Содержание
- 2. Aims and objectives Aims: 1) Introduce types of economies; 2) Introduce special vocabulary. Objectives: 1) Show
- 3. Plan 1) Types of Economic Systems 2) Traditional Economy 3) Market Economy 4) Mixed Economy 5)
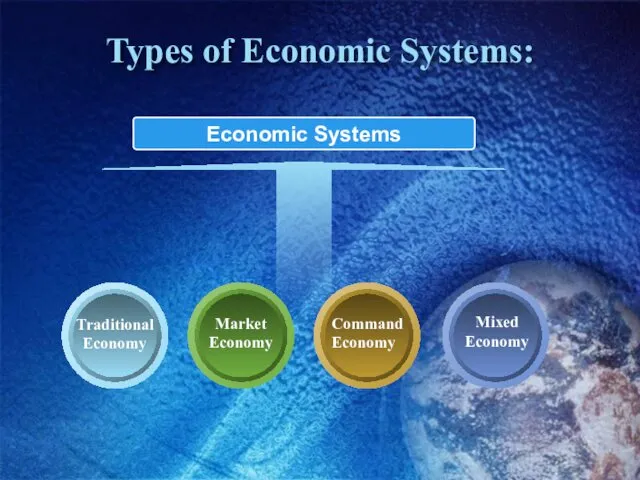
- 4. Types of Economic Systems: Economic Systems Traditional Economy Command Economy Market Economy Mixed Economy
- 5. Economic Systems Economic Systems – method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and
- 6. Types of Economic Systems: Traditional Economy – relies on habit, custom, or ritual to decide questions
- 7. Types of Economic Systems: Market Economy – decisions on production and consumption of goods and services
- 8. Types of Economic Systems: Mixed Economy – market-based economic system in which the government plays a
- 9. Types of Economic Systems: Command Economy – a central authority is in command of the economy
- 10. Comparing Mixed Economies An economic system that permits the conduct of business with minimal government intervention
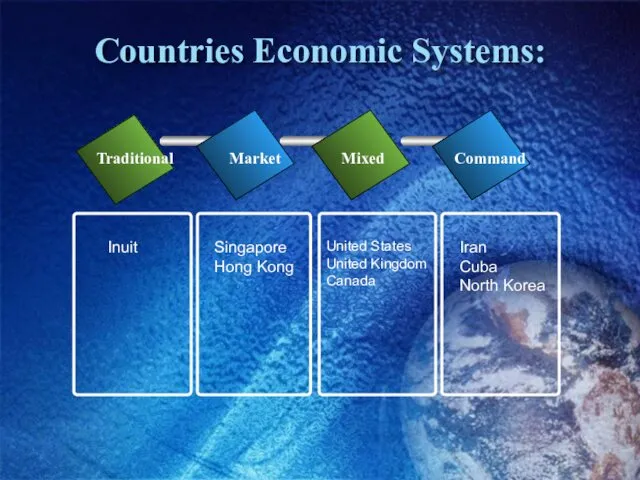
- 11. Countries Economic Systems: Traditional Market Mixed Command Inuit Singapore Hong Kong United States United Kingdom Canada
- 12. 3 Economics WHAT goods and services should be produced? HOW should these goods and services be
- 13. Traditional economies The highest goals of people in a traditional economy are economic stability and security.
- 14. Do you know any barter countries? Which ones?
- 15. Inuit (North America)
- 16. Command economies Rulers at the top of these early civilizations—kings, pharaohs, emperors—commanded the populace to devote
- 17. Can you tell us, what countries do u know with command economy?
- 18. North Korea
- 19. Market Economies: Decision Making by Individuals The newest economic system to emerge in human history is
- 20. USA
- 21. Let us repeat 1) Traditional Economy centers on families, clans, or tribes decisions are based on
- 22. Can you reckon some pluses and minuses of Tradition economy? + -
- 23. Tradition economy Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages: little disagreement over goals, roles methods of production, distribution determined
- 24. Let us repeat Command Economy…. Who can tell about this? You can work together ☺
- 25. Command Economy (centrally planned economy) government (or a king, a leader, a marshal) makes economic decisions
- 26. Let us repeat Market Economy (no interruption from government) driven by choices of consumers and producers
- 27. Let us repeat Mixed economy has elements of traditional, command, market systems most common type of
- 28. Types of Mixed Economies U.S. basically has market system European countries greater mix of market and
- 29. So, who can summarize?
- 30. Vocabulary Centrally planned or command economy –an economy where all economic decisions are taken by the
- 31. Vocabulary Planning – establishment of objectives for man and organization and determination of the best ways
- 32. Vocabulary Subsidy –monetary grant or gift. Partnership –unincorporated business owned and operated by two or more
- 34. Скачать презентацию




























 О социально-экономическом развитии Лоухского муниципального района
О социально-экономическом развитии Лоухского муниципального района Қазақстандағы жел энергиясының даму жолдары
Қазақстандағы жел энергиясының даму жолдары Рыночное равновесие. Тема 8
Рыночное равновесие. Тема 8 Обществознание. Экономика. Тест. Занятие №10
Обществознание. Экономика. Тест. Занятие №10 Управление качеством
Управление качеством Мировая экономика: основные черты и тенденции развития мировой экономики и мирового хозяйства
Мировая экономика: основные черты и тенденции развития мировой экономики и мирового хозяйства Экономическое развитие Аксубаевского муниципального района
Экономическое развитие Аксубаевского муниципального района Основные направления социально-экономического развития Республики Беларусь
Основные направления социально-экономического развития Республики Беларусь Международная торговля товарами и услугами (часть 2)
Международная торговля товарами и услугами (часть 2) Государственное регулирование сельскохозяйственных рынков. (Тема 6)
Государственное регулирование сельскохозяйственных рынков. (Тема 6) Первоначальное накопление капитала. Лекция 4
Первоначальное накопление капитала. Лекция 4 Макроэкономическое равновесие в Модель AD – AS
Макроэкономическое равновесие в Модель AD – AS Макроэкономическая нестабильность. Безработица и инфляция
Макроэкономическая нестабильность. Безработица и инфляция Структура споживання родин із різним рівнем доходів
Структура споживання родин із різним рівнем доходів Теоретические основы планирования на предприятии
Теоретические основы планирования на предприятии Мировая экономика
Мировая экономика Социальные проблемы: макроэкономический анализ
Социальные проблемы: макроэкономический анализ Косметическая отрасль Республики Беларусь
Косметическая отрасль Республики Беларусь Особые экономические зоны как разновидность СЭЗ
Особые экономические зоны как разновидность СЭЗ Организационно-кадровый и социальный аудит
Организационно-кадровый и социальный аудит Внешняя среда организации и ее анализ. PEST
Внешняя среда организации и ее анализ. PEST Переваги та недоліки вступу України до ЄС
Переваги та недоліки вступу України до ЄС Теория и практика государственного регулирования конкурентоспособности территории
Теория и практика государственного регулирования конкурентоспособности территории Семейное хозяйство (5 класс)
Семейное хозяйство (5 класс) Солнечные коллекторы
Солнечные коллекторы Методики оценки стоимости предприятия
Методики оценки стоимости предприятия Рынок и рыночный механизм
Рынок и рыночный механизм Экономическая теория. Предмет и метод. Тема 1
Экономическая теория. Предмет и метод. Тема 1