Содержание
- 2. Carbon dioxide in blood CO2 is more soluble than oxygen but also reacts chemically with water
- 3. Carbon dioxide in blood there is much more CO2 in blood than oxygen both more dissolved
- 4. Carbon dioxide in arterial blood there is almost three times as much CO2 in arterial blood
- 5. Acid base balance CO2 is a major part of the system controlling pH of blood much
- 6. Dissolution of CO2 in water at a pCO2 of 5.3 kpa water dissolves 1.2 mmol.l-1 dissolved
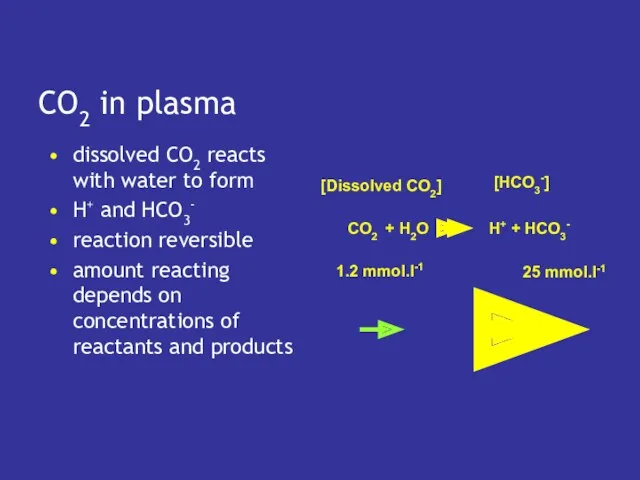
- 7. CO2 in plasma dissolved CO2 reacts with water to form H+ and HCO3- reaction reversible amount
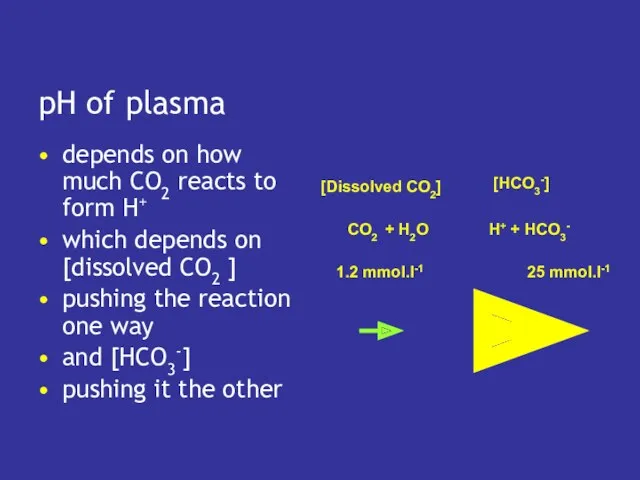
- 8. pH of plasma depends on how much CO2 reacts to form H+ which depends on [dissolved
- 9. Dissolved CO2 depends directly on pCO2 if pCO2 rises pH will fall if pCO2 falls pH
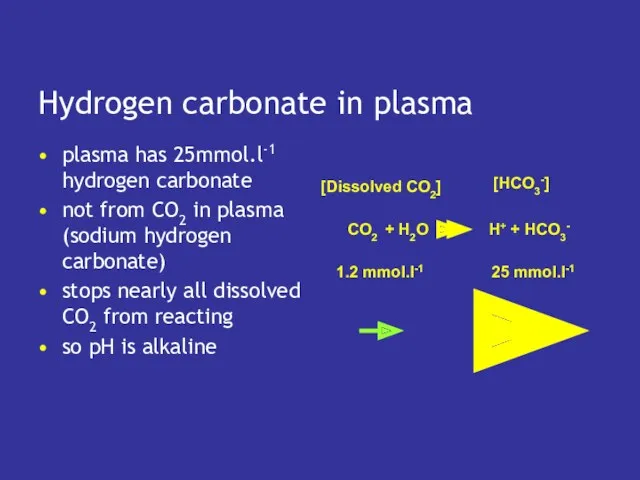
- 10. Hydrogen carbonate in plasma plasma has 25mmol.l-1 hydrogen carbonate not from CO2 in plasma (sodium hydrogen
- 11. Henderson Hasselbalch equation the above in maths pH=pK + log ([HCO3-]/(pCO2 x 0.23)) pK = 6.1
- 12. In arterial blood the pCO2 is a critical determinant of pH but so is [HCO3-] where
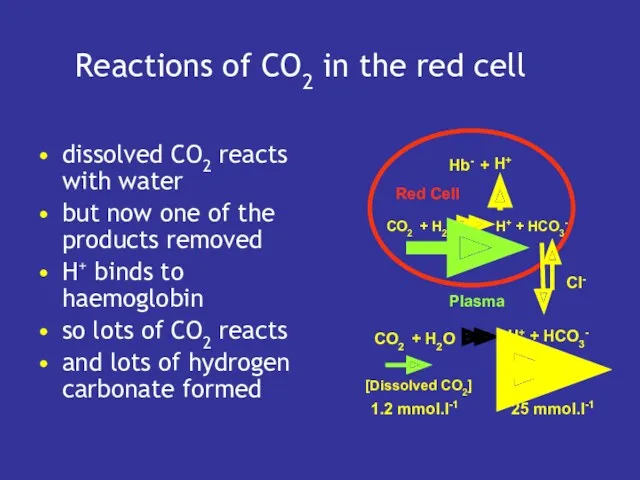
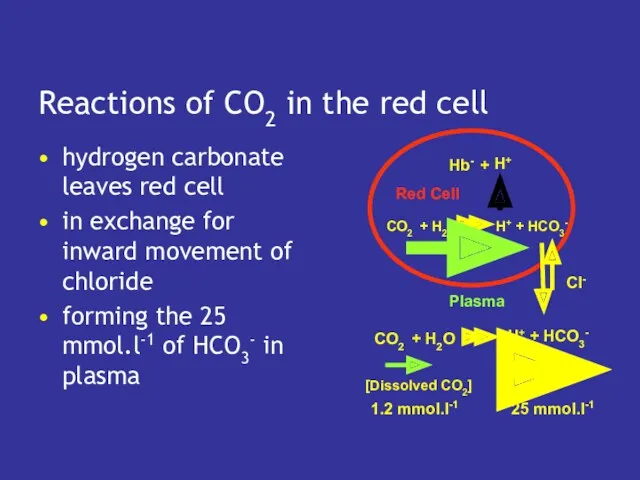
- 13. Reactions of CO2 in the red cell dissolved CO2 reacts with water but now one of
- 14. Reactions of CO2 in the red cell hydrogen carbonate leaves red cell in exchange for inward
- 15. So the pH of plasma depends on the ratio of the reaction of CO2 in the
- 16. Plasma hydrogen carbonate does not change much with pCO2 because the reactions of CO2 in the
- 17. Don’t forget the kidney in the whole body the kidney controls the hydrogen carbonate concentration in
- 18. Buffering if the body produces acid this reacts with hydrogen carbonate to form CO2 which is
- 19. Arterial pCO2 determined by alveolar pCO2 determines dissolved CO2 and so affects pH
- 20. What about venous blood? in venous blood pCO2 is higher so more CO2 dissolves but
- 21. Buffering of H+ by Hb depends on oxygenation the more oxygen bound the less CO2 is
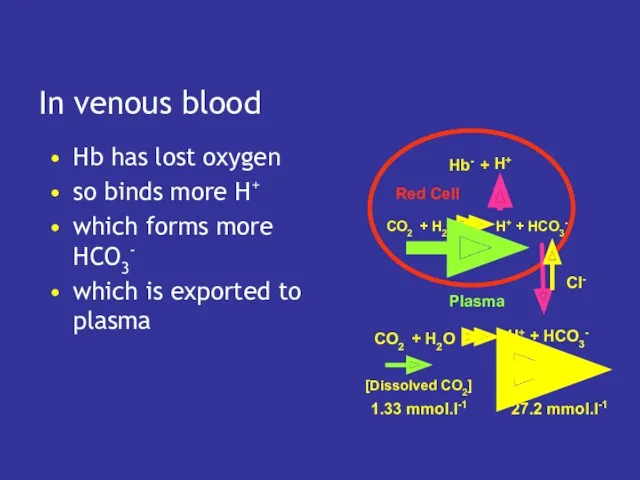
- 22. In venous blood Hb has lost oxygen so binds more H+ which forms more HCO3- which
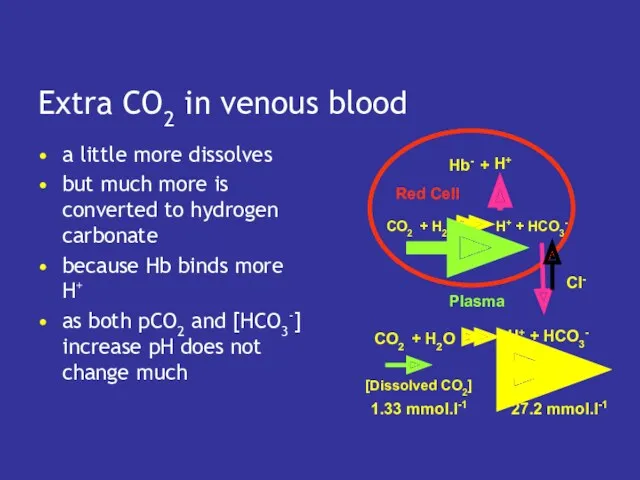
- 23. Extra CO2 in venous blood a little more dissolves but much more is converted to hydrogen
- 24. When venous blood reaches the lungs Hb picks up oxygen so gives up H+ reacts with
- 25. Carbamino compounds CO2 also binds directly to proteins contributes to CO2 transport but not acid base
- 26. The numbers - arterial blood plasma dissolves 0.7 mmol CO2 per litre of blood (plasma only
- 27. The total - arterial blood contains 21.5 mmol CO2 per litre
- 28. The numbers - venous blood plasma dissolves 0.8 mmol CO2 per litre of blood (plasma only
- 29. The total - venous blood contains 23.5 mmol CO2 per litre
- 30. Transported carbon dioxide = 23.5 -21.5 = 2 mmol per litre of blood only about 10%
- 32. Скачать презентацию






















 Гистология. Электронный альбом
Гистология. Электронный альбом Овощи и фрукты – самые витаминные продукты
Овощи и фрукты – самые витаминные продукты Виртуальная экскурсия в природную экосистему Пионерского озера и прибрежных территорий часть 1
Виртуальная экскурсия в природную экосистему Пионерского озера и прибрежных территорий часть 1 Розмноження медоносних бджіл
Розмноження медоносних бджіл Птахи нашої місцевості
Птахи нашої місцевості Животные крайнего Севера
Животные крайнего Севера Популяции
Популяции Гүлдің құрылысы
Гүлдің құрылысы prezentatsiya_k_uroku_leksicheskie_sredstva_vyrazitelnosti_7_klass
prezentatsiya_k_uroku_leksicheskie_sredstva_vyrazitelnosti_7_klass Гаструляция и становление антериальнопостериальной оси тела эмбриона
Гаструляция и становление антериальнопостериальной оси тела эмбриона Кормление кроликов
Кормление кроликов Division Lichenophyta
Division Lichenophyta Исследовательская деятельность на уроках биологии и во внеурочное время как средство развития творческих способностей
Исследовательская деятельность на уроках биологии и во внеурочное время как средство развития творческих способностей Липидтердің алмасуы Липидтердің анаболитикалық және катаболитикалық жолдармен пайда болуы және биологиялық рөлі
Липидтердің алмасуы Липидтердің анаболитикалық және катаболитикалық жолдармен пайда болуы және биологиялық рөлі Одноклітинні організми. Лабораторне дослідження
Одноклітинні організми. Лабораторне дослідження Анатомо-физиологические особенности сердечно- сосудистой системы. Анатомия сердца
Анатомо-физиологические особенности сердечно- сосудистой системы. Анатомия сердца Типы межклеточной сигнализации
Типы межклеточной сигнализации Тип Хордовые. Бесчерепные. Ланцетник
Тип Хордовые. Бесчерепные. Ланцетник Значение органов выделения. Строение и функции кожи
Значение органов выделения. Строение и функции кожи Развитие эмбриологии в XVI—XVIII и начале XIX века. (Лекция 10)
Развитие эмбриологии в XVI—XVIII и начале XIX века. (Лекция 10) Желудочно-кишечный тракт
Желудочно-кишечный тракт Кошка, как объект физического исследования
Кошка, как объект физического исследования Многообразие и значение пресмыкающихся
Многообразие и значение пресмыкающихся Физиология и биохимия микроорганизмов. Биохимическая идентификация бактерий (часть 2)
Физиология и биохимия микроорганизмов. Биохимическая идентификация бактерий (часть 2) Гаплоидтық технология
Гаплоидтық технология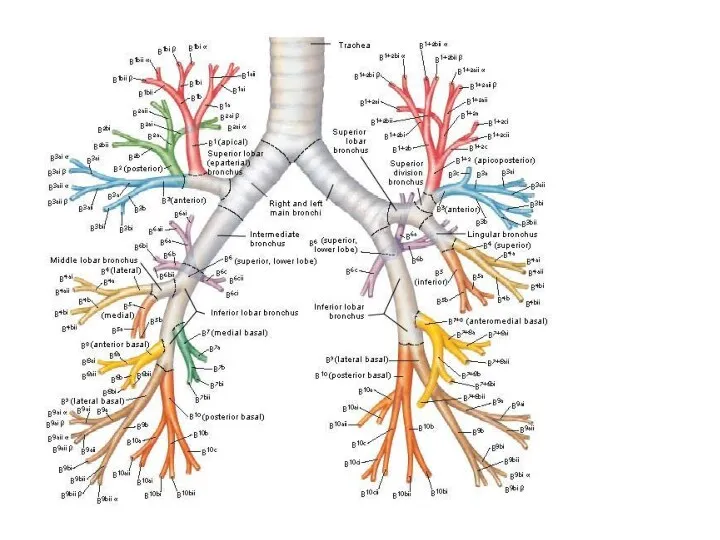 Бронхиальное дерево
Бронхиальное дерево Лекарственные растения Мангистауской области
Лекарственные растения Мангистауской области Биология – наука о живом мире. Общие свойства живых организмов
Биология – наука о живом мире. Общие свойства живых организмов