Содержание
- 2. DNA
- 3. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA - a polymer of deoxyribo-nucleotides. Usually double stranded. And have double-helix structure. found
- 4. DNA as an acidic substance present in nucleus was first identified by Friedrich Meischer in 1868.
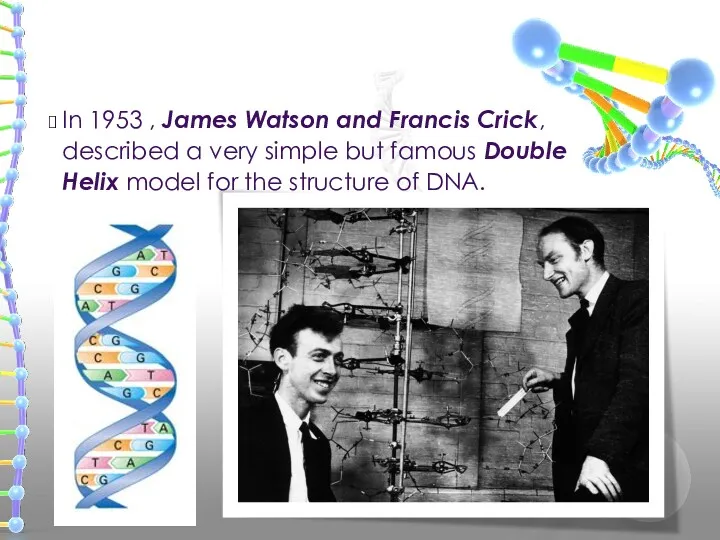
- 5. In 1953 , James Watson and Francis Crick, described a very simple but famous Double Helix
- 6. FRANCIS CRICK AND JAMES WATSON
- 7. The scientific framework for their breakthrough was provided by other scientists including Linus Pauling Rosalind Franklin
- 8. She worked in same laboratory as Maurice Wilkins. She study X-ray diffraction to study wet fibers
- 9. She made marked advances in X-ray diffraction techniques with DNA The diffraction pattern she obtained suggested
- 10. Rosalind Franklin Maurice Wilkins
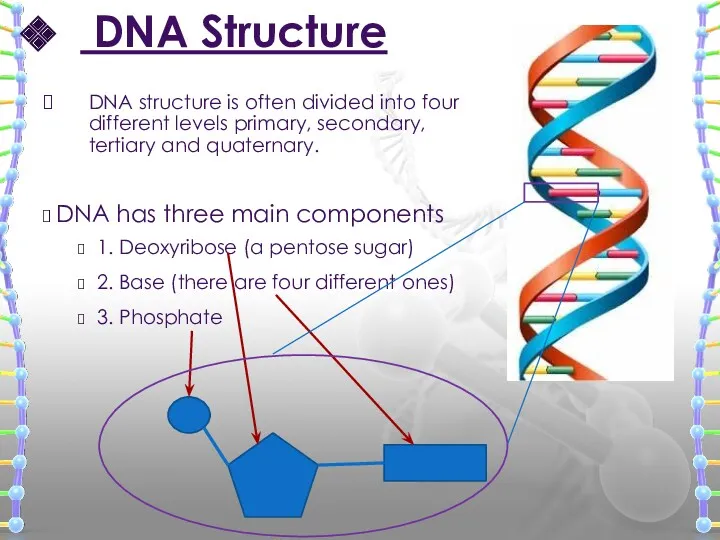
- 11. DNA Structure DNA has three main components 1. Deoxyribose (a pentose sugar) 2. Base (there are
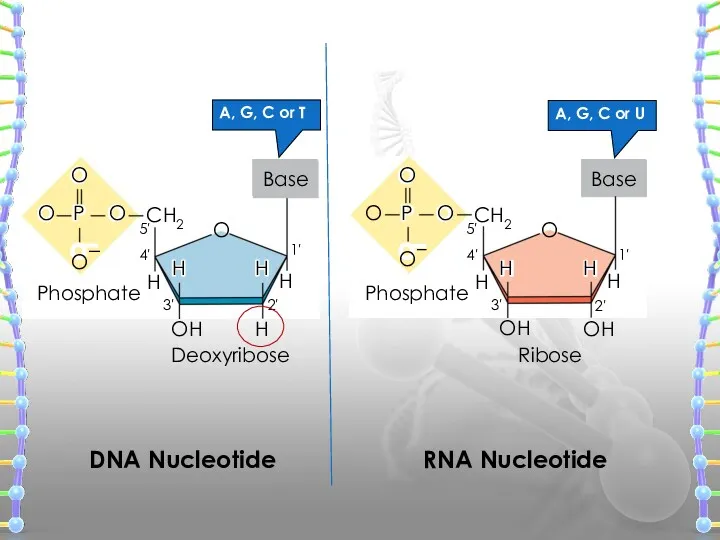
- 12. H H OH O CH2 Base Phosphate Ribose OH 5′ 4′ 1′ 3′ 2′ O O
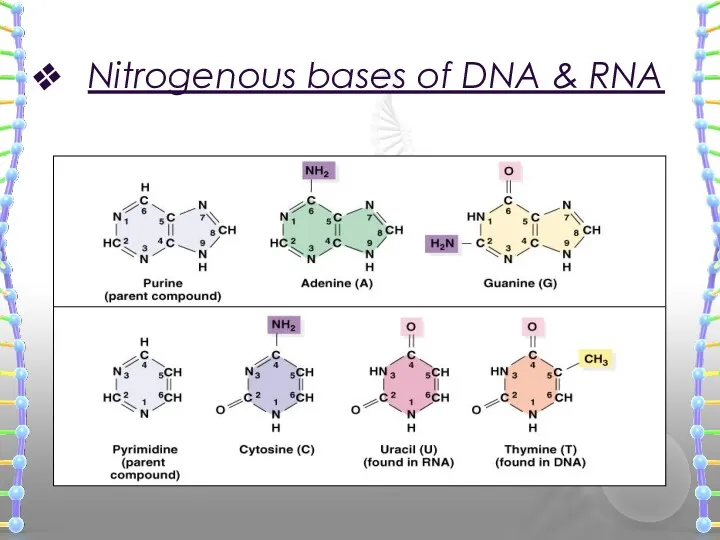
- 13. The Nitrogenous Bases THEY ARE DIVIDED INTO TWO GROUPS Pyrimidines and purines PYRIMIDINES (MADE OF ONE
- 14. Nitrogenous bases of DNA & RNA
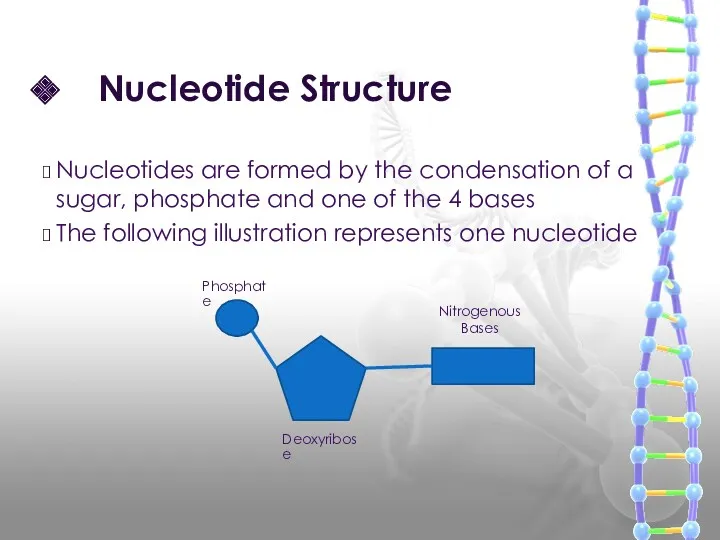
- 15. Nucleotide Structure Nucleotides are formed by the condensation of a sugar, phosphate and one of the
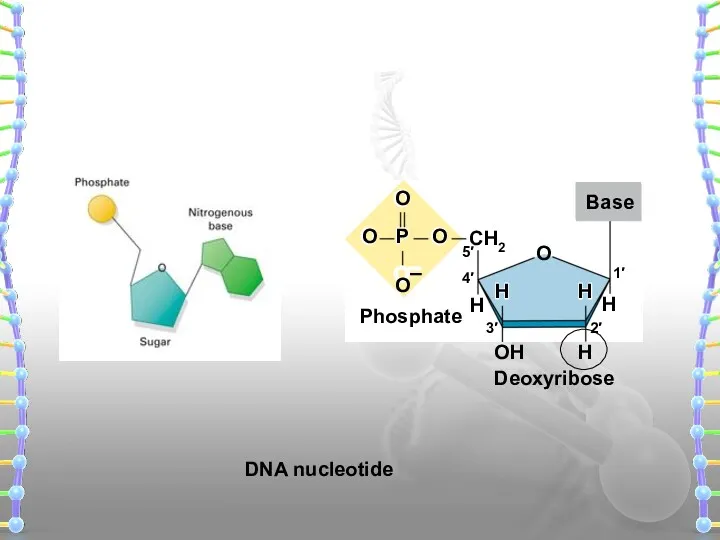
- 16. H H H O CH2 Base DNA nucleotide Phosphate Deoxyribose 5′ OH 4′ 1′ 3′ 2′
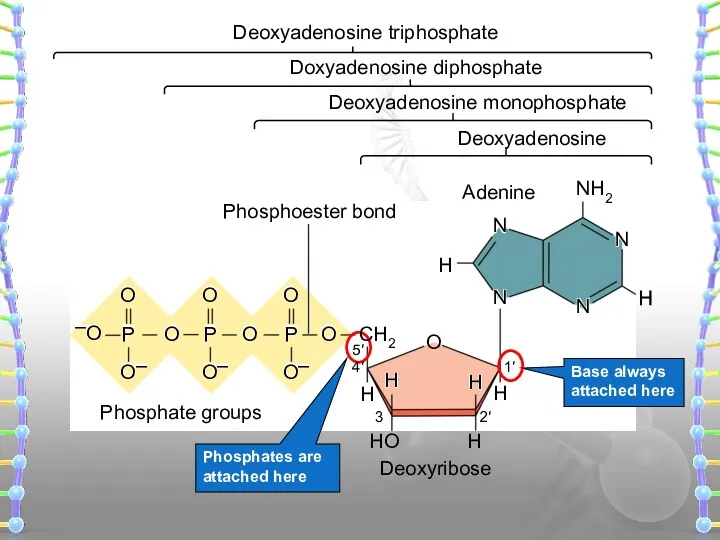
- 17. Base + sugar ? nucleoside Example Adenine + ribose = Adenosine Adenine + deoxyribose = Deoxyadenosine
- 18. Base always attached here Deoxyadenosine Deoxyadenosine monophosphate Doxyadenosine diphosphate Adenine Phosphate groups Phosphoester bond Deoxyribose H
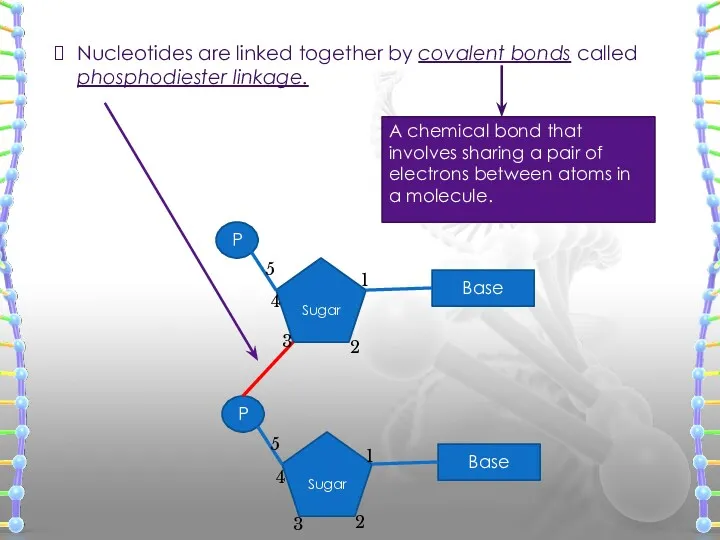
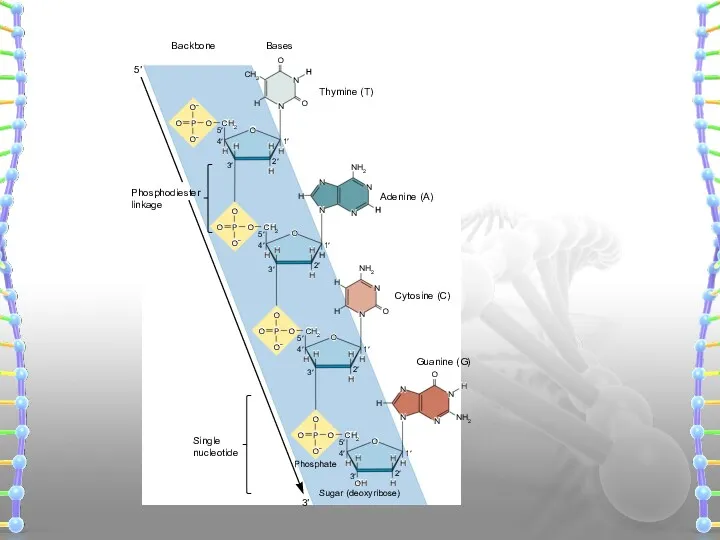
- 19. Nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds called phosphodiester linkage. 1 2 3 4 5 1
- 20. NH2 N O N O N O N Adenine (A) Guanine (G) Thymine (T) Bases Backbone
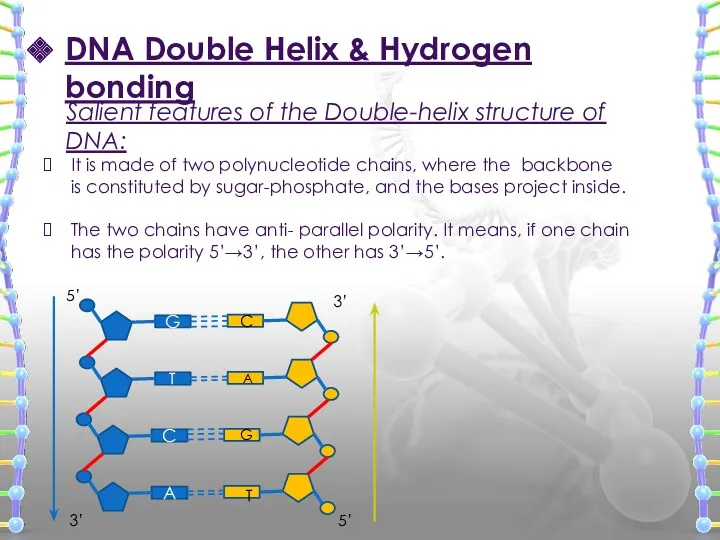
- 21. DNA Double Helix & Hydrogen bonding Salient features of the Double-helix structure of DNA: It is
- 24. Скачать презентацию











 Ланцюги живлення тварин
Ланцюги живлення тварин Живые прототипы – ключ к новой технике
Живые прототипы – ключ к новой технике Методы исследования биологии
Методы исследования биологии Биотехнология и биоэкономика: состояние и перспективы
Биотехнология и биоэкономика: состояние и перспективы Саморазвитие экосистемы
Саморазвитие экосистемы Смена времен года. (Окружающий мир. 2 класс)
Смена времен года. (Окружающий мир. 2 класс) Тонкая кишка
Тонкая кишка Китообразные. Ластоногие. Хоботные. Хищники
Китообразные. Ластоногие. Хоботные. Хищники Обмен веществ и энергии. Терморегуляция. Лекция № 20
Обмен веществ и энергии. Терморегуляция. Лекция № 20 Пищеварение и его значение
Пищеварение и его значение Терморегуляция. Зависимость температуры тела от температуры среды
Терморегуляция. Зависимость температуры тела от температуры среды Всё о птицах. Викторина
Всё о птицах. Викторина Анатомо-физиологические особенности кожи и миофасциальной структуры лица
Анатомо-физиологические особенности кожи и миофасциальной структуры лица Презентация к уроку биологии Взаимоотношения у животных 2 часть Диск
Презентация к уроку биологии Взаимоотношения у животных 2 часть Диск Екологічні фактори. Форми біотичних зв’язків
Екологічні фактори. Форми біотичних зв’язків Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Книга памятников природе
Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Книга памятников природе Дидактическая игра четвертый лишний. Насекомые
Дидактическая игра четвертый лишний. Насекомые Секреты природы. Грызуны живого уголка
Секреты природы. Грызуны живого уголка Значение бактерий
Значение бактерий Форменные элементы крови. Эритроциты. Гемоглобин. Лейкоциты
Форменные элементы крови. Эритроциты. Гемоглобин. Лейкоциты Значение дыхания. Органы дыхания
Значение дыхания. Органы дыхания Слава воде. Организм человека и вода
Слава воде. Организм человека и вода Сердечно-сосудистая система. Физиологические свойства и функции сердца
Сердечно-сосудистая система. Физиологические свойства и функции сердца Общие вопросы анатомии и физиологии пищеварительной системы. Анатомия органов пищеварения
Общие вопросы анатомии и физиологии пищеварительной системы. Анатомия органов пищеварения Грибы
Грибы Технология возделывания чечевицы
Технология возделывания чечевицы Углеводы. Строение и функции
Углеводы. Строение и функции Отчет по весенней экскурсии: Многообразие животного мира и приспособленность животных к различным средам обитания
Отчет по весенней экскурсии: Многообразие животного мира и приспособленность животных к различным средам обитания