Слайд 2

Lecture’s topics
What is a decision?
How are decisions made?
What are the
main decision making conditions?
How can quantitative methods help in the decision making process?
Слайд 3

Decisions
A decision is a specific commitment to action –
usually requiring
a commitment of resources.
Слайд 4

Decisions
Decisions are made with regard to all aspects of
the management
process: inputs, outputs and
transformations.
Слайд 5

Decisions
Input decisions
How to raise capital, who to employ etc.
Output decisions
What products
to make, how to distribute them etc.
Transformation decisions
How to carry out a particular process, how to manage the finances etc.
Слайд 6
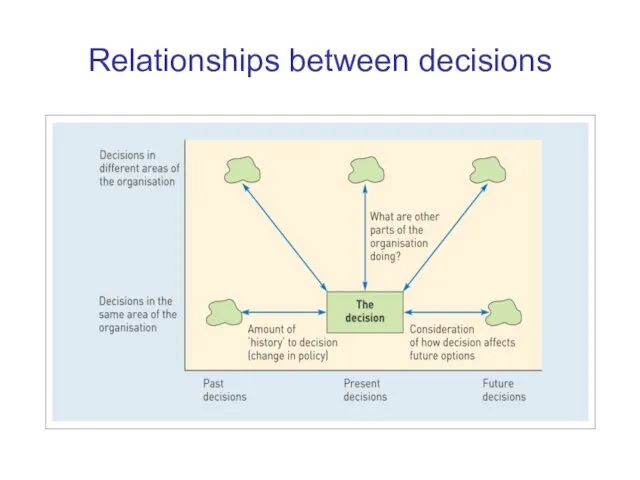
Relationships between decisions
Слайд 7

Types of decisions
Strategic decisions:
long-term decisions on the future direction of the
organisation
relate to the world outside the organisation and can require the commitment of major resources
Слайд 8

Types of decisions
Operational decisions:
shorter-term decisions often on day-to-day matters and within
established policy
Слайд 9

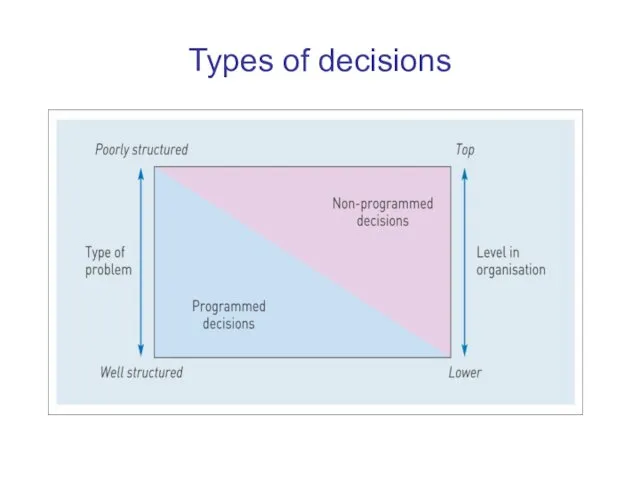
Types of decisions
Programmed decisions:
deal with familiar problems or with well structured
situations
are based on established procedures or policies
often handled by computers
Слайд 10

Types of decisions
Non-programmed decisions:
deal with unstructured situations requiring a unique solution
depend
on personal judgement
Слайд 11
Слайд 12

Student activity
Think of an important decision that you have taken
sometime
in your life. Then answer the following:
Why did you have to take a decision in this case?
What were your alternative options?
What factors did you consider when you took your decision?
Did you make the right decision?
Слайд 13

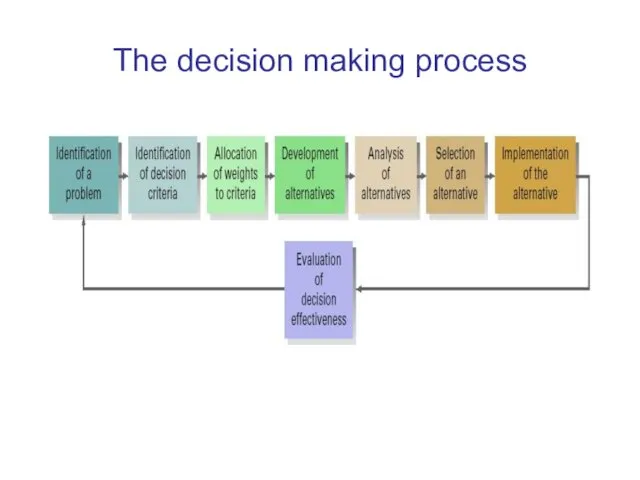
The decision making process
An eight-step process that includes identifying a
problem,
selecting and implementing a solution,
and evaluating its effectiveness.
Слайд 14
The decision making process
Слайд 15

The decision making process
Step 1: Identification of a problem
A problem is
a discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs.
Need to compare current state of affairs to some standard.
Identifying what a problem is is subjective and can be difficult.
Danger of solving the wrong problem!!
Слайд 16

The decision making process
Step 2: Identification of decision criteria
What guides the
decision maker in their decision.
Some are objective (e.g. price, delivery time etc.) while others are subjective (e.g. appearance, ease of use etc.).
Not always explicitly stated.
Слайд 17

The decision making process
Step 3: Allocation of weights to decision
criteria
Not all
decision criteria identified in the previous step are equally important.
Assign weights to the decision criteria in order to give them their relative priority in the decision.
Слайд 18

The decision making process
Step 4: Development of alternatives
Make a list of
the alternatives that could succeed in solving the problem.
Developing too few alternatives limits choice.
Developing too many alternatives can be counter-productive – more choice means more stress, frustration and anxiety that we might make the wrong decision.
Слайд 19

The decision making process
Step 5: Analysis of alternatives
Compare each alternative with
the criteria and weights established in steps 2 & 3.
Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each alternative.
Some assessments are objective but others are based on personal judgement.
Слайд 20

The decision making process
Step 6: Selection of an alternative
Choose the best
alternative out of those evaluated in the previous step.
Quantitative methods can help in this selection.
Слайд 21

The decision making process
Step 7: Implementation of the alternative
chosen
Putting a
decision into action
Includes conveying the decision to the persons who will be affected by it and getting their commitment to it.
Слайд 22

The decision making process
Step 8: Evaluation of decision effectiveness
Appraise the result
of the decision to see whether it has solved the problem.
Слайд 23

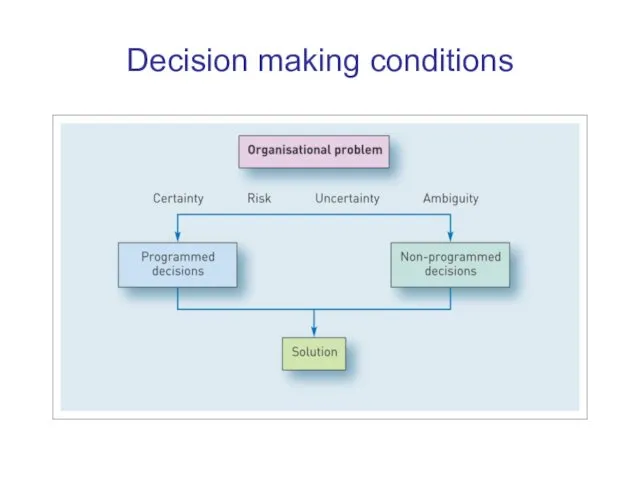
Decision making conditions
Certainty:
The decision maker knows exactly what will happen in
the future.
Uncertainty:
The decision maker doesn’t know what will happen in the future.
Слайд 24

Decision making conditions
Risk:
The decision maker doesn’t know what will happen in
the future but can estimate the likelihood of the alternative outcomes.
Слайд 25

Decision making conditions
Ambiguity:
The decision maker is uncertain about their goals and
how best to achieve them.
Слайд 26
Decision making conditions
Слайд 27

Decision making using Quantitative methods
Quantitative methods can be used to select
the best alternative.
Normally used for programmed decisions.
Different methods are based on different criteria and produce different results.
Слайд 28

An Example
Type of Condition of Market
investment Good Moderate Poor
A 200 100 50
B 400 -40 -90
C 550 -80 -120
Слайд 29
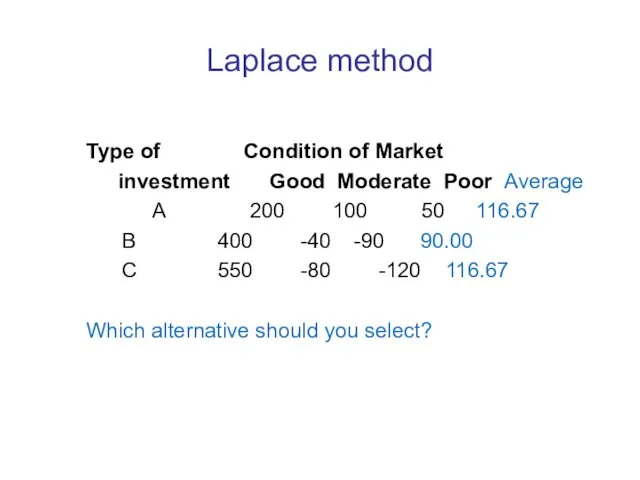
Laplace method
Type of Condition of Market
investment Good Moderate Poor Average
A 200 100 50 116.67
B 400 -40 -90 90.00
C 550 -80 -120 116.67
Which alternative should you select?
Слайд 30

Maximax method (optimistic)
Type of Condition of Market
investment Good Moderate Poor
Max
A 200 100 50 200
B 400 -40 -90 400
C 550 -80 -120 550
Which alternative should you select?
Слайд 31

Maximin method (pessimistic)
Type of Condition of Market
investment Good Moderate Poor
Min
A 200 100 50 50
B 400 -40 -90 -90
C 550 -80 -120 -120
Which alternative should you select?
Слайд 32
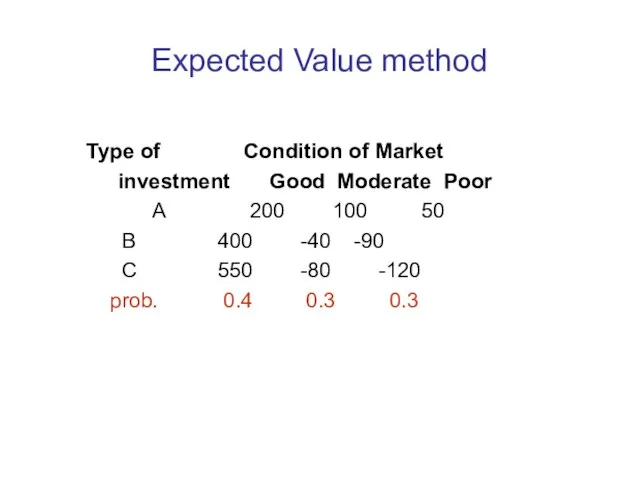
Expected Value method
Type of Condition of Market
investment Good Moderate Poor
A 200 100 50
B 400 -40 -90
C 550 -80 -120
prob. 0.4 0.3 0.3































 Курс повышения квалификации Бизнес-риторика
Курс повышения квалификации Бизнес-риторика Zarządzanie informacją w organizacji wykład. Informacyjne a procesy biznesowe
Zarządzanie informacją w organizacji wykład. Informacyjne a procesy biznesowe Туристское агенство Life Travel
Туристское агенство Life Travel Государственная поддержка малого бизнеса в Китае
Государственная поддержка малого бизнеса в Китае Проект Маникюрный кабинет
Проект Маникюрный кабинет Бизнес-план. Автомойка(Самообслуживания)
Бизнес-план. Автомойка(Самообслуживания) Магистерская программа Электронный бизнес
Магистерская программа Электронный бизнес Переработка нейлоновых сетей. Бизнес-план
Переработка нейлоновых сетей. Бизнес-план DreamTrips. Путешествуйте вместе с семьей и друзьями
DreamTrips. Путешествуйте вместе с семьей и друзьями Чайный чемпионат. Возможности для ресторанного и чайного бизнеса
Чайный чемпионат. Возможности для ресторанного и чайного бизнеса Кейтеринг в системе потребительской кооперации
Кейтеринг в системе потребительской кооперации Raketa это онлайн-платформа для управления корпоративными поездками
Raketa это онлайн-платформа для управления корпоративными поездками Toyota Motor Corporation
Toyota Motor Corporation Шағын кәсіпкерлік
Шағын кәсіпкерлік Корпоративная и социальная ответственность Мегафон и Билайн
Корпоративная и социальная ответственность Мегафон и Билайн Создание кооператива
Создание кооператива Стратегия развития компании
Стратегия развития компании Коммерческое предложение. Евразийский международный фестиваль культур в Беларуси
Коммерческое предложение. Евразийский международный фестиваль культур в Беларуси Бизнес-модели социального предпринимательства
Бизнес-модели социального предпринимательства Бизнес-модель. Профориентация молодежи и взрослых
Бизнес-модель. Профориентация молодежи и взрослых Венчурлік бизнесті ұйымдастыру
Венчурлік бизнесті ұйымдастыру Бизнес-игра Construction Team
Бизнес-игра Construction Team Станция СТО сельскохозяйственной техники
Станция СТО сельскохозяйственной техники Торгово-развлекательный центр в городе Тихорецк
Торгово-развлекательный центр в городе Тихорецк Персональный бренд. От хобби к бизнесу. Для проекта Женское дело
Персональный бренд. От хобби к бизнесу. Для проекта Женское дело Проект компании Legal Sellers Workshop
Проект компании Legal Sellers Workshop Сучасні тенденції світового туризму
Сучасні тенденції світового туризму Бизнес-планирование и бизнес-план. Подготовка молодёжи к предпринимательской деятельности
Бизнес-планирование и бизнес-план. Подготовка молодёжи к предпринимательской деятельности