Содержание
- 2. © Wiley 2010 Learning Objectives Define and explain OM Explain the role of OM in business
- 3. © Wiley 2010 Learning Objectives – con’t Identify current trends in OM Describe the flow of
- 4. © Wiley 2010 Operations Management is: The business function responsible for planning, coordinating, and controlling the
- 5. © Wiley 2010 Operations Management is: A management function An organization’s core function In every organization
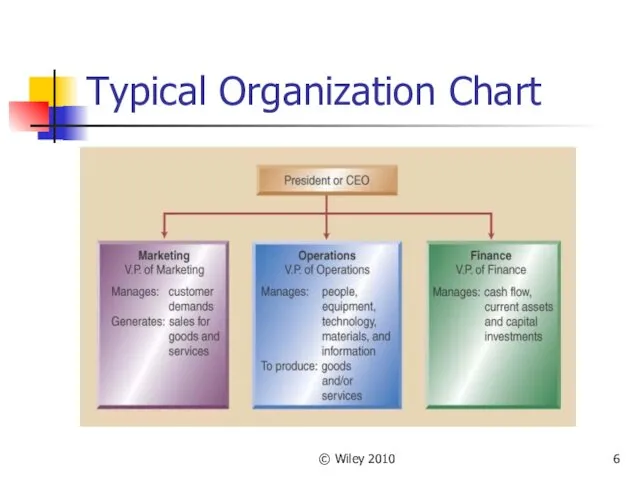
- 6. © Wiley 2010 Typical Organization Chart
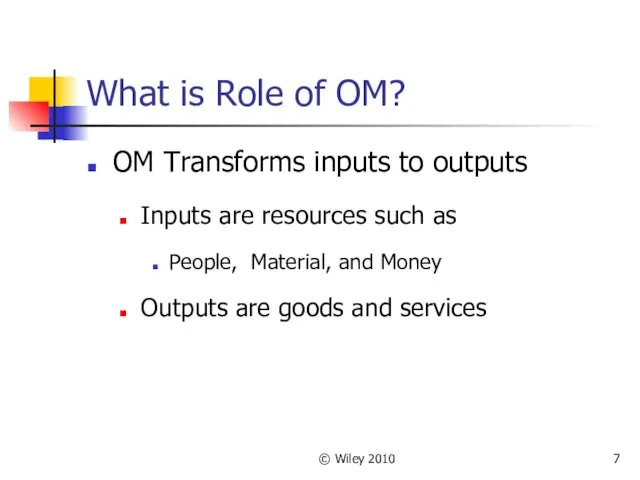
- 7. © Wiley 2010 What is Role of OM? OM Transforms inputs to outputs Inputs are resources
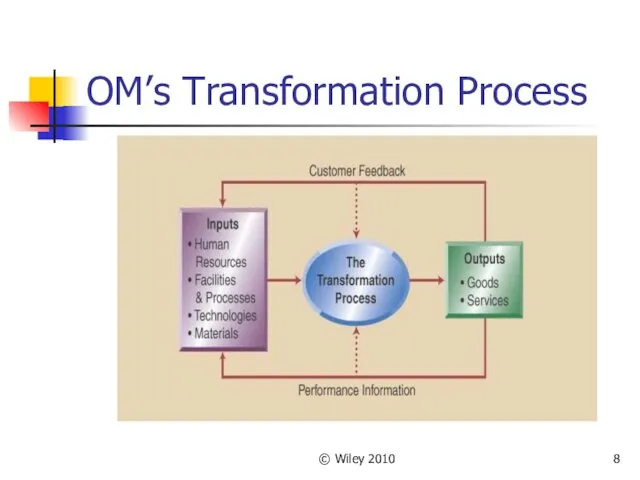
- 8. © Wiley 2010 OM’s Transformation Process
- 9. © Wiley 2010 OM’s Transformation Role To add value Increase product value at each stage Value
- 10. © Wiley 2010 Manufacturers vs Service Organizations Services: Intangible product Product cannot be inventoried High customer
- 11. © Wiley 2010 Similarities for Service/Manufacturers Both use technology Both have quality, productivity, & response issues
- 12. © Wiley 2010 Service vs Manufacturing Manufacturing often provides services Services often provides tangible goods Some
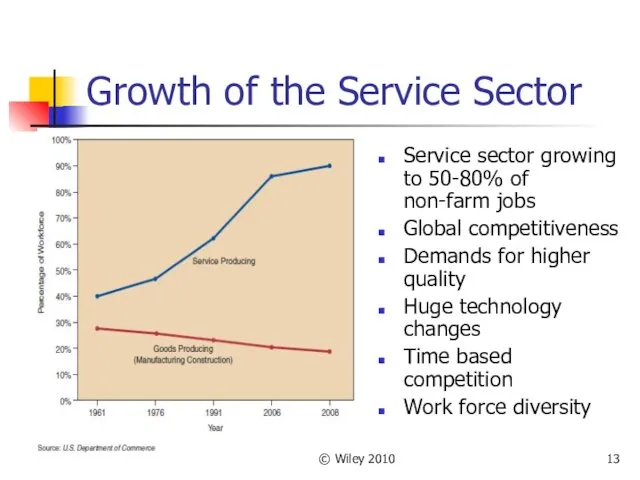
- 13. © Wiley 2010 Growth of the Service Sector Service sector growing to 50-80% of non-farm jobs
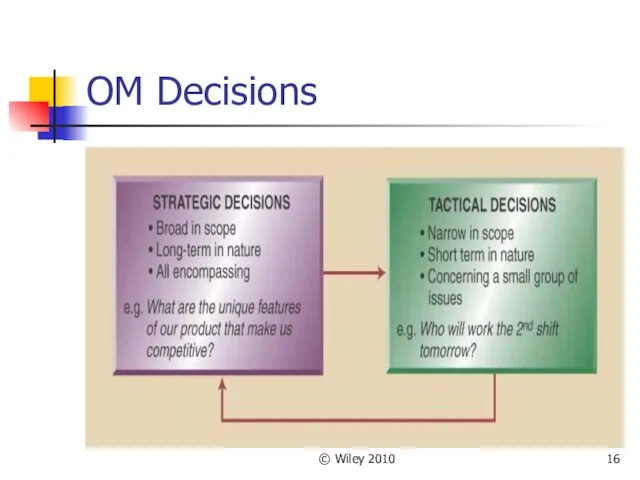
- 14. © Wiley 2010 OM Decisions All organizations make decisions and follow a similar path First decisions
- 15. © Wiley 2010 OM Decisions Following decisions focus on specifics - Tactical decision Tactical decisions: focus
- 16. © Wiley 2010 OM Decisions
- 17. © Wiley 2010 Plan of Book-Chapters link to Types of OM Decisions
- 18. © Wiley 2010 Historical Development of OM Industrial revolution Late 1700s Scientific management Early 1900s Human
- 19. © Wiley 2010 Historical Development con’t Reengineering 1990s Global competition 1980s Flexibility 1990s Time-Based Competition 1990s
- 20. © Wiley 2010 Today’s OM Environment Customers demand better quality, greater speed, and lower costs Companies
- 21. © Wiley 2010 OM in Practice OM has the most diverse organizational function Manages the transformation
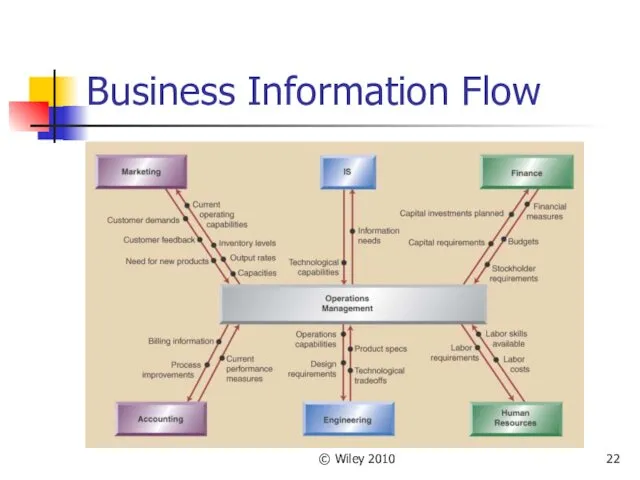
- 22. © Wiley 2010 Business Information Flow
- 23. © Wiley 2010 OM Across the Organization Most businesses are supported by the functions of operations,
- 24. © Wiley 2010 OM Across the Organization – con’t Marketing is not fully able to meet
- 25. © Wiley 2010 Chapter 1 Highlights OM is the business function that is responsible for managing
- 26. © Wiley 2010 Chapter 1 Highlights – con’t Many historical milestones have shaped OM. Some of
- 28. Скачать презентацию


















 Аутсорсингова модель бізнесу компанії
Аутсорсингова модель бізнесу компанії Компания Форпост
Компания Форпост Структура бизнес-плана
Структура бизнес-плана Fitoria. Метод генерации идей
Fitoria. Метод генерации идей Социальное проектирование: виды, возможности и значение для НКО
Социальное проектирование: виды, возможности и значение для НКО Кафе-піцерія New York Street Pizza
Кафе-піцерія New York Street Pizza Современные форматы предприятий общественного питания
Современные форматы предприятий общественного питания Detox Urban - Компания чайных ценителей и бренд чая
Detox Urban - Компания чайных ценителей и бренд чая Business Communications (lecture 14). Crisis Communications
Business Communications (lecture 14). Crisis Communications Эксклюзивный договор Агентства Недвижимости Луиза
Эксклюзивный договор Агентства Недвижимости Луиза Построение устойчивого бизнеса
Построение устойчивого бизнеса Business and community: Cooperation
Business and community: Cooperation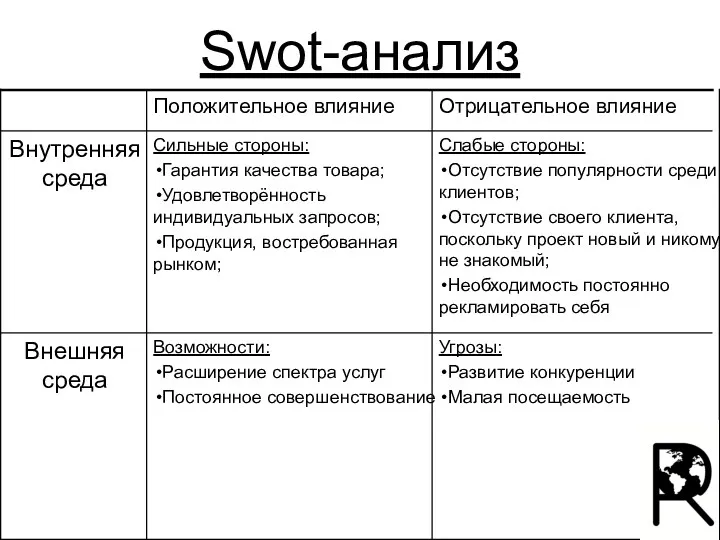 Swot-анализ
Swot-анализ Представляем вашему вниманию Модуль С
Представляем вашему вниманию Модуль С Компания Бизнес диалог
Компания Бизнес диалог Фонд по содействию кредитованию субъектов малого и среднего предпринимательства Республики Карелия
Фонд по содействию кредитованию субъектов малого и среднего предпринимательства Республики Карелия Бизнес-этика
Бизнес-этика Туристік табиғатты пайдаланудың функциональдық моделі
Туристік табиғатты пайдаланудың функциональдық моделі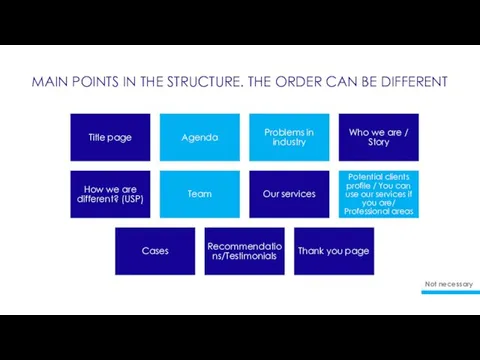 Main points in the structure. The order can be different
Main points in the structure. The order can be different Наша визитная карточка. Интерфакс
Наша визитная карточка. Интерфакс Консультация для поступающих в магистратуру. Туристская индустрия
Консультация для поступающих в магистратуру. Туристская индустрия Бизнес-инкубатор. Поддержка начинающих предпринимателей
Бизнес-инкубатор. Поддержка начинающих предпринимателей Генерирование и оценка бизнес-идеи
Генерирование и оценка бизнес-идеи Ежегодная свадебная премия Притяжение
Ежегодная свадебная премия Притяжение Бизнес-план швейного ателье И’Талия
Бизнес-план швейного ателье И’Талия Достық ауылдық округінде инвестициялық жобаларды іске асыру мүмкіндіктері
Достық ауылдық округінде инвестициялық жобаларды іске асыру мүмкіндіктері Сети отелей Swissotel
Сети отелей Swissotel Стандарти обслуговування
Стандарти обслуговування