Содержание
- 2. Tissue. The basic types of tissues. The common characteristics of epithelia. Histogenesis of the epithelia. The
- 3. The tissue – is the morphological or morphofisiological system. Tissue is the team of the same
- 4. The tissues are systems of cells and noncellular structures characterized by similar structural, functional properties and
- 5. Differentiation – the morphofunctional exchange of the same organized cells. The main result of the differentiation
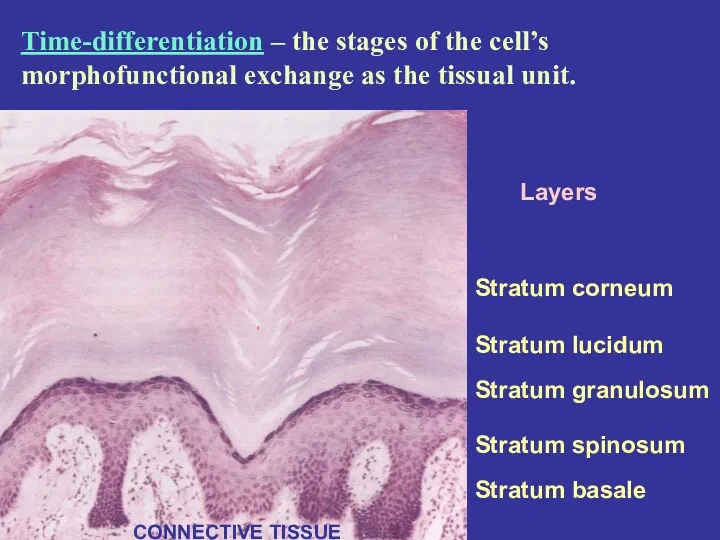
- 6. Layers Stratum corneum Stratum lucidum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale CONNECTIVE TISSUE Time-differentiation – the
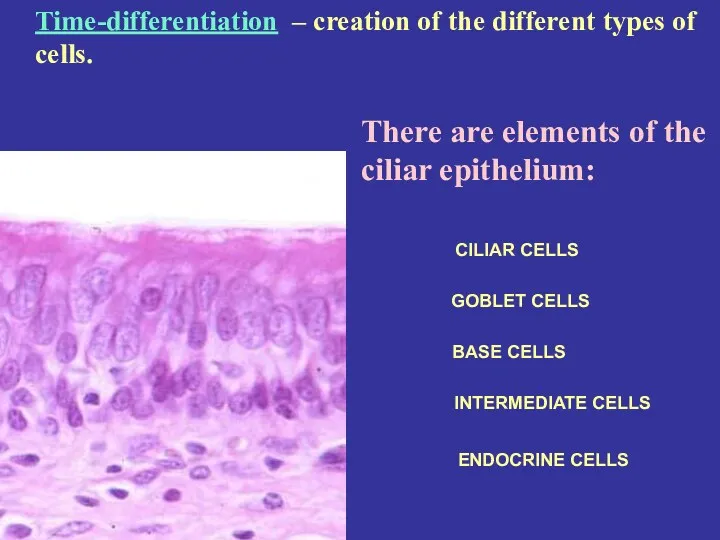
- 7. There are elements of the ciliar epithelium: CILIAR CELLS GOBLET CELLS BASE CELLS INTERMEDIATE CELLS ENDOCRINE
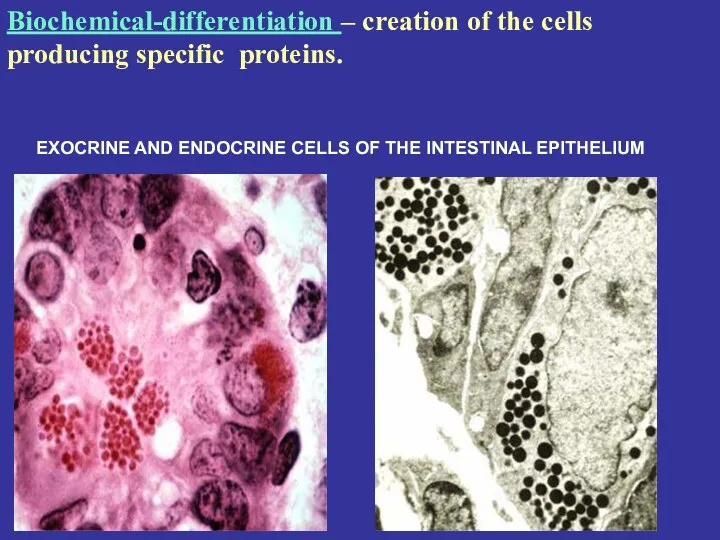
- 8. EXOCRINE AND ENDOCRINE CELLS OF THE INTESTINAL EPITHELIUM Biochemical-differentiation – creation of the cells producing specific
- 9. First of all start to differentiate the steam cells source the differon. Steam cell’s characteristics: They
- 10. Regeneration – the capability of the tissue to recover itself after violation. There are known different
- 11. Physiological regeneration – the recovering of the cell’s population after the death of the some cells.
- 12. The History. 1665 год. Robert Hook was describe the “cell”. 1830 год. Jan Purcinje - cytoplasm.
- 13. THE BASIC TYPES OF TISSUES EPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE (SUPPORT) AND BLOOD MUSCLE NERVOUS
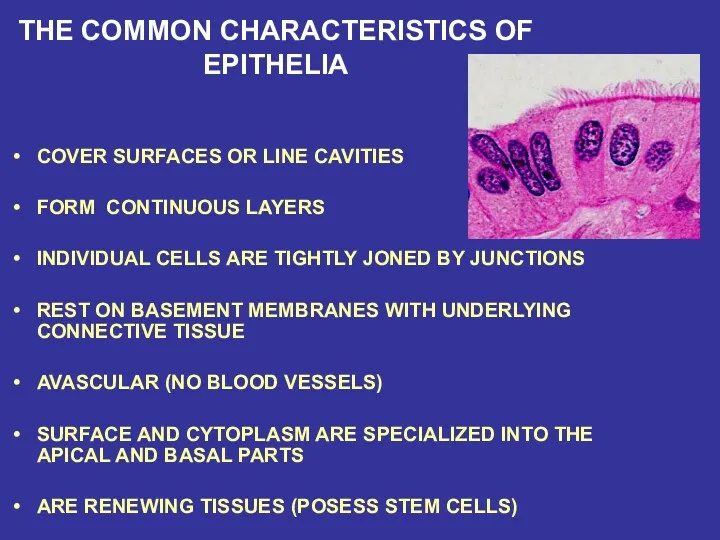
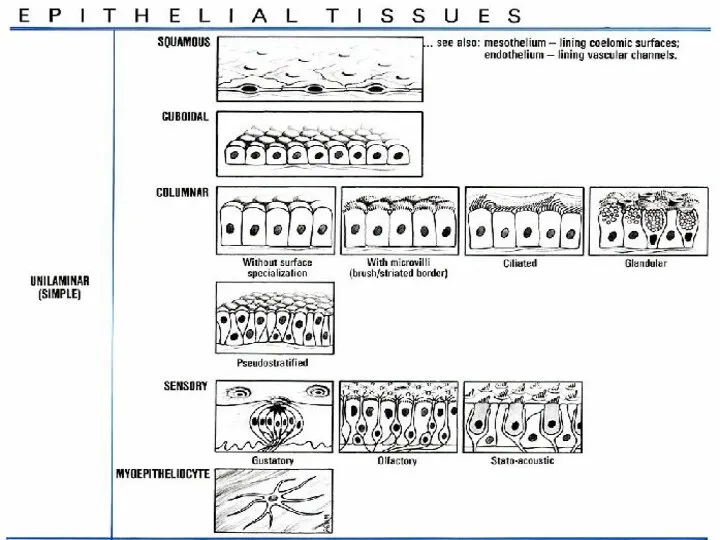
- 14. THE COMMON CHARACTERISTICS OF EPITHELIA COVER SURFACES OR LINE CAVITIES FORM CONTINUOUS LAYERS INDIVIDUAL CELLS ARE
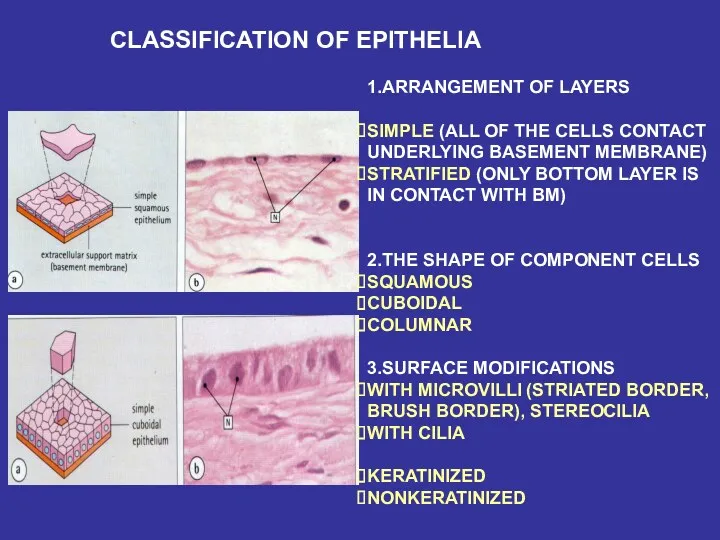
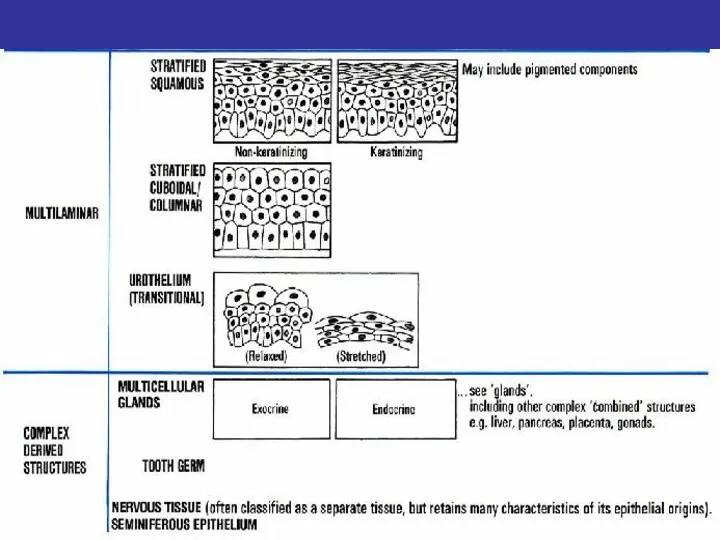
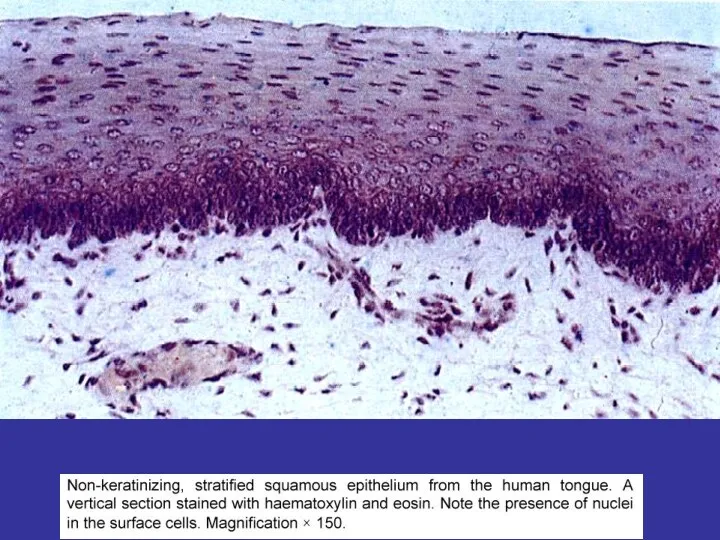
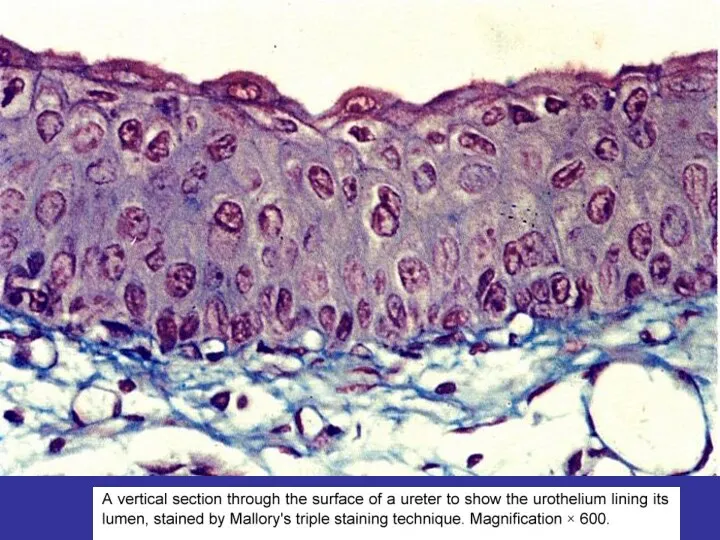
- 15. CLASSIFICATION OF EPITHELIA 1.ARRANGEMENT OF LAYERS SIMPLE (ALL OF THE CELLS CONTACT UNDERLYING BASEMENT MEMBRANE) STRATIFIED
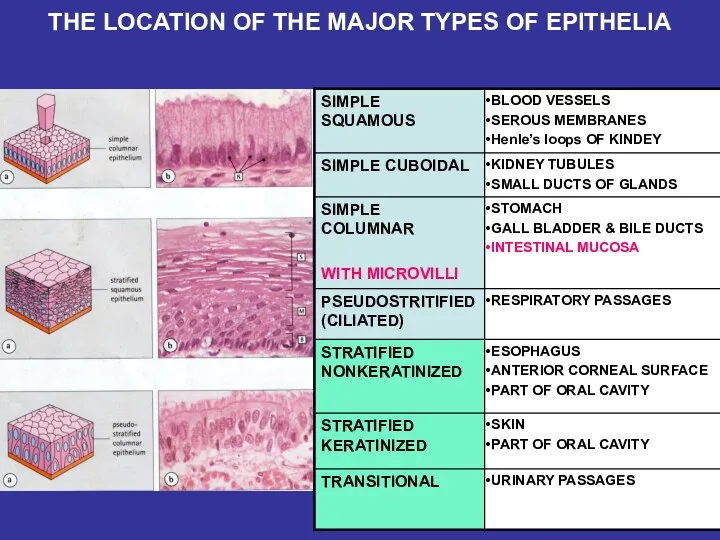
- 16. THE LOCATION OF THE MAJOR TYPES OF EPITHELIA
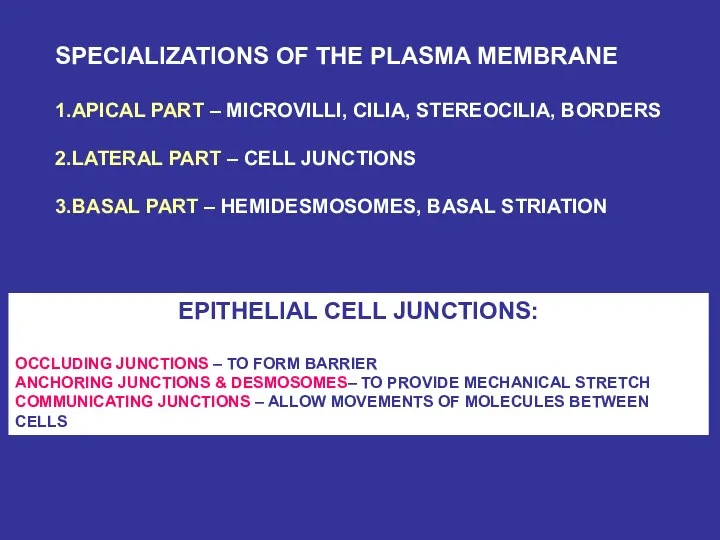
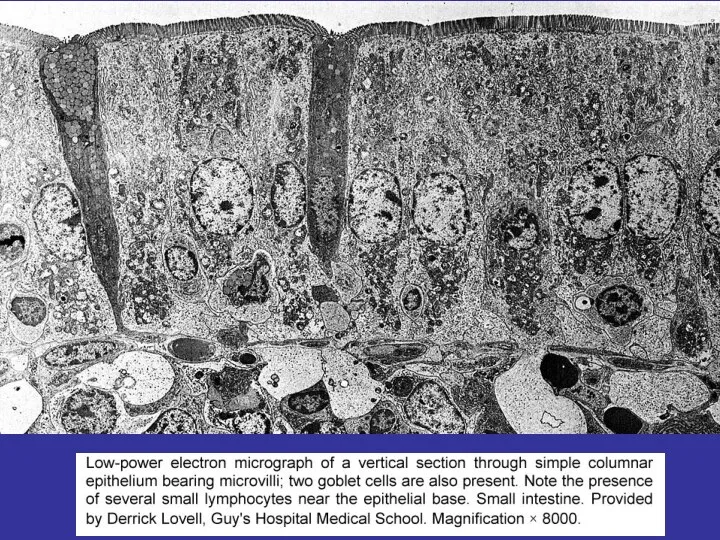
- 17. SPECIALIZATIONS OF THE PLASMA MEMBRANE 1.APICAL PART – MICROVILLI, CILIA, STEREOCILIA, BORDERS 2.LATERAL PART – CELL
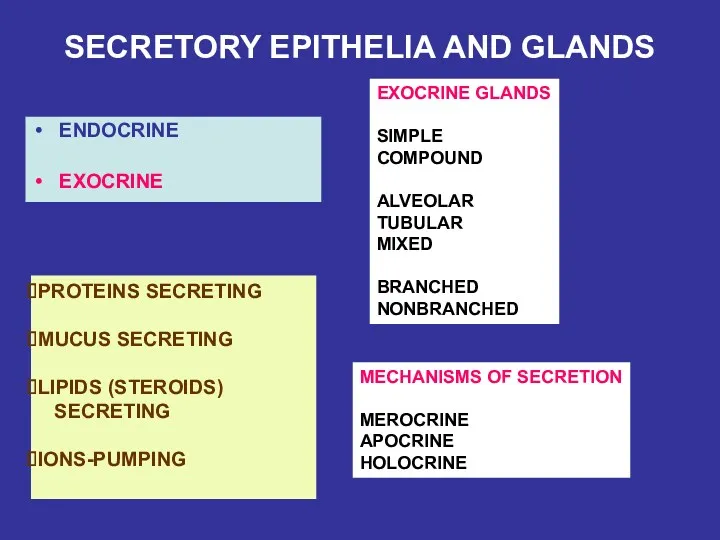
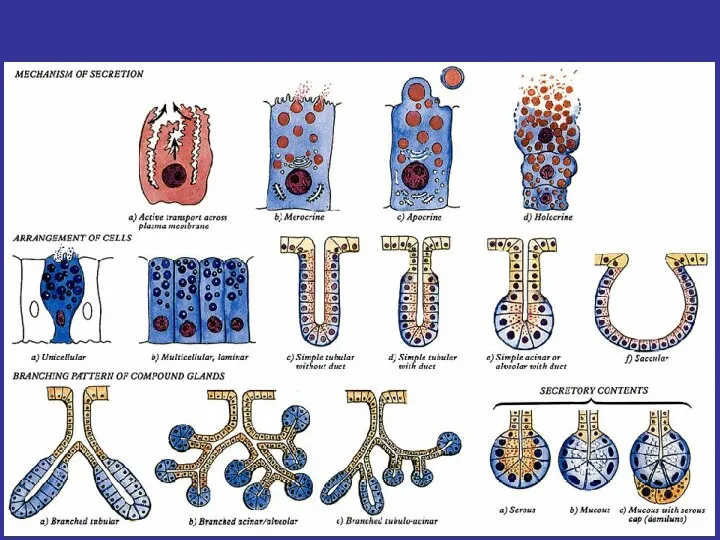
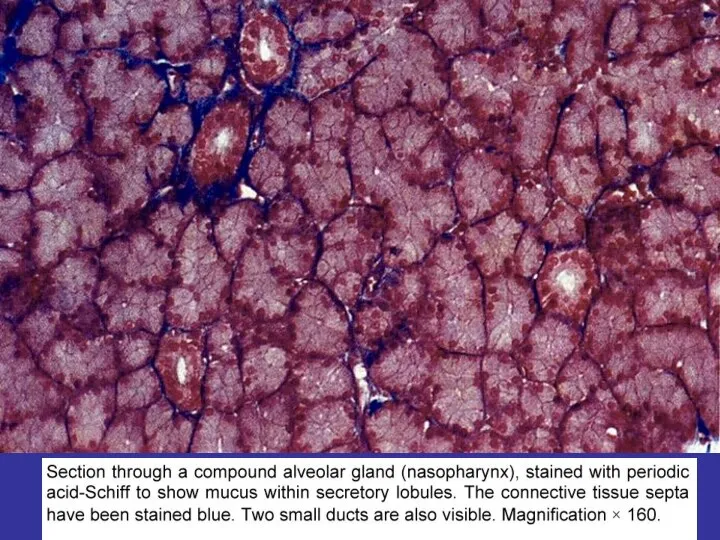
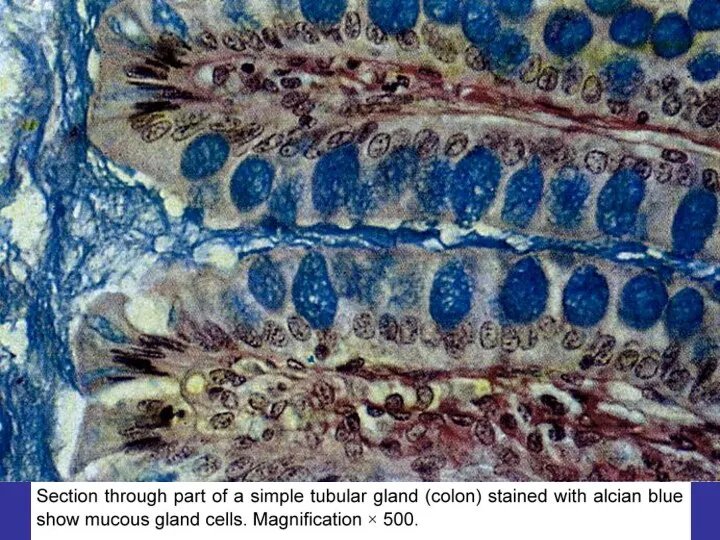
- 25. SECRETORY EPITHELIA AND GLANDS ENDOCRINE EXOCRINE EXOCRINE GLANDS SIMPLE COMPOUND ALVEOLAR TUBULAR MIXED BRANCHED NONBRANCHED PROTEINS
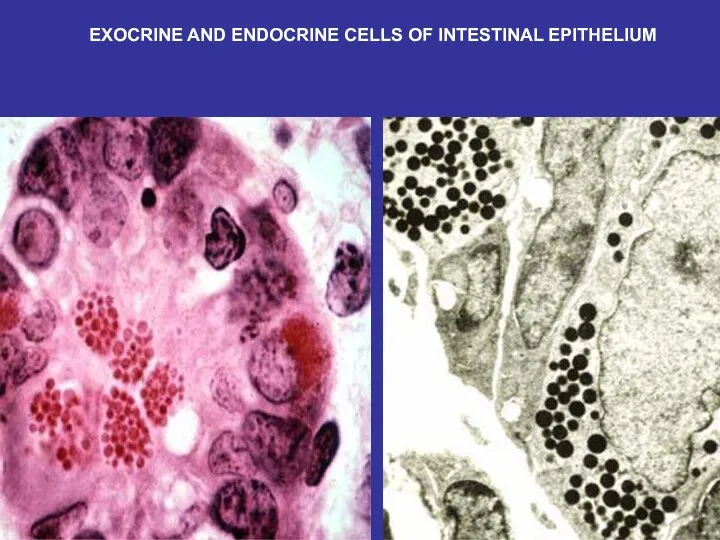
- 27. EXOCRINE AND ENDOCRINE CELLS OF INTESTINAL EPITHELIUM
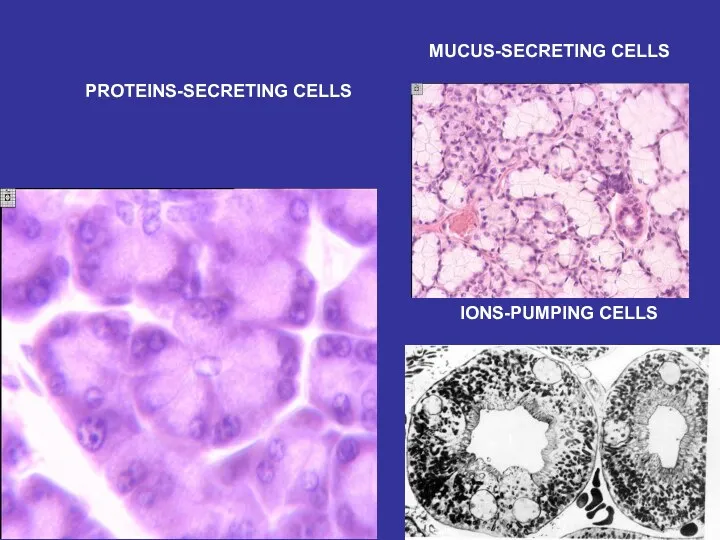
- 28. PROTEINS-SECRETING CELLS MUCUS-SECRETING CELLS IONS-PUMPING CELLS
- 32. Скачать презентацию










 Анатомия и физиология женских половых органов
Анатомия и физиология женских половых органов Вчення про тканини. Епітелій
Вчення про тканини. Епітелій Антропология, как комплексное учение о человеке. Место человека в животном мире и этапы антропогенеза
Антропология, как комплексное учение о человеке. Место человека в животном мире и этапы антропогенеза Строение стебля
Строение стебля Анатомия внутреннего уха
Анатомия внутреннего уха Физиология центральной нервной системы
Физиология центральной нервной системы Генетически модифицированные организмы (ГМО)
Генетически модифицированные организмы (ГМО) Презентация 1
Презентация 1 Лабораторная работа на тему Приспособленность организмов к их среде обитания
Лабораторная работа на тему Приспособленность организмов к их среде обитания Молодежный инновационный форум Воронежской области
Молодежный инновационный форум Воронежской области Нуклеиновые кислоты и их роль в жизнедеятельности клетки
Нуклеиновые кислоты и их роль в жизнедеятельности клетки презентация к семинару
презентация к семинару Презентация к уроку биологии 6 кл.
Презентация к уроку биологии 6 кл. Вредители и болезни газонных растений и меры борьбы с ними
Вредители и болезни газонных растений и меры борьбы с ними Химерные мыши
Химерные мыши Лишайники. Внешнее строение лишайников
Лишайники. Внешнее строение лишайников Общая характеристика подтипа Позвоночные. Часть1
Общая характеристика подтипа Позвоночные. Часть1 Значення та охорона членистоногих
Значення та охорона членистоногих Животные Омского Прииртышья (насекомые). Занятие № 39
Животные Омского Прииртышья (насекомые). Занятие № 39 Кровеносная система. Строение сердца. Строение сосудов
Кровеносная система. Строение сердца. Строение сосудов Системная биология: предмет, инструменты, экспериментальные методы
Системная биология: предмет, инструменты, экспериментальные методы Моторика (регуляция движений)
Моторика (регуляция движений) История развития генетики. Основные понятия
История развития генетики. Основные понятия Режимы и способы хранения картофеля, плодов, и овощей. Лекция №3-4
Режимы и способы хранения картофеля, плодов, и овощей. Лекция №3-4 Тренировочные задания по биологии в формате ГИА
Тренировочные задания по биологии в формате ГИА Hedera helix
Hedera helix Деление клетки. Митоз. Жизненный цикл клетки
Деление клетки. Митоз. Жизненный цикл клетки Физиология памяти человека
Физиология памяти человека