Содержание
- 2. Полет Amphibia
- 3. Полет Reptilia
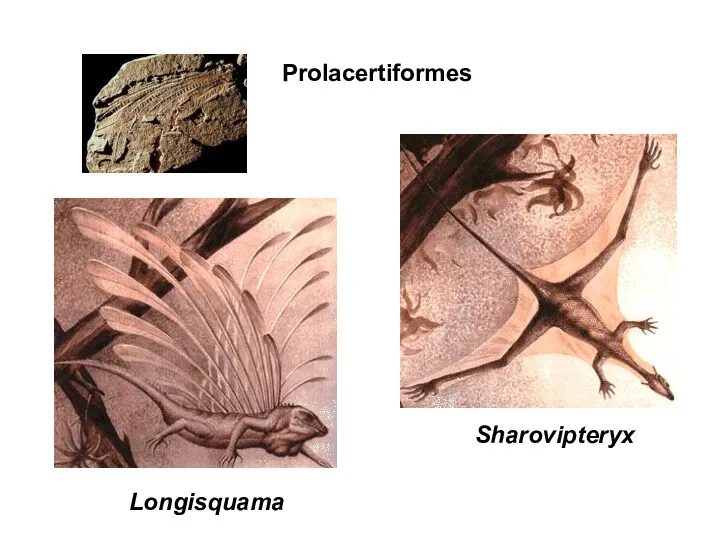
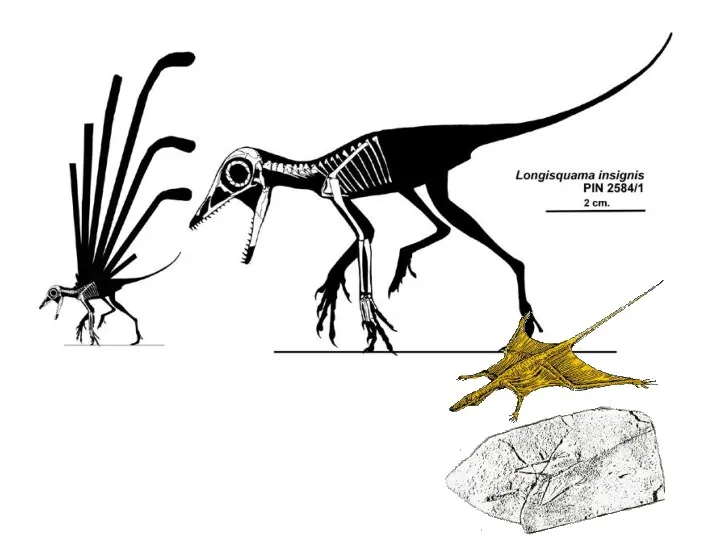
- 4. Sharovipteryx Longisquama Prolacertiformes
- 6. Icarosaurus
- 7. Полет Mammalia
- 8. Pterosauromorpha Активный полет
- 10. Активный полет Aves
- 11. Активный полет Chiroptera (Mammalia)
- 12. КТО ТАКИЕ ПТИЦЫ? ОТ КОГО ОНИ ПРОИЗОШЛИ? КАК ВОЗНИК ПОЛЕТ У ПТИЦ?
- 13. КТО ТАКИЕ ПТИЦЫ?
- 14. Перья
- 15. Контурные перья Hollow quill Rachis subdivided into barbs Barbs connected by barbules When used in flight,
- 16. Пух No barbules Found beneath contours Conserve head Abundant in waterfowl
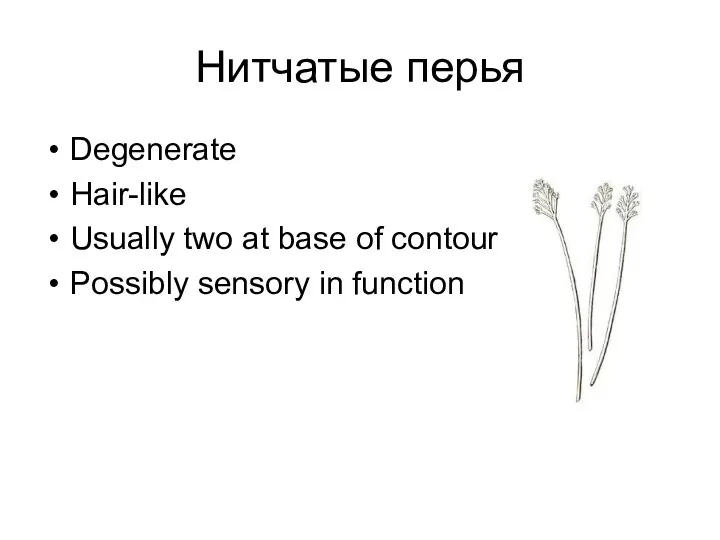
- 17. Нитчатые перья Degenerate Hair-like Usually two at base of contour Possibly sensory in function
- 18. Пудретки Similar to down feathers Tips disintegrate Produce talc-like powder Waterproofs animal
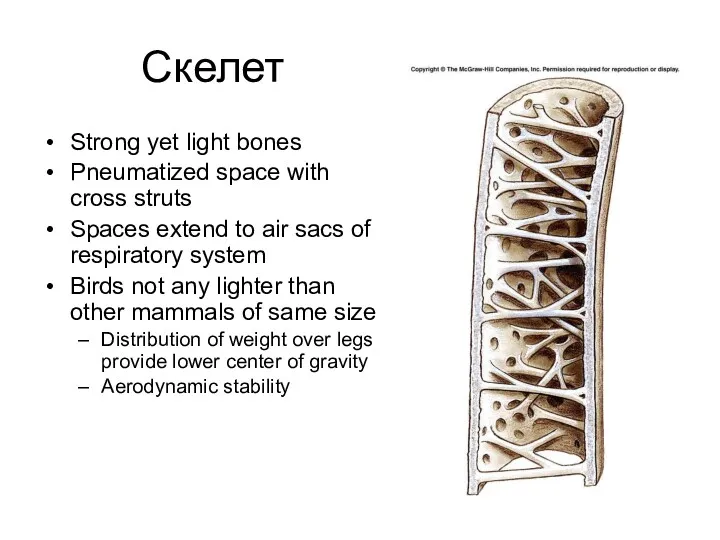
- 19. Скелет Strong yet light bones Pneumatized space with cross struts Spaces extend to air sacs of
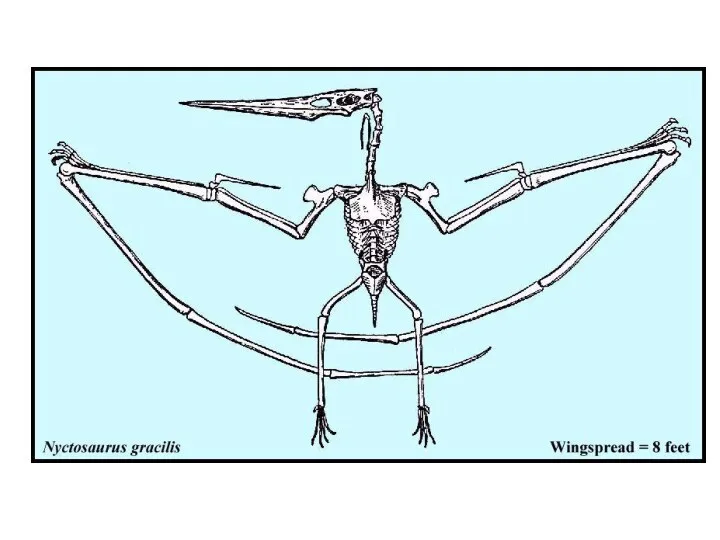
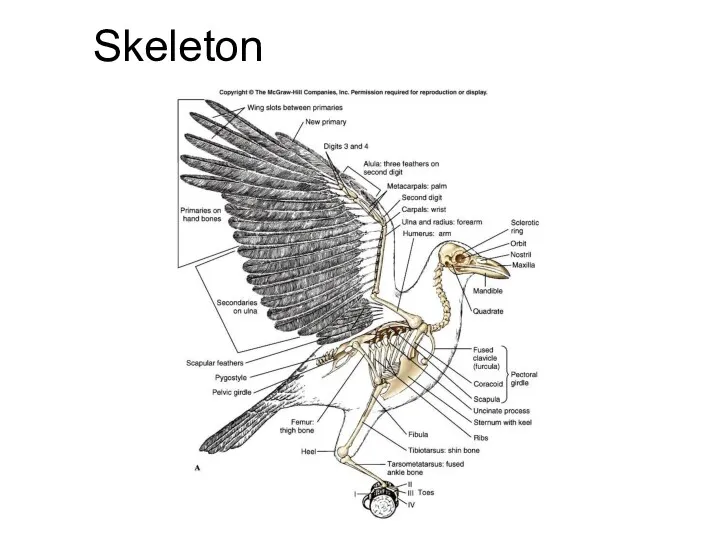
- 20. Skeleton
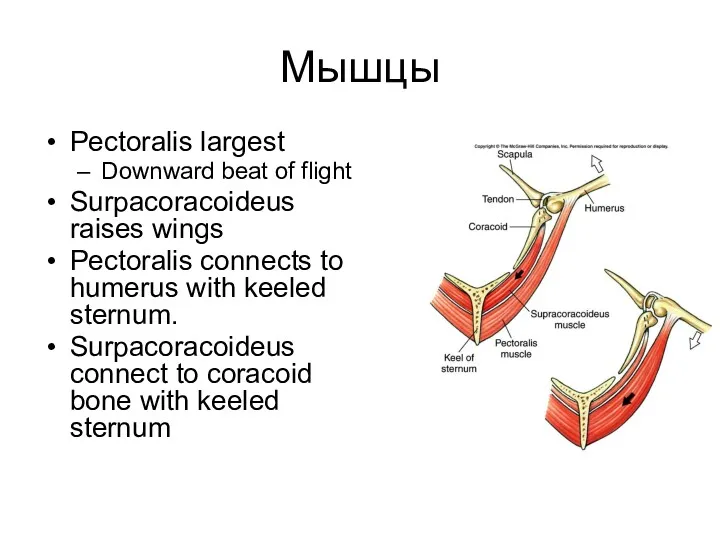
- 21. Мышцы Pectoralis largest Downward beat of flight Surpacoracoideus raises wings Pectoralis connects to humerus with keeled
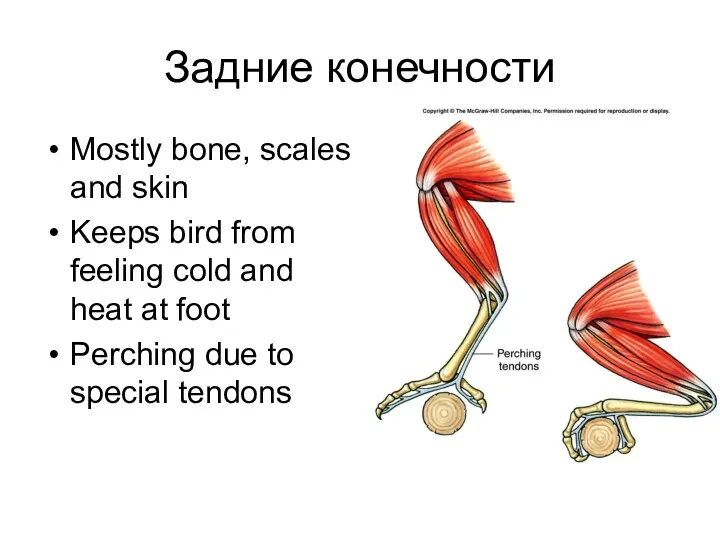
- 22. Задние конечности Mostly bone, scales and skin Keeps bird from feeling cold and heat at foot
- 23. Feeding & Digestion Diet Euryphagous (omnivores) Stenophagous (select diet) Large appetites due to high metabolic requirements
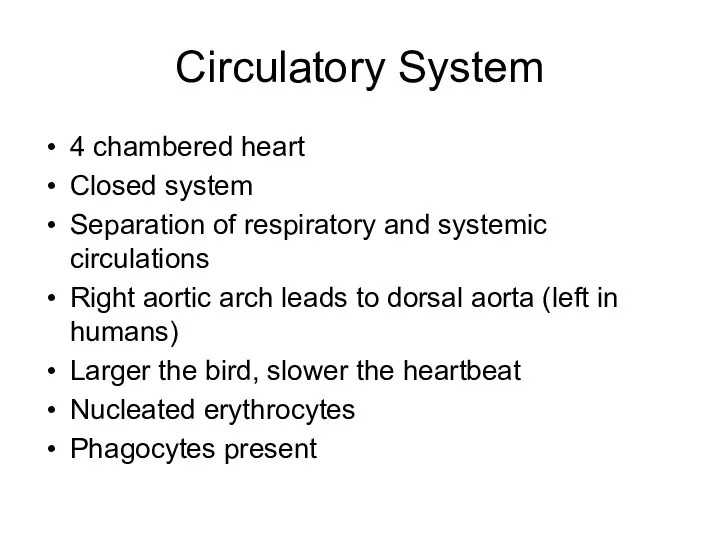
- 24. Circulatory System 4 chambered heart Closed system Separation of respiratory and systemic circulations Right aortic arch
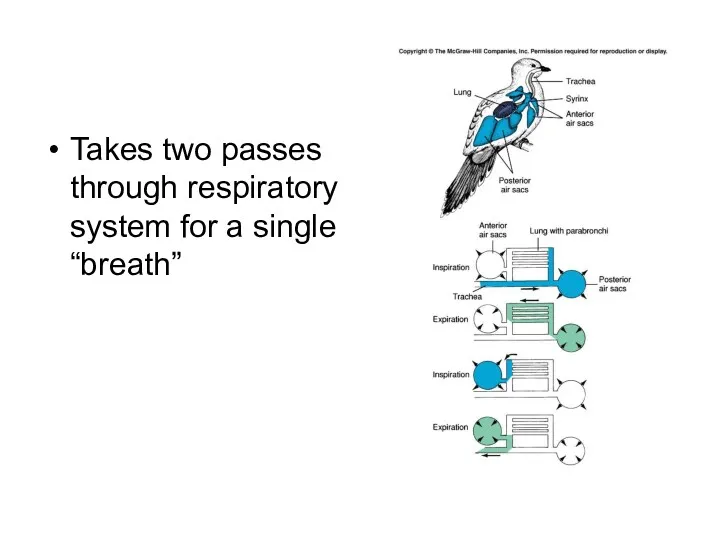
- 25. Respiratory System 9 interconnecting air sacs paired in thorax and abdomen Divide into extensions to bones
- 26. Takes two passes through respiratory system for a single “breath”
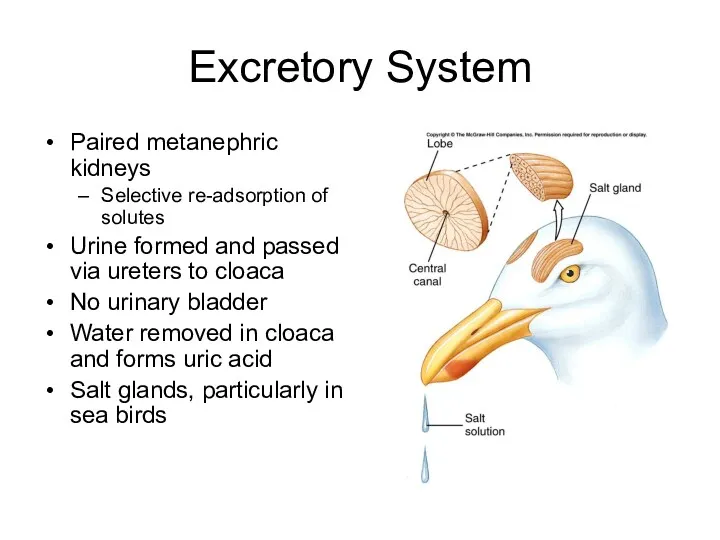
- 27. Excretory System Paired metanephric kidneys Selective re-adsorption of solutes Urine formed and passed via ureters to
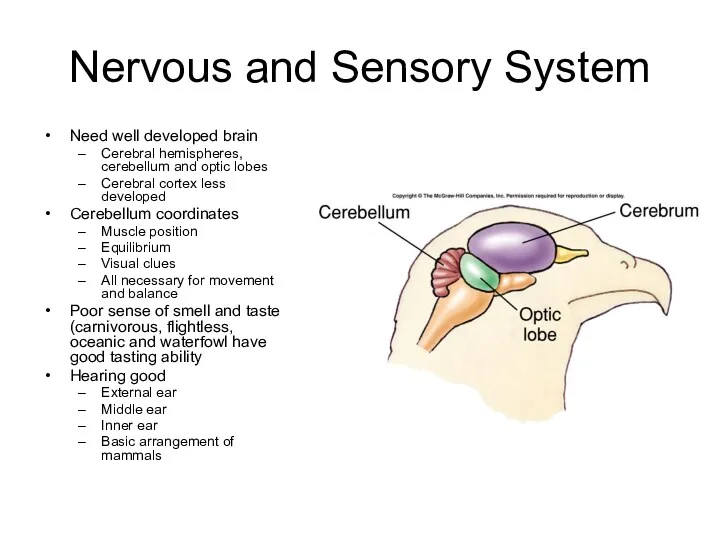
- 28. Nervous and Sensory System Need well developed brain Cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and optic lobes Cerebral cortex
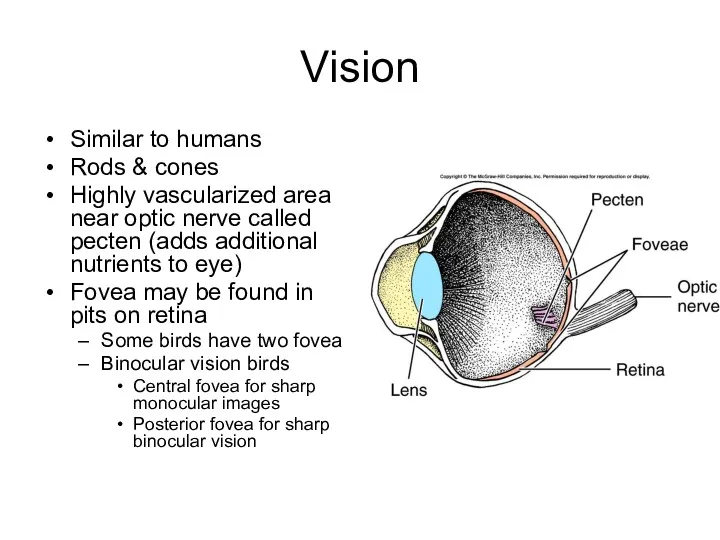
- 29. Vision Similar to humans Rods & cones Highly vascularized area near optic nerve called pecten (adds
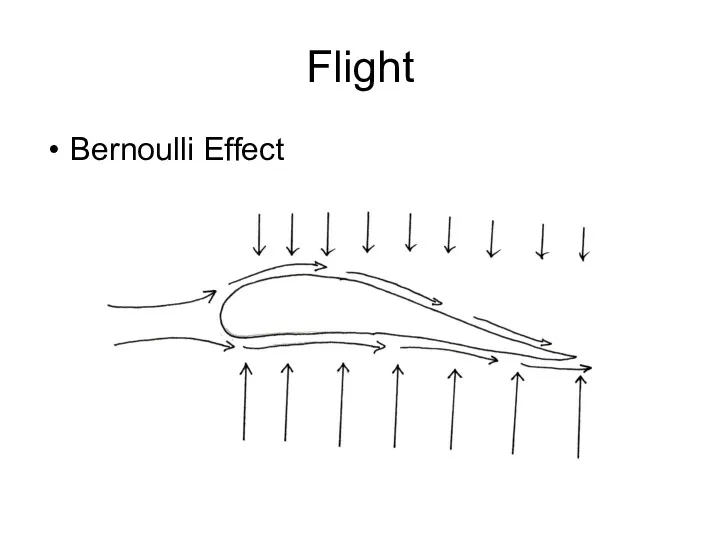
- 30. Flight Bernoulli Effect
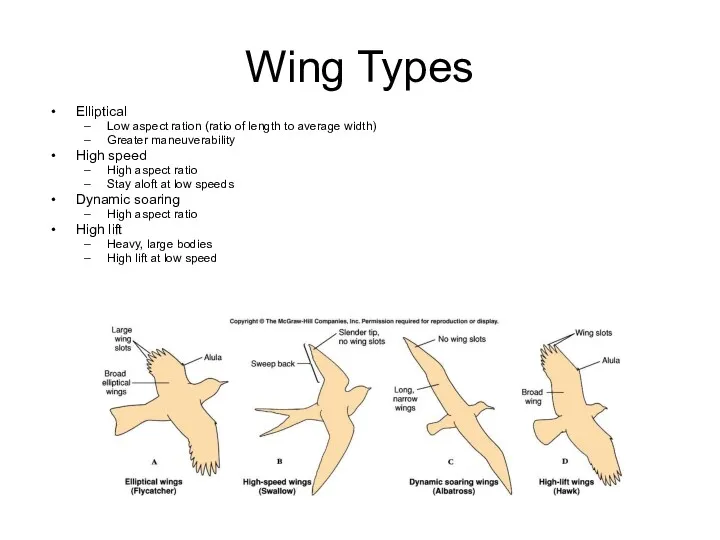
- 31. Wing Types Elliptical Low aspect ration (ratio of length to average width) Greater maneuverability High speed
- 32. Migration & Navigation Most have established routes ½ of all species migrate Most from north to
- 33. Direction Finding Factors Use of topographical landmarks Flock behavior by following experienced birds Innate sense of
- 34. Behavior Complex behavior Breeding Nesting Courtship Feeding, etc.
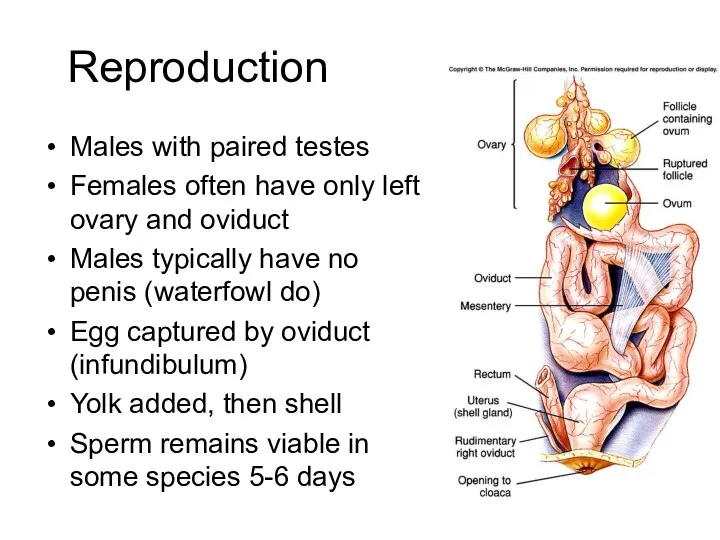
- 35. Reproduction Males with paired testes Females often have only left ovary and oviduct Males typically have
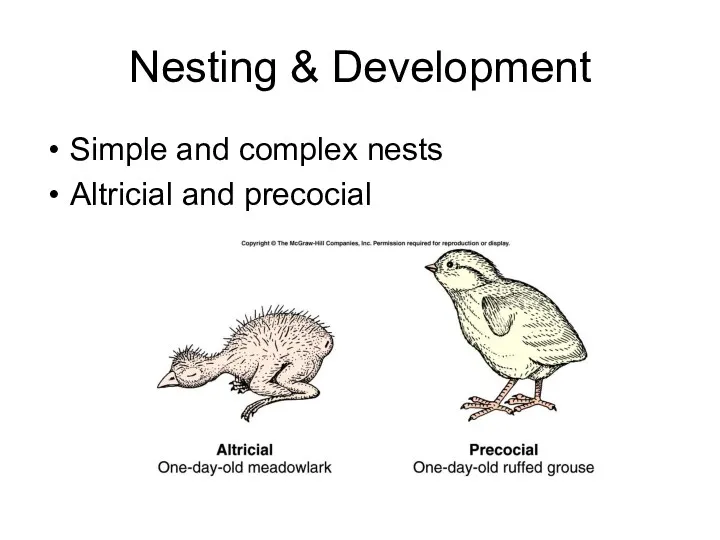
- 36. Nesting & Development Simple and complex nests Altricial and precocial
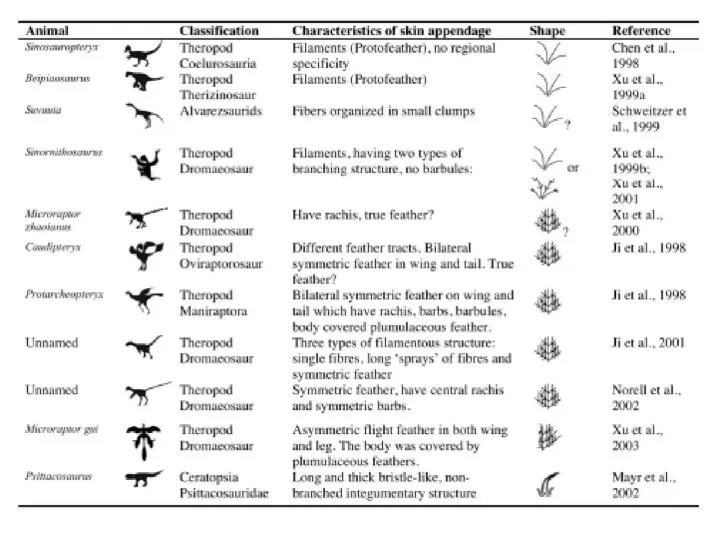
- 37. Первоначальная функция перьев?
- 38. Перьеподобные структуры характерны для Archosauria
- 39. Возникновение полета «Лесная» гипотеза «Степная» гипотеза
- 40. Гипотеза происхождения птиц от динозавров (теропод) Авиализация теропод
- 41. Tyrannosaurus Tyrannosauridae
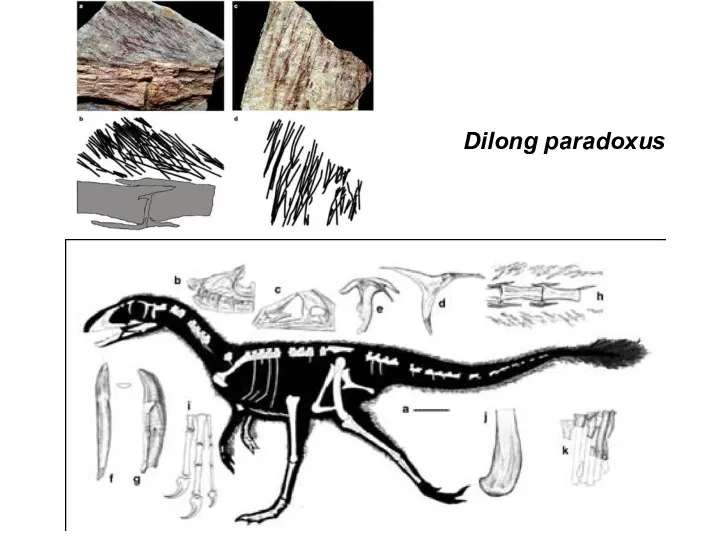
- 42. Dilong paradoxus
- 43. Dilong paradoxus
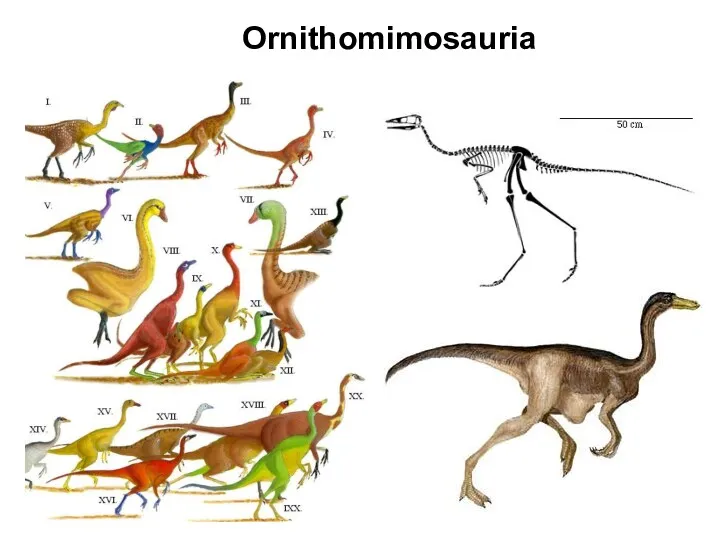
- 44. Ornithomimosauria
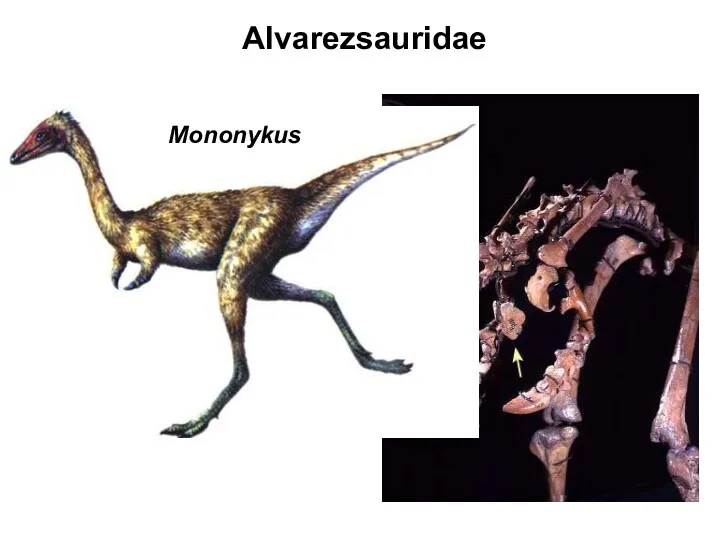
- 45. Mononykus Alvarezsauridae
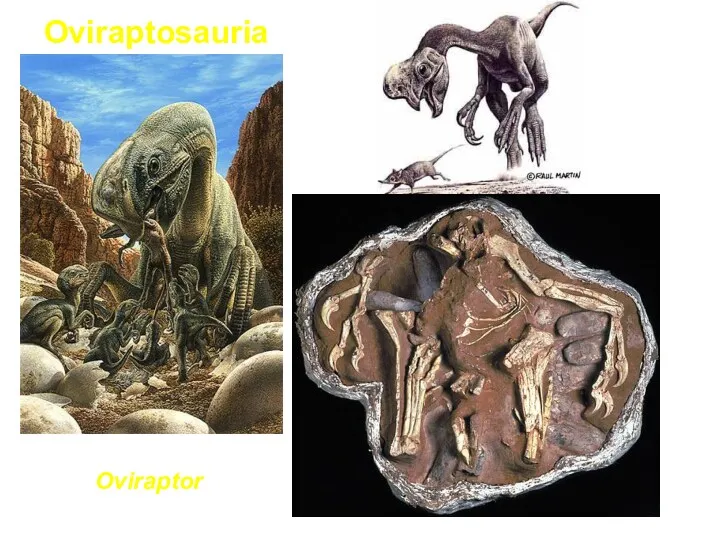
- 46. Oviraptor Oviraptosauria
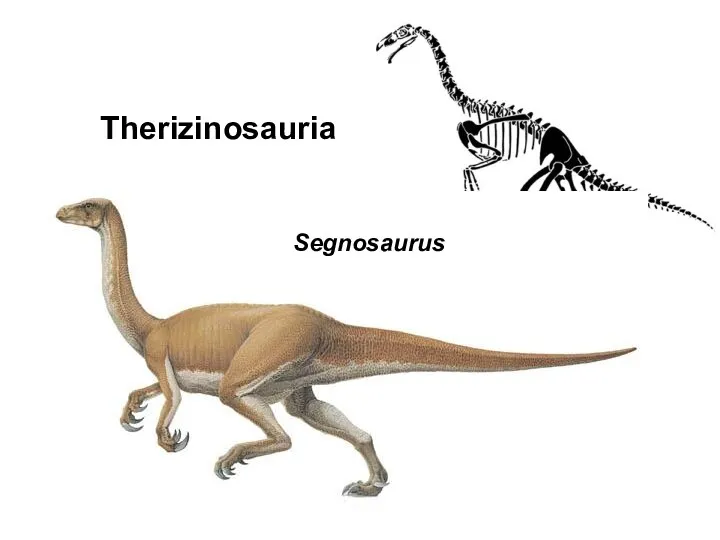
- 47. Therizinosauria Segnosaurus
- 48. Dromaeosaurus Dromaeosauridae
- 49. Troodon Troodontidae
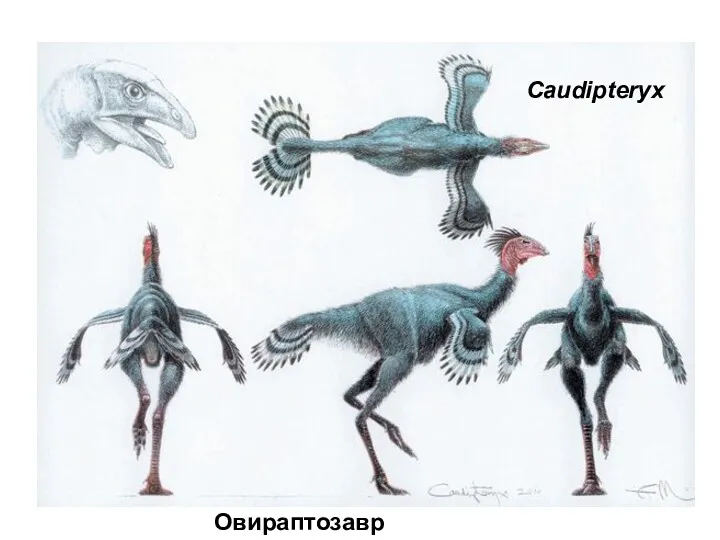
- 51. Caudipteryx Овираптозавр
- 52. Beipiaosaurus Теризинозаврид
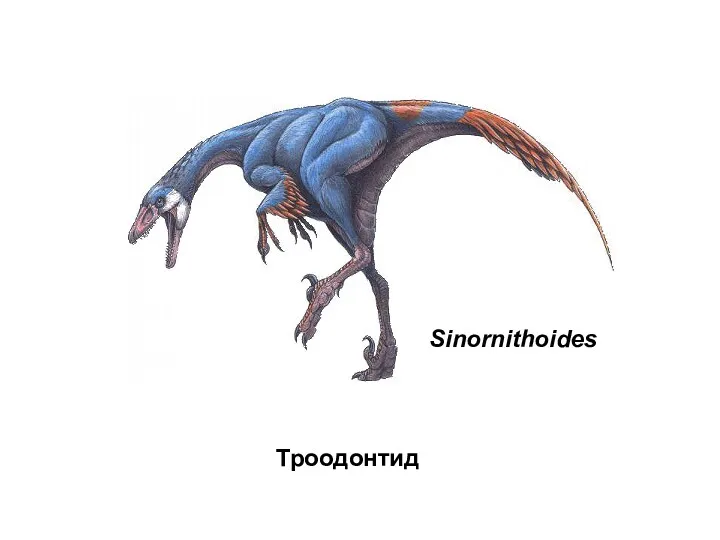
- 53. Sinornithoides Троодонтид
- 54. Microraptor gui Дромеозаврид
- 58. Кто такой археоптерикс?
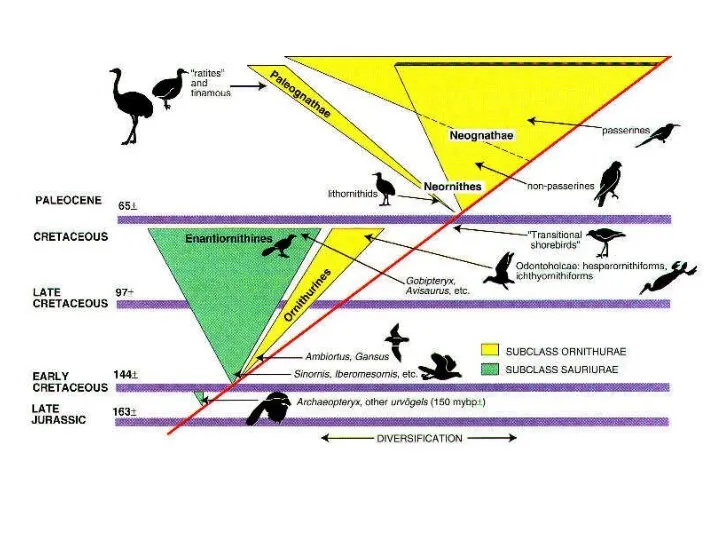
- 59. Мезозойские группы птиц
- 61. Энантиорнисы
- 62. Гесперорнисы
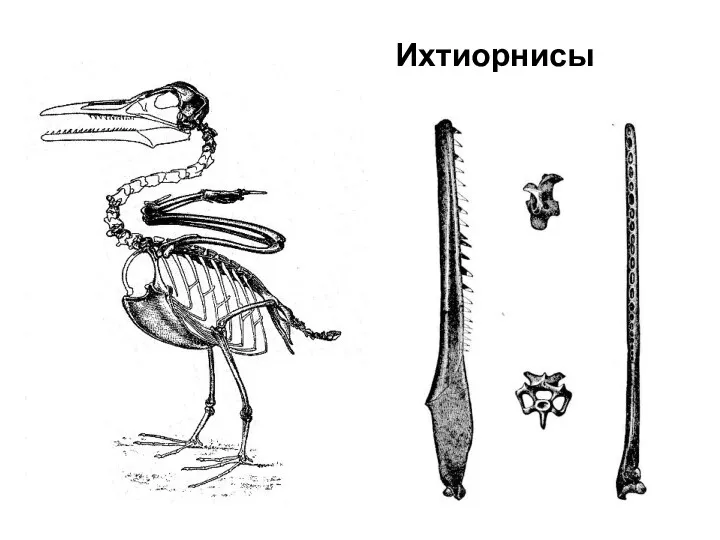
- 63. Ихтиорнисы
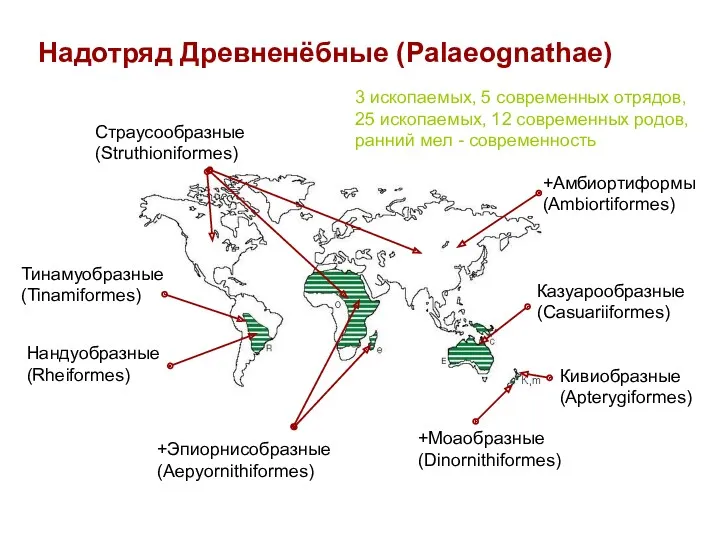
- 65. Тинамуобразные (Tinamiformes) Нандуобразные (Rheiformes) Казуарообразные (Casuariiformes) Страусообразные (Struthioniformes) Кивиобразные (Apterygiformes) +Моаобразные (Dinornithiformes) +Эпиорнисобразные (Aepyornithiformes) 3 ископаемых,
- 66. Отряд Эпиорнисобразные (Aepyornithiformes) Отряд Моаобразные (Dinornithiformes)
- 67. «Водные птицы» Гагарообразные (Gaviiformes) Поганкообразные (Podicipediformes) Ржанкообразные (Charadriiformes) Гусеобразные (Anseriformes) Журавлеобразные (Gruiformes) Аистообразные (Ciconiiformes) Пеликанообразные (Pelecaniformes)
- 68. Отряд Диатримообразные (Diatrymiformes) Diatryma 2 рода Палеоцен – эоцен С. Америка, Евразия
- 69. Форорациды Phororhacos Палеоген – неоген С. Америка, Евразия Пеликанообразные (Pelecaniformes)
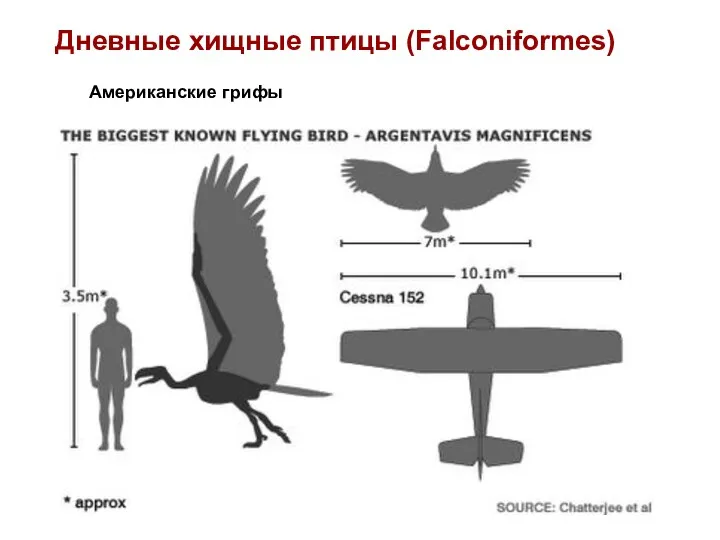
- 70. Дневные хищные птицы (Falconiformes) Американские грифы
- 71. Higher-order phylogeny of modern birds (Theropoda, Aves: Neornithes) based on comparative anatomy. II. Analysis and discussion
- 73. Скачать презентацию









































 Прокариотическая клетка
Прокариотическая клетка Предмет и задачи зоопсихологии и сравнительной психологии
Предмет и задачи зоопсихологии и сравнительной психологии Разработка интеллектуальной системы освещения растений
Разработка интеллектуальной системы освещения растений Эволюция человека. Первые современные люди - неоантропы
Эволюция человека. Первые современные люди - неоантропы Вирусы – неклеточная форма жизни
Вирусы – неклеточная форма жизни Растения вида эхеверия
Растения вида эхеверия класс костные рыбы
класс костные рыбы урок -игра при обобщении темы Строение и функции клеток. Метаболизм
урок -игра при обобщении темы Строение и функции клеток. Метаболизм Растительная клетка
Растительная клетка Фиксация молекулярного азота (азотфиксация, диазотрофия) микроорганизмами
Фиксация молекулярного азота (азотфиксация, диазотрофия) микроорганизмами Отдел: Покрытосеменные. Класс: Однодольные. Семейство: Злаки (Мятликовые)
Отдел: Покрытосеменные. Класс: Однодольные. Семейство: Злаки (Мятликовые) Спинной мозг
Спинной мозг Генетика онтогенеза
Генетика онтогенеза Отряд грызуны
Отряд грызуны Достижения в получении трансгенных животных
Достижения в получении трансгенных животных Гормоны. Системы регуляции организма
Гормоны. Системы регуляции организма Классификация вирусов по Балтимору
Классификация вирусов по Балтимору Микробиология ғылым ретінде. Микробиология пәні
Микробиология ғылым ретінде. Микробиология пәні Сосуды верхней конечности. (Занятие 3)
Сосуды верхней конечности. (Занятие 3) Скелетные ткани: хрящевые костные
Скелетные ткани: хрящевые костные Функциональная анатомия костной системы
Функциональная анатомия костной системы Живые клетки
Живые клетки Законы зависимости организмов от факторов среды
Законы зависимости организмов от факторов среды Миграция животных
Миграция животных Процеси гниття. Хімізм процесу гниття
Процеси гниття. Хімізм процесу гниття Беспозвоночные животные
Беспозвоночные животные Анатомо-физиологические особенности нервной системы. Развитие нервной системы в онтогенезе
Анатомо-физиологические особенности нервной системы. Развитие нервной системы в онтогенезе Общая характеристика класса земноводные, или амфибии
Общая характеристика класса земноводные, или амфибии