Содержание
- 2. Asexual Reproduction: requires only 1 parent and the offspring are an exact copy of the parent---a
- 3. Asexual Reproduction: Organisms that reproduce asexually cannot develop much variety, because they are “copying” the original
- 4. Methods of asexual reproduction: Binary fission Budding Fragmentation Parthenogenesis
- 5. Binary fission Single-celled organisms (Amoeba, paramecium, euglena) which use asexual reproduction can do so simply by
- 6. When conditions are good, such as plenty of water, food, right temperatures, etc., binary fission is
- 7. Budding- an offspring grows out of the body of the parent. Hydra Budding offspring Cactus Budding
- 8. Budding cont. Green plants are quite sophisticated in their methods of asexual reproduction. Offspring may be
- 9. Regeneration In this form, the body of the parent breaks into distinct pieces, each of which
- 10. Fragmentation In this form, the organism fragments into smaller pieces and each piece forms a new
- 11. Fragmentation- plant cuttings Some plants can grow from cutting them up and replanting them.
- 12. Sporulation In this form, the parent organism produces tiny spores that it releases. They will then
- 13. Parthenogenesis Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction in which females produce eggs that develop without
- 14. Asexual Reproduction: Advantages of Asexual Reproduction • uses less energy (it is not necessary to find
- 15. Asexual Reproduction: Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction • the species does not adapt at all or adapts
- 16. What is sexual reproduction? Requiring 2 parents male and female (egg & sperm) The egg and
- 17. Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction produces a greater chance of variation within a species than asexual reproduction
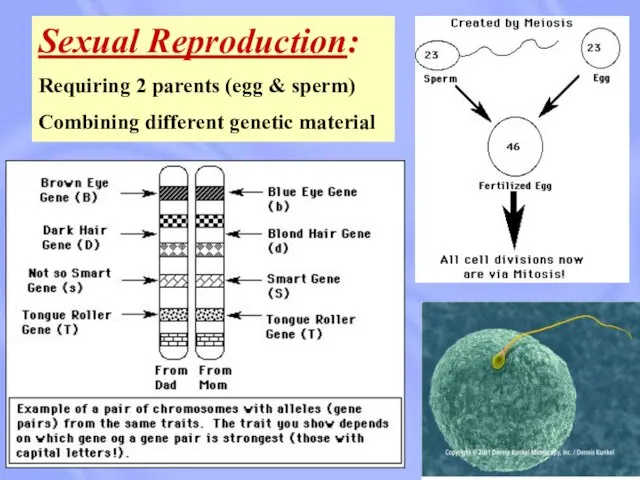
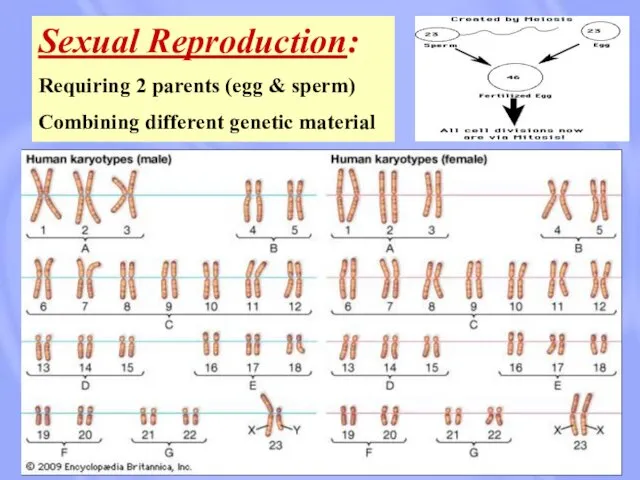
- 18. Sexual Reproduction: Requiring 2 parents (egg & sperm) Combining different genetic material
- 19. Sexual Reproduction: Requiring 2 parents (egg & sperm) Combining different genetic material
- 20. Sexual Reproduction Adv. • increases the genetic variability in organisms of the same species and even
- 21. Sexual Reproduction Adv. • the variability of organisms within a species guarantees that a higher proportion
- 22. Sexual Reproduction Dis. • finding a reproductive partner and producing gametes demands the output of a
- 23. Methods of sexual reproduction: Pollination External Fertilization Internal Fertilization
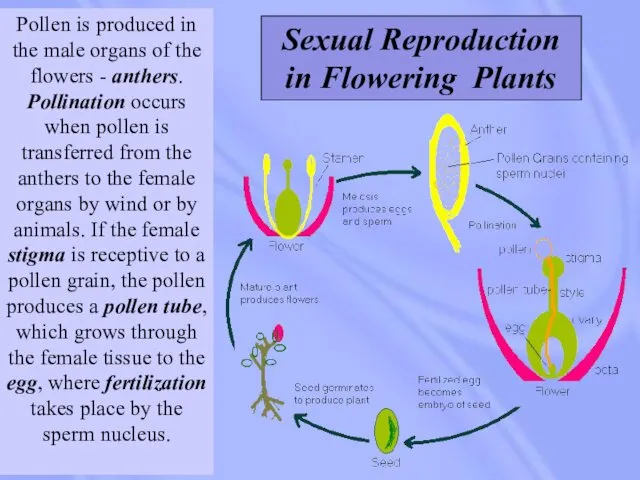
- 24. Pollen is produced in the male organs of the flowers - anthers. Pollination occurs when pollen
- 25. External Fertilization External fertilization usually requires a medium such as water, which the sperms can use
- 26. Internal Fertilization Fertilization occurs within the female. Internal fertilization occurs in mammals, insects, birds, reptiles. Mammals
- 28. Скачать презентацию





















 Эволюция черепа, жаберного и челюстного аппарата позвоночных
Эволюция черепа, жаберного и челюстного аппарата позвоночных Особенности пищеварения у собак и котов. Питательные и биологически активные вещества
Особенности пищеварения у собак и котов. Питательные и биологически активные вещества Растениеводство. Системы земледелия
Растениеводство. Системы земледелия Биологические и хозяйственные особенности кур
Биологические и хозяйственные особенности кур Формирование целостной картины мира. Играем на лугу. Луг и его обитатели
Формирование целостной картины мира. Играем на лугу. Луг и его обитатели Копитні ссавці
Копитні ссавці Задания ЕГЭ по теме Клетка
Задания ЕГЭ по теме Клетка Применение активных дрожжей в кормлений животных
Применение активных дрожжей в кормлений животных Влияние света на проращивание семян (часть 1)
Влияние света на проращивание семян (часть 1) Ошущение. Возникновение ощущений
Ошущение. Возникновение ощущений Тип Членистоногие, класс Паукообразные
Тип Членистоногие, класс Паукообразные Птицы Африки
Птицы Африки Стрес та його чинники. Адаптація людини до стресу
Стрес та його чинники. Адаптація людини до стресу Биология – наука о живой природе
Биология – наука о живой природе Презентация по теме Проектная деятельность
Презентация по теме Проектная деятельность Взаимодействие микроорганизмов с человеком и животными
Взаимодействие микроорганизмов с человеком и животными Молекулярні механізми скорочення м’язового волокна
Молекулярні механізми скорочення м’язового волокна Ядовитые растения
Ядовитые растения Факторы среды, влияющие на размножение и формирование пола у животных. (Лекция 3)
Факторы среды, влияющие на размножение и формирование пола у животных. (Лекция 3) Красная книга Таштагольского района
Красная книга Таштагольского района Фенологические наблюдения за природой
Фенологические наблюдения за природой Анатомия ЦНС. Задний мозг. Варолиев мост
Анатомия ЦНС. Задний мозг. Варолиев мост Экология человека
Экология человека Строение и жизнедеятельность бактерий
Строение и жизнедеятельность бактерий Молекулярно-биологические методы диагностики
Молекулярно-биологические методы диагностики Всё о мёде, способы фальсификации
Всё о мёде, способы фальсификации Электрофорез белков в полиакриламидном геле и вестерн-блоттинг
Электрофорез белков в полиакриламидном геле и вестерн-блоттинг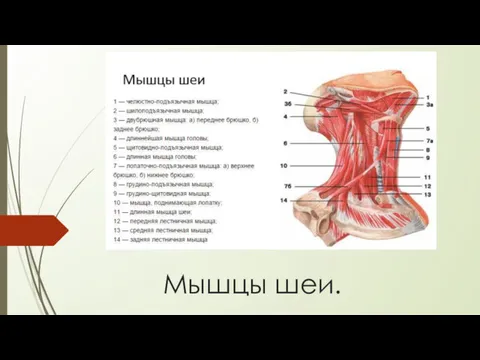 Мышцы шеи
Мышцы шеи