Содержание
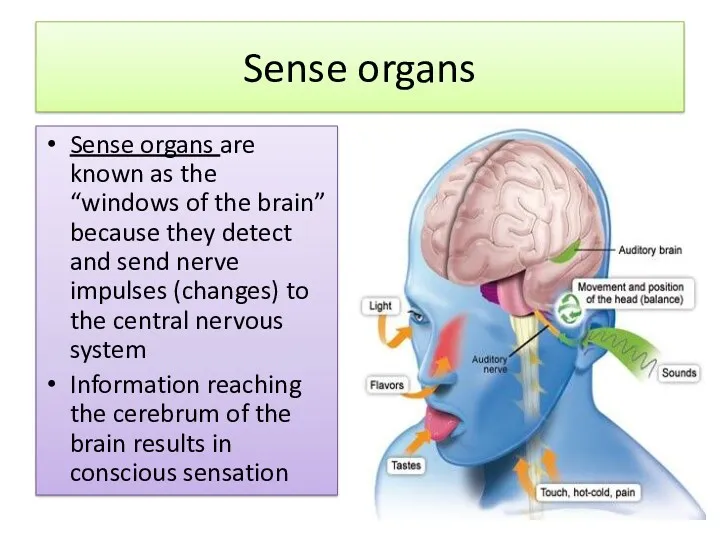
- 2. Sense organs Sense organs are known as the “windows of the brain” because they detect and
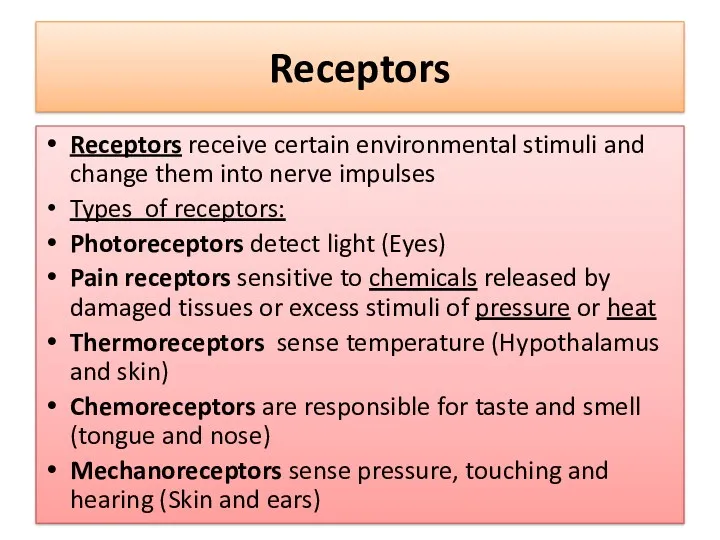
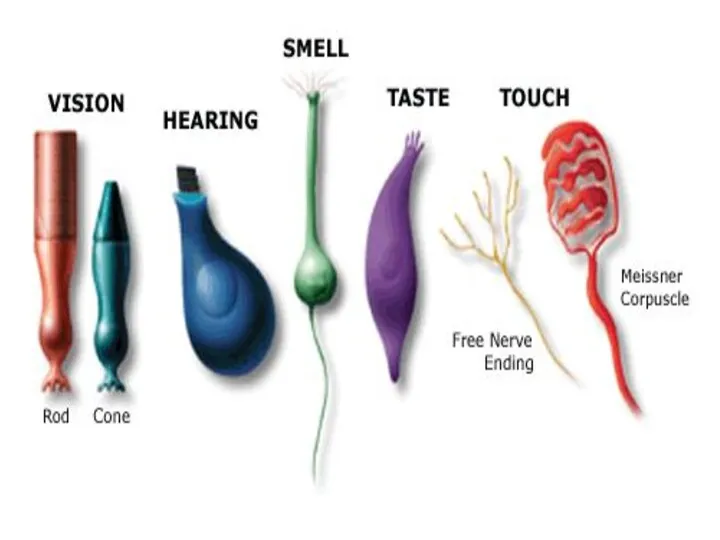
- 3. Receptors Receptors receive certain environmental stimuli and change them into nerve impulses Types of receptors: Photoreceptors
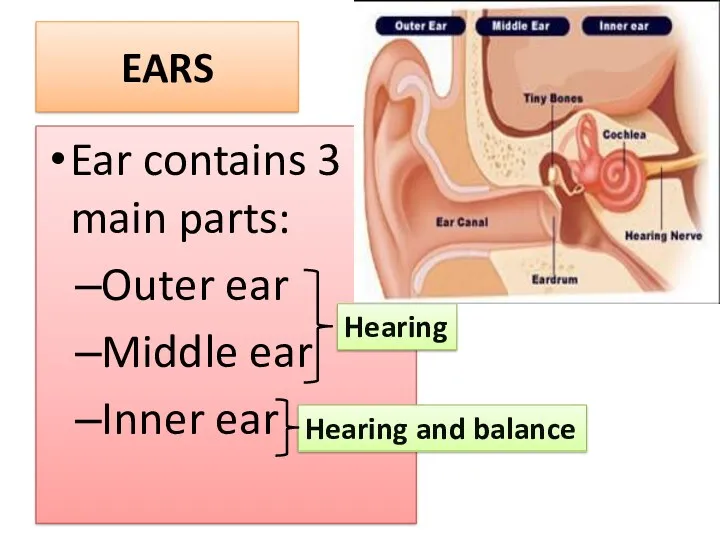
- 5. It has 2 sensory functions: Hearing Maintaning balance or equilibrium EARS
- 6. EARS Ear contains 3 main parts: Outer ear Middle ear Inner ear Hearing Hearing and balance
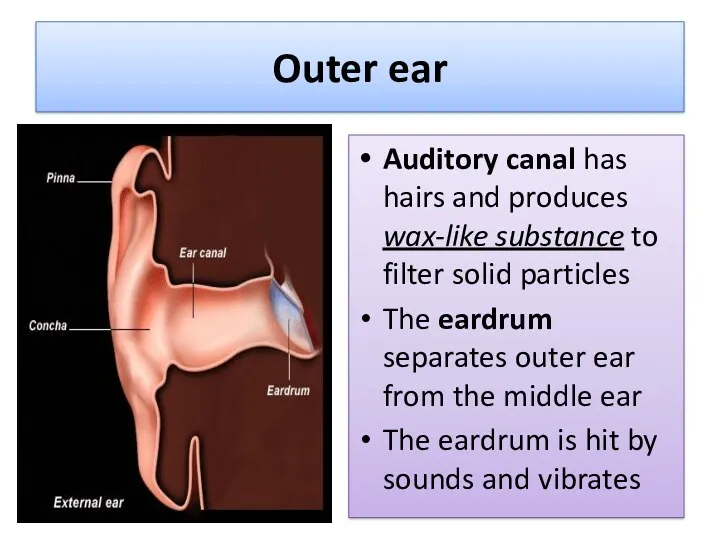
- 7. Outer ear Auditory canal has hairs and produces wax-like substance to filter solid particles The eardrum
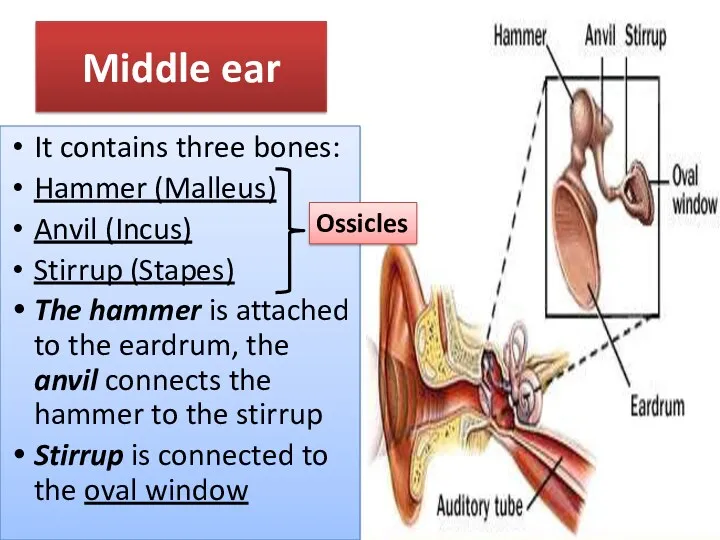
- 8. Middle ear It contains three bones: Hammer (Malleus) Anvil (Incus) Stirrup (Stapes) The hammer is attached
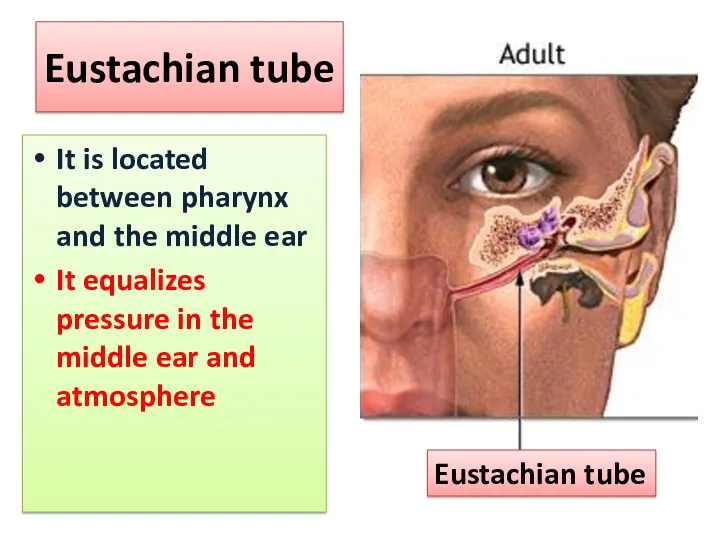
- 9. Eustachian tube It is located between pharynx and the middle ear It equalizes pressure in the
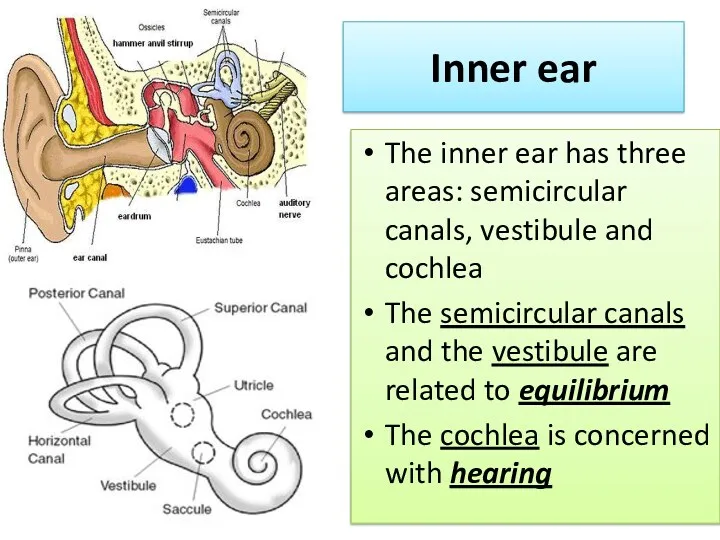
- 10. Inner ear The inner ear has three areas: semicircular canals, vestibule and cochlea The semicircular canals
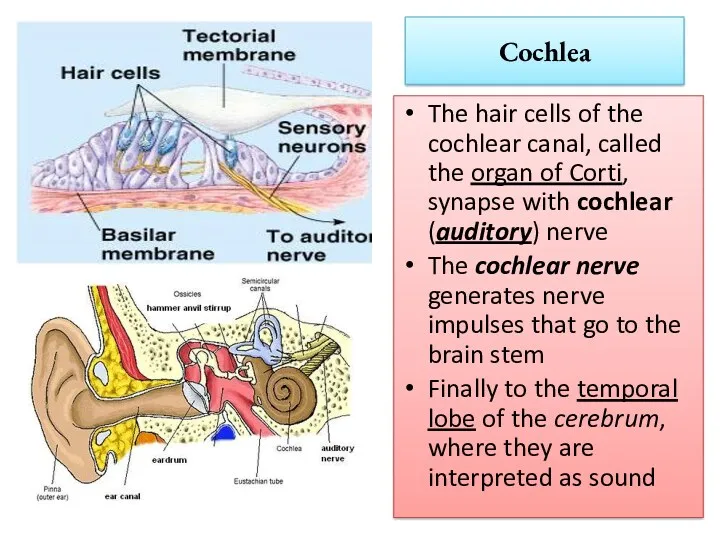
- 11. Cochlea The hair cells of the cochlear canal, called the organ of Corti, synapse with cochlear
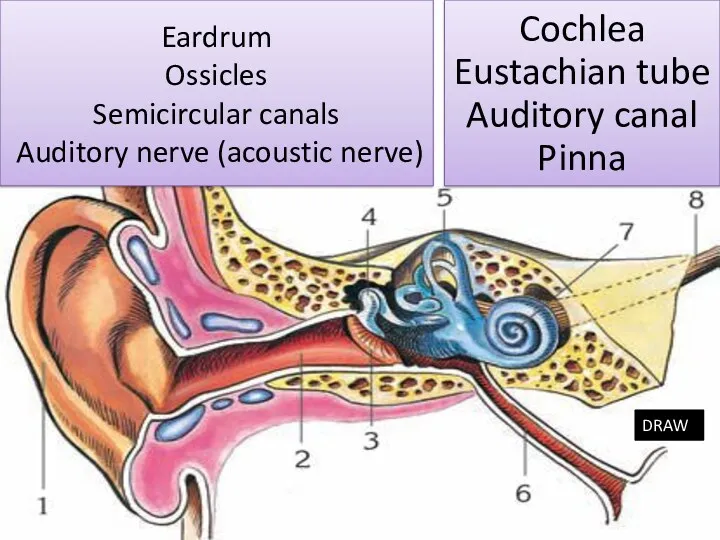
- 12. Eardrum Ossicles Semicircular canals Auditory nerve (acoustic nerve) Cochlea Eustachian tube Auditory canal Pinna DRAW
- 13. Nose Nose is the organ of the body involved in both respiration and smell The reception
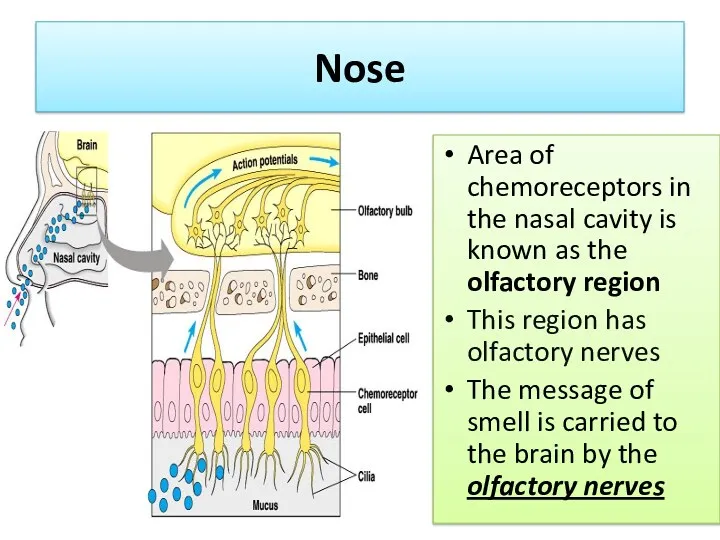
- 14. Nose Area of chemoreceptors in the nasal cavity is known as the olfactory region This region
- 16. Скачать презентацию

 Antigen-antibody reactions and selected tests
Antigen-antibody reactions and selected tests Строение эукариотических клеток
Строение эукариотических клеток Лекарственные растения рек Золотой Китат и Алчедат
Лекарственные растения рек Золотой Китат и Алчедат Огуречные именины. Правила игры
Огуречные именины. Правила игры Семейство Паслёновые
Семейство Паслёновые Поведінка риб
Поведінка риб Хищные растения
Хищные растения Майстерність маскування
Майстерність маскування Разнообразие животных
Разнообразие животных Применение БАДов
Применение БАДов Органические вещества
Органические вещества урок красная книга Мордовии
урок красная книга Мордовии Типы развития насекомых. Насекомые с неполным превращением
Типы развития насекомых. Насекомые с неполным превращением ВКР: Иммобилизованный биокатализатор на основе адгезированных амидазосодержащих клеток родококков для синтеза акриловой кислоты
ВКР: Иммобилизованный биокатализатор на основе адгезированных амидазосодержащих клеток родококков для синтеза акриловой кислоты Морфокинезиологический анализ пояса верхних конечностей
Морфокинезиологический анализ пояса верхних конечностей Грудная клетка. Лекция № 10
Грудная клетка. Лекция № 10 Nepryamoy_ontogenez
Nepryamoy_ontogenez Исследовательская работа Мой домашний питомец
Исследовательская работа Мой домашний питомец Живые ископаемые
Живые ископаемые Коммуникации у животных
Коммуникации у животных Расы человека
Расы человека Ферменты – 1
Ферменты – 1 Тип Nemathelminthes (Круглые Черви)
Тип Nemathelminthes (Круглые Черви) Будова і функції шкіри
Будова і функції шкіри Healthy eating
Healthy eating Покрытосеменные. Отличительные признаки покрытосеменных
Покрытосеменные. Отличительные признаки покрытосеменных Структура і функції білків. Ферменти. Вітаміни, гормони, фактори росту, їх роль у життєдіяльності організмів
Структура і функції білків. Ферменти. Вітаміни, гормони, фактори росту, їх роль у життєдіяльності організмів Питание бактерий
Питание бактерий