Содержание
- 3. Review: Colonialism, Environment and Modern World Colonialism?Commercial capitalism?commodification of nature (3 C’s) Utilitarian views of nature
- 4. Question: Does colonialism leave any legacies that shape our world today? That shape the nations that
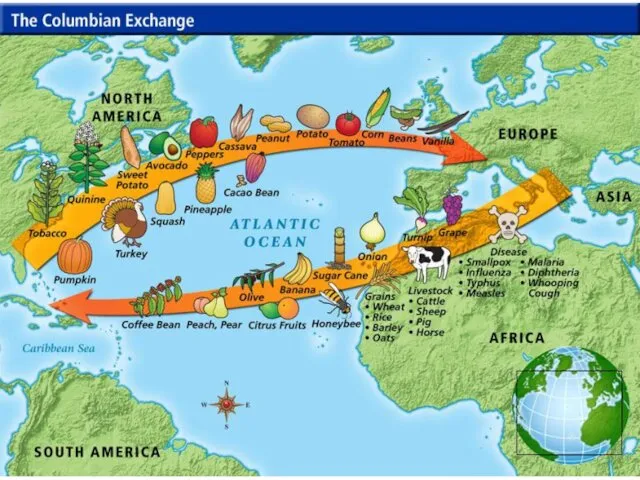
- 5. What was the Columbian Exchange? A. A now defunct clothing company B. The crossing of pathogens,
- 6. Energy, Mining, and the Industrial Revolution
- 7. Fossil capitalism Capitalism and Endless accumulation Energy transition or energy aggregation Old energy regime Geography of
- 8. How did fossil capitalism come about and what is its significance for the global environment? Endless
- 9. Fossil capitalism Capitalism and Endless accumulation Energy transition or energy aggregation Old energy regime Geography of
- 11. Transition to fossil fuels (coal) did not happen everywhere simultaneously Geography of coal and transport costs
- 13. Fossil capitalism Capitalism and Endless accumulation Energy transition or energy aggregation Old energy regime Geography of
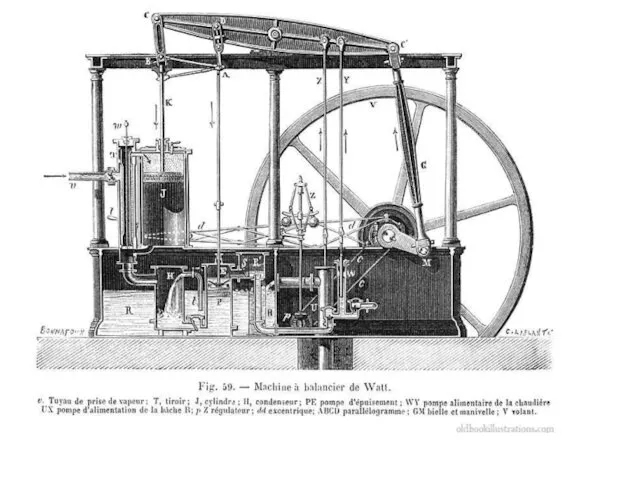
- 14. Coal and 1st industrial Revolution: some consequences Railroad, iron, and steel Profits reach new levels A
- 16. Fossil capitalism Capitalism and Endless accumulation Energy transition or energy aggregation Old energy regime Geography of
- 17. Coal, labor wars, and Carbon democracy Coal workforce and poential disruption The power and the threat
- 21. Oil and second industrial revolution: some effects Resources and raw materials from distant places (in colonized
- 23. Fossil capitalism Capitalism and Endless accumulation Energy transition or energy aggregation Old energy regime Geography of
- 25. Скачать презентацию




















 Декларация о плате за негативное воздействие на окружающую среду
Декларация о плате за негативное воздействие на окружающую среду Экологические проблемы мировой энергетики
Экологические проблемы мировой энергетики Здоровый образ жизни
Здоровый образ жизни Состав промышленных выбросов и отходов различных производств
Состав промышленных выбросов и отходов различных производств Пути решения раздельного сбора мусора в Московской области
Пути решения раздельного сбора мусора в Московской области Жизнь без мусора. Из мусорной кучки классные штучки
Жизнь без мусора. Из мусорной кучки классные штучки Чтоб жила Земля
Чтоб жила Земля Сукцессия. Зарождение и смена биогеоценоза
Сукцессия. Зарождение и смена биогеоценоза Environmental Protection
Environmental Protection Фотоконкурс Большой год. Привлечения местного населения для изучение птиц
Фотоконкурс Большой год. Привлечения местного населения для изучение птиц Естественные сообщества живых организмов, компоненты биогеоценозов. 11 класс
Естественные сообщества живых организмов, компоненты биогеоценозов. 11 класс Сторінками червоної книги України
Сторінками червоної книги України Природоохранные концепции и межгосударственные соглашения
Природоохранные концепции и межгосударственные соглашения Биосфера. Адам әрекетінің әсері. Биосфера ластануының негізгі ерекшеліктері
Биосфера. Адам әрекетінің әсері. Биосфера ластануының негізгі ерекшеліктері Методы и технические средства защиты гидросферы
Методы и технические средства защиты гидросферы Тенденции урбанизации. Экологические проблемы урбанизации: техногенные биогеохимические аномалии
Тенденции урбанизации. Экологические проблемы урбанизации: техногенные биогеохимические аномалии Как перерабатывать макулатуру
Как перерабатывать макулатуру Правовое регулирование экологической сертификации. (Лекция 4)
Правовое регулирование экологической сертификации. (Лекция 4) Биохимические и морфологические изменения у березы бородавчатой под влиянием воздушного загрязнения
Биохимические и морфологические изменения у березы бородавчатой под влиянием воздушного загрязнения Топырақ экологиясы
Топырақ экологиясы Первоцветы
Первоцветы Профессия: эколог
Профессия: эколог Борьба с природоохранными нарушениями на примере несанкционированного размещения отходов
Борьба с природоохранными нарушениями на примере несанкционированного размещения отходов Экологическая газета для любознательных
Экологическая газета для любознательных Рациональное использование природных ресурсов
Рациональное использование природных ресурсов Земля - наш общий дом
Земля - наш общий дом Ландшафтоведение. Типы морфолитогенеза (часть 1)
Ландшафтоведение. Типы морфолитогенеза (часть 1) Загрязнение атмосферы
Загрязнение атмосферы