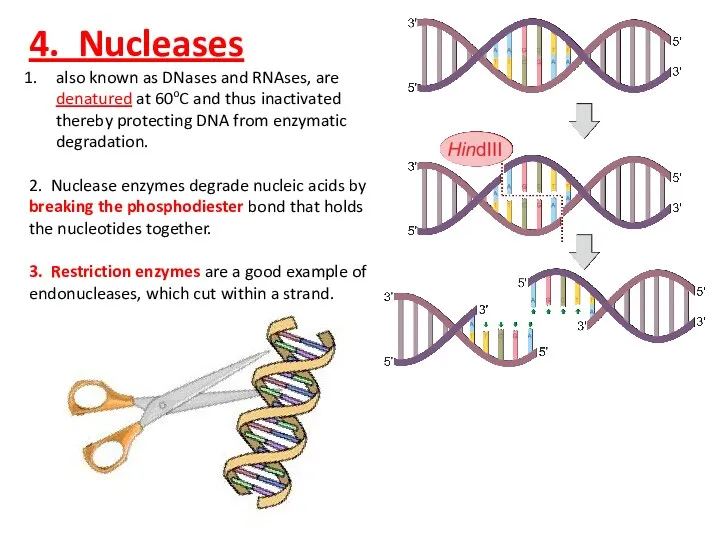
- 8. 4. Nucleases also known as DNases and RNAses, are denatured at 60oC and thus inactivated thereby
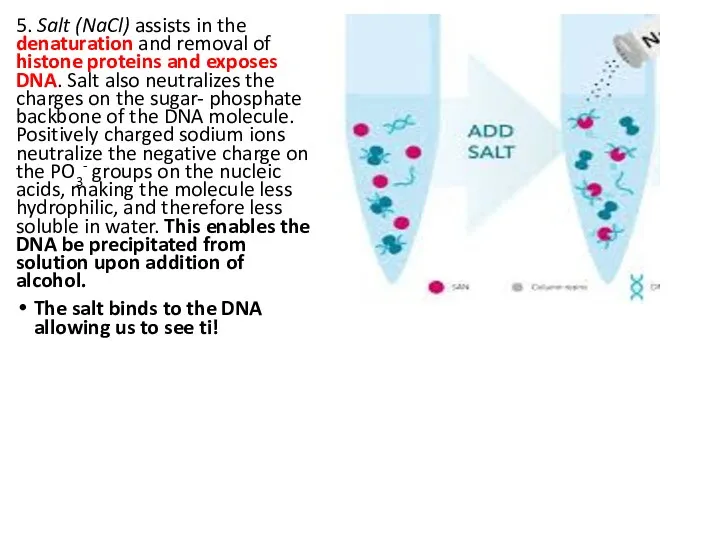
- 9. 5. Salt (NaCl) assists in the denaturation and removal of histone proteins and exposes DNA. Salt
- 11. Скачать презентацию


 Endangered species of lions
Endangered species of lions Кольчатые черви
Кольчатые черви Types of vegetables and their classification
Types of vegetables and their classification Основы медицинской паразитологии
Основы медицинской паразитологии Физические основы деятельности систем дыхания, кровообращения и энергообмена при мышечных движениях
Физические основы деятельности систем дыхания, кровообращения и энергообмена при мышечных движениях Контейнерные технологии
Контейнерные технологии Нарушение кожных покровов и их причины.8 класс
Нарушение кожных покровов и их причины.8 класс Эволюция приматов
Эволюция приматов Высшие растения. Отдел мхи
Высшие растения. Отдел мхи Моё увлечение - конный спорт
Моё увлечение - конный спорт Проект – Первоцвіти – провісники весни
Проект – Первоцвіти – провісники весни Хвойные растения
Хвойные растения изменчивость
изменчивость Сорные растения
Сорные растения Общая характеристика и разнообразие хрящевых рыб. Их роль в водной экосистеме
Общая характеристика и разнообразие хрящевых рыб. Их роль в водной экосистеме Род сосна
Род сосна Генетически модифицированные организмы
Генетически модифицированные организмы opylenie
opylenie Физминутка
Физминутка Практическая работа №1. Алгоритм решения прямых задач
Практическая работа №1. Алгоритм решения прямых задач Физиология пищеварения
Физиология пищеварения Рептилії
Рептилії Лекция 7. Антропология. Факторы роста и развития. Биологический и хронологический возраст. Продолжительность жизни
Лекция 7. Антропология. Факторы роста и развития. Биологический и хронологический возраст. Продолжительность жизни Тип Плоские черви. Класс Ленточные черви. Филогения животных организмов с элементами медицинской гельминтологии
Тип Плоские черви. Класс Ленточные черви. Филогения животных организмов с элементами медицинской гельминтологии Система и многообразие органического мира
Система и многообразие органического мира Урок биологии в 5 кл. Красная книга Чувашской Республики
Урок биологии в 5 кл. Красная книга Чувашской Республики Повреждение ядра клетки
Повреждение ядра клетки Репетитор ЕГЭ. Человек
Репетитор ЕГЭ. Человек