Содержание
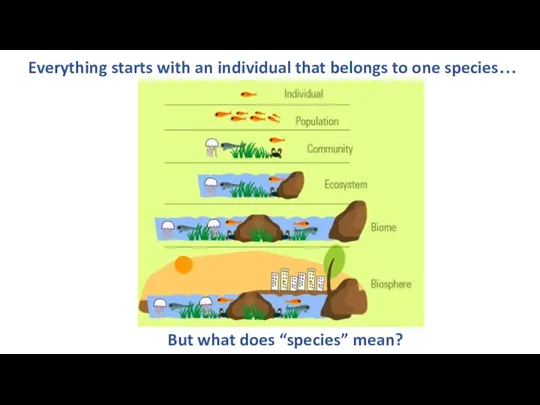
- 2. Everything starts with an individual that belongs to one species… But what does “species” mean?
- 3. What species do you already know? Ceratophylum demersum Myriophyllum spicatum Homo sapiens
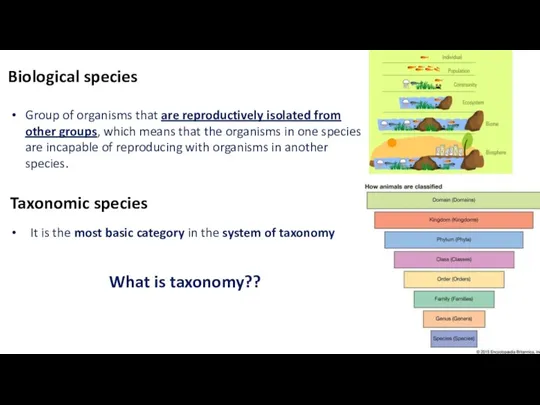
- 4. Biological species Taxonomic species
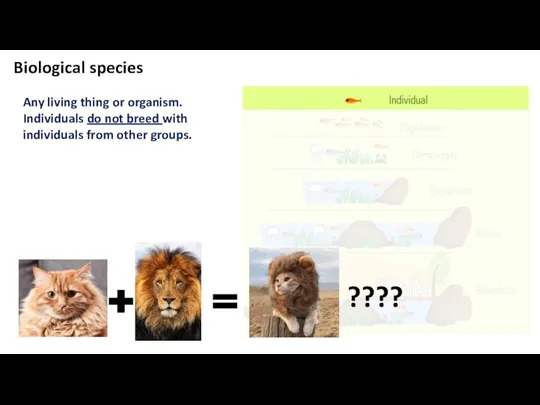
- 5. Biological species Any living thing or organism. Individuals do not breed with individuals from other groups.
- 6. Biological species Taxonomic species It is the most basic category in the system of taxonomy Group
- 7. Taxonomist
- 8. Taxonomy Derived from the Greek taxis (“arrangement”) and nomos (“law”) Taxonomy is the “science of classification”
- 9. Benefits of Classifying (taxonomy) Accurately and uniformly names organisms Prevents misnomers such as “starfish” or “jellyfish”
- 10. Confusion in Using Different Languages for Names
- 11. Latin Names are Understood by all Taxonomists
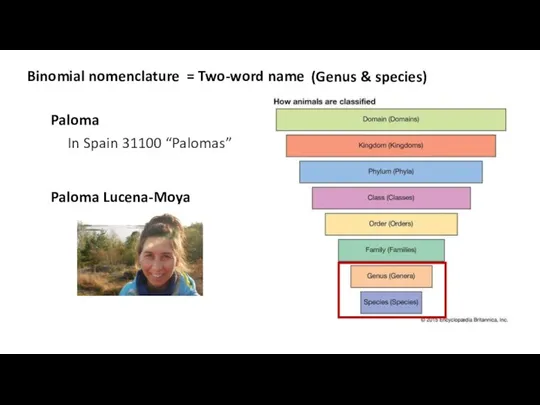
- 12. Binomial nomenclature = Two-word name (Genus & species) Paloma In Spain 31100 “Palomas” Paloma Lucena-Moya
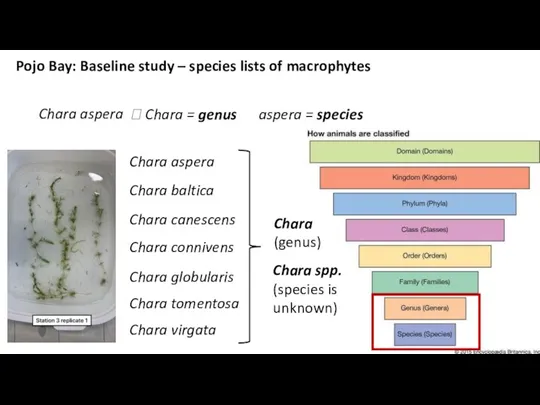
- 13. Chara canescens Chara connivens Chara globularis Chara tomentosa Chara virgata Pojo Bay: Baseline study – species
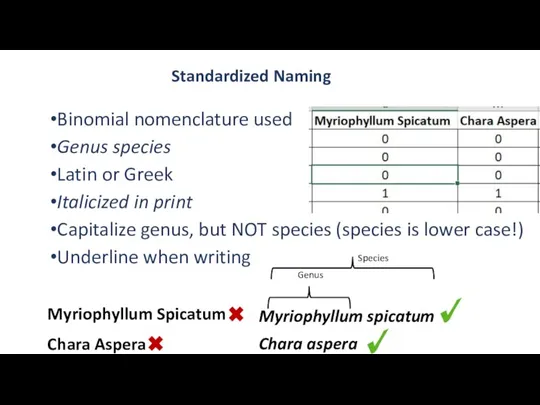
- 14. Standardized Naming Binomial nomenclature used Genus species Latin or Greek Italicized in print Capitalize genus, but
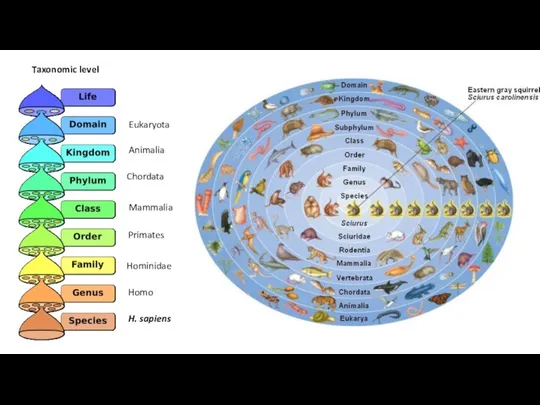
- 15. Taxonomic level Eukaryota Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primates Hominidae Homo H. sapiens
- 16. Taxonomy of Red-throated Diver – Gavia stellata Animalia Chordata Vertebrata Tetrapoda Aves Gaviiformes Gaviidae stellata Gavia
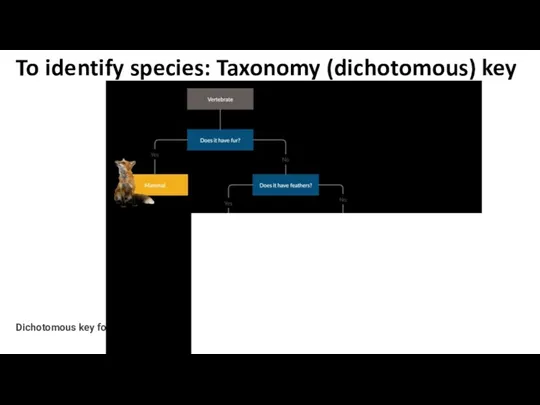
- 17. To identify species: Taxonomy (dichotomous) key Please think in one vertebrate animal !! (keep in mind!)
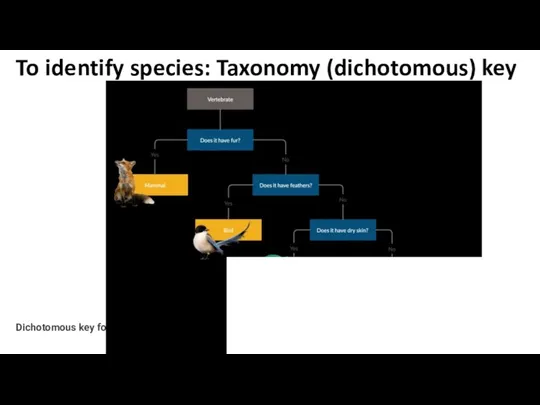
- 18. Dichotomous key for animals To identify species: Taxonomy (dichotomous) key
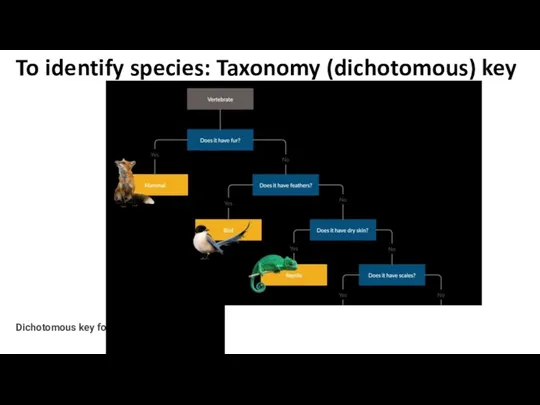
- 19. Dichotomous key for animals To identify species: Taxonomy (dichotomous) key
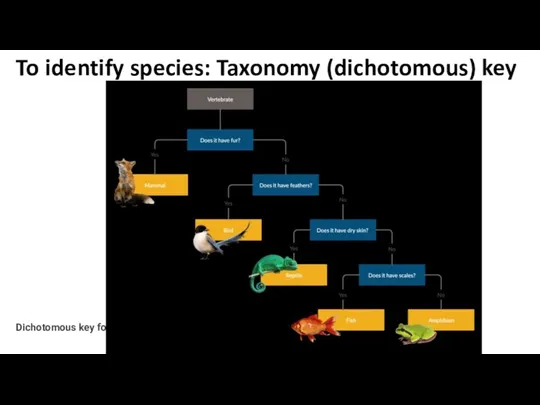
- 20. Dichotomous key for animals To identify species: Taxonomy (dichotomous) key
- 21. Dichotomous key for animals To identify species: Taxonomy (dichotomous) key
- 22. Dichotomous key for animals To identify species: Taxonomy (dichotomous) key
- 23. To identify species: Taxonomy (dichotomous) key “Dichotomous” means “divided into two parts” dichotomous keys always give
- 24. Why do we need to learn about species? Threatened species Indicator species Species lists Management, Habitat
- 25. How to find information about species?
- 26. HMAP Project: History of Marine Animal Populations http://www.coml.org/history-marine-animal-populations-hmap/
- 27. http://stateofthebalticsea.helcom.fi/
- 28. European Register of Marine Species http://www.marbef.org/data/erms.php
- 29. http://www.marinespecies.org/index.php WoRMS: World Register of Marine Species
- 30. VELMU http://www.ymparisto.fi/en-US/VELMU
- 31. https://www.nobanis.org/ European Network on Invasive Alien Species
- 32. Choose one species from the Baltic area and one species from your home country (does not
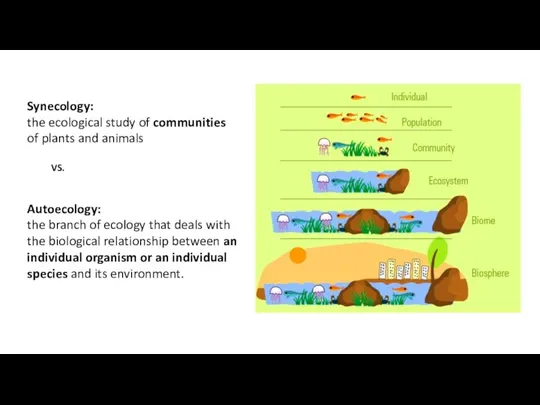
- 34. Synecology: the ecological study of communities of plants and animals Autoecology: the branch of ecology that
- 35. Phytoplankton From the Greek words phyto (plant) and plankton (made to wander or drift) Phytoplankton are
- 36. When conditions are right, phytoplankton populations can grow explosively, a phenomenon known as a bloom. Blooms
- 37. Phytobenthos Phyto + benthos (benthos = from Greek, “the depths”). Microscopic plants that live attached to
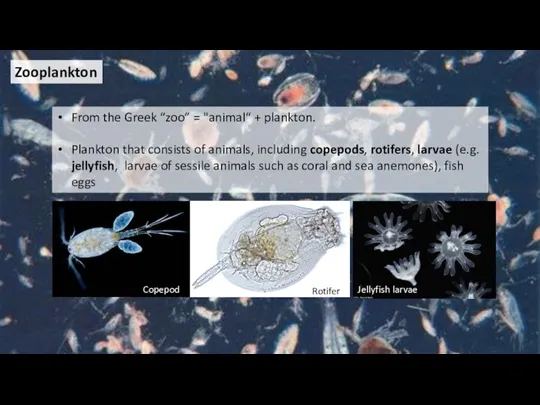
- 38. Zooplankton From the Greek “zoo” = "animal“ + plankton. Plankton that consists of animals, including copepods,
- 39. Zoo + “benthos”? Benthos is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the
- 40. Bioinvasions (in the Baltic Sea) Alien species (=nonnative, nonindigenous, exotic, introduced) Invasive species ? alien species
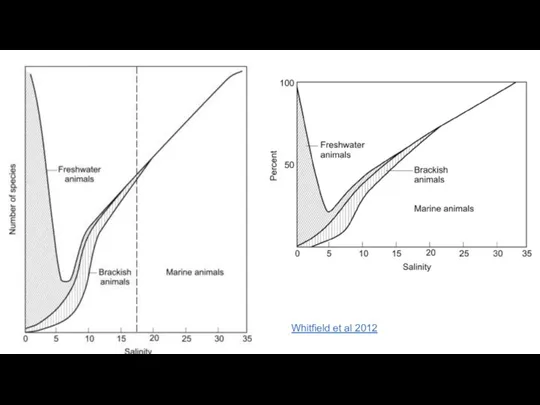
- 41. Whitfield et al 2012
- 43. Скачать презентацию






















 Общая характеристика царства животные
Общая характеристика царства животные Sense organs. Ear and nose
Sense organs. Ear and nose Предмет, задачи, методы исследования. Учение И.П. Павлова о высшей нервной деятельности
Предмет, задачи, методы исследования. Учение И.П. Павлова о высшей нервной деятельности Условия роста и развития растения
Условия роста и развития растения Вирусные болезни растений. Фитопатогенные вирусы и микоплазмы. (Лекция 6)
Вирусные болезни растений. Фитопатогенные вирусы и микоплазмы. (Лекция 6) Капітальний та поточний ремонт об'єктів благоустрою зеленого господарства
Капітальний та поточний ремонт об'єктів благоустрою зеленого господарства Органические вещества
Органические вещества Химический состав клеток
Химический состав клеток Morphometrical and histological comparative analyses of omnivorous birds gastrointestinal tract
Morphometrical and histological comparative analyses of omnivorous birds gastrointestinal tract Фізіологія дихальної системи. Зовнішнє дихання
Фізіологія дихальної системи. Зовнішнє дихання Международный день птиц. Сказка Курочка Ряба - Машина времени
Международный день птиц. Сказка Курочка Ряба - Машина времени Игра В мире животных
Игра В мире животных Конкурс:Экология. Книга. Мы. Лучший библиотечный цветник
Конкурс:Экология. Книга. Мы. Лучший библиотечный цветник Молюски, їхня різноманітність та значення
Молюски, їхня різноманітність та значення Липидтер алмасуы
Липидтер алмасуы Выделение. Процесс выделения у растений и животных
Выделение. Процесс выделения у растений и животных мультимедийная презентация к уроку Водоросли Разнообразие растений. значение растений в природе и жизни человека
мультимедийная презентация к уроку Водоросли Разнообразие растений. значение растений в природе и жизни человека Конкурс внутреннего и внешнего озеленения образовательных организаций
Конкурс внутреннего и внешнего озеленения образовательных организаций 4 стихии зарождения жизни
4 стихии зарождения жизни Скелет туловища и верхних и нижних конечностей
Скелет туловища и верхних и нижних конечностей Физиология питания и пищеварения. Пищеварение в полости рта
Физиология питания и пищеварения. Пищеварение в полости рта Вены большого круга кровообращения
Вены большого круга кровообращения Дикие животные леса. Для дошкольников. (Часть 1)
Дикие животные леса. Для дошкольников. (Часть 1) Павукоподібні
Павукоподібні Красная книга Донецка
Красная книга Донецка Проектно-исследовательские технологии в эколого-биологической деятельности
Проектно-исследовательские технологии в эколого-биологической деятельности По лесным тропинкам. Часть 2
По лесным тропинкам. Часть 2 Тип Хордовые
Тип Хордовые