Содержание
- 2. Overview Special features Stages of electricity production Production function and costs Natural monopoly Regulation Technological change
- 3. Special features Demand fluctuations within the day, across seasons Demand = load Peak vs. offpeak demand
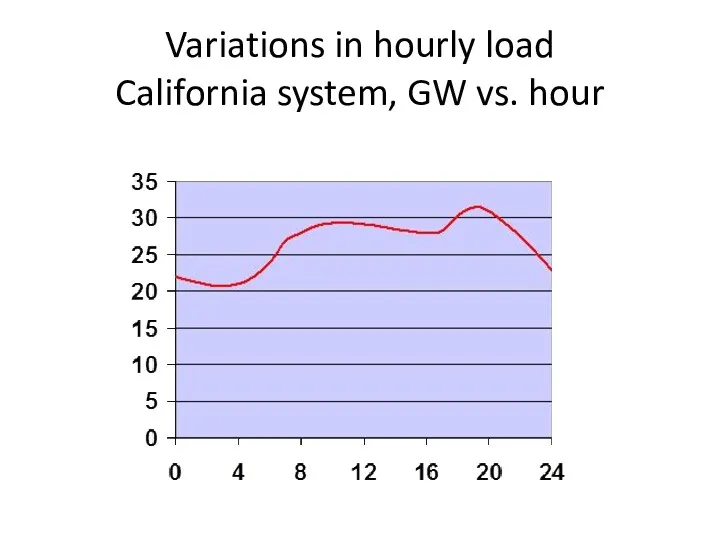
- 4. Variations in hourly load California system, GW vs. hour
- 5. Special features Not storable (electricity today is not a substitute for electricity tomorrow)
- 6. Special features High costs of shortages Blackouts or brownouts Capacity >= load “peak load problem”
- 7. Special features Electricity is a secondary source of energy Electricity is both an output and an
- 8. Special features Electricity consuming capital is long lived (… years) Electricity producing capital is long lived
- 9. Special features Summary Demand fluctuations (within the day, across seasons) Not storable (electricity today is not
- 10. Production process Generation Transmission Distribution
- 11. Production process Generation Electricity is a secondary energy source Transformation of one energy into electricity Mechanical
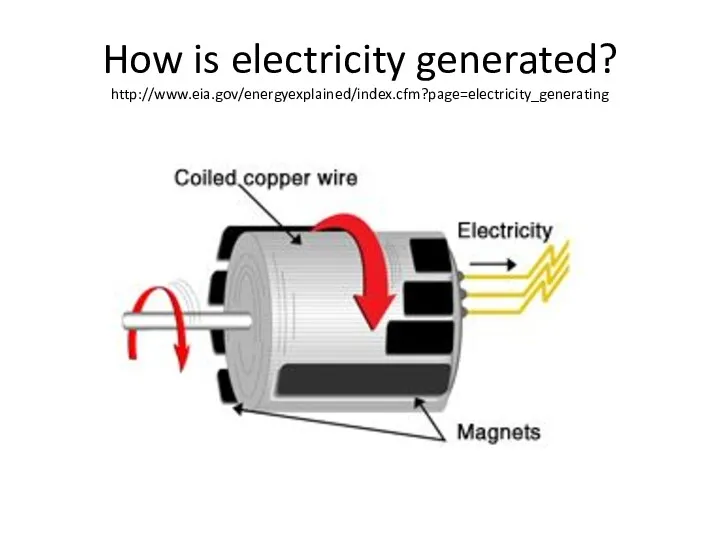
- 12. How is electricity generated? http://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/index.cfm?page=electricity_generating
- 13. Supply chain video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=20Vb6hlLQSg
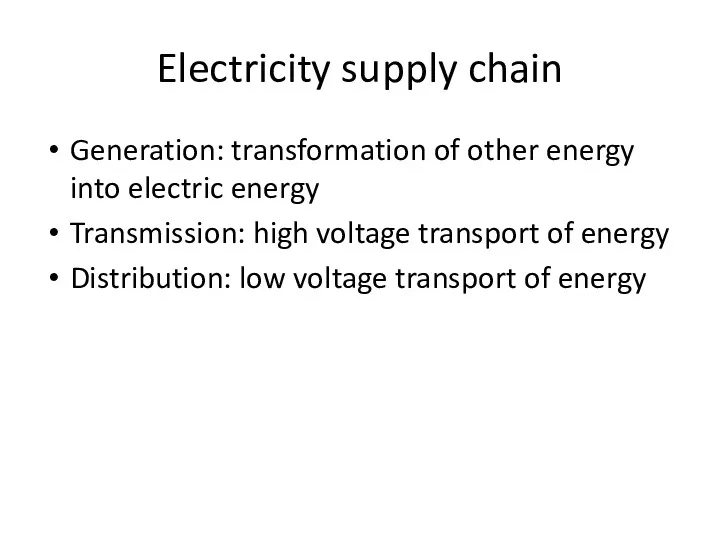
- 14. Electricity supply chain Generation: transformation of other energy into electric energy Transmission: high voltage transport of
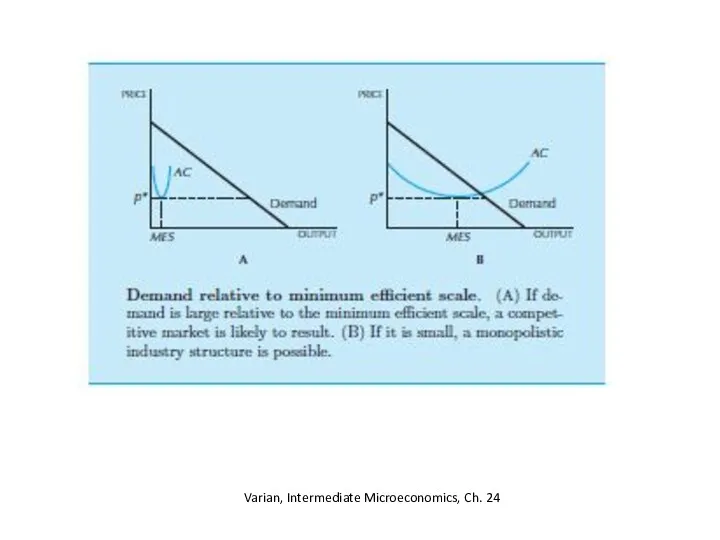
- 15. Minimum efficient scale MES is the level of output that minimizes average cost relative to the
- 16. Varian, Intermediate Microeconomics, Ch. 24
- 17. Modelling electricity markets High fixed cost Low variable cost Average cost declines as Q grows
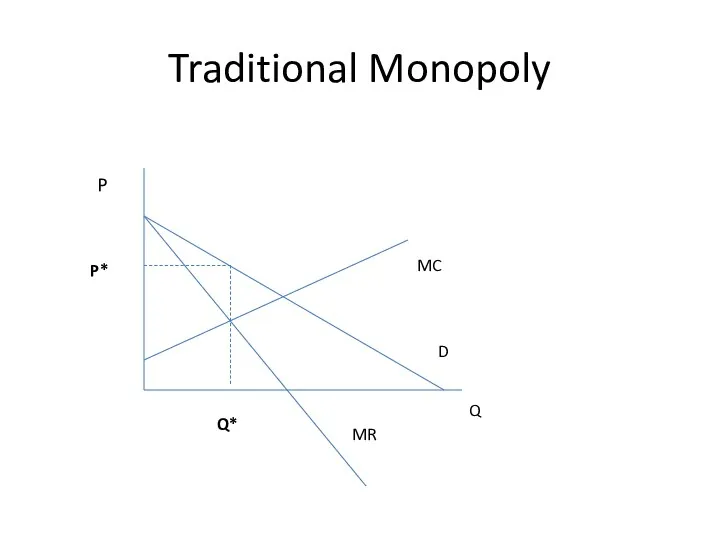
- 18. Traditional Monopoly Q P D MR MC Q* P*
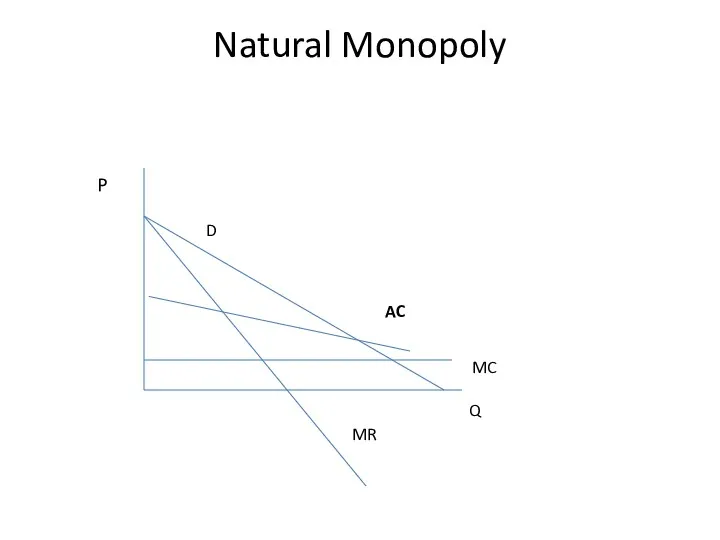
- 19. Natural Monopoly Q P D MR MC AC
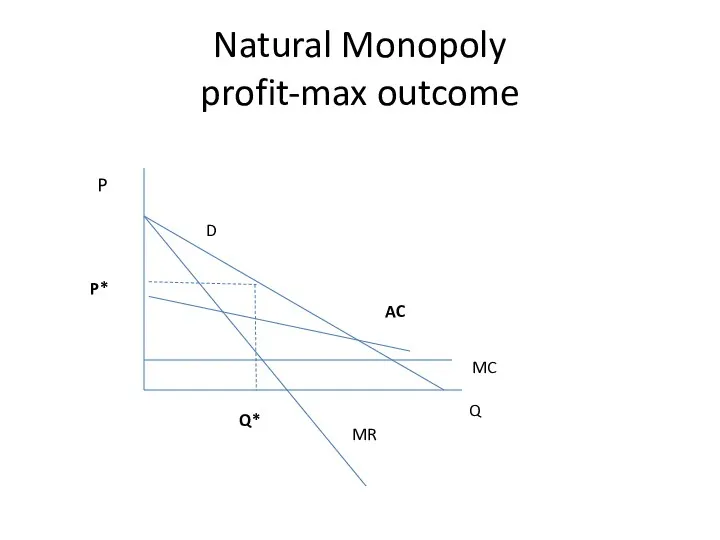
- 20. Natural Monopoly profit-max outcome Q P D MR MC Q* P* AC
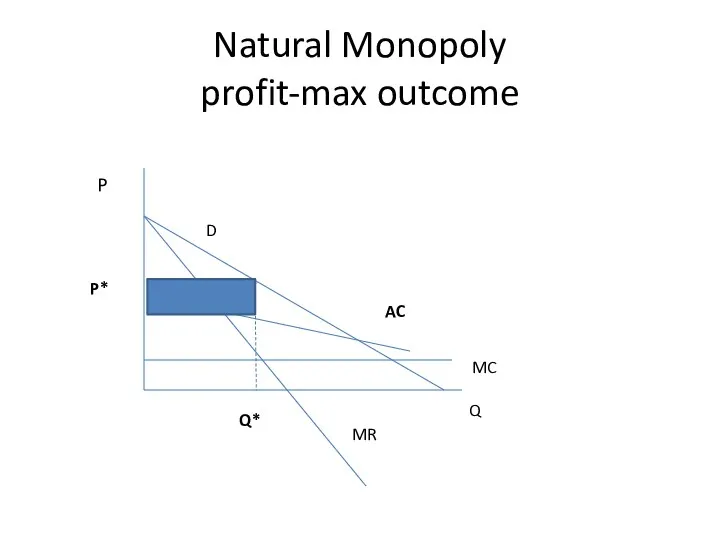
- 21. Natural Monopoly profit-max outcome Q P D MR MC Q* P* AC
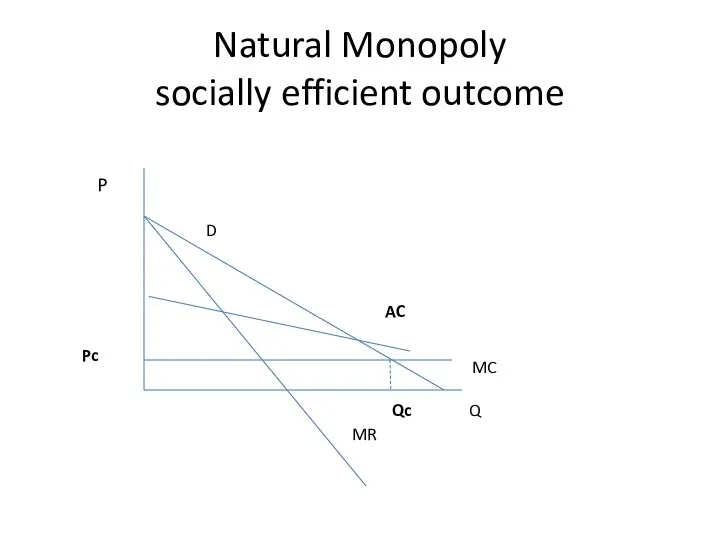
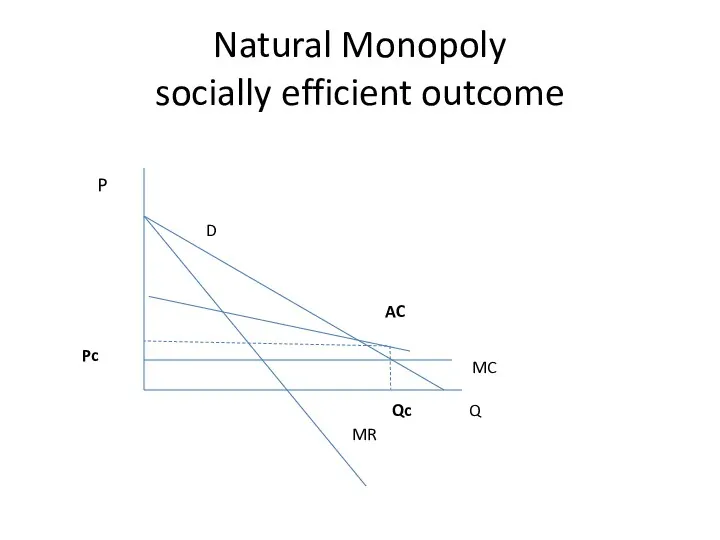
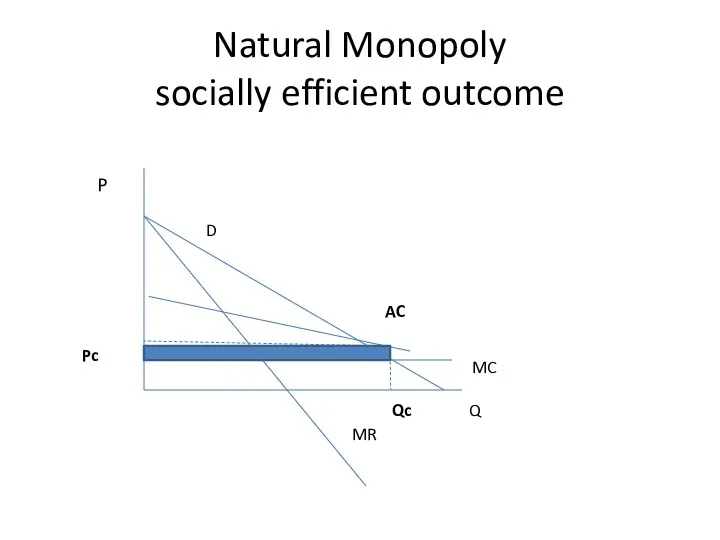
- 22. Natural Monopoly socially efficient outcome Q P D MR MC Qc Pc AC
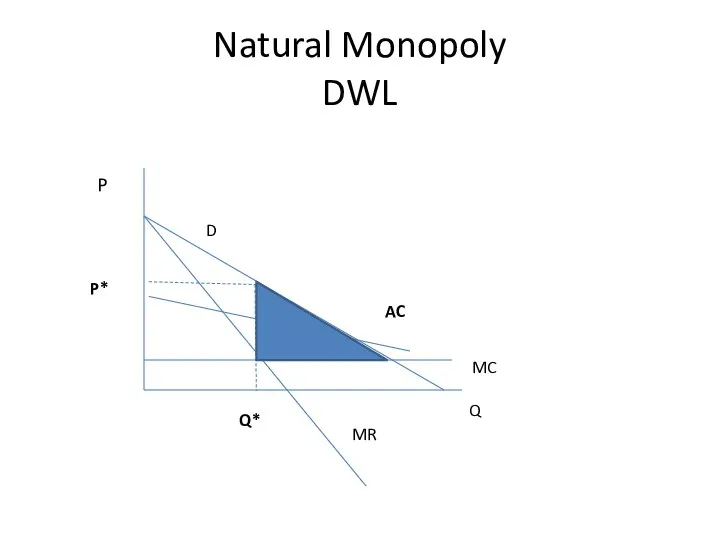
- 23. Natural Monopoly DWL Q P D MR MC Q* P* AC
- 24. Natural Monopoly socially efficient outcome Q P D MR MC Qc Pc AC
- 25. Natural Monopoly socially efficient outcome Q P D MR MC Qc Pc AC
- 26. Natural Monopoly Policy 1. Public Ownership 2. Private Ownership + regulation
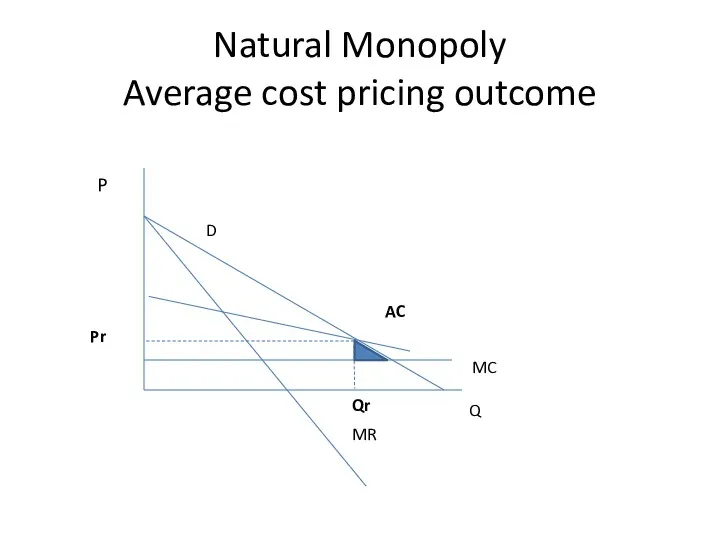
- 27. Natural Monopoly Average cost pricing outcome Q P D MR MC Qr Pr AC
- 28. Differentiating peak & off-peak demand
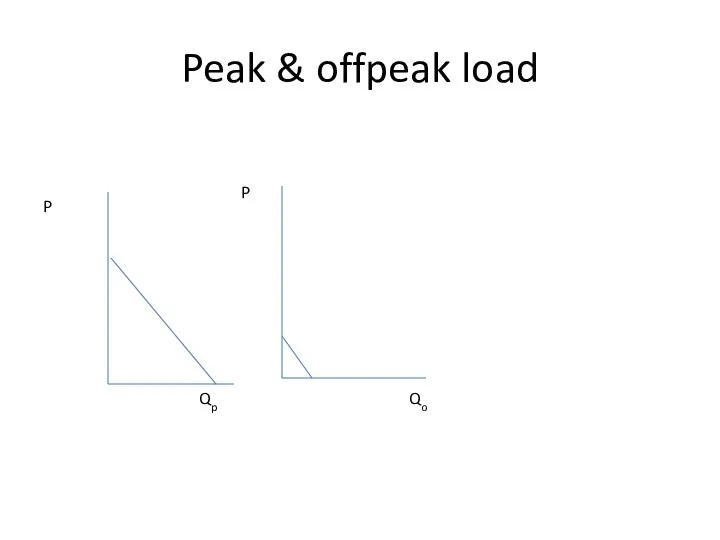
- 29. Peak & offpeak load P P Qp Qo
- 30. Which prices to charge? How to distribute costs among two consumer groups? Fixed cost? ~ “Capital
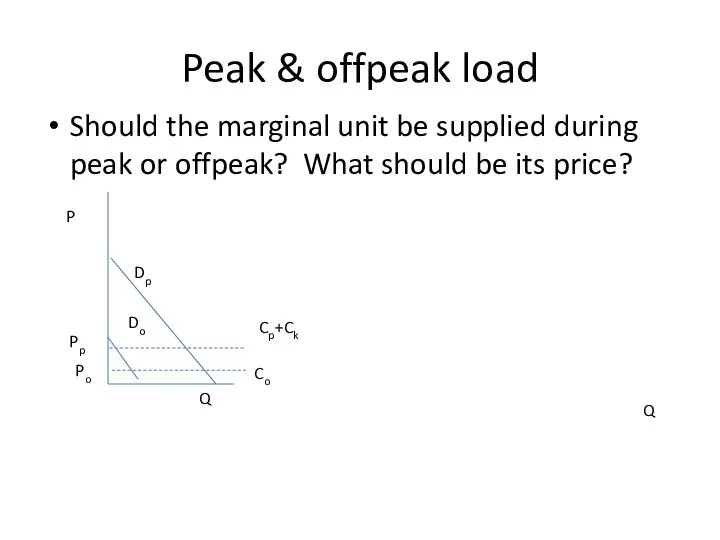
- 31. Peak & offpeak load Should the marginal unit be supplied during peak or offpeak? What should
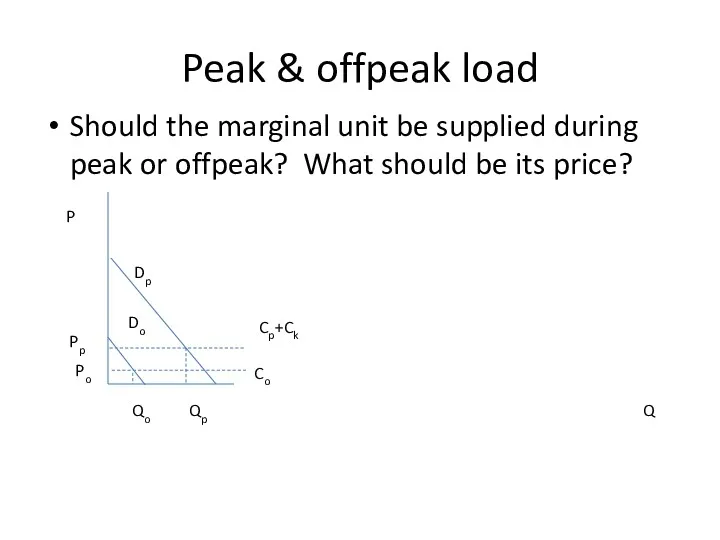
- 32. Peak & offpeak load Should the marginal unit be supplied during peak or offpeak? What should
- 33. Smart meters and differentiating peak & off-peak demand
- 34. Peak-load pricing Electricity prices in Astana: 23:00-7:00 => 3.21 KZT/ kWh 7:00-23:00 => 14.52 KZT/ kWh
- 35. Peak-load pricing Summary Peak-load pricing allows a utility to cover the fixed cost. Peak-load pricing became
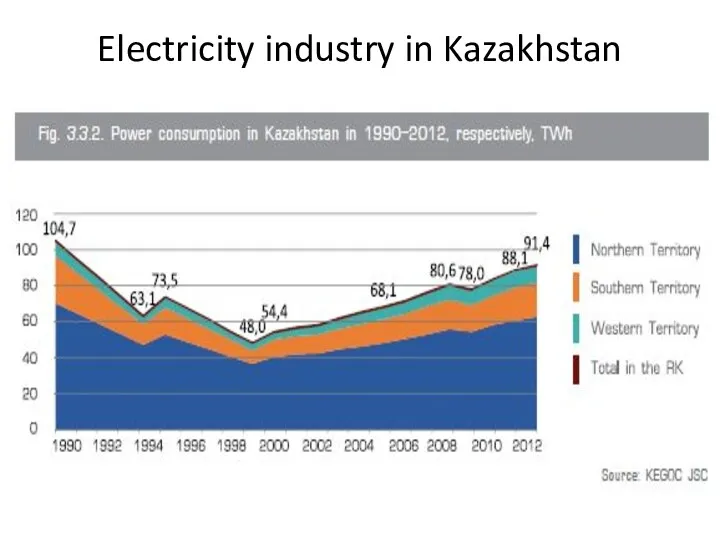
- 36. Electricity industry in Kazakhstan
- 37. Industry structure Generation: mostly privately owned Transmission: KEGOC, state-owned Distribution: 15 regional distribution companies, state/privately owned
- 44. Review Special features Stages of electricity production Production function and costs Natural monopoly Regulation
- 46. Скачать презентацию
















 Экономический анализ. Анализ маркетинговой деятельности предприятия
Экономический анализ. Анализ маркетинговой деятельности предприятия Оборотні кошти підприємства
Оборотні кошти підприємства Единое экономическое пространство
Единое экономическое пространство Роль и место внешней торговли в развитии мировой экономики
Роль и место внешней торговли в развитии мировой экономики Объект и предмет исследования в экономической науке
Объект и предмет исследования в экономической науке Исследование устойчивости функционирования объектов экономики
Исследование устойчивости функционирования объектов экономики Макроэкономическая нестабильность. Инфляция
Макроэкономическая нестабильность. Инфляция Цели и методы государственного регулирования цен в рыночной экономике
Цели и методы государственного регулирования цен в рыночной экономике Конкуренция и монополия
Конкуренция и монополия Россия и Африка: сотрудничество и перспективы развития
Россия и Африка: сотрудничество и перспективы развития World economics: middle-income trap / china
World economics: middle-income trap / china 日本经济
日本经济 Россия в системе международного (мирового) разделения труда
Россия в системе международного (мирового) разделения труда Становление рыночной экономики в современной России
Становление рыночной экономики в современной России The development of economic relations between China and Kyrgyzstan. Сurrent status and controversies
The development of economic relations between China and Kyrgyzstan. Сurrent status and controversies Глобальні проблеми людства
Глобальні проблеми людства Динамика народонаселения в мире и России. Демографические проблемы
Динамика народонаселения в мире и России. Демографические проблемы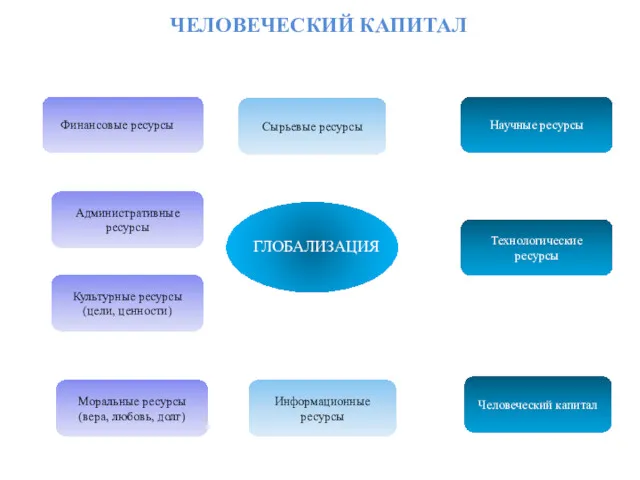 Человеческий капитал
Человеческий капитал Мировая экономика. Экономическая глобализация
Мировая экономика. Экономическая глобализация Ғылыми-техникалық революция және дүниежүзілік шаруашылықтың дамуы
Ғылыми-техникалық революция және дүниежүзілік шаруашылықтың дамуы Экономическая среда бизнеса. Конкуренция в экономической среде бизнеса
Экономическая среда бизнеса. Конкуренция в экономической среде бизнеса Технико-экономический анализ деятельности предприятия. Анализ трудовых ресурсов предприятия
Технико-экономический анализ деятельности предприятия. Анализ трудовых ресурсов предприятия Своя игра Экономика. Обществознание. 11 класс. Часть 2
Своя игра Экономика. Обществознание. 11 класс. Часть 2 Основы поведения субъектов современной рыночной экономики
Основы поведения субъектов современной рыночной экономики Особенности политического и социально-экономического положения развитых государств мира 1940 - 2010 годы
Особенности политического и социально-экономического положения развитых государств мира 1940 - 2010 годы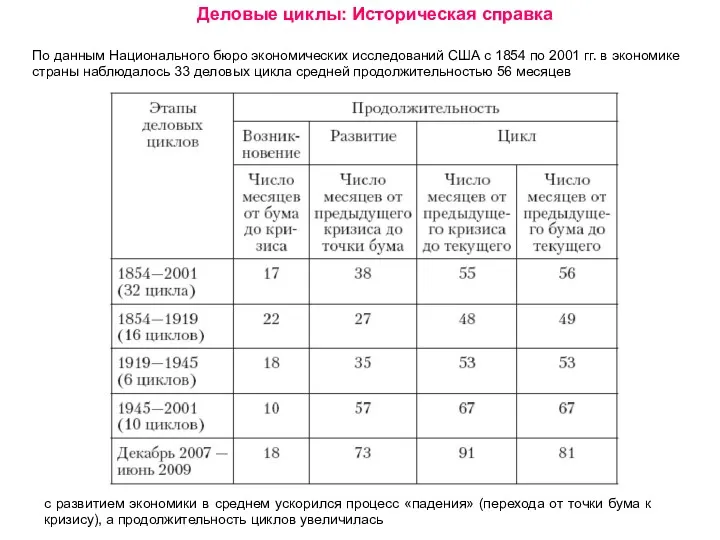 Деловые циклы
Деловые циклы Нормирование труда
Нормирование труда Дорожная карта Healthnet
Дорожная карта Healthnet