Содержание
- 2. Revisiting the Market Equilibrium Do the equilibrium price and quantity maximize the total welfare of buyers
- 3. Welfare Economics Welfare economics is the study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being.
- 4. Welfare Economics Equilibrium in the market results in maximum benefits, and therefore maximum total welfare for
- 5. Welfare Economics Consumer surplus measures economic welfare from the buyer’s side. Producer surplus measures economic welfare
- 6. Consumer Surplus Willingness to pay is the maximum price that a buyer is willing and able
- 7. Consumer Surplus Consumer surplus is the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good
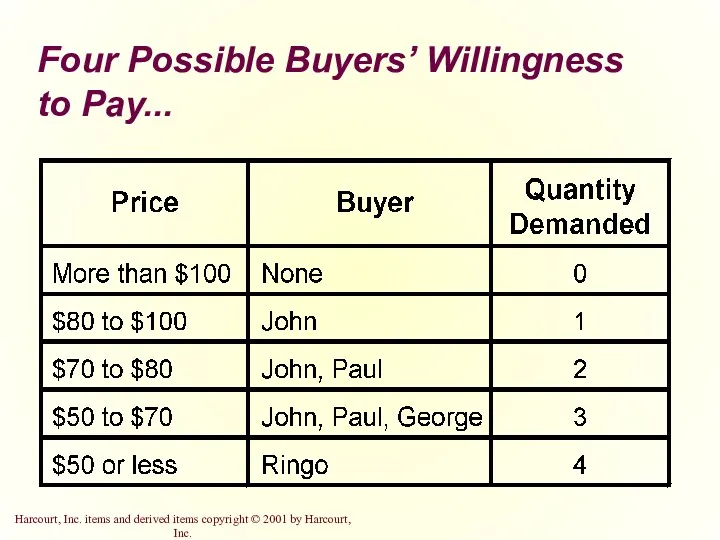
- 8. Four Possible Buyers’ Willingness to Pay...
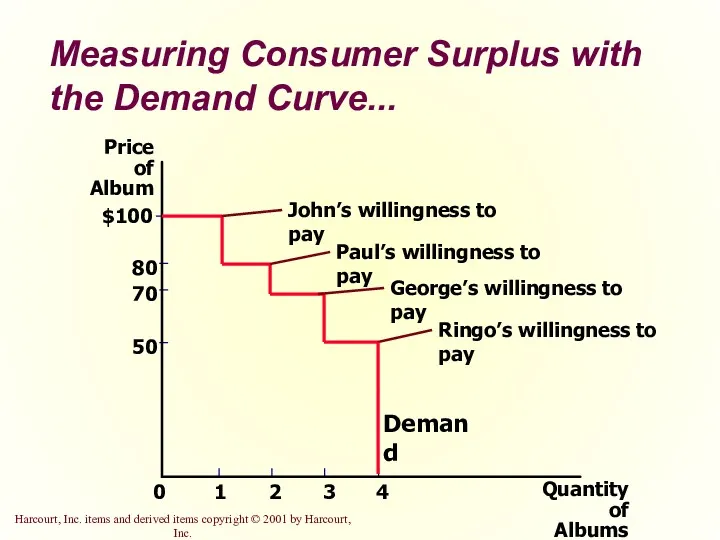
- 9. Consumer Surplus The market demand curve depicts the various quantities that buyers would be willing and
- 10. Four Possible Buyers’ Willingness to Pay...
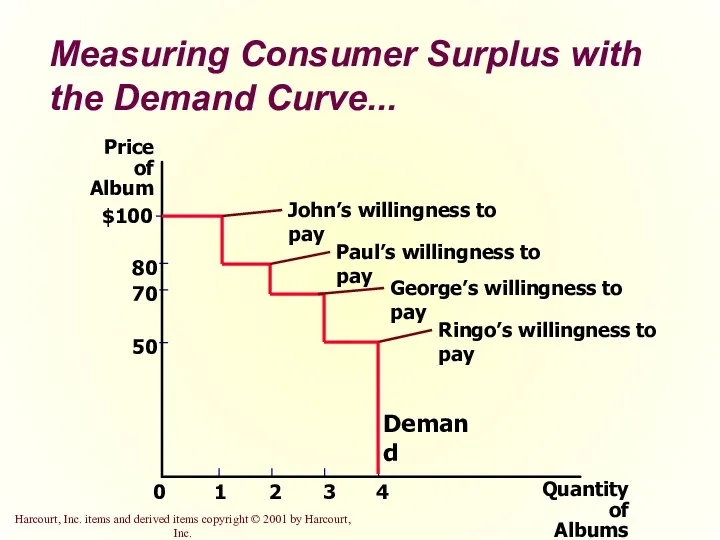
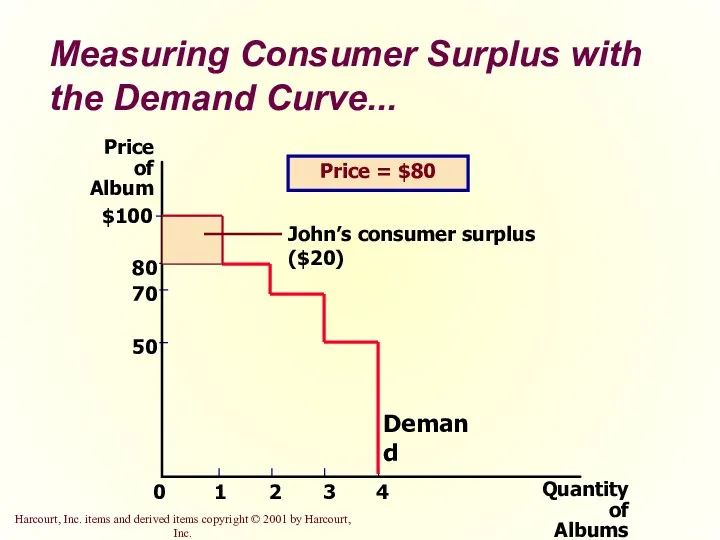
- 11. Measuring Consumer Surplus with the Demand Curve... Price of Album 50 70 80 0 $100 1
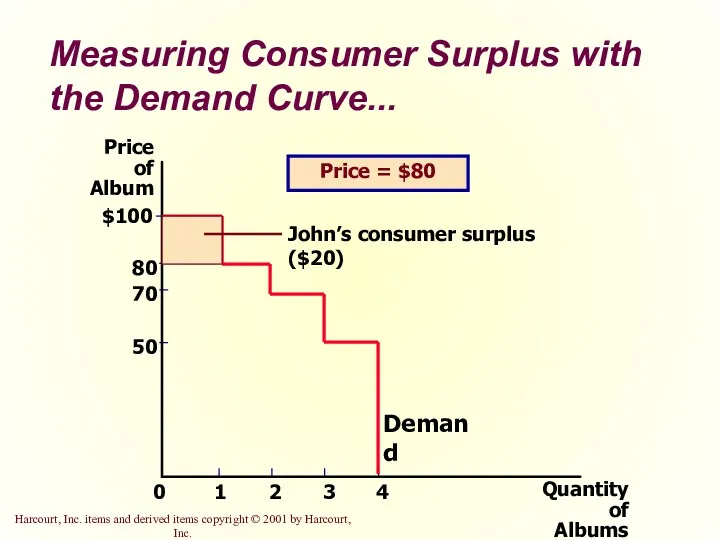
- 12. Measuring Consumer Surplus with the Demand Curve... Price of Album 50 70 80 0 $100 1
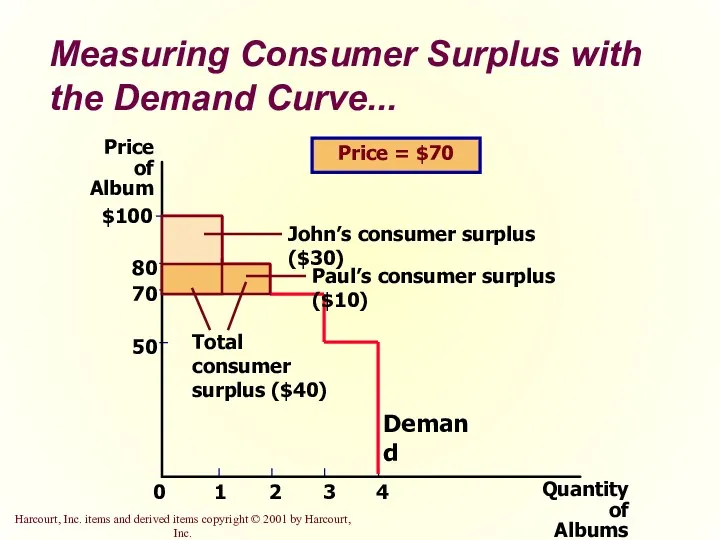
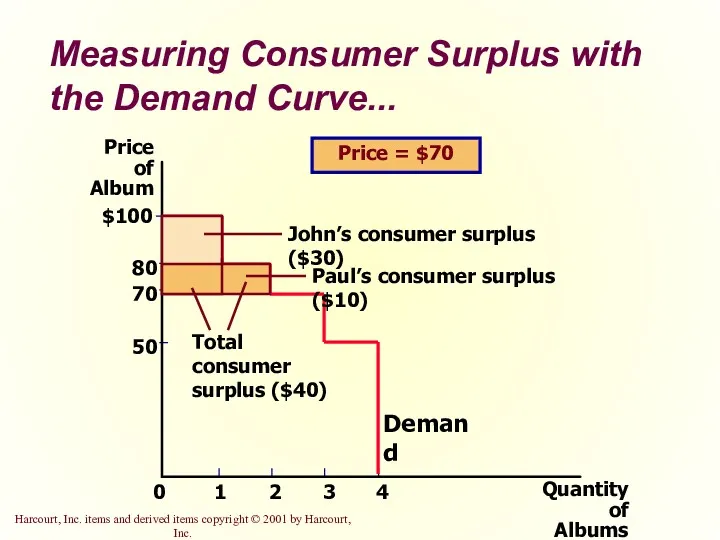
- 13. Measuring Consumer Surplus with the Demand Curve... Price of Album 50 70 80 0 $100 1
- 14. Measuring Consumer Surplus with the Demand Curve The area below the demand curve and above the
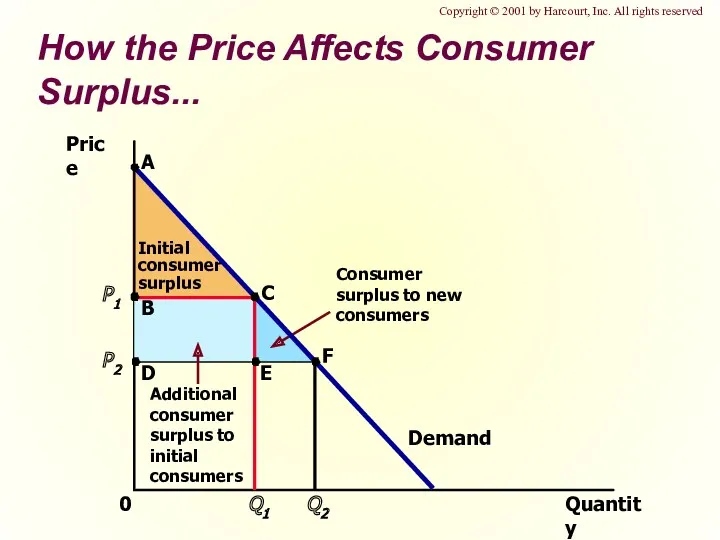
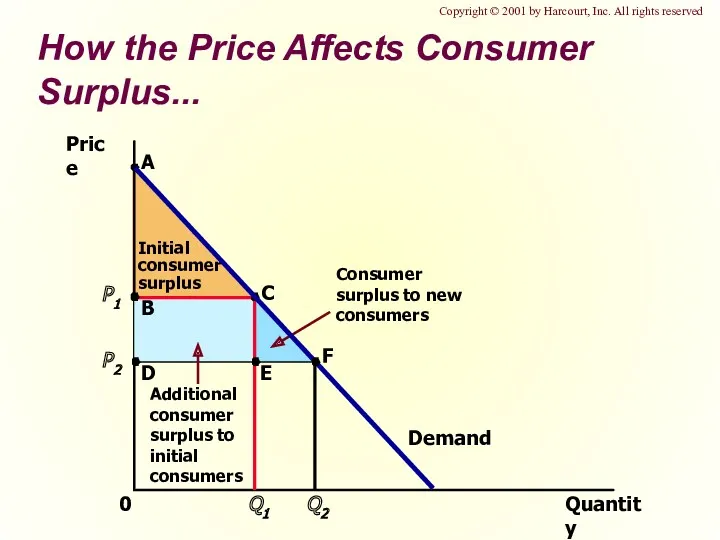
- 15. How the Price Affects Consumer Surplus... Quantity Price 0 Demand Copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
- 16. Consumer Surplus and Economic Well-Being Consumer surplus, the amount that buyers are willing to pay for
- 17. Producer Surplus Producer surplus is the amount a seller is paid minus the cost of production.
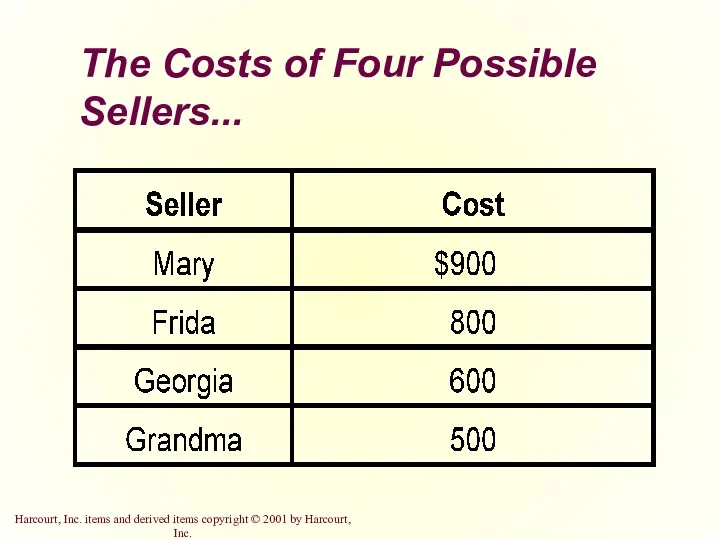
- 18. The Costs of Four Possible Sellers...
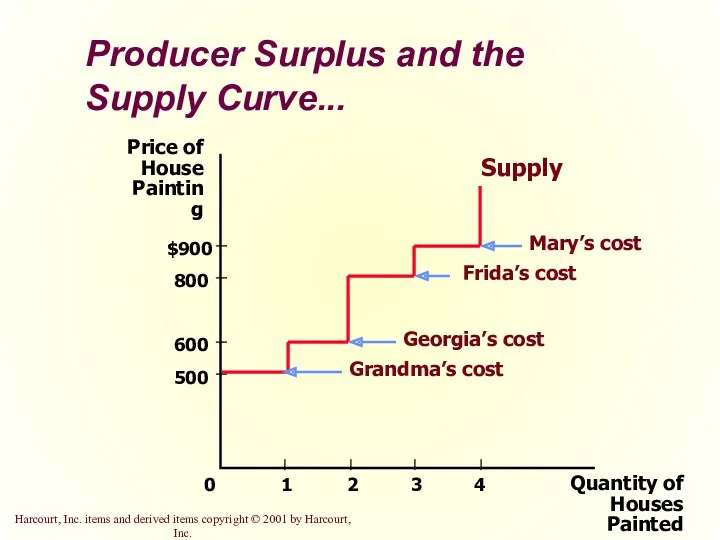
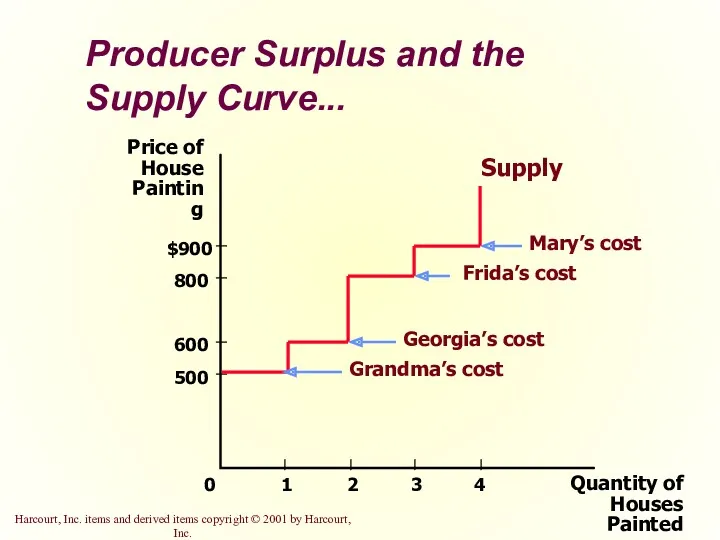
- 19. Producer Surplus and the Supply Curve Just as consumer surplus is related to the demand curve,
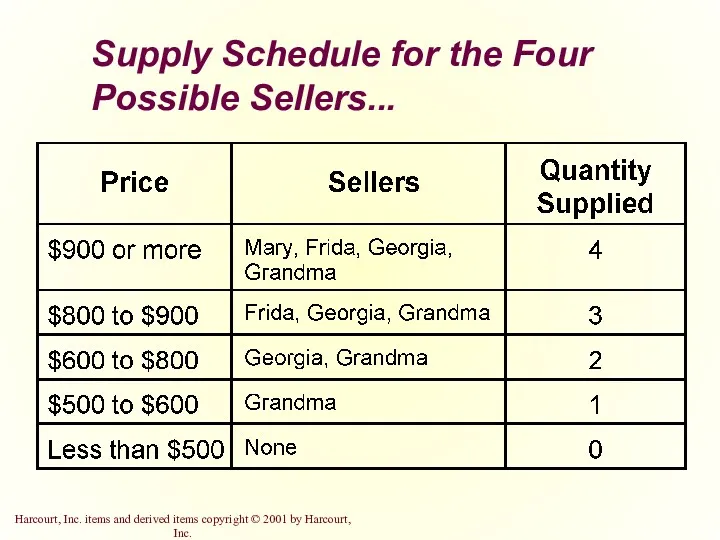
- 20. Supply Schedule for the Four Possible Sellers...
- 21. Producer Surplus and the Supply Curve... Quantity of Houses Painted Price of House Painting 500 800
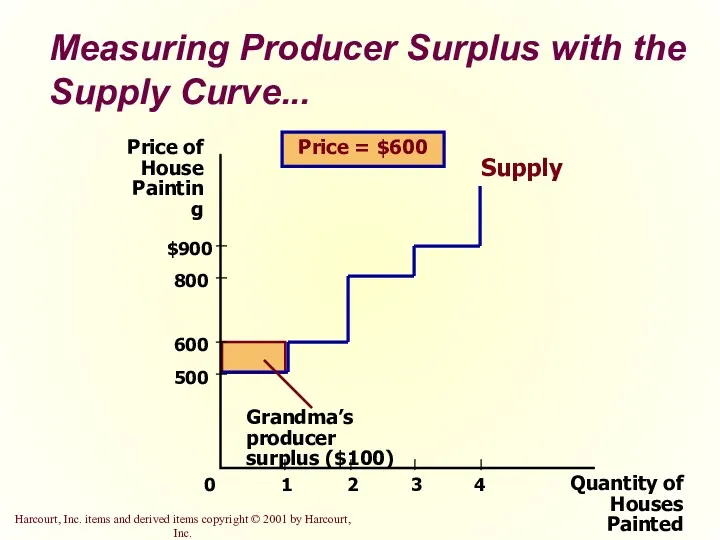
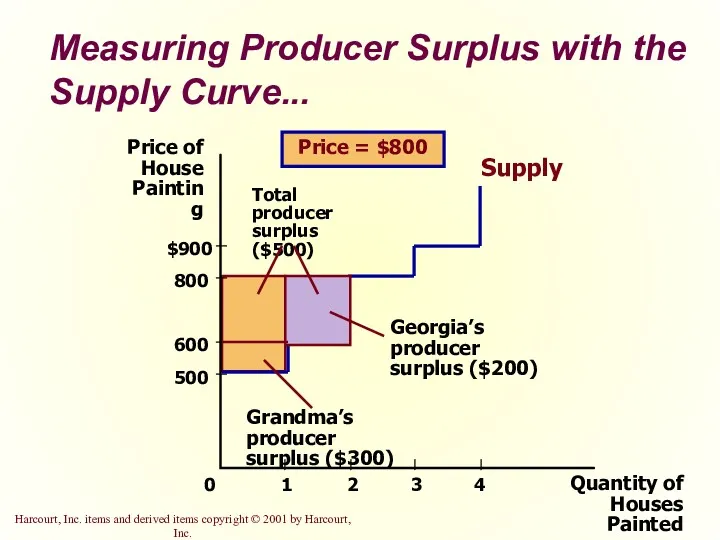
- 22. The area below the price and above the supply curve measures the producer surplus in a
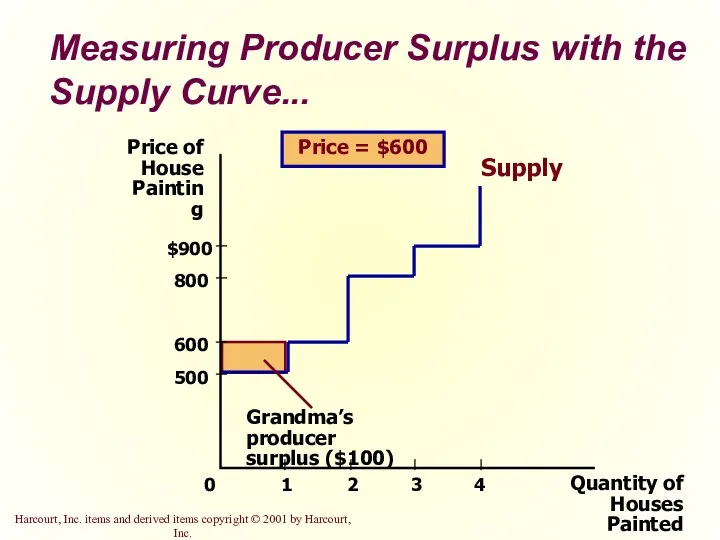
- 23. Measuring Producer Surplus with the Supply Curve... Quantity of Houses Painted Price of House Painting 500
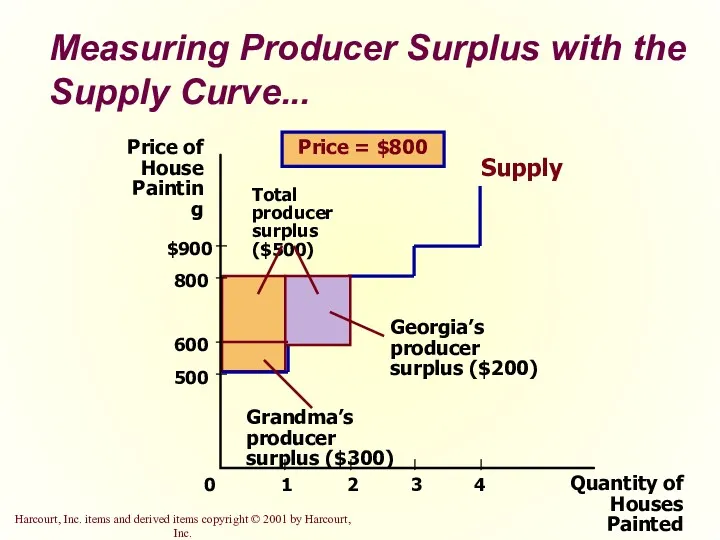
- 24. Measuring Producer Surplus with the Supply Curve... Quantity of Houses Painted Price of House Painting 500
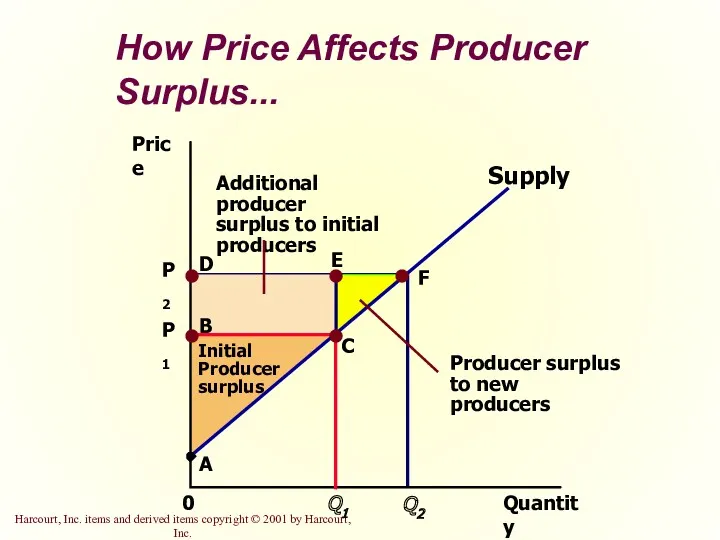
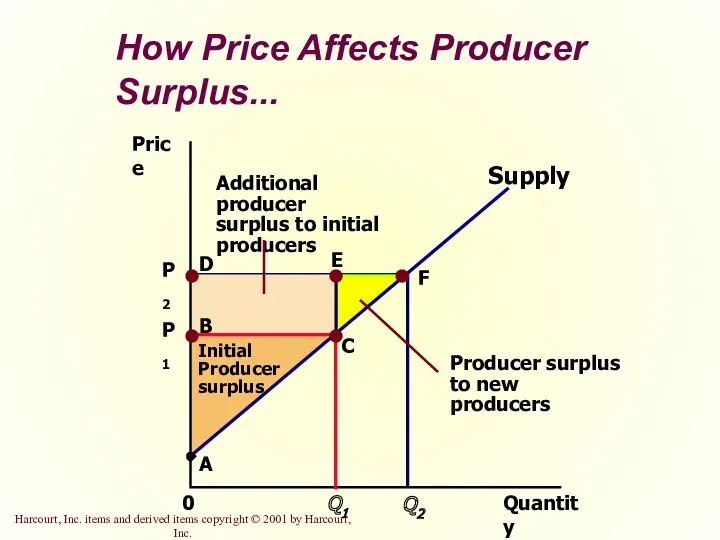
- 25. How Price Affects Producer Surplus... Quantity Price 0 Supply Initial Producer surplus
- 26. Market Efficiency Consumer surplus and producer surplus may be used to address the following question: Is
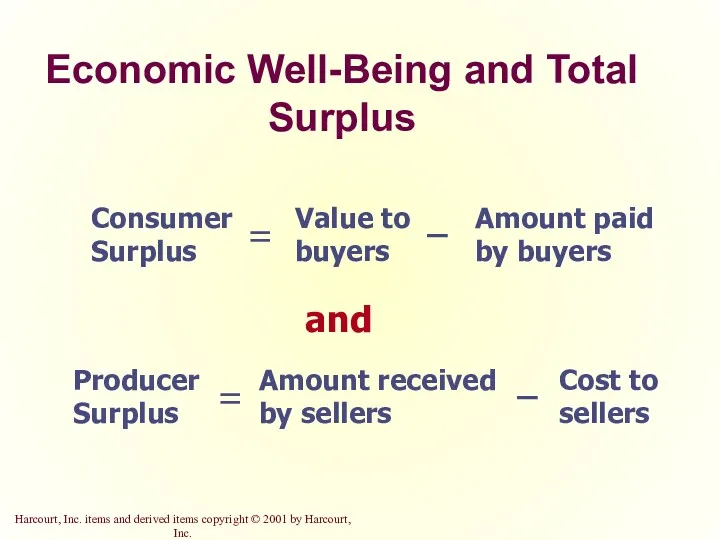
- 27. Economic Well-Being and Total Surplus and
- 28. Economic Well-Being and Total Surplus or
- 29. Market Efficiency Market efficiency is achieved when the allocation of resources maximizes total surplus.
- 30. Market Efficiency In addition to market efficiency, a social planner might also care about equity –
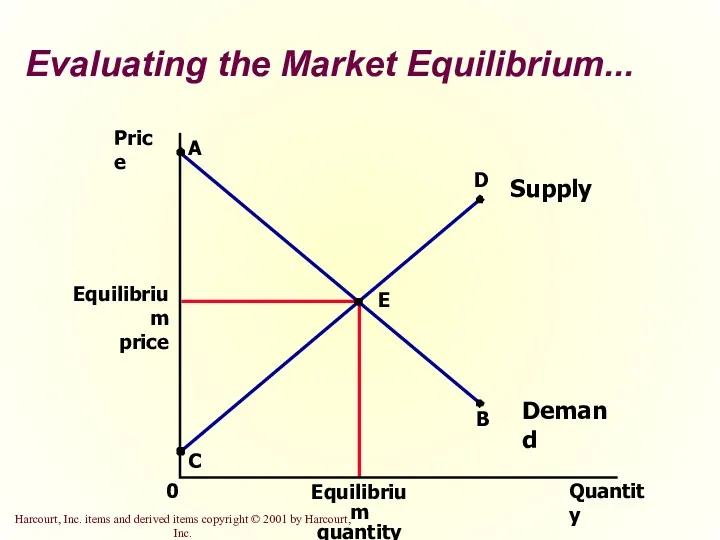
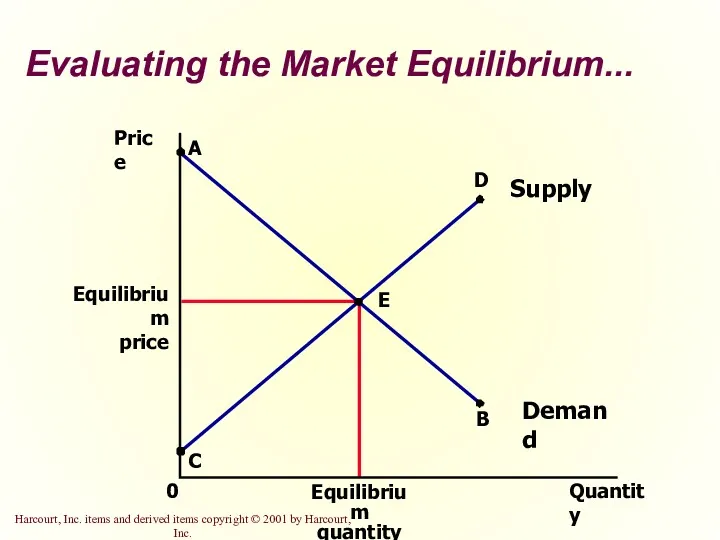
- 31. Evaluating the Market Equilibrium... Price Equilibrium price 0 Quantity Equilibrium quantity A Supply C B Demand
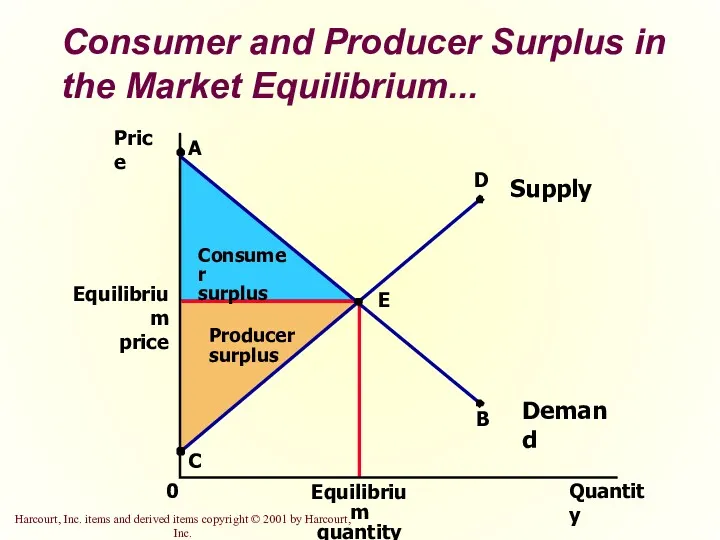
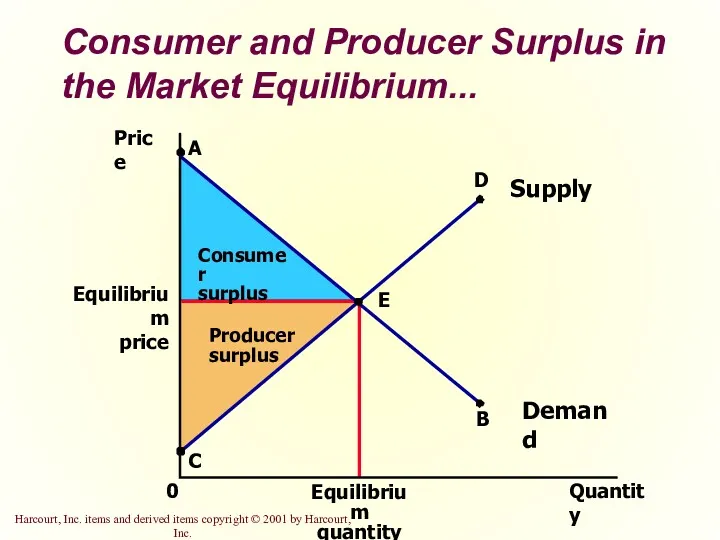
- 32. Consumer and Producer Surplus in the Market Equilibrium... Price Equilibrium price 0 Quantity Equilibrium quantity A
- 33. Three Insights Concerning Market Outcomes Free markets allocate the supply of goods to the buyers who
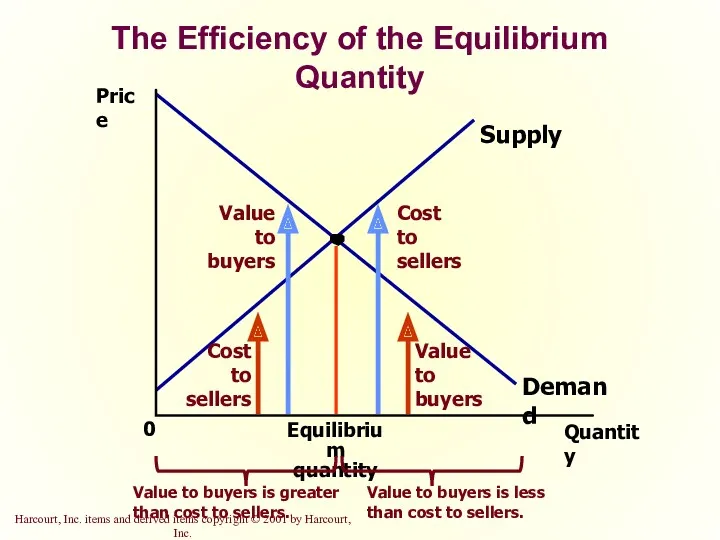
- 34. Price 0 Quantity Equilibrium quantity Supply Demand Cost to sellers Value to buyers Value to buyers
- 35. The Efficiency of the Equilibrium Quantity Because the equilibrium outcome is an efficient allocation of resources,
- 36. Market Power If a market system is not perfectly competitive, market power may result. Market power
- 37. Externalities Externalities are created when a market outcome affects individuals other than buyers and sellers in
- 38. Summary Consumer surplus measures the benefit buyers get from participating in a market. Consumer surplus can
- 39. Summary Producer surplus measures the benefit sellers get from participating in a market. Producer surplus can
- 40. Summary The equilibrium of demand and supply maximizes the sum of consumer and producer surplus. This
- 41. Summary An allocation of resources that maximizes the sum of consumer and producer surplus is said
- 43. Measuring Consumer Surplus with the Demand Curve...
- 44. Measuring Consumer Surplus with the Demand Curve...
- 45. Measuring Consumer Surplus with the Demand Curve...
- 46. How the Price Affects Consumer Surplus...
- 47. Producer Surplus and the Supply Curve...
- 48. Measuring Producer Surplus with the Supply Curve...
- 49. Measuring Producer Surplus with the Supply Curve...
- 50. How Price Affects Producer Surplus...
- 51. Evaluating the Market Equilibrium...
- 52. Consumer and Producer Surplus in the Market Equilibrium...
- 54. Скачать презентацию


























 Институциональные аспекты рыночного хозяйства
Институциональные аспекты рыночного хозяйства Қазақстан-Қытай шекарааралық ынтымақтастығы
Қазақстан-Қытай шекарааралық ынтымақтастығы Теория потребительского поведения
Теория потребительского поведения Праця та соціально-трудові відносини як предмет наукового економічного дослідження
Праця та соціально-трудові відносини як предмет наукового економічного дослідження Малайзия мемлекеті
Малайзия мемлекеті Сыртқы экономикалық қызмет субъектілерін жіктеп көрсету, кепілдіктерінің мәнін терең ашып түсіндіру
Сыртқы экономикалық қызмет субъектілерін жіктеп көрсету, кепілдіктерінің мәнін терең ашып түсіндіру Алкогольная промышленность
Алкогольная промышленность Модель связей различных отраслей экономики
Модель связей различных отраслей экономики Экономические основы здравоохранения Российской Федерации
Экономические основы здравоохранения Российской Федерации Экономический рост. Сбережения и инвестиции. Тема 6
Экономический рост. Сбережения и инвестиции. Тема 6 Национальная инновационная система России глазами российских и зарубежных экспертов. Часть 1
Национальная инновационная система России глазами российских и зарубежных экспертов. Часть 1 DeltaSecurity. System to check contractors for reliability to provide economical security of the company
DeltaSecurity. System to check contractors for reliability to provide economical security of the company Халықаралық экономикалық қатынастар
Халықаралық экономикалық қатынастар Итоги исполнения местных бюджетов Калининградской области
Итоги исполнения местных бюджетов Калининградской области Основы технологии проектирования устойчивого развития или технологии бездефектного управления
Основы технологии проектирования устойчивого развития или технологии бездефектного управления Основы теории спроса и предложения
Основы теории спроса и предложения Энергетические рынки, тарифы, цены, конкуренция
Энергетические рынки, тарифы, цены, конкуренция Економічна характеристика Південної Кореї
Економічна характеристика Південної Кореї Общее экономическое равновесие и экономика благосостояния
Общее экономическое равновесие и экономика благосостояния Основы рационального природопользования
Основы рационального природопользования Государственная экономическая политика
Государственная экономическая политика Монополистическая конкуренция. Внешние эффекты
Монополистическая конкуренция. Внешние эффекты Финансовый рынок
Финансовый рынок Инновационная и инвестиционная деятельность предприятия. (Тема 10)
Инновационная и инвестиционная деятельность предприятия. (Тема 10) Содержание, предмет, принципы экономического анализа. Роль экономического анализа в условиях рыночной экономики
Содержание, предмет, принципы экономического анализа. Роль экономического анализа в условиях рыночной экономики Макроэкономические факторы конкурентоспособности товаров и услуг
Макроэкономические факторы конкурентоспособности товаров и услуг Предприятие – основное звено экономики
Предприятие – основное звено экономики Хозяйство России. Экономика
Хозяйство России. Экономика