Содержание
- 2. Presentation program Aim of SEM investigation Investigated materials Condition for specimens Preparation Specimen fixation Replica Examples
- 3. Aim of SEM investigation Materials are investigated for: Mikrostructure determination (SE, BSE, AE, EBSD – Electron
- 4. Analytical SEM JEOL JSM-6610A
- 5. Low vacuum SEM JSM- 5800LV
- 6. Types of specimens for SEM investigation Four types of specimens: 1. Metalic 2. Polymer 3. Biological
- 7. Metalic specimens For current conductive metalic specimens any additional preparation is not necessary. They can be
- 8. Specimens from polymers and composites Polymer specimens must be sputtered by the layer of current conductive
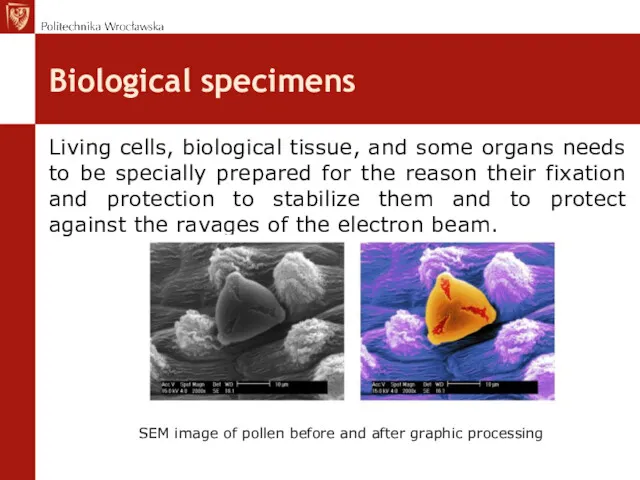
- 9. Biological specimens Living cells, biological tissue, and some organs needs to be specially prepared for the
- 10. Biological specimens Biological specimens must be: Dried, because inside the SEM chamber the material will be
- 11. Flower petals sprinkled by gold
- 12. Samples of powder sputerred by gold
- 13. Biological specimens covered by gold
- 14. Specimen size Specime sizes are limited by dimensions of SEM support table. Typical values are: -
- 15. Specimens embeding Specimens are embeded at epoxy resin for the reason of better mounting and correction
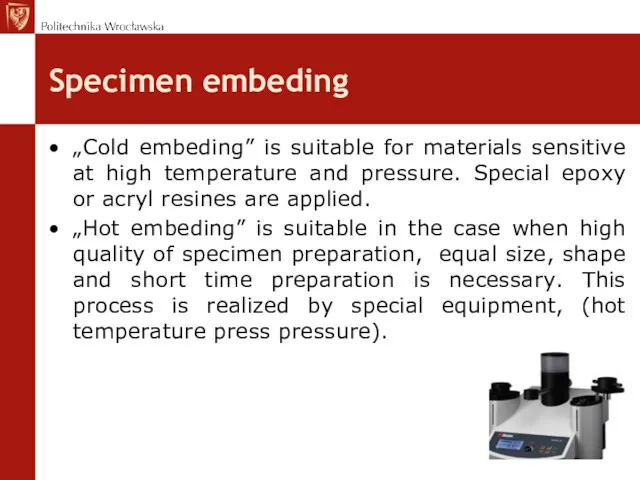
- 16. Specimen embeding „Cold embeding” is suitable for materials sensitive at high temperature and pressure. Special epoxy
- 17. Electrical current conductivity Specimens analyzed by SEM methods must conduct electrical current. If specimen doesn’t conduct
- 18. Specimen preparation Cutting, to obtain dimensions limited by support table disposed inside specimen chamber Cleaning and
- 19. Specimen preparation Grinding, by using special waterproof fine grain grinding papers.
- 20. Specimen preparation Mechanical polishing by using special velvet tissue immersed by diamant paste or water suspension
- 21. Specimen preparation Etching is the last operation necessary for microstructure visualisation. It is realised by application
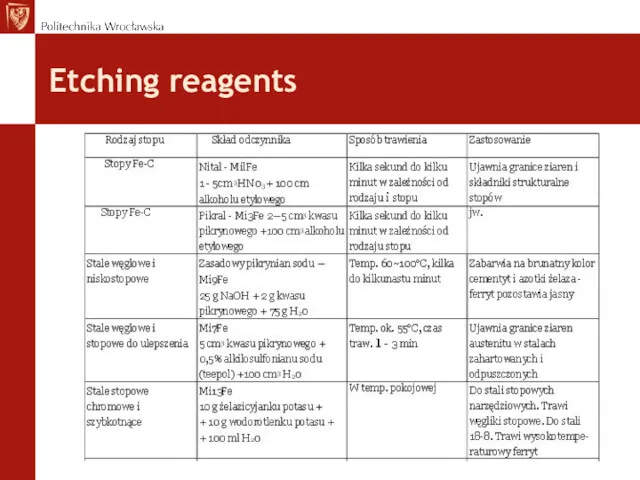
- 22. Etching reagents
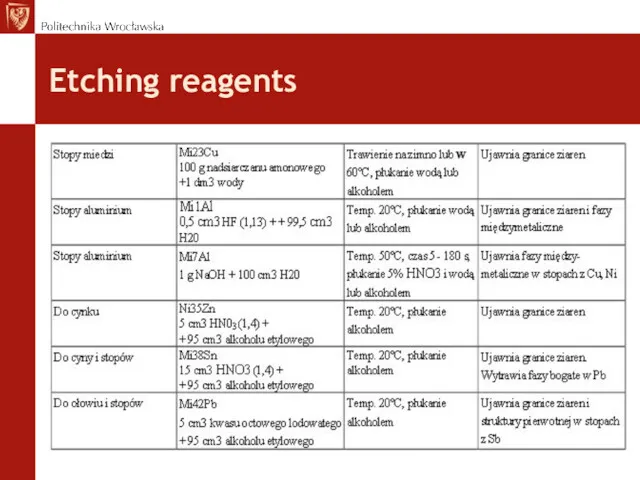
- 23. Etching reagents
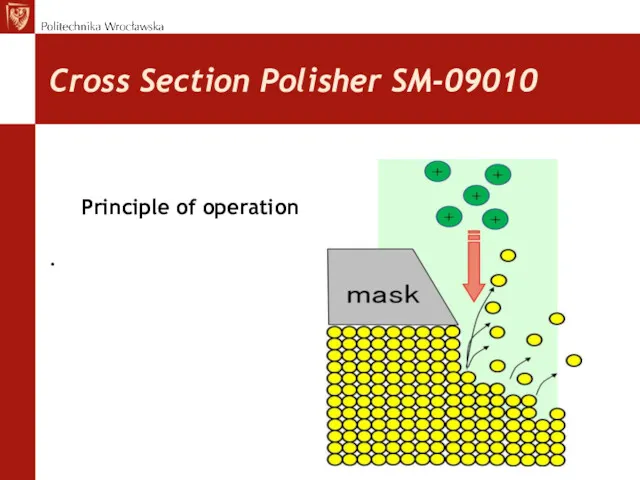
- 24. Cross Section Polisher SM-09010 Cross Section Polisher, makes cross section perpendicullar to the specimen surface. It
- 25. Cross Section Polisher SM-09010 Principle of operation .
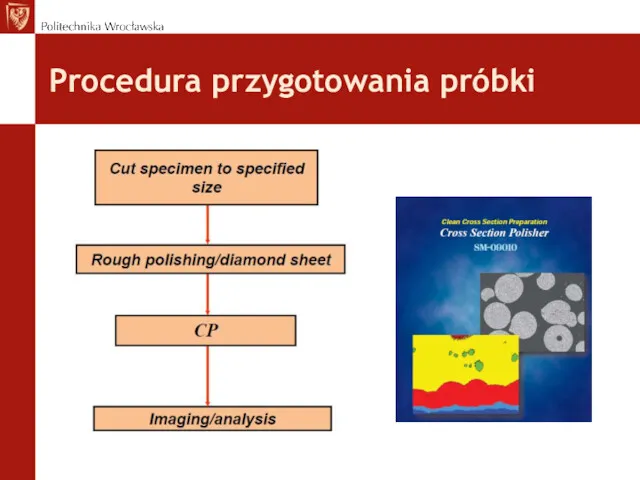
- 26. Procedura przygotowania próbki
- 27. Specimens cutting Saw equipment for sample precission cutting
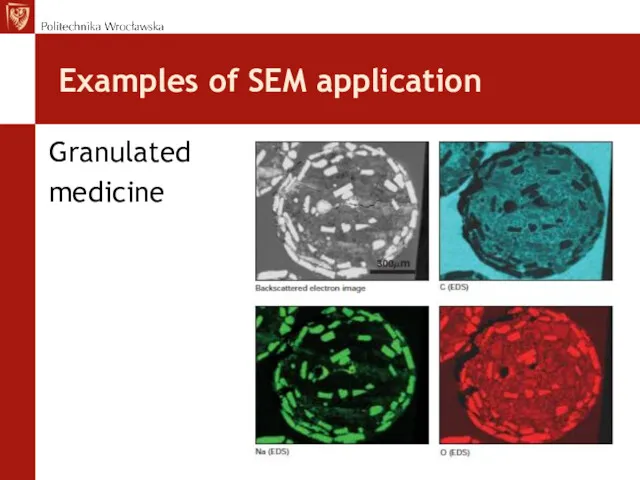
- 28. Examples of SEM application Granulated medicine
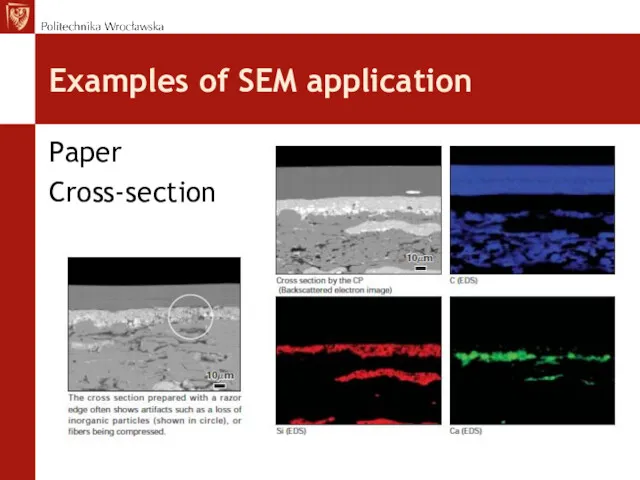
- 29. Examples of SEM application Paper Cross-section
- 30. Evaporisation / sputerring Is realised for covering the surface specimen by C, Au, Pt or Cu
- 31. Evaporation
- 32. Cathode sputtering
- 33. Specimen fixation Current conductive plasticine Sticky carbon discs
- 34. Specimen fixation Double Scotch tape Silver glue
- 35. Specimen fixed to the holder
- 36. Specimens inside the holder
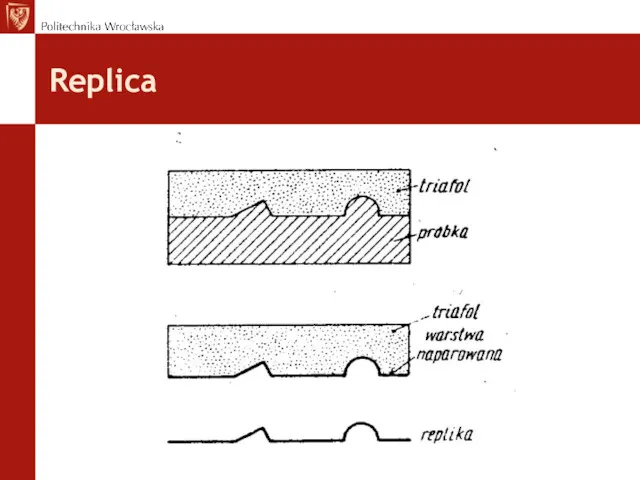
- 37. Replica The aim is to obtain direct microstructure of construction elements without their cutting or destruction.
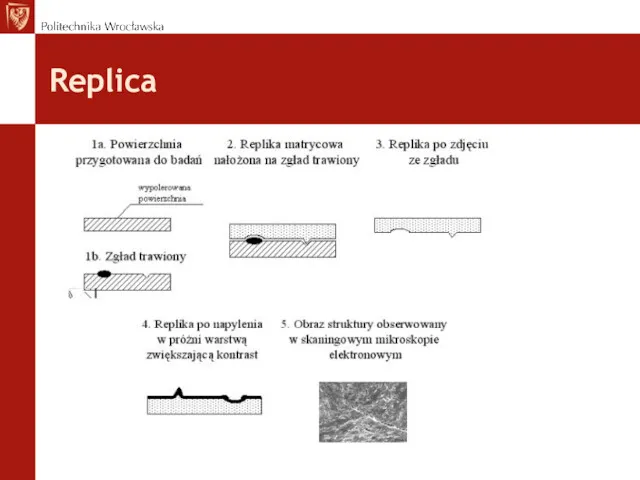
- 38. Replica
- 39. Replica
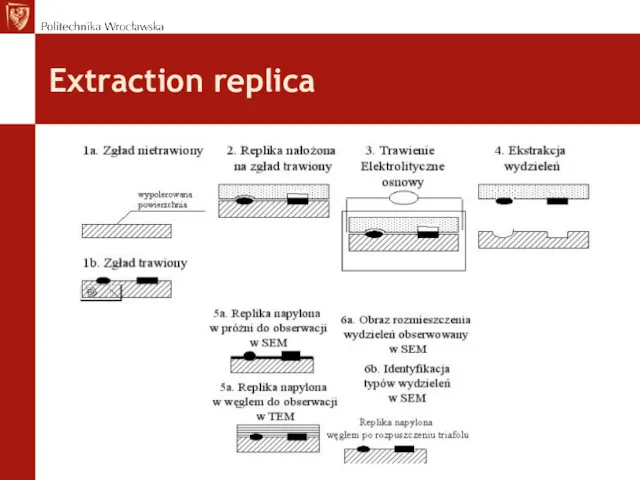
- 40. Extraction replica
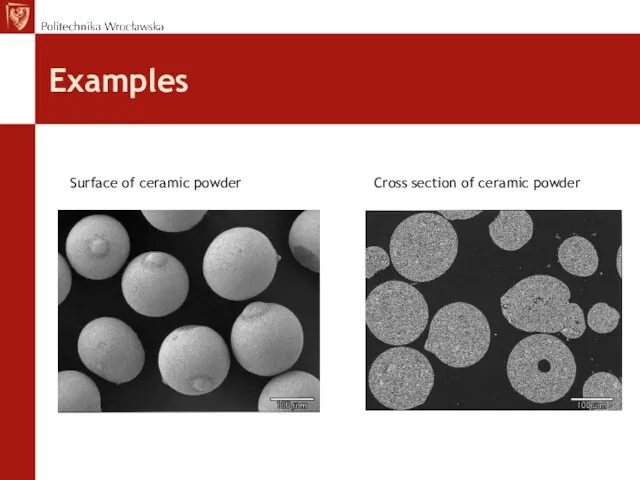
- 41. Examples Surface of ceramic powder Cross section of ceramic powder
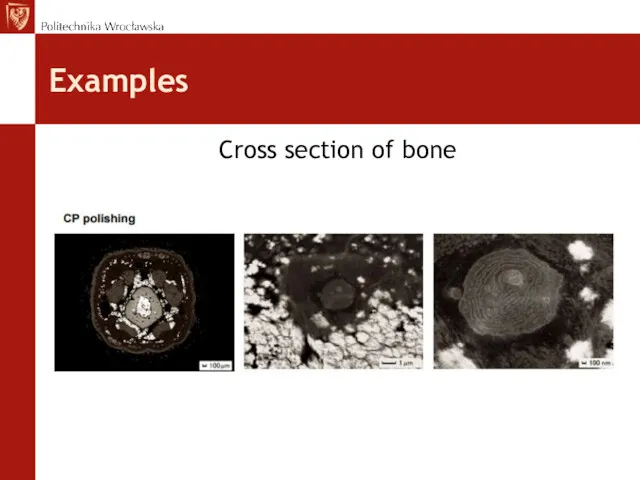
- 42. Examples Cross section of bone
- 43. Pollen of flowers
- 44. Part of insect head
- 45. Brittle fracture
- 47. Скачать презентацию































 Рефлекторная регуляция
Рефлекторная регуляция Ленинградский зоопарк
Ленинградский зоопарк Изменчивость: наследственная и ненаследственная. Мутации
Изменчивость: наследственная и ненаследственная. Мутации Орієнтування тварин
Орієнтування тварин Витамины. Какие манипуляции с продуктами позволяют сохранить в них витамины
Витамины. Какие манипуляции с продуктами позволяют сохранить в них витамины Репликация. Синтез ДНК по матрице ДНК
Репликация. Синтез ДНК по матрице ДНК Строение клетки ткани
Строение клетки ткани Живое вещество биосферы, его функции
Живое вещество биосферы, его функции Репликация. Прокариоты. Репликация фагов
Репликация. Прокариоты. Репликация фагов Zoológico de Madrid
Zoológico de Madrid Собачий клещ (Ixodes ricinus)
Собачий клещ (Ixodes ricinus) Ландшафтні квіткові композиції для оздоблення прибудинкових територій
Ландшафтні квіткові композиції для оздоблення прибудинкових територій ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ДЛЯ ИНТЕРАКТИВНОЙ ДОСКИ. Тест Рыбы 7 класс.
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ ДЛЯ ИНТЕРАКТИВНОЙ ДОСКИ. Тест Рыбы 7 класс. Презентация по биологии на тему _Плауны,хвощи,папоротники_(5 класс) (1)
Презентация по биологии на тему _Плауны,хвощи,папоротники_(5 класс) (1) Основы систематики микроорганизмов
Основы систематики микроорганизмов Хрящевые рыбы
Хрящевые рыбы Основы сравнительной эмбриологии
Основы сравнительной эмбриологии Клетка и методы цитологии
Клетка и методы цитологии Орган слуха и равновесия
Орган слуха и равновесия Функциональная анатомия вегетативной нервной системы. Симпатическая часть ВНС (лекция № 23)
Функциональная анатомия вегетативной нервной системы. Симпатическая часть ВНС (лекция № 23) Комнатные растения в интерьере помещения
Комнатные растения в интерьере помещения Хронобиология и биоритмы человека
Хронобиология и биоритмы человека Окапи
Окапи Соединительная ткань
Соединительная ткань Овчарки со всего мира. Фотографии
Овчарки со всего мира. Фотографии Общие признаки для всех живых организмов
Общие признаки для всех живых организмов Изоляция
Изоляция Соцветия. Строение соцветия
Соцветия. Строение соцветия