Содержание
- 2. Plan of lecture: 1 Type of root systems. Morphology of root. 2 Anatomical structure of root.
- 3. Main literatures: 1 Бавтуто Г.А. Практикум по анатомии и морфологии растений. – Минск: Новое знание, 2002.
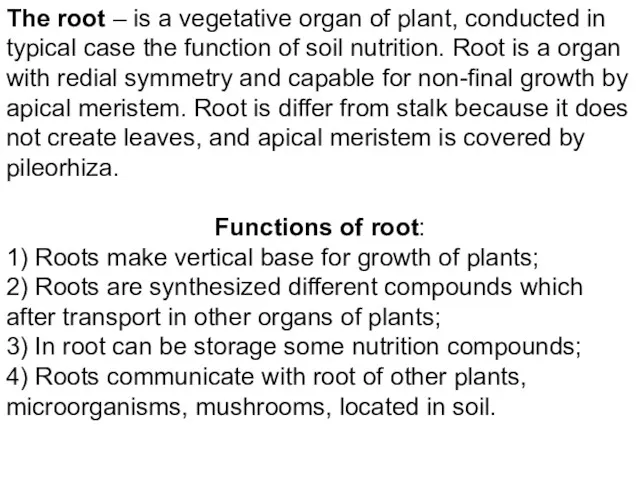
- 4. The root – is a vegetative organ of plant, conducted in typical case the function of
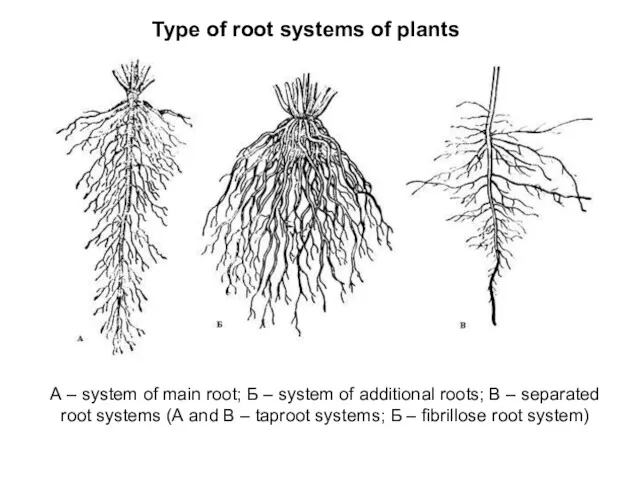
- 5. Type of root systems of plants А – system of main root; Б – system of
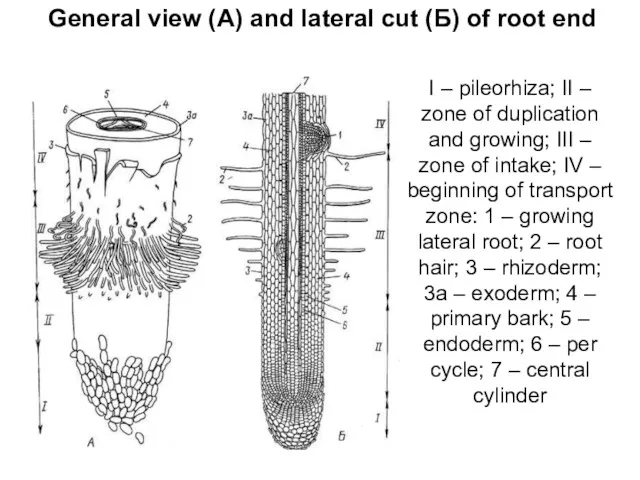
- 6. I – pileorhiza; II – zone of duplication and growing; III – zone of intake; IV
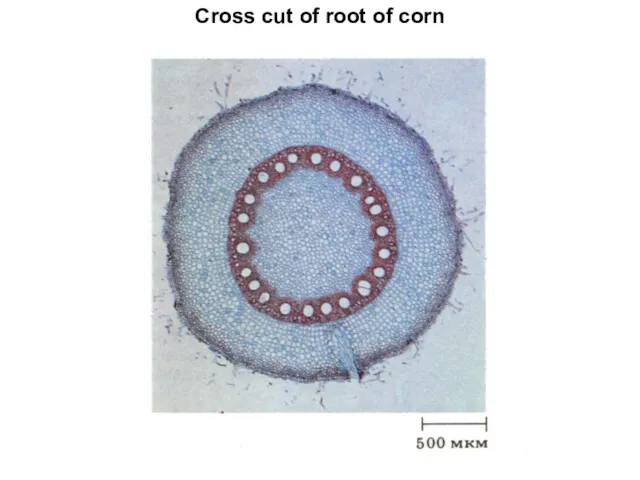
- 7. Cross cut of root of corn
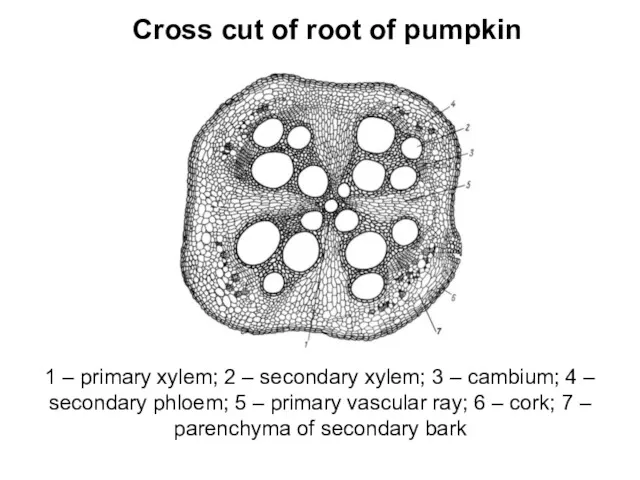
- 8. Cross cut of root of pumpkin 1 – primary xylem; 2 – secondary xylem; 3 –
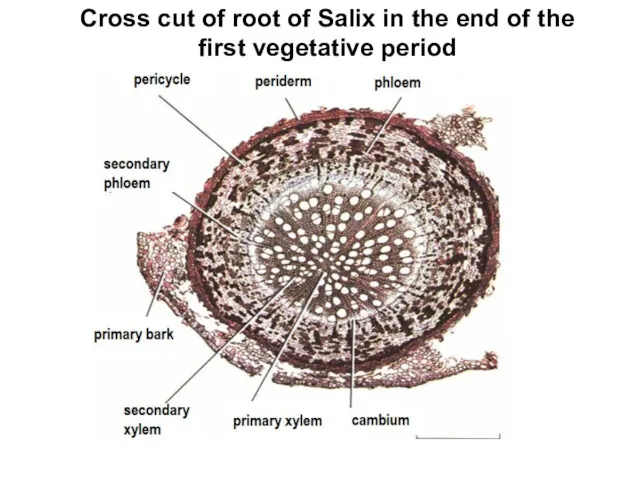
- 9. Cross cut of root of Salix in the end of the first vegetative period
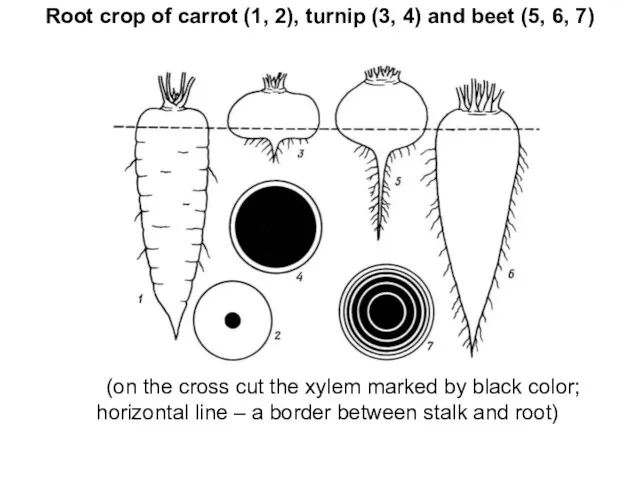
- 10. Root crop of carrot (1, 2), turnip (3, 4) and beet (5, 6, 7) (on the
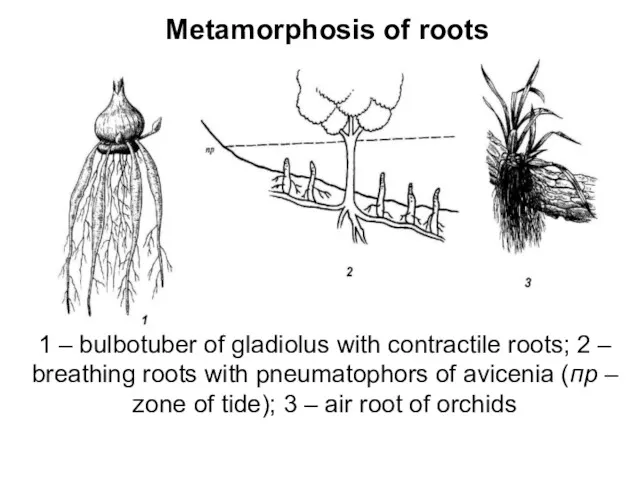
- 11. Metamorphosis of roots 1 – bulbotuber of gladiolus with contractile roots; 2 – breathing roots with
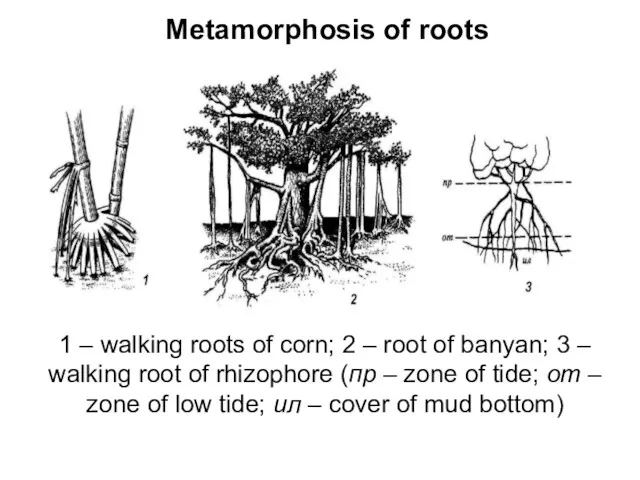
- 12. Metamorphosis of roots 1 – walking roots of corn; 2 – root of banyan; 3 –
- 13. Control questions: 1 What are the main and additional functions of roots? 2 Which root systems
- 15. Скачать презентацию


 Широколиственный лес
Широколиственный лес Царство грибов
Царство грибов Многообразие живой природы
Многообразие живой природы конспект урока по биологии 8 класс с мультимедийной презентацией Пищеварительная система
конспект урока по биологии 8 класс с мультимедийной презентацией Пищеварительная система Проект учащихся 5 класса ВЛИЯНИЕ СВЕТА НА ПРОРАСТАНИЕ СЕМЯН ПОДСОЛНЕЧНИКА
Проект учащихся 5 класса ВЛИЯНИЕ СВЕТА НА ПРОРАСТАНИЕ СЕМЯН ПОДСОЛНЕЧНИКА Органическое вещество почвы
Органическое вещество почвы Круговорот веществ в природе
Круговорот веществ в природе Цветок. Плод. Семя
Цветок. Плод. Семя Семейства растений. Семейства крестоцветные и розоцветные
Семейства растений. Семейства крестоцветные и розоцветные Плаунтәрізді өсімдіктер
Плаунтәрізді өсімдіктер Общая характеристика грибов
Общая характеристика грибов Биоценозы. Концепция биоценоза
Биоценозы. Концепция биоценоза Органические вещества в составе клетки
Органические вещества в составе клетки Уровни организации живых организмов
Уровни организации живых организмов Лесные ягоды. Грибы
Лесные ягоды. Грибы Отдел зеленые водоросли. Класс харовые
Отдел зеленые водоросли. Класс харовые Методы изучения биологии
Методы изучения биологии Рослини Миколаївщини
Рослини Миколаївщини Презентация по биологии Внутренняя среда организма. Кровь
Презентация по биологии Внутренняя среда организма. Кровь Определение пола и наследование, сцепленное с полом
Определение пола и наследование, сцепленное с полом Гормоны строение, классификация, функции, биосинтез, транспорт. (Лекция 10)
Гормоны строение, классификация, функции, биосинтез, транспорт. (Лекция 10) презент плесн.грибы
презент плесн.грибы Хрящевые рыбы
Хрящевые рыбы Покровные и проводящие растительные ткани
Покровные и проводящие растительные ткани Червона книга України
Червона книга України Формирование УУД на уроках биологии и химии.
Формирование УУД на уроках биологии и химии. Атлас млекопитающих Москвы и Подмосковья
Атлас млекопитающих Москвы и Подмосковья Презентация Вид. Критерии вида
Презентация Вид. Критерии вида