2
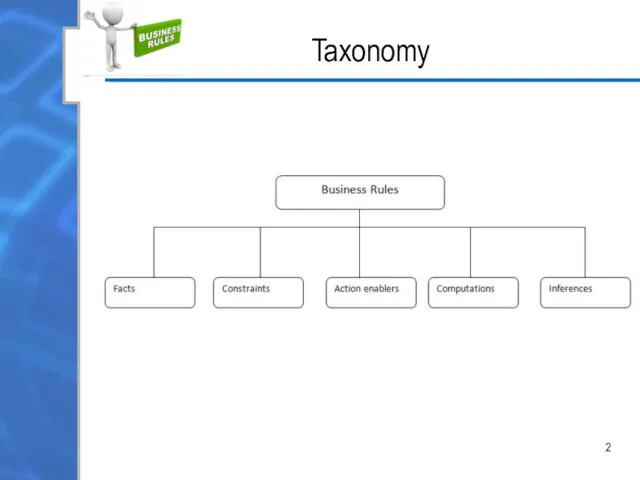
Constraints — determine what operations the system and its users can
perform.
Some constraints in BR:
must, can not, can not, only, etc.
Examples:
- a loan agreement for a person under 18 years old must be signed by one of his parents or a legal guardian;
a regular visitor of the library can postpone for himself up to 10 books;
commercial flight crews must rest every 24 hours for at least 8 hours;
Deliveries must be completed between 10:00am and 2:00pm local time.
All meals in a single order must be paid for using the same payment method.
Constraints









 Частный детский сад Росточек
Частный детский сад Росточек ЖК Көркем фото – видео студиясы
ЖК Көркем фото – видео студиясы Forms of business organization
Forms of business organization Новая Стартовая программа
Новая Стартовая программа Бизнес-деятельность организации
Бизнес-деятельность организации Гостиница Националь, Москва
Гостиница Националь, Москва Сколько стоит бизнес
Сколько стоит бизнес Игровой клуб “Monster Kill”
Игровой клуб “Monster Kill” Легкая кухня. Школа бизнеса 2023
Легкая кухня. Школа бизнеса 2023 Факторы успеха Вашего бизнеса
Факторы успеха Вашего бизнеса Инвестициялық жобалар
Инвестициялық жобалар Картели и синдикаты
Картели и синдикаты Поддержка сельской молодежи
Поддержка сельской молодежи Презентация Гостиница Волга - Тверь (Майоров).html
Презентация Гостиница Волга - Тверь (Майоров).html Аутсорсинг, його переваги і недоліки
Аутсорсинг, його переваги і недоліки Доставка здорового питания на неделю
Доставка здорового питания на неделю Проектный марафон
Проектный марафон Бизнес жоспар. Көкөніс өсіретін жылыжай
Бизнес жоспар. Көкөніс өсіретін жылыжай Transcend the Crypto Universe
Transcend the Crypto Universe Организация IT-компании
Организация IT-компании Аналіз сучасних підходів до класифікації підприємств готельного господарства
Аналіз сучасних підходів до класифікації підприємств готельного господарства Кофейня Sweet cat
Кофейня Sweet cat Открытие Таиланда и особенности оформления туристской визы (TR) в Таиланд / 24 декабря 2020
Открытие Таиланда и особенности оформления туристской визы (TR) в Таиланд / 24 декабря 2020 Спортивно-развлекательная площадка JumpShot
Спортивно-развлекательная площадка JumpShot Стартовый семинар для новых бизнес-партнеров
Стартовый семинар для новых бизнес-партнеров Організація харчування туристів в зеленому сільському туризмі
Організація харчування туристів в зеленому сільському туризмі Molniya club Закрытый клуб предпринимателей
Molniya club Закрытый клуб предпринимателей Технопарк в сфере высоких технологий Анкудиновка
Технопарк в сфере высоких технологий Анкудиновка