Содержание
- 2. DEFINATION Natural selection, process that results in the adaptation of an organism to its environment by
- 3. A) Aristotle considered whether different forms might have appeared accidentally, but only the useful forms survived.
- 4. B) Lamarckism, a theory of evolution based on the principle that physical changes in organisms during
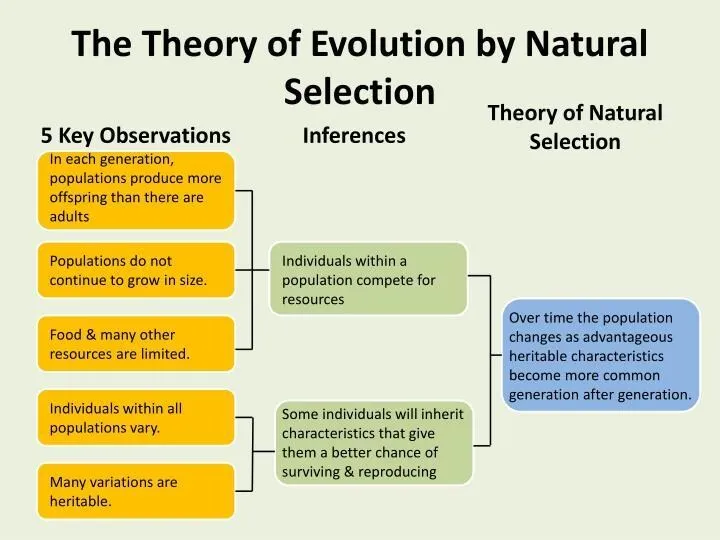
- 5. 3. DARWIN’S THEORY Darwin proposed that: individual organisms within a particular species show a wide range
- 6. 4. MAIN POINTS
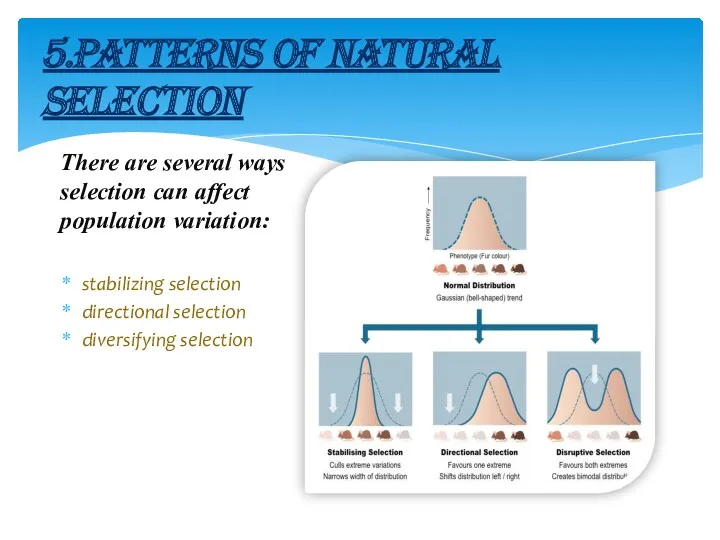
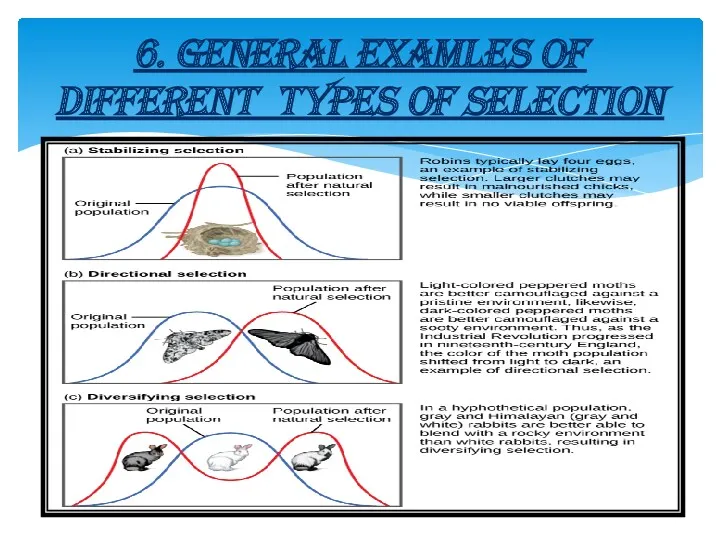
- 8. 5.PATTERNS OF NATURAL SELECTION There are several ways selection can affect population variation: stabilizing selection directional
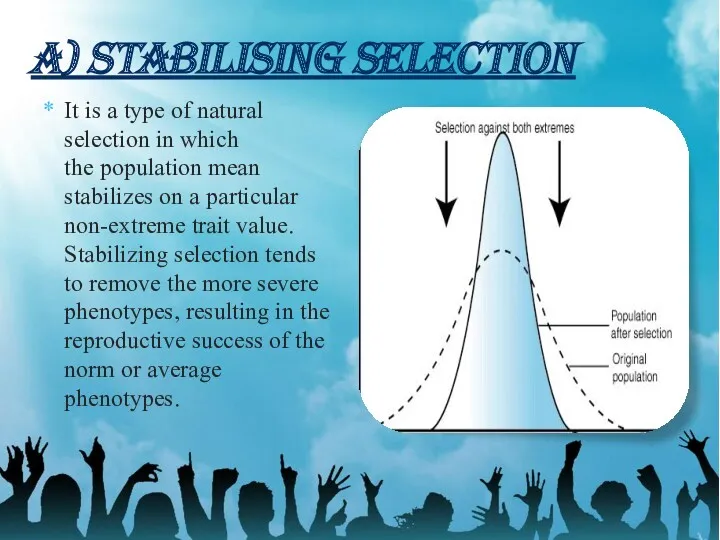
- 9. A) STABILISING SELECTION It is a type of natural selection in which the population mean stabilizes
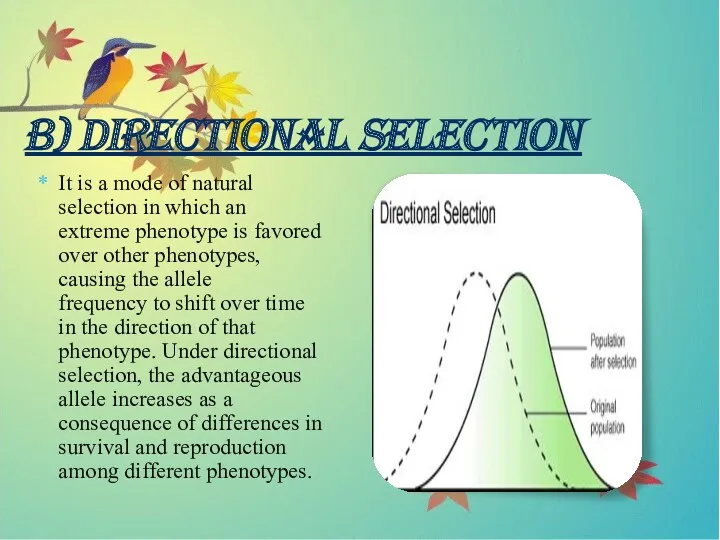
- 10. B) DIRECTIONAL SELECTION It is a mode of natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is
- 11. C) DISRUPTIVE SELECTION Its also called diversifying selection, describes changes in population genetics in which extreme
- 12. 6. GENERAL EXAMLES OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF SELECTION
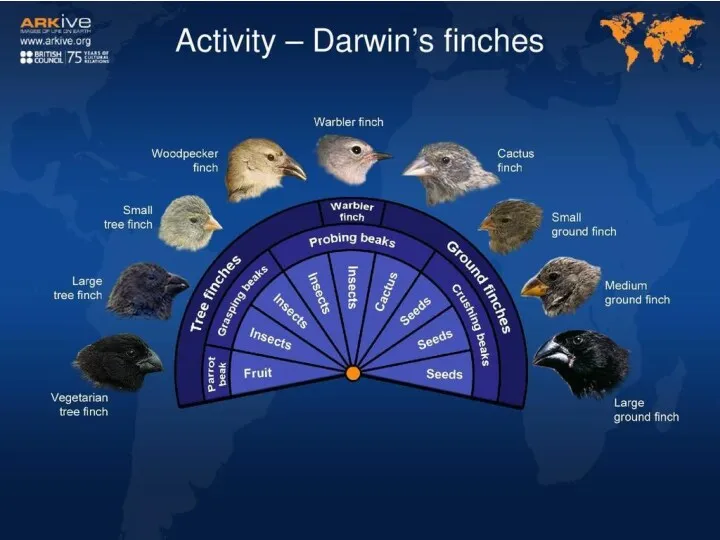
- 13. 7. EVIDENCE OF NATURAL SELECTION: Charles Darwin speculated about how natural selection could cause a “land
- 15. 8. EXTERNAL LINKS
- 17. Скачать презентацию







 Зимующие птицы
Зимующие птицы Перспективы развития биологии
Перспективы развития биологии Класс птицы (aves)
Класс птицы (aves) Как любят птицы
Как любят птицы Селекция животных. Особенности секции животных
Селекция животных. Особенности секции животных Гипотезы происхождения жизни на Земле
Гипотезы происхождения жизни на Земле Строение волос
Строение волос Комнатные растения и уход за ними
Комнатные растения и уход за ними Строение белков
Строение белков Структура и функция рефлекторной дуги
Структура и функция рефлекторной дуги Морфология бактерий
Морфология бактерий презентация по биологии на тему Основные понятия генетики для 9 класса
презентация по биологии на тему Основные понятия генетики для 9 класса Tiere
Tiere Системна радіобіологія: від молекули до організму. Системна радіобіологія: від організму до популяції
Системна радіобіологія: від молекули до організму. Системна радіобіологія: від організму до популяції Көмірсулардың катаболиттік және анаболиттік жолдарын айырбастау және көмірсулардың биологиялық рөлі туралы түсінік беру
Көмірсулардың катаболиттік және анаболиттік жолдарын айырбастау және көмірсулардың биологиялық рөлі туралы түсінік беру Отдел Покрытосеменные. Знакомство с многообразием цветковых растений
Отдел Покрытосеменные. Знакомство с многообразием цветковых растений Покормите птиц зимой
Покормите птиц зимой Задания линии 2 и 22 по экспериментам в КИМ ЕГЭ по биологии 2022
Задания линии 2 и 22 по экспериментам в КИМ ЕГЭ по биологии 2022 Клинико-генеалогический метод. Правила составления родословной
Клинико-генеалогический метод. Правила составления родословной Черви. Современное эволюционное древо животных
Черви. Современное эволюционное древо животных Генетика
Генетика Генетика пола. Сцепленное с полом наследование
Генетика пола. Сцепленное с полом наследование Полиморфизм человеческих популяций. Генетический груз. Популяционная структура человечества
Полиморфизм человеческих популяций. Генетический груз. Популяционная структура человечества Классный час Твоё здоровье и питание
Классный час Твоё здоровье и питание Загадки о животных (1 класс)
Загадки о животных (1 класс) Пленки Лэнгмюра - Блоджетт
Пленки Лэнгмюра - Блоджетт Грибы НСО. Съедобные и несъедобные
Грибы НСО. Съедобные и несъедобные Культивирование и рост микроорганизмов
Культивирование и рост микроорганизмов