Содержание
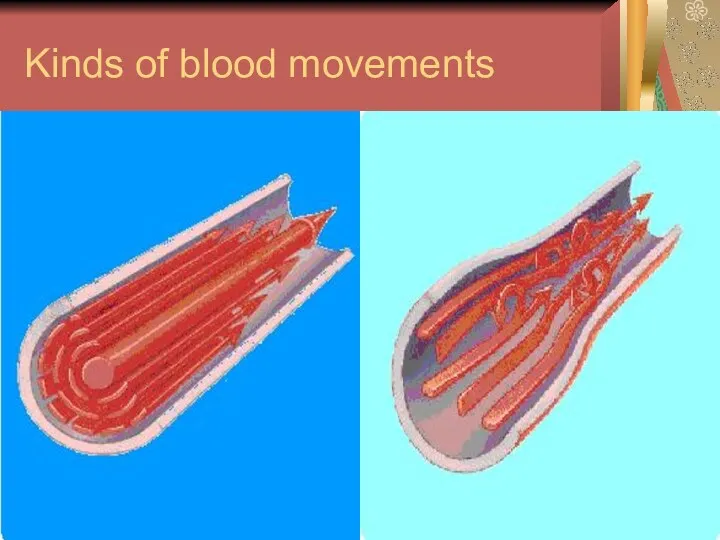
- 2. Kinds of blood movements
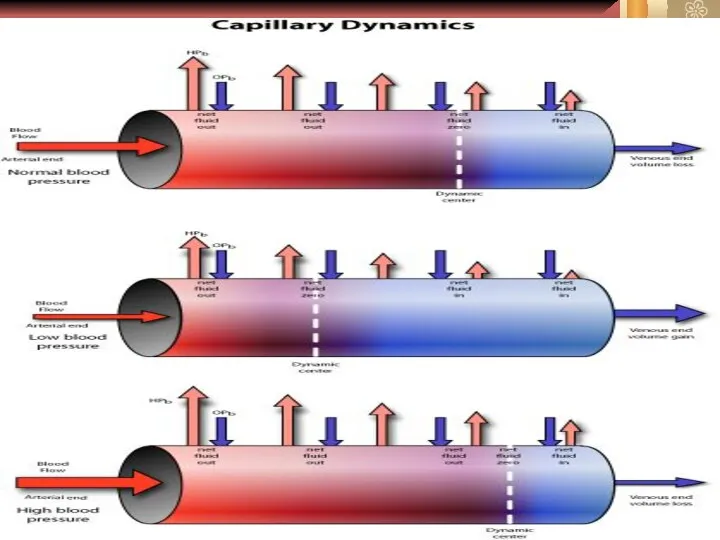
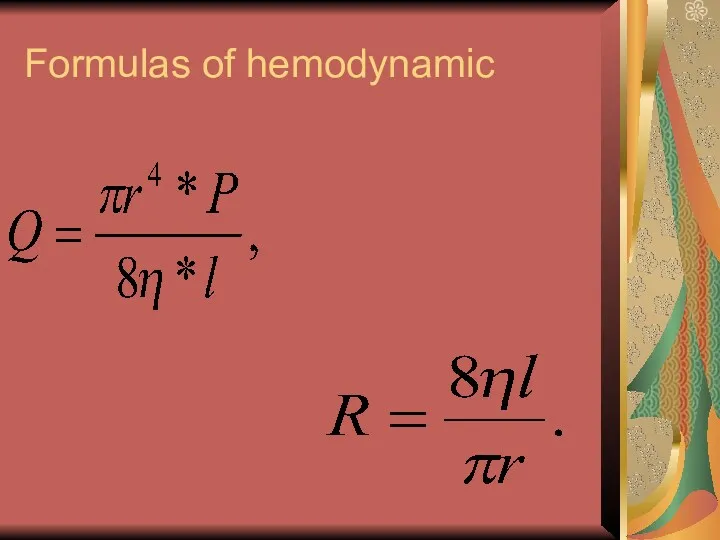
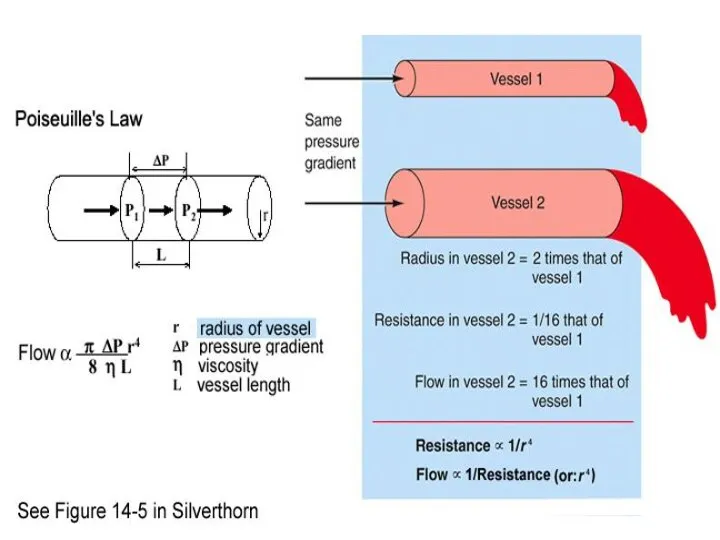
- 4. Formulas of hemodynamic
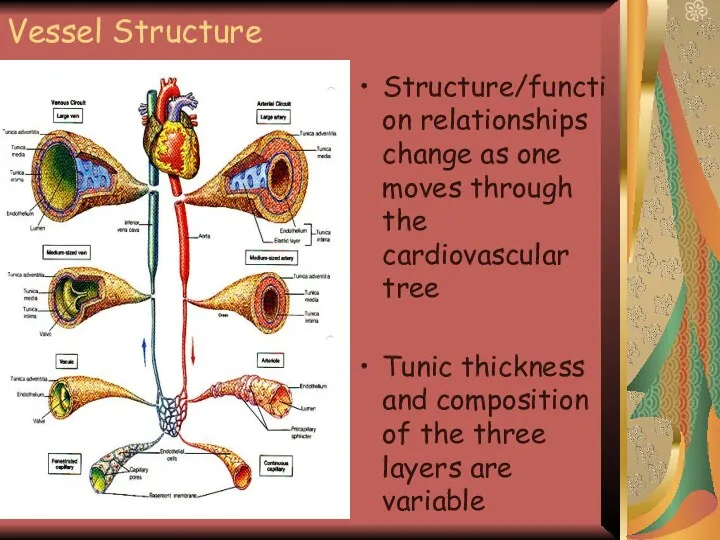
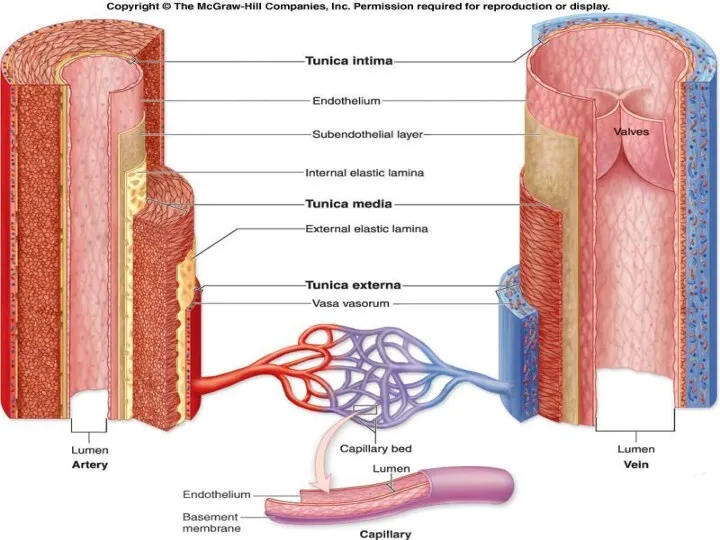
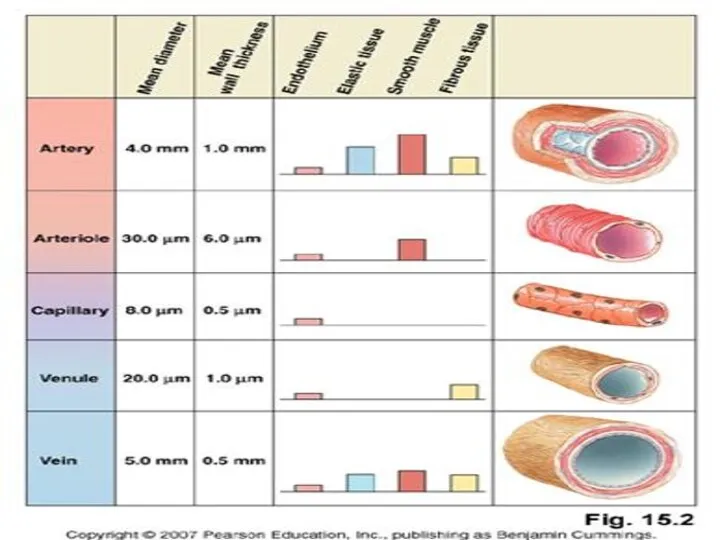
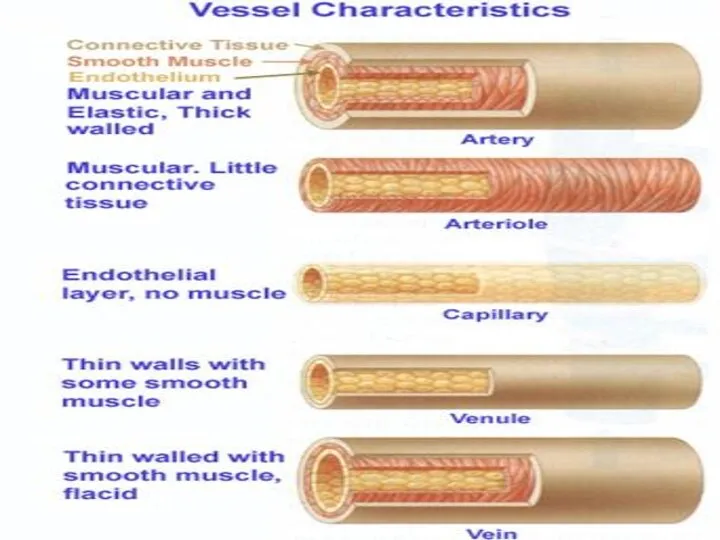
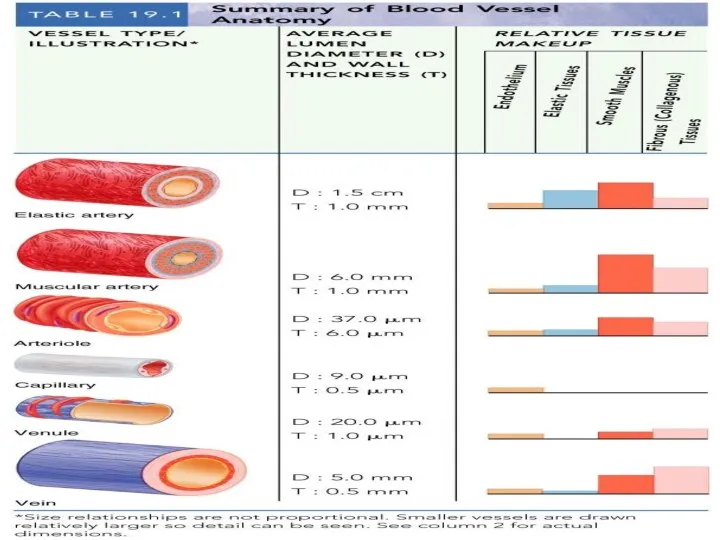
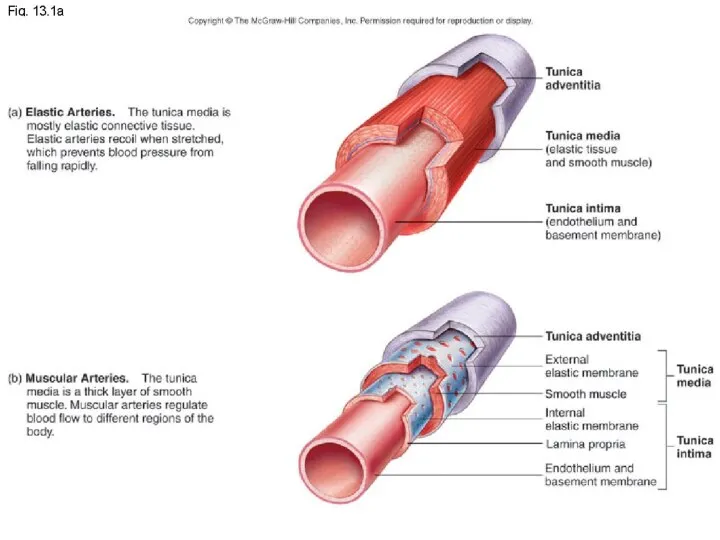
- 6. Vessel Structure Structure/function relationships change as one moves through the cardiovascular tree Tunic thickness and composition
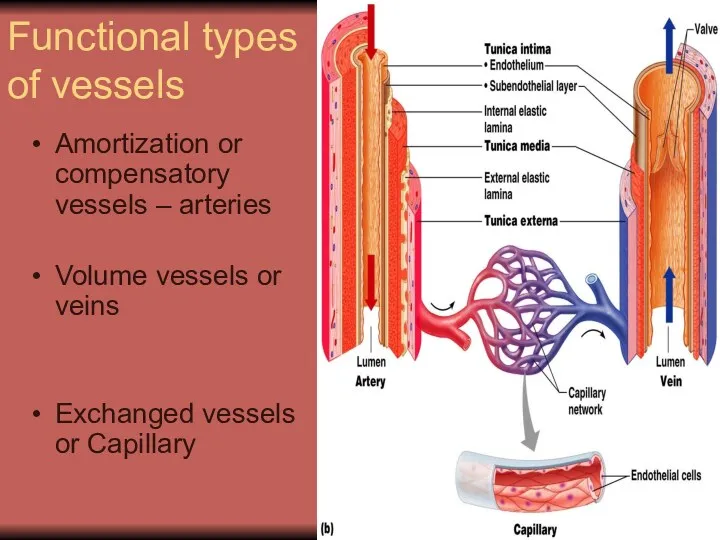
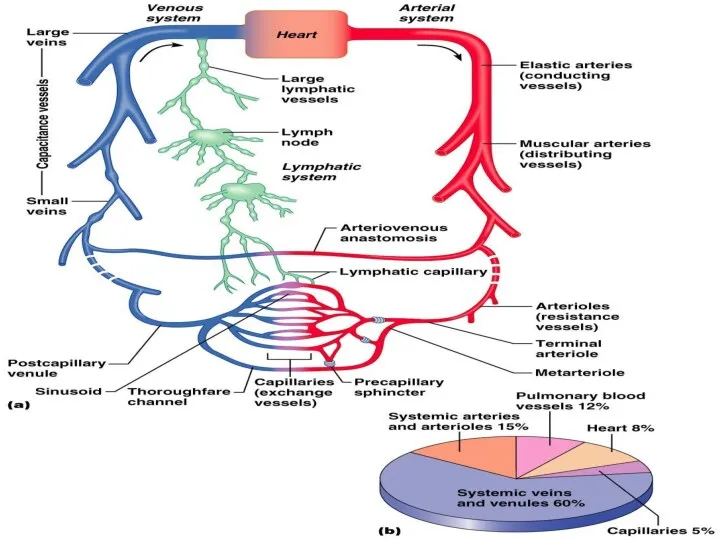
- 11. Functional types of vessels Amortization or compensatory vessels – arteries Volume vessels or veins Exchanged vessels
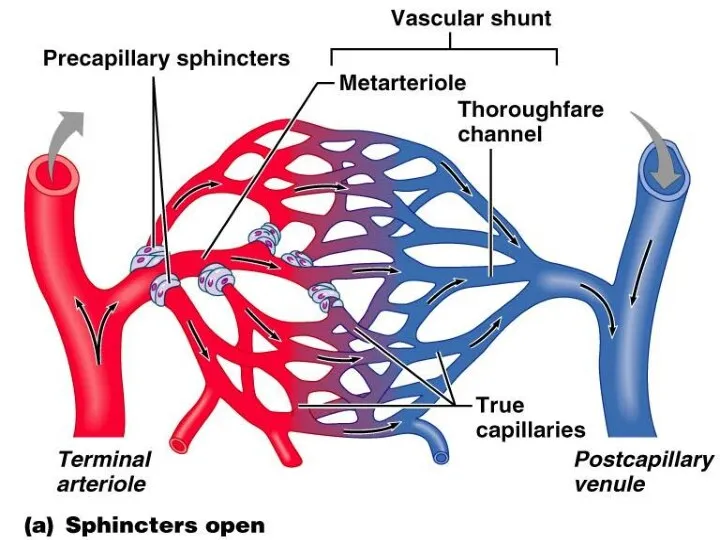
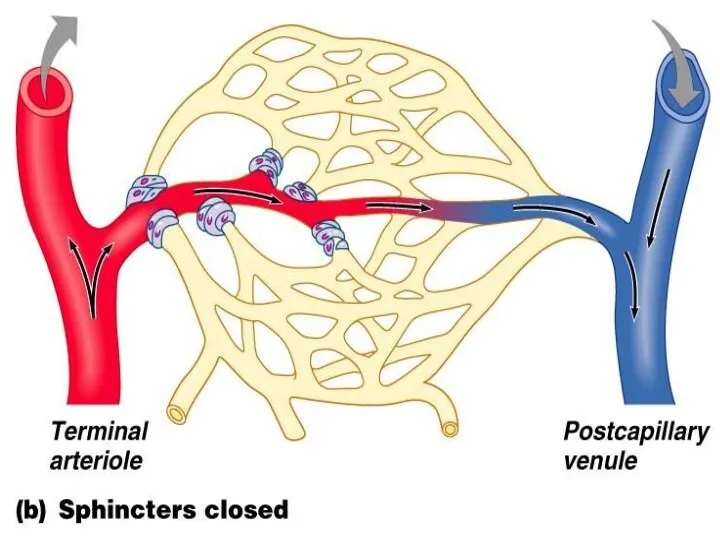
- 12. Functional types of vessels Resistive vessels or arterioles, smallest arteries; lead to capillary beds Sphincters Shunts
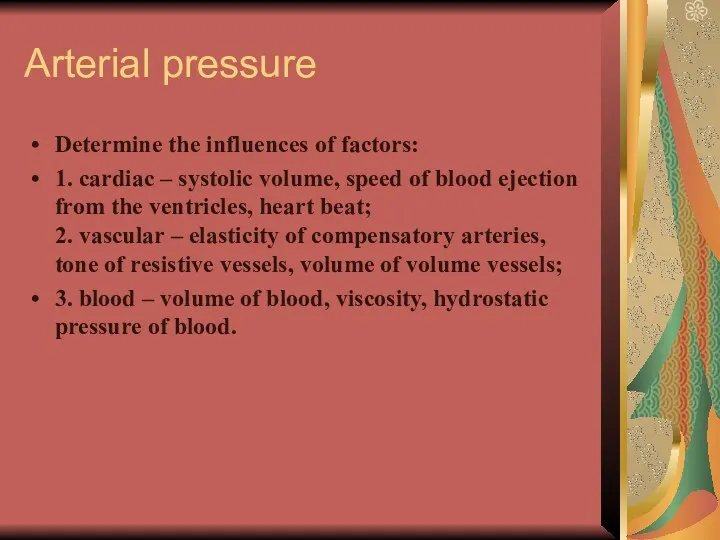
- 17. Arterial pressure Determine the influences of factors: 1. cardiac – systolic volume, speed of blood ejection
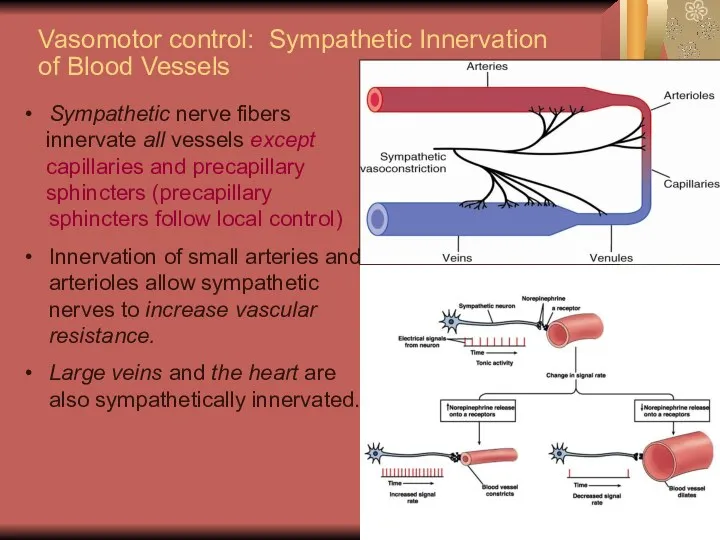
- 19. Vasomotor control: Sympathetic Innervation of Blood Vessels Sympathetic nerve fibers innervate all vessels except capillaries and
- 20. Kinds of arterial pressure 1. Systolic or maximal 2. Side or absolute systolic 3. Stroke (hemodynamic)
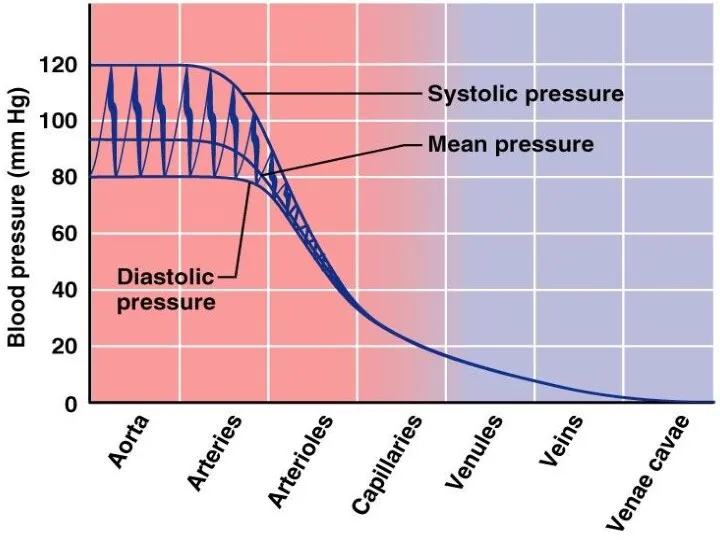
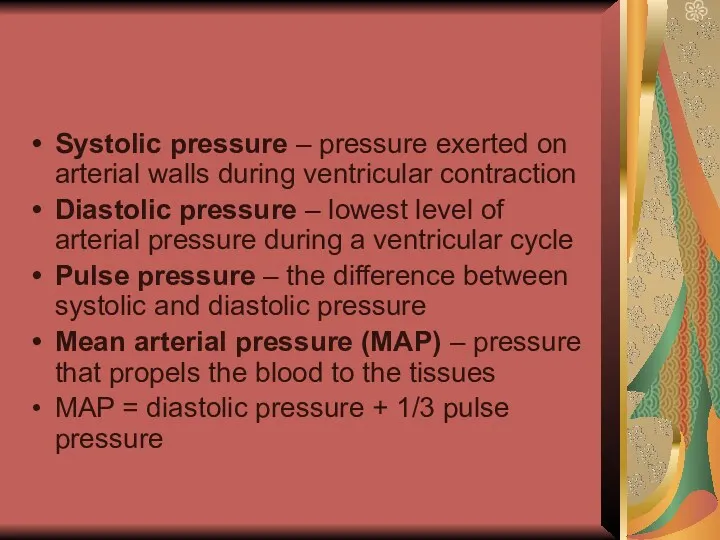
- 21. Systolic pressure – pressure exerted on arterial walls during ventricular contraction Diastolic pressure – lowest level
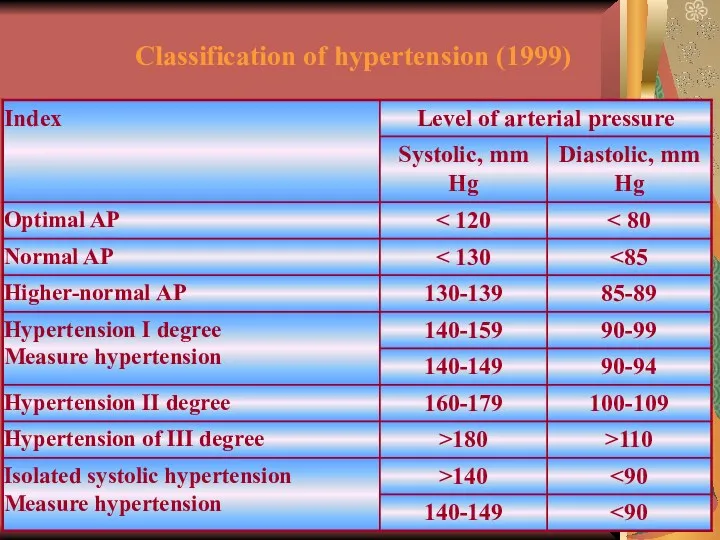
- 22. Classification of hypertension (1999)
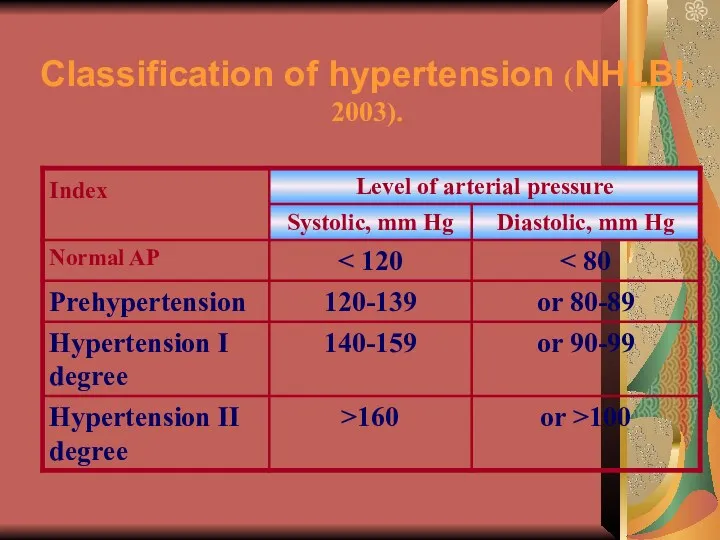
- 23. Classification of hypertension (NHLBI, 2003).
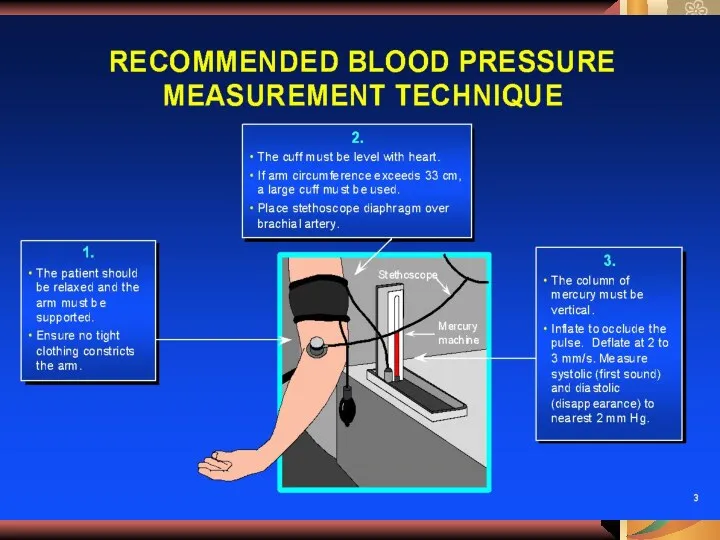
- 24. Apparatuses
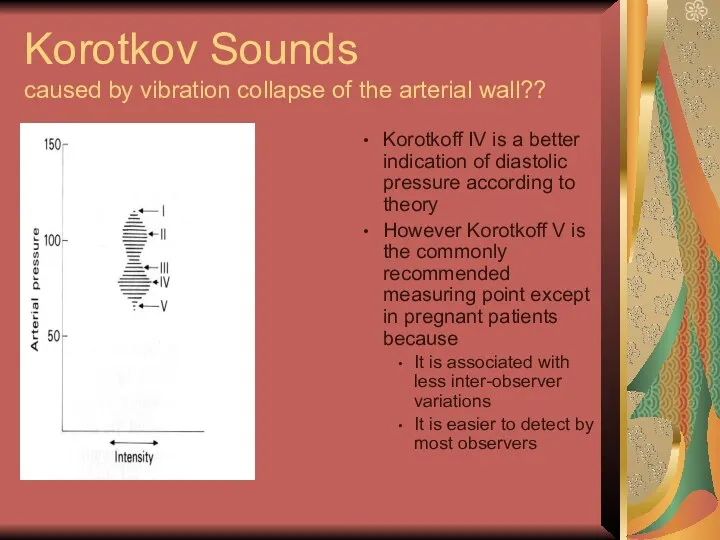
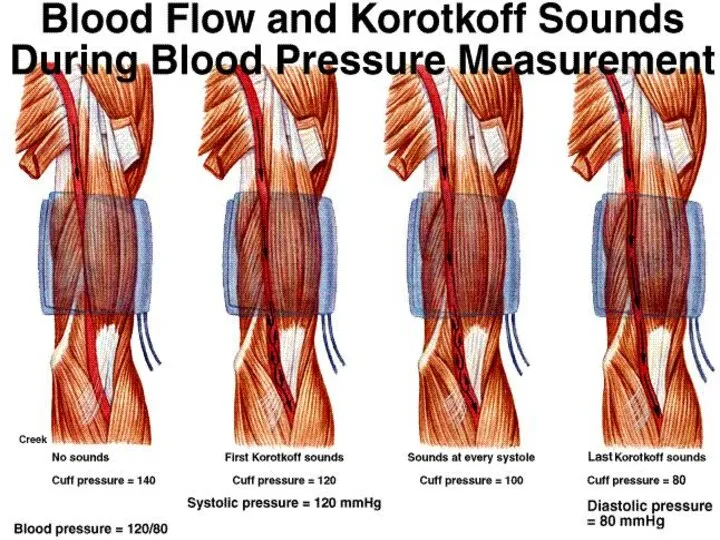
- 26. Korotkov Sounds caused by vibration collapse of the arterial wall?? Korotkoff IV is a better indication
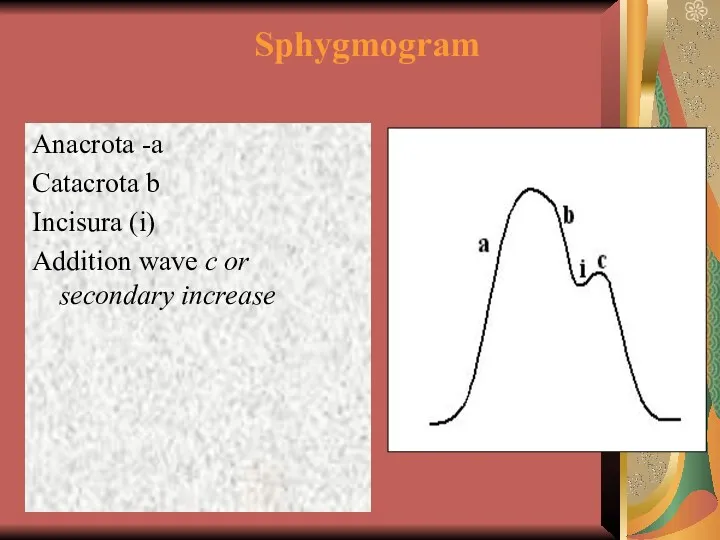
- 28. Sphygmogram Anacrota -а Catacrota b Incisura (i) Addition wave с or secondary increase
- 31. Скачать презентацию



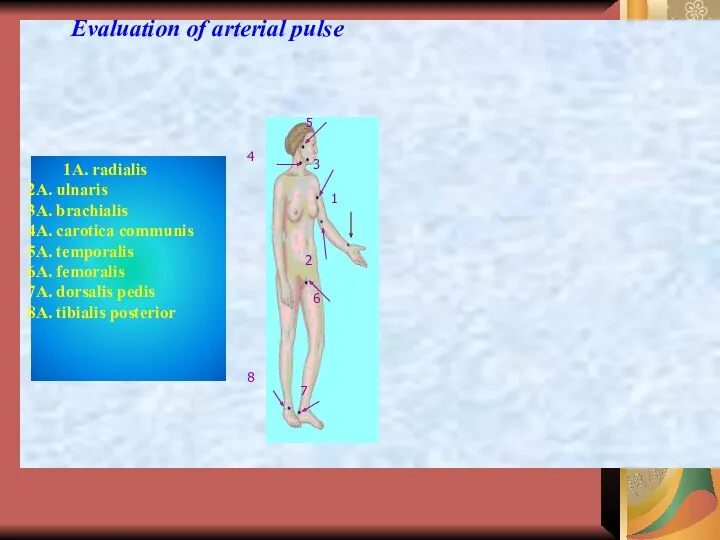
 Урок по биологии 8 класс Строение органа слуха
Урок по биологии 8 класс Строение органа слуха Презентация по биологии Кровообращение
Презентация по биологии Кровообращение Вирусы (2). Лекция 10
Вирусы (2). Лекция 10 Гости с севера. Птицы зимой
Гости с севера. Птицы зимой Анатомия и физиология больших пищеварительных желёз: поджелудочная железа, большие слюнные железы
Анатомия и физиология больших пищеварительных желёз: поджелудочная железа, большие слюнные железы Животные зимой
Животные зимой connective_tissue
connective_tissue Насекомые в природе
Насекомые в природе Биологиялық дозиметрия (электрондық парамагниттік резонанс және тағы басқалары) және олардың тәжірибеде қолданылуы
Биологиялық дозиметрия (электрондық парамагниттік резонанс және тағы басқалары) және олардың тәжірибеде қолданылуы Биохимия крови
Биохимия крови Систематика растений
Систематика растений Биология. Живая природа
Биология. Живая природа Введение в спланхнологию
Введение в спланхнологию Rat Dissection
Rat Dissection Понятие биотехнологии, ее задачи, подбор и культивирование биологических объектов
Понятие биотехнологии, ее задачи, подбор и культивирование биологических объектов Вегетативне розмноження рослин
Вегетативне розмноження рослин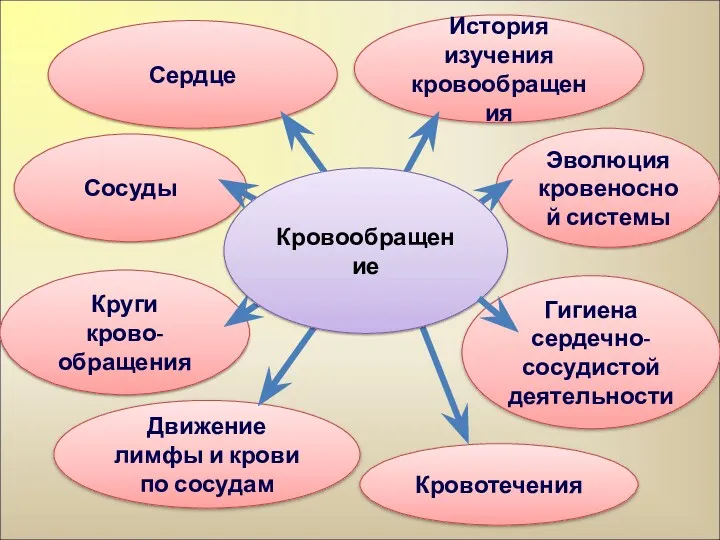 Движение крови и лимфы. Профилактика
Движение крови и лимфы. Профилактика Комнатные растения в интерьере квартиры
Комнатные растения в интерьере квартиры Самопрезентация руководителя кружка Зеленый патруль
Самопрезентация руководителя кружка Зеленый патруль Пищеварение. Типы желез в желудке
Пищеварение. Типы желез в желудке Бактериологическая лаборатория, режим работы
Бактериологическая лаборатория, режим работы Моховидные. Строение и размножение мхов
Моховидные. Строение и размножение мхов Неандертальцы
Неандертальцы Антуриум Огненный
Антуриум Огненный Ядовитые растения
Ядовитые растения Антропология. Ранние этапы эволюции человека
Антропология. Ранние этапы эволюции человека Птицы, обитающие возле жилья человека
Птицы, обитающие возле жилья человека Размножение и развитие птиц
Размножение и развитие птиц