Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives To define globalization and international business and show how they affect each other; To
- 3. Reference Chapter one: Globalization and International Business; International Business: Environments & Operations by John D. Daniels,
- 4. Before globalization
- 5. Globalization
- 6. Listening material related to globalization Listening material 1-1: Listening material 1-2: Listening material 1-3:
- 7. Globalization Globalization is the ongoing process that deepens and broadens the relationships and interdependence among countries.
- 8. What does globalization mean?
- 9. What does “Made in China” mean? Clearly, it is becoming more and more difficult to define
- 10. 'Made in China' labels don't tell whole story These days, "Made in China" is actually "Made
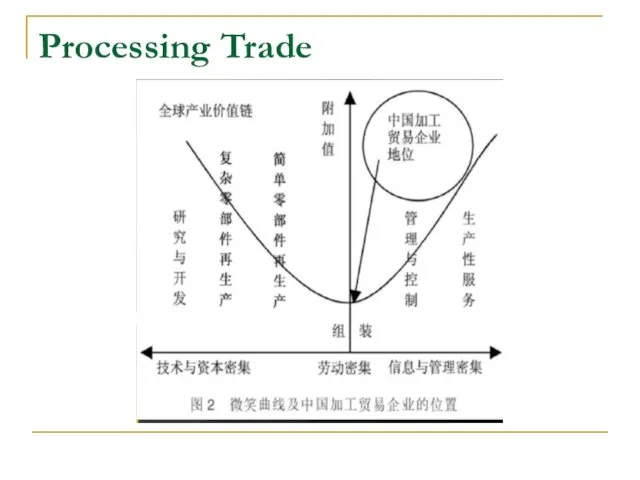
- 11. Processing Trade
- 12. Transforming and Upgrading
- 13. Made in China 2025
- 14. Factors in Increased Globalization Globalization has been growing rapidly in recent decades because of: technological expansion,
- 15. Class Discussion Question Factors which decreased Globalization?
- 16. What is International Business? International business consists of all commercial transactions—including sales, investments, and transportation—that take
- 17. Class Discussion Question (in pairs) Why is international business necessary?
- 18. Sample Answer: “Why is international business necessary?” It’s necessary because international business may lead to improved
- 19. Uncomfortable with Globalization
- 20. Antiglobalization To thwart the globalization process, antiglobalization forces regularly protest international conferences—sometimes violently. Critics of globalization
- 21. Antiglobalization(逆全球化)
- 22. Studying International Business is Important Because Most companies are either international or compete with international companies;
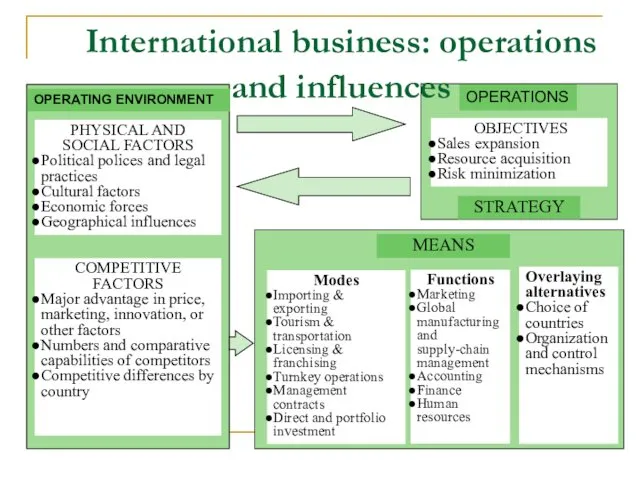
- 23. International business: operations and influences PHYSICAL AND SOCIAL FACTORS Political polices and legal practices Cultural factors
- 24. Why Companies Engage in International Business (Operations) There are three major operating objectives that underlie the
- 25. Modes of Operations in International Business (Means) Merchandise exports and imports Service exports and imports Tourism
- 26. 1. Merchandise exports and imports Exporting and importing are the most popular modes of international business,
- 27. 2. Service Exports and Imports Service exports and imports are international non-product sales and purchases. Currently,
- 28. China’s foreign service trade deficit widens
- 29. Key Concepts ~ ‘Turnkey Operations’ On an international level, companies may pay fees for engineering services
- 30. The Incredible Chinese high-speed rail
- 31. China and Russia to build new high-speed railway
- 32. Key Concepts ~ ‘ Management Contracts’ Companies also pay fees for management contracts—arrangements in which one
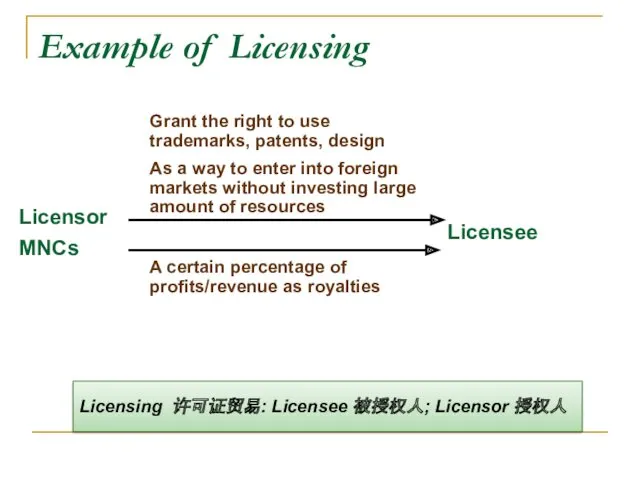
- 33. Asset Use When one company allows another to use its assets—such as trademarks, patents, copyrights, or
- 34. Example of Licensing Licensor MNCs Licensee Grant the right to use trademarks, patents, design As a
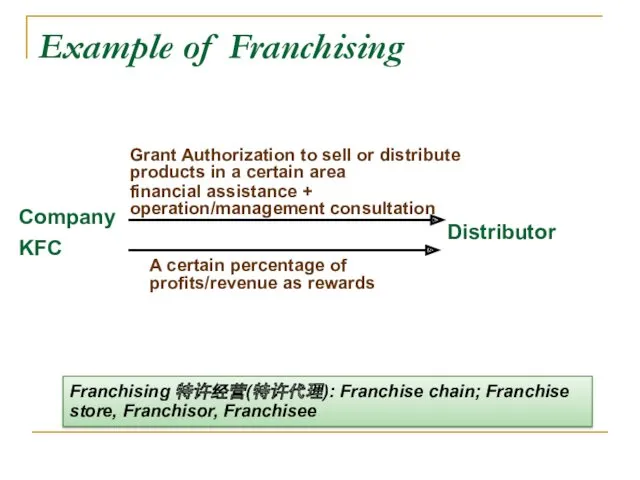
- 35. Example of Franchising Company KFC Distributor Grant Authorization to sell or distribute products in a certain
- 36. Licensing
- 37. Franchising
- 38. 3. Investments Foreign investment means ownership of foreign property in exchange for a financial return, such
- 39. Key Concepts ~ ‘Direct Investment’ In foreign direct investment (FDI), the investor takes a controlling interest
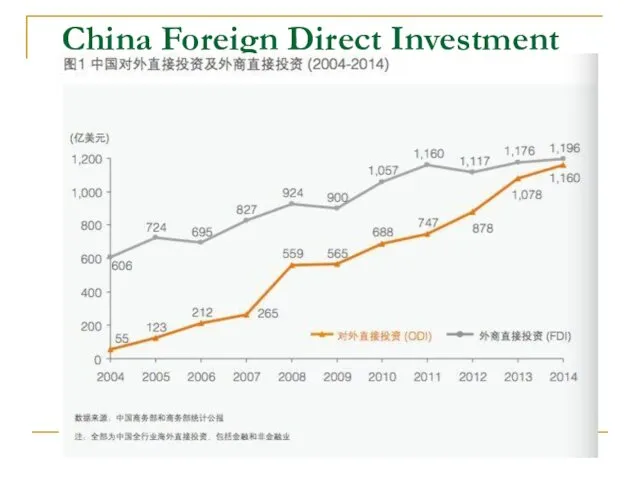
- 40. China Foreign Direct Investment
- 41. China urges firms to tighten foreign investments audits
- 42. Key Concepts ~ ‘Portfolio Investment’ A portfolio investment is a noncontrolling financial interest in another entity.
- 43. Multinational Enterprises An MNE, sometimes called multinational corporation (MNC) or transnational corporation (TNC) is a company
- 44. International Business Differs from Domestic Business (Operating environment) The conditions in a company’s external environment that
- 46. Скачать презентацию






































 Компания PepsiCo
Компания PepsiCo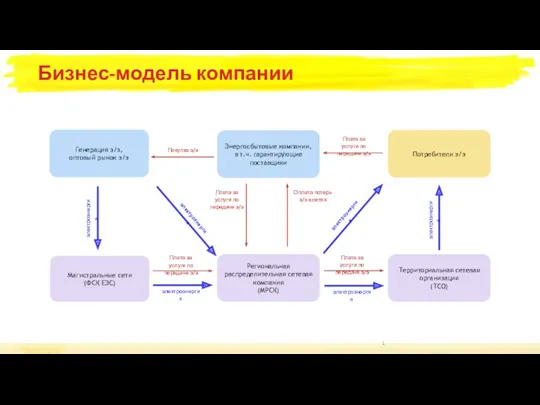 Бизнес-модель компании
Бизнес-модель компании Молодёжное предпринимательство как социальная практика
Молодёжное предпринимательство как социальная практика Шаурмечная У Армэна
Шаурмечная У Армэна Эксклюзивный договор Агентства Недвижимости Луиза
Эксклюзивный договор Агентства Недвижимости Луиза Цесна Астык Концерні
Цесна Астык Концерні Контракт купли-продажи как способ оформления международной сделки
Контракт купли-продажи как способ оформления международной сделки Ресторан Діамант
Ресторан Діамант Меренга. Уникальный торговый продукт
Меренга. Уникальный торговый продукт Дизайн МАФа
Дизайн МАФа Фриланс – удаленная работа
Фриланс – удаленная работа Проект создания и развития крестьянского (фермерского) хозяйства по табунному коневодству
Проект создания и развития крестьянского (фермерского) хозяйства по табунному коневодству Методические материалы по бизнес-планированию
Методические материалы по бизнес-планированию Ресторанный бизнес в наше время
Ресторанный бизнес в наше время Агротуризм. Многофункциональный проект. ООО Ясень
Агротуризм. Многофункциональный проект. ООО Ясень Об основных результатах реформы контроля и надзора
Об основных результатах реформы контроля и надзора Гостиницы Японии (Токио)
Гостиницы Японии (Токио) School of Business. Motivation
School of Business. Motivation Бизнес-навигатор МСП
Бизнес-навигатор МСП Гостиница. Вид гостиницы
Гостиница. Вид гостиницы Molniya club Закрытый клуб предпринимателей
Molniya club Закрытый клуб предпринимателей Кирово-Чепецкий район. Анализ рынка недвижимости
Кирово-Чепецкий район. Анализ рынка недвижимости Разработка бизнес-модели компании швейного производства в современных условиях
Разработка бизнес-модели компании швейного производства в современных условиях MOL Europe BV region south east monthly country game plan calls & performance reviews
MOL Europe BV region south east monthly country game plan calls & performance reviews Battle of minds 2.0: глобальна онлайн гра
Battle of minds 2.0: глобальна онлайн гра Пилигрим. Туристическая компания
Пилигрим. Туристическая компания Бизнес-план студии художественной ковки
Бизнес-план студии художественной ковки LG Group (Life is Good, элджи груп) – тұрмыстық электроника
LG Group (Life is Good, элджи груп) – тұрмыстық электроника