Содержание
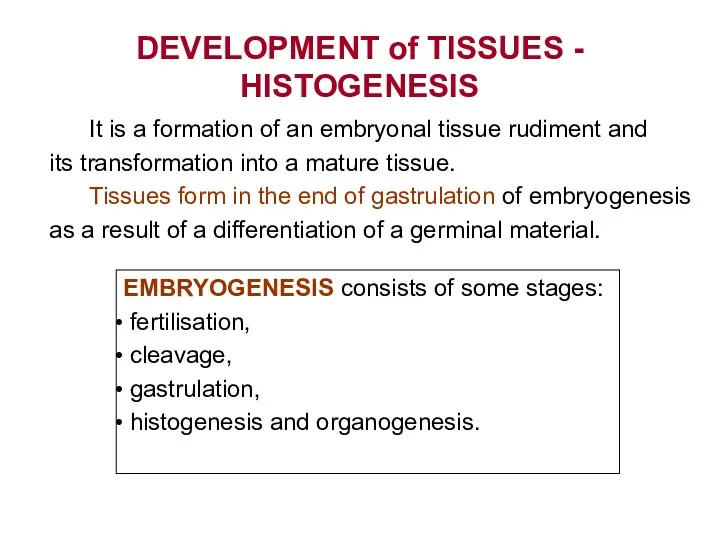
- 2. DEVELOPMENT of TISSUES - HISTOGENESIS It is a formation of an embryonal tissue rudiment and its
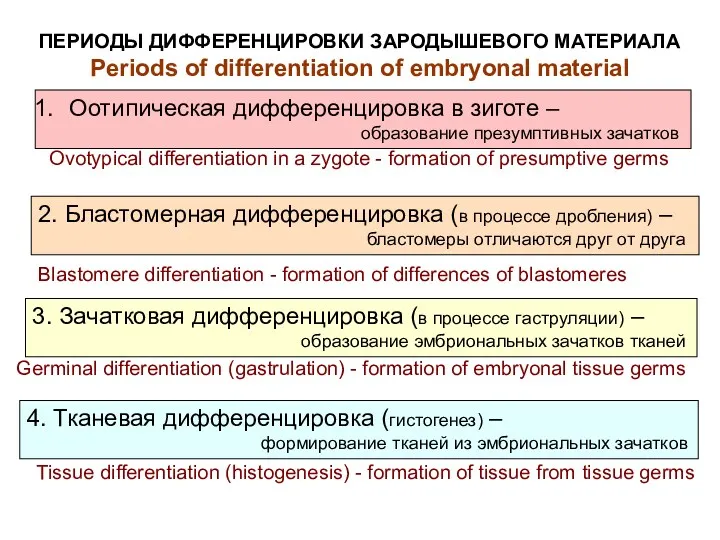
- 3. ПЕРИОДЫ ДИФФЕРЕНЦИРОВКИ ЗАРОДЫШЕВОГО МАТЕРИАЛА Periods of differentiation of embryonal material Оотипическая дифференцировка в зиготе – образование
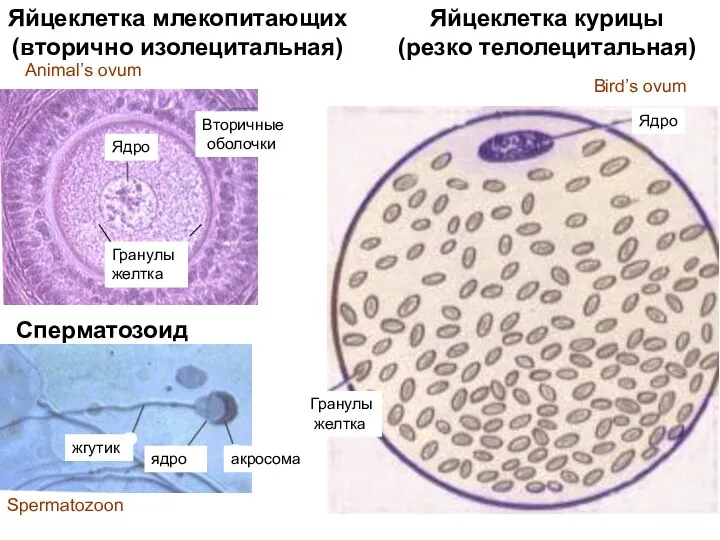
- 4. Сперматозоид акросома ядро жгутик Яйцеклетка курицы (резко телолецитальная) Гранулы желтка Ядро Яйцеклетка млекопитающих (вторично изолецитальная) Ядро
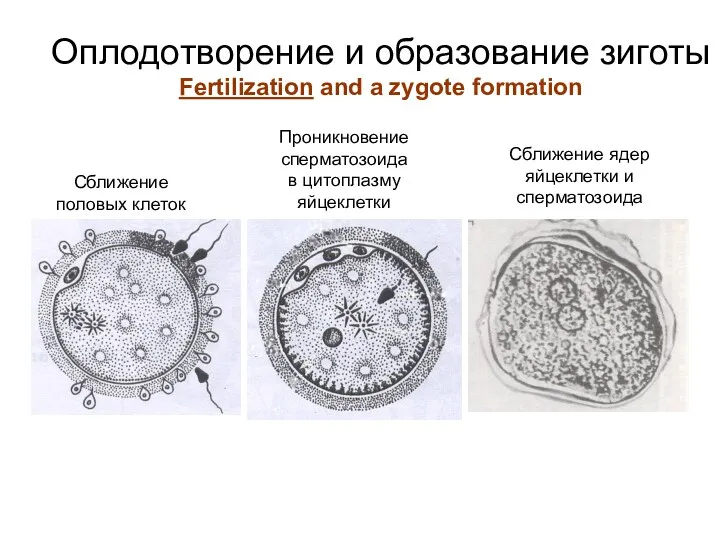
- 5. Оплодотворение и образование зиготы Fertilization and a zygote formation Сближение половых клеток Проникновение сперматозоида в цитоплазму
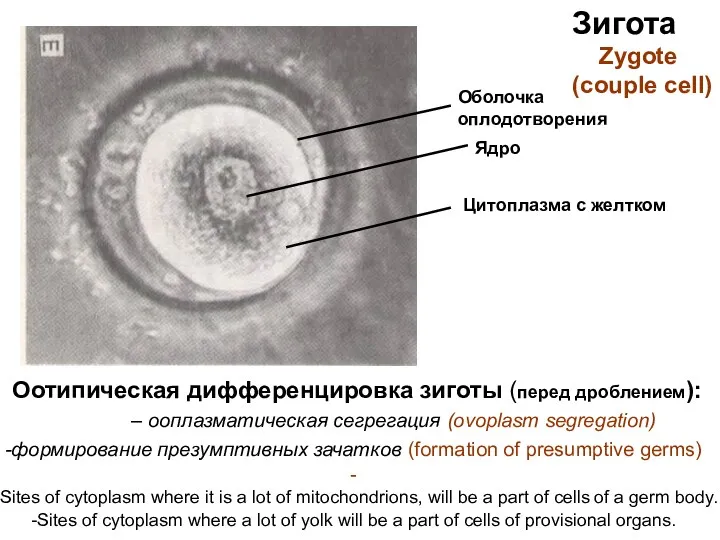
- 6. Зигота Zygote (couple cell) Ядро Цитоплазма с желтком Оболочка оплодотворения Оотипическая дифференцировка зиготы (перед дроблением): –
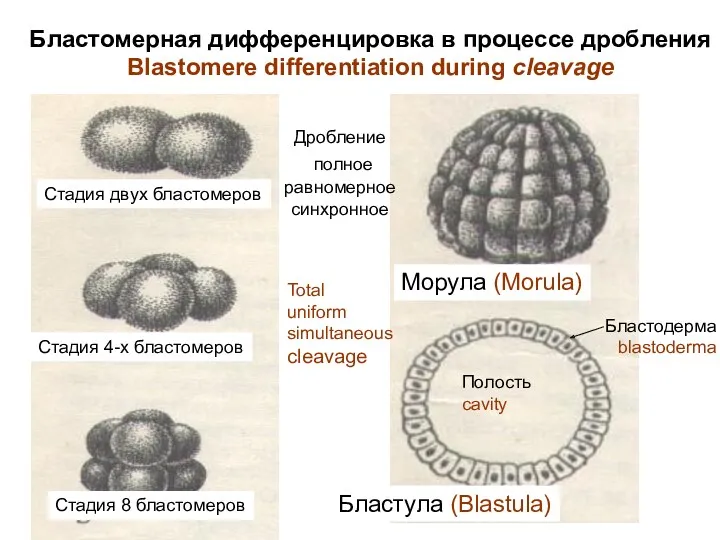
- 7. Бластомерная дифференцировка в процессе дробления Blastomere differentiation during cleavage Differences of cleavage from mitosis: daughter cells
- 8. 1. Blastomeres form the dense cellular ball – MORULA. 2. Cells of morula allocate a liquid
- 9. Морула (Morula) Бластула (Blastula) Стадия двух бластомеров Стадия 4-х бластомеров Стадия 8 бластомеров Полость cavity Бластодерма
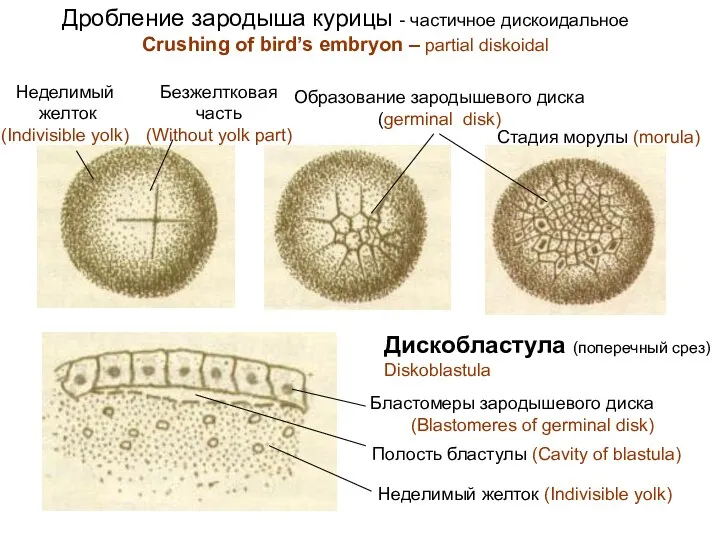
- 10. Дробление зародыша курицы - частичное дискоидальное Crushing of bird’s embryon – partial diskoidal Образование зародышевого диска
- 11. Зачатковая дифференцировка Germinal differentiation Gastrulation happens to 2 stages: 1 stage – formation of germ layers
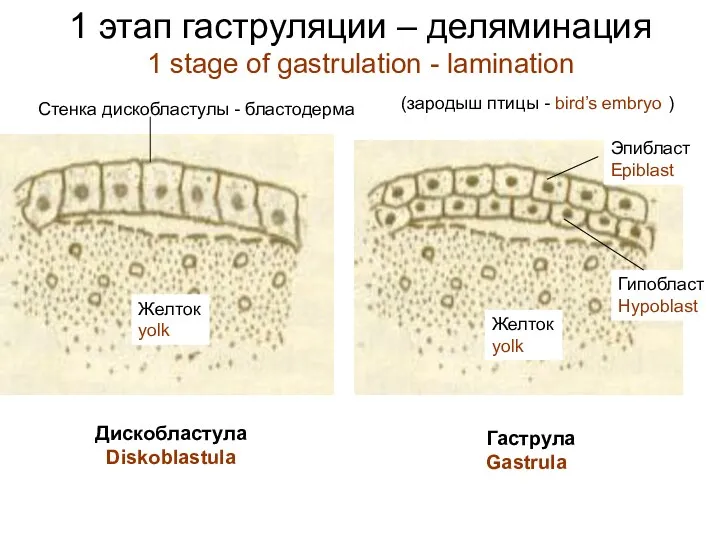
- 12. 1 этап гаструляции – деляминация 1 stage of gastrulation - lamination Дискобластула Diskoblastula Гаструла Gastrula Стенка
- 13. 2nd stage of gastrulation – immigration, germ differentiation Blastomeres installate between ectoderm and entoderm and build
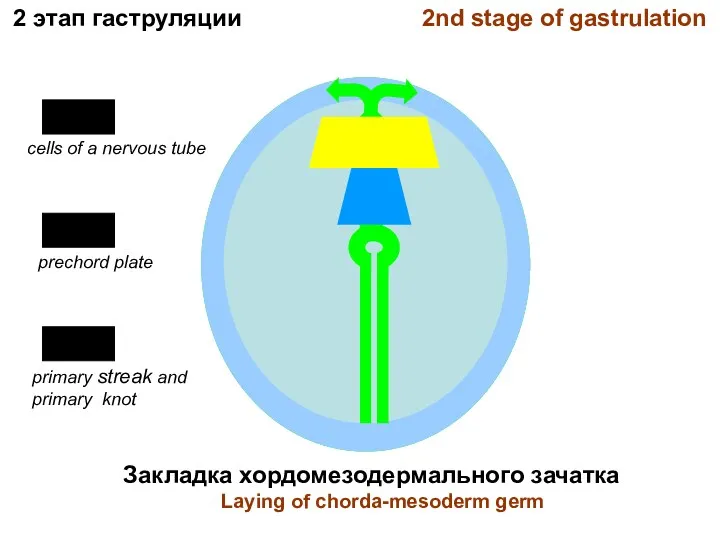
- 14. Закладка хордомезодермального зачатка Laying of chorda-mesoderm germ 2 этап гаструляции 2nd stage of gastrulation primary streak
- 15. A chord and mesoderm are pawned from a primary strip. A head chord shoot is pawned
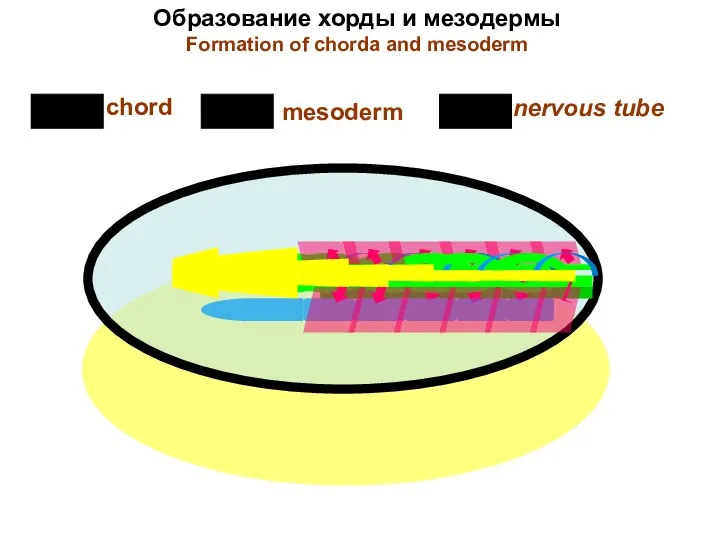
- 16. Образование хорды и мезодермы Formation of chorda and mesoderm chord mesoderm nervous tube
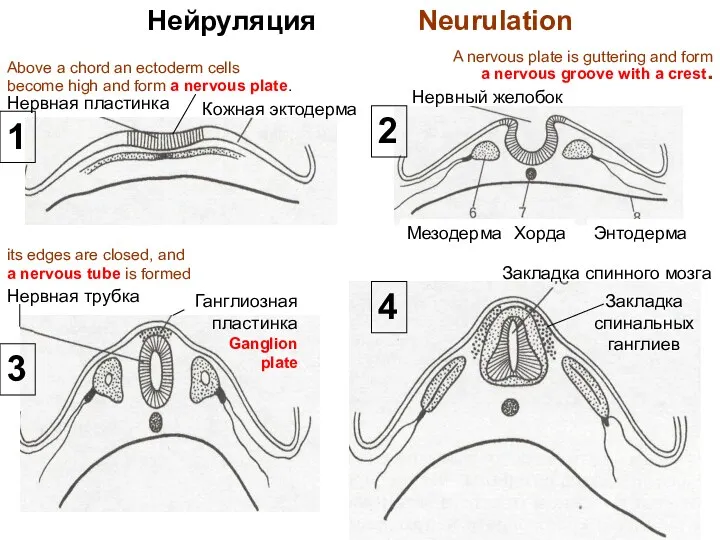
- 17. Neurulation Above a chord an ectoderm cells become high and form a nervous plate. Then it
- 18. Нейруляция Neurulation Нервная пластинка Кожная эктодерма Нервный желобок Энтодерма Хорда Мезодерма Нервная трубка Закладка спинного мозга
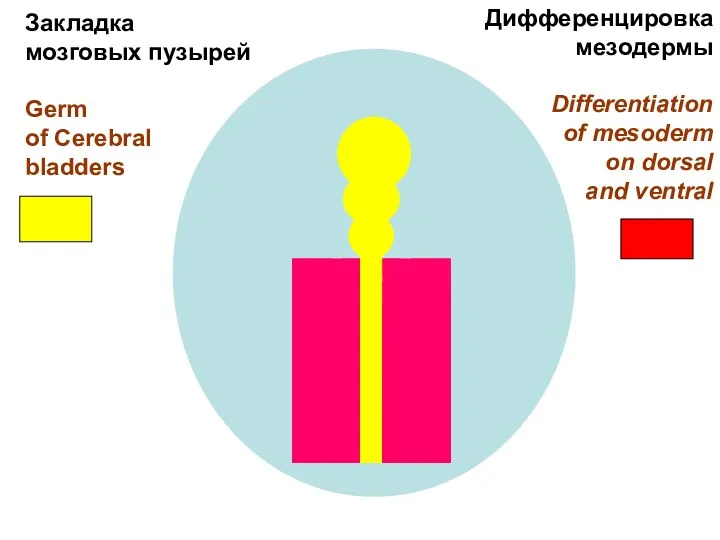
- 19. Закладка мозговых пузырей Germ of Cerebral bladders Дифференцировка мезодермы Differentiation of mesoderm on dorsal and ventral
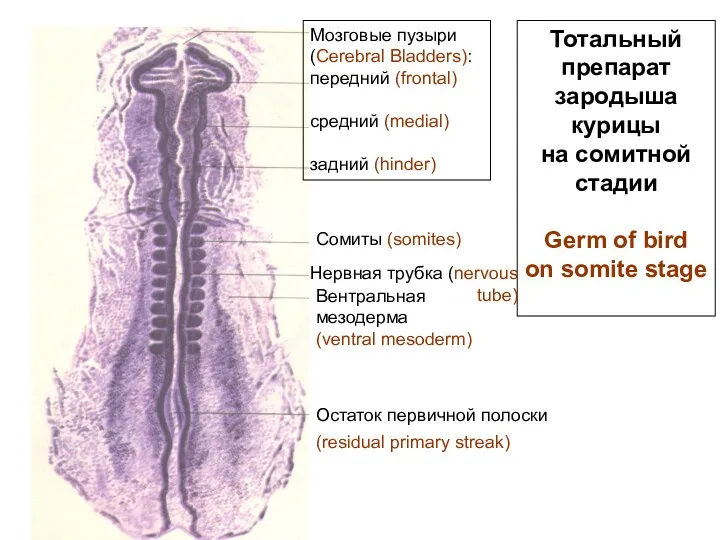
- 20. Тотальный препарат зародыша курицы на сомитной стадии Germ of bird on somite stage Мозговые пузыри (Cerebral
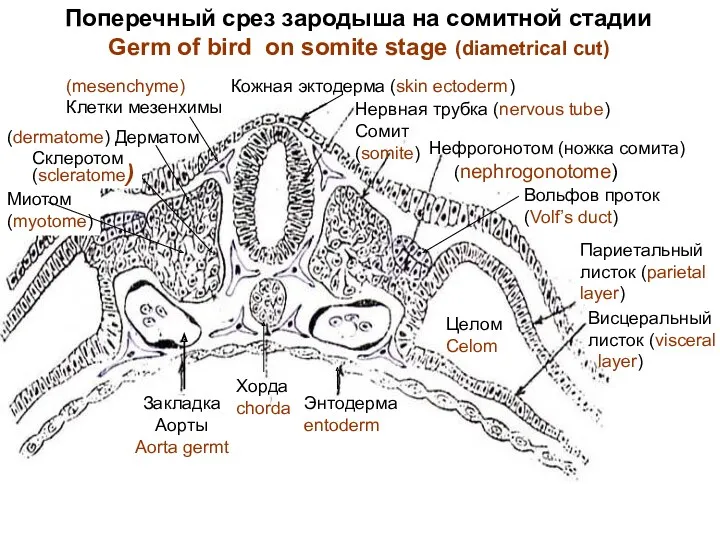
- 21. Dorsal mesoderm is segmented on somites. Ventral mesoderm is split on 2 layers - parietal (near
- 22. Поперечный срез зародыша на сомитной стадии Germ of bird on somite stage (diametrical cut) Кожная эктодерма
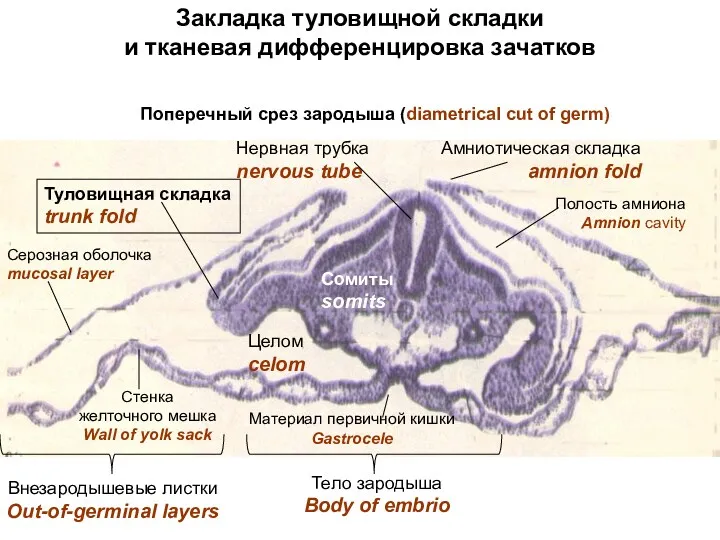
- 23. Закладка туловищной складки и тканевая дифференцировка зачатков Туловищная складка trunk fold Амниотическая складка amnion fold Нервная
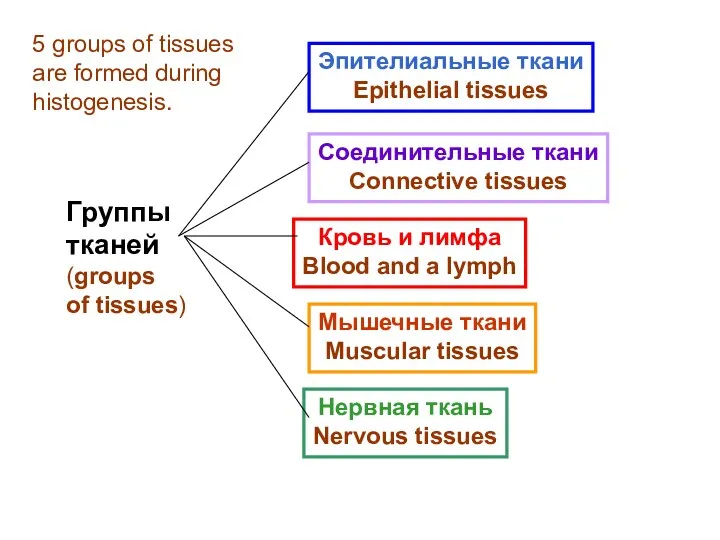
- 24. Группы тканей (groups of tissues) Эпителиальные ткани Epithelial tissues Соединительные ткани Connective tissues Кровь и лимфа
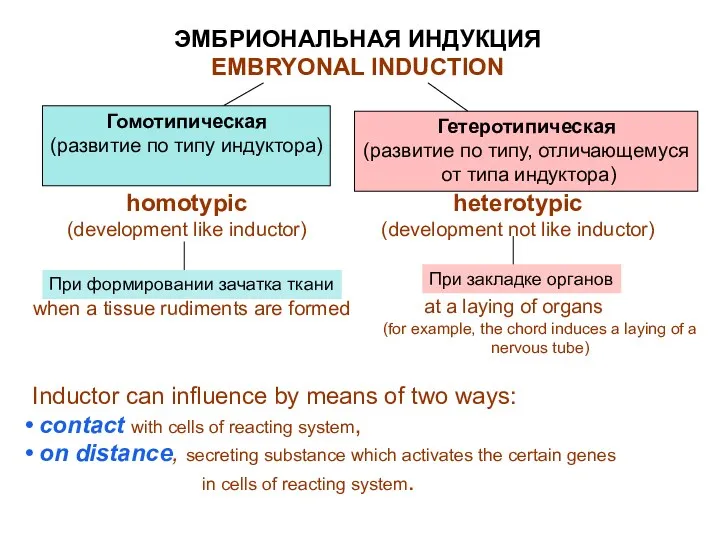
- 25. Влияние одних частей зародыша (индукторов) на другие части (реагирующие системы) называется ЭМБРИОНАЛЬНАЯ ИНДУКЦИЯ (Шпеман, 1901) Индуктор
- 26. ЭМБРИОНАЛЬНАЯ ИНДУКЦИЯ EMBRYONAL INDUCTION Гомотипическая (развитие по типу индуктора) При формировании зачатка ткани Гетеротипическая (развитие по
- 27. Этапы дифференцировки клетки 1 этап – ДЕТЕРМИНАЦИЯ – латентный (скрытый), обратимый. Клетка не меняет строение, но
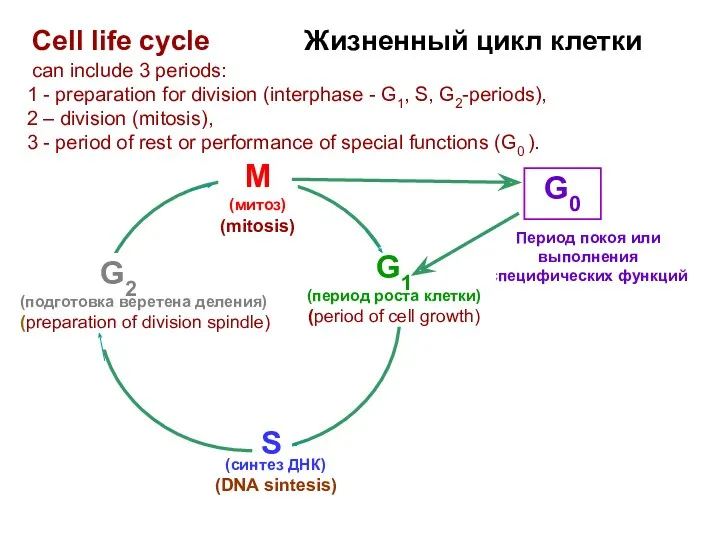
- 28. Период покоя или выполнения специфических функций G1 (период роста клетки) (period of cell growth) G2 (подготовка
- 30. Скачать презентацию







 Общая экология. Экология популяций
Общая экология. Экология популяций Головной мозг - строение
Головной мозг - строение Презентация Глобальный экологический кризис
Презентация Глобальный экологический кризис Презентация по биологии Гуморальная регуляция для 8 класса
Презентация по биологии Гуморальная регуляция для 8 класса Экзотические животные Африки
Экзотические животные Африки Приспособленность живых организмов к среде обитания
Приспособленность живых организмов к среде обитания Вид. Критерии вида. 9 класс
Вид. Критерии вида. 9 класс Презентация Растения хищники
Презентация Растения хищники Строение бактериальной клетки
Строение бактериальной клетки Микробиологическая лаборатория, устройства оснащения, правила работы, изучение морфологии бактерий
Микробиологическая лаборатория, устройства оснащения, правила работы, изучение морфологии бактерий Окружающая среда
Окружающая среда Життя підводних мешканців
Життя підводних мешканців Сухоцветы. Составление зимних букетов
Сухоцветы. Составление зимних букетов Вирусология и открытие вирусов
Вирусология и открытие вирусов Витамин А
Витамин А Матричный принцип, как основа современной эволюционной теории
Матричный принцип, как основа современной эволюционной теории Презентация к уроку биологии в 6 классе
Презентация к уроку биологии в 6 классе Функциональная структура биосферы
Функциональная структура биосферы Вторично чувствующие органы чувств: орган слуха, орган равновесия, орган вкуса
Вторично чувствующие органы чувств: орган слуха, орган равновесия, орган вкуса Африканская улитка - гигантская ахатина
Африканская улитка - гигантская ахатина Кейс-метод
Кейс-метод Этапы развития жизни на Земли
Этапы развития жизни на Земли Возрастная периодизация
Возрастная периодизация Наследование групп крови человека
Наследование групп крови человека Червонокнижні види рослин України
Червонокнижні види рослин України Нуклеиновые кислоты: состав, строение, функции. Биология. 10 класс
Нуклеиновые кислоты: состав, строение, функции. Биология. 10 класс Ткани животных и растений
Ткани животных и растений Биохимия липидов. Классификация, биологические функции. Переваривание и всасывание. Обмен липопротеидов
Биохимия липидов. Классификация, биологические функции. Переваривание и всасывание. Обмен липопротеидов