Содержание
- 2. PLAN Biocenosis, biogeocoenosis and Consept of Ecosystem The State of the Species Under Various Forms of
- 3. Sinecology or Community Ecology studies the community species composition, their spatial pattern, and communities change with
- 4. Biocenosis is the community of populations of different species living and interacting in a given habitat
- 5. Ecosystem (ecological system) is the community of all populations of different species living on the common
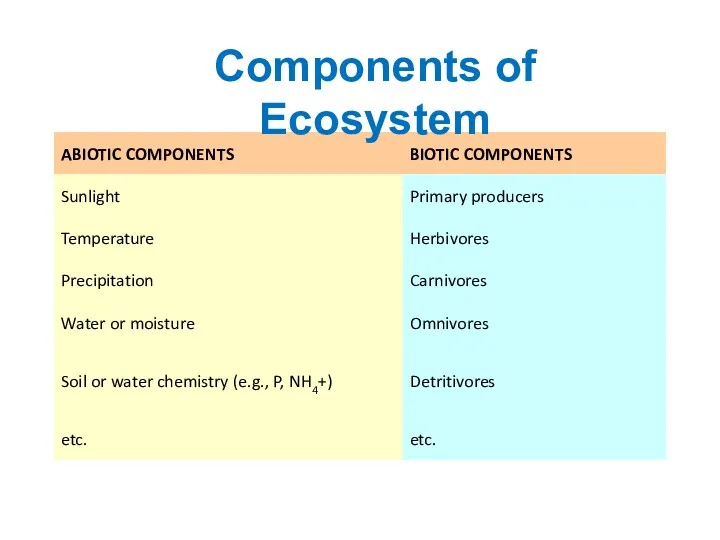
- 6. Components of Ecosystem
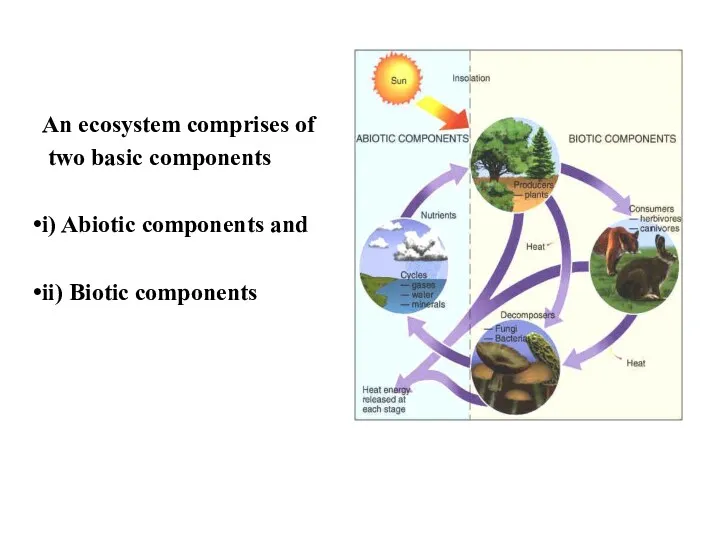
- 7. An ecosystem comprises of two basic components i) Abiotic components and ii) Biotic components
- 8. The state of the species (population) under various forms of relationship is indicated by conventional signs
- 9. All biotic links can be divided into six groups: 1) "++"- mutually beneficial, symbiotic relationships. In
- 10. 2)“+0”- useful and neutral, or commensalism (shark and sucker fish).The followings should be distinguished in his
- 11. 3) "0" - negative-neutral, or amensalizm (grass under the trees are suffering from severe shading). 4)
- 12. 5) "+-"- useful and harmful; in this group the following may be distingushed: a) carnivorism, b)
- 13. 6 )"--"- mutually harmful, when species that have identical ecological requirements enter into competition
- 14. Trophic Structure of Biocenosis. All living things can be classified according to the way they obtain
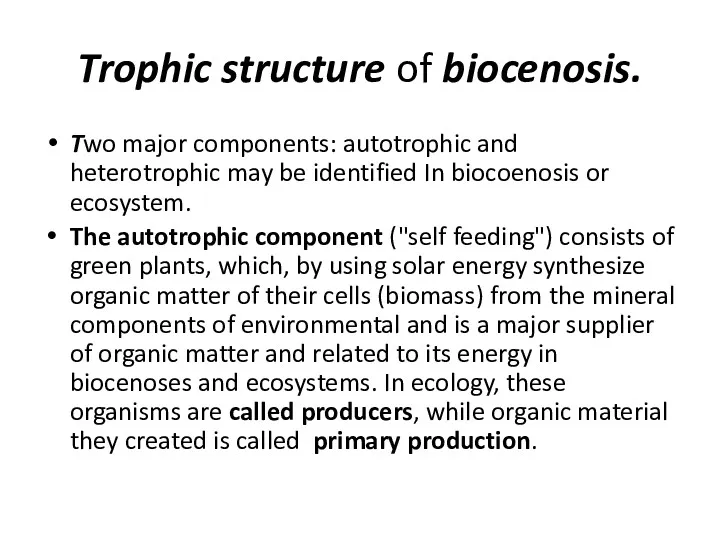
- 15. Trophic structure of biocenosis. Two major components: autotrophic and heterotrophic may be identified In biocoenosis or
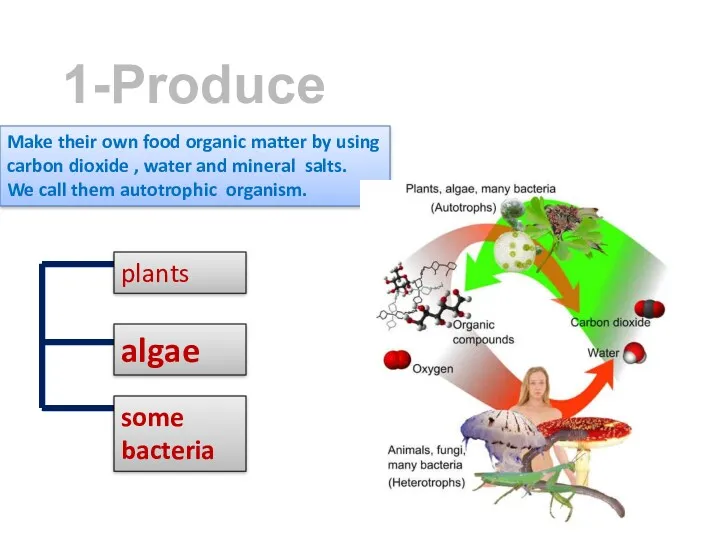
- 16. 1-Producers Make their own food organic matter by using carbon dioxide , water and mineral salts.
- 17. Heterotrophic component Heterotrophic component ("eating others") consists of organisms that derive their energy from food resulted
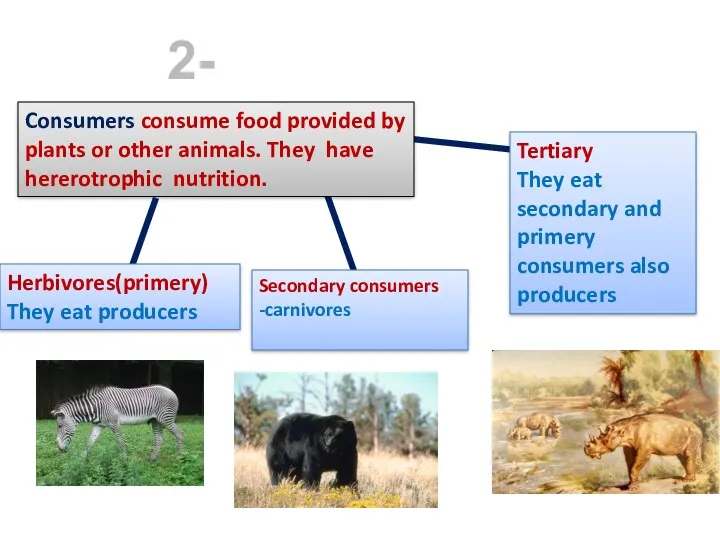
- 18. 2- Consumers Consumers consume food provided by plants or other animals. They have hererotrophic nutrition. Herbivores(primery)
- 19. Decomposers are heterotrophic organisms (fungi and bacteria) that subsist on dead organic matter and during their
- 20. 3-Decomposers They decomposed organic matter like dead animal and plants into inorganic matter. And then inorganic
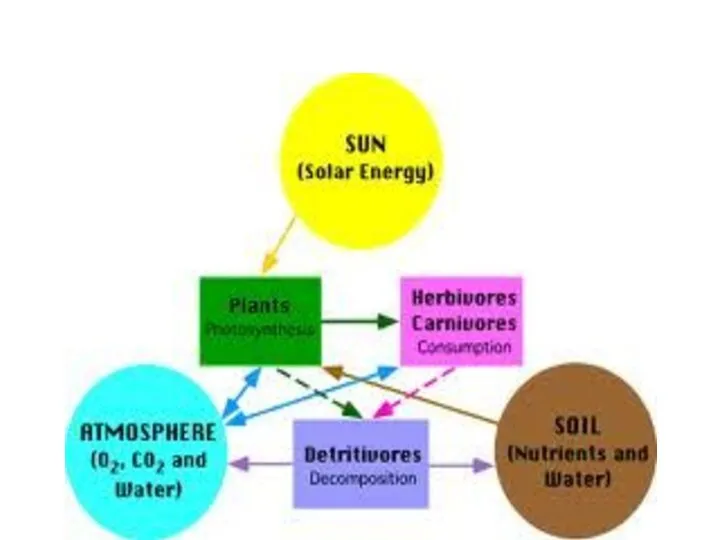
- 21. Joint effect of these three groups of organisms maintains a relatively endless circle of matter in
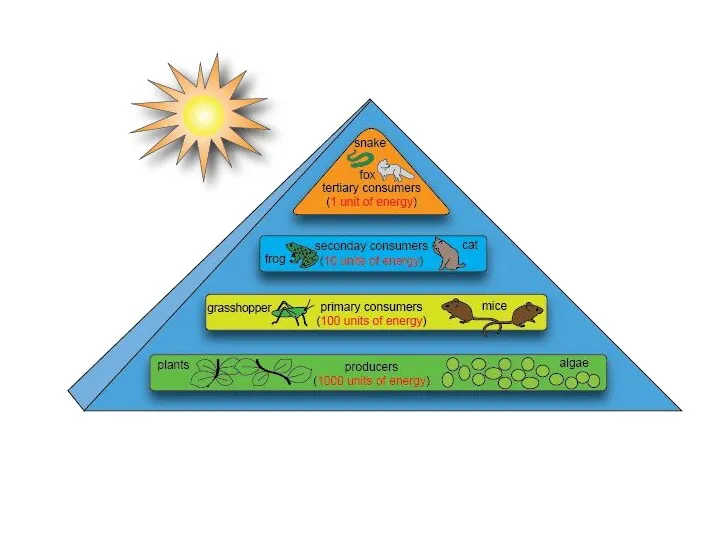
- 22. Food chains and trophic levels Matter and energy have been transferring through a series of organisms,
- 24. Energy flow and circulation of chemical elements in the ecosystem Any ecosystem consists of biotic and
- 26. Food chains A food chain shows which plants or animals eat or get eaten by others
- 27. All living organisms appear to be consumers of food, that is of matter and energy. In
- 28. Energy can be defined as an ability to do work. All living organisms can be considered
- 29. Living organisms can only use two forms of energy: photoenergy and chemical energy. All organisms are
- 30. Organisms synthesizing all necessary organic matter by means of light energy (photosynthesis) belong to a phototrophic
- 31. Chemotrophic organisms synthesize organic matter through the energy of chemical bonds of various substances. This includes
- 32. Succession Any ecosystem undergoes changes both in time and space, in addition, changes are seen in
- 34. Скачать презентацию
























 Популяции
Популяции Изучение строения и функций органов пищеварения
Изучение строения и функций органов пищеварения Своя игра Общие сведения о мире животных
Своя игра Общие сведения о мире животных Вплив факторів зовнішнього середовища на мікроорганізми
Вплив факторів зовнішнього середовища на мікроорганізми Витамины.
Витамины. Исследования метагенома
Исследования метагенома Значение бактерий
Значение бактерий Лесные птицы
Лесные птицы Особливості будови клітин
Особливості будови клітин Этапы развития жизни на Земли
Этапы развития жизни на Земли Класс Птицы. Размножение и развитие. Годовой жизненный цикл и сезонные явления
Класс Птицы. Размножение и развитие. Годовой жизненный цикл и сезонные явления Вкус
Вкус Биология барсука
Биология барсука Отдел моховидные
Отдел моховидные Введення в курс фізіології
Введення в курс фізіології Экскурсия в науку (по кабинету биологии)
Экскурсия в науку (по кабинету биологии) 20231022_himicheskiy_sostav_kletki
20231022_himicheskiy_sostav_kletki Ультраструктура бактериальной клетки
Ультраструктура бактериальной клетки Физиология и биохимия микроорганизмов
Физиология и биохимия микроорганизмов Забота о потомстве
Забота о потомстве Огляд відділів хромофітових водоростей (Stramenopiles)
Огляд відділів хромофітових водоростей (Stramenopiles) История изучения клетки. Клеточная теория
История изучения клетки. Клеточная теория Источники микрофлоры сырья и пищевых продуктов
Источники микрофлоры сырья и пищевых продуктов Полезные и вредные комнатные растения
Полезные и вредные комнатные растения Везикулярная система клетки
Везикулярная система клетки Эндокринная система
Эндокринная система Животные Красной книги Московской области
Животные Красной книги Московской области Introduction. Types of plant kingdom
Introduction. Types of plant kingdom