Содержание
- 2. Externalities TOPIC OUTLINE Externalities: Basic Concepts Positive Externalities Inefficiency with a Positive Externality Public Policy to
- 3. Externalities Externalities: Basic Concepts
- 4. Externalities Externalities Definition A cost or benefit arising from production that falls on someone other than
- 5. Externalities Externalities Positive externality or external benefit A production or consumption activity that creates an external
- 6. Externalities Positive Externalities
- 7. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES Private Benefits and Social Benefits Marginal private benefit The benefit to the consumer
- 8. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES Private Benefits and Social Benefits Marginal social benefit The marginal benefit enjoyed by
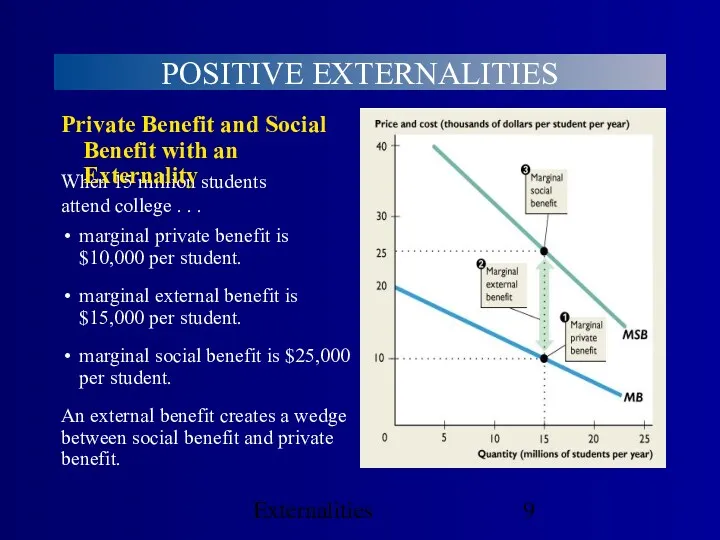
- 9. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES When 15 million students attend college . . . marginal external benefit is
- 10. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES Economic Efficiency with a Positive Externality Market equilibrium is inefficient with a positive
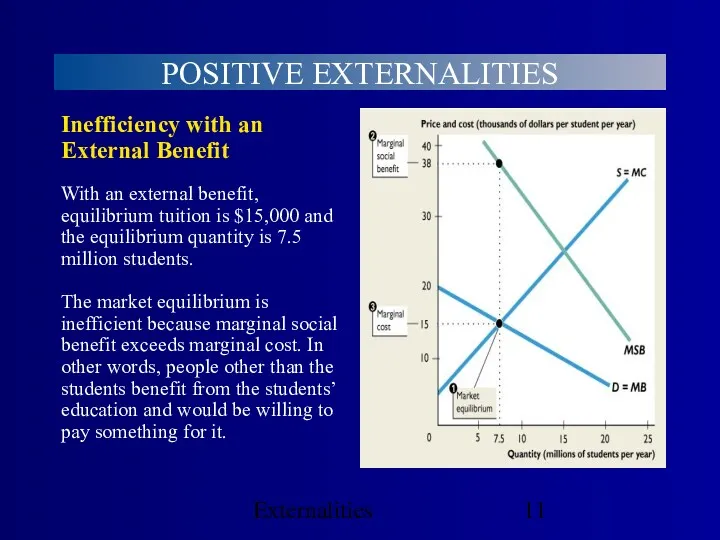
- 11. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES Inefficiency with an External Benefit With an external benefit, equilibrium tuition is $15,000
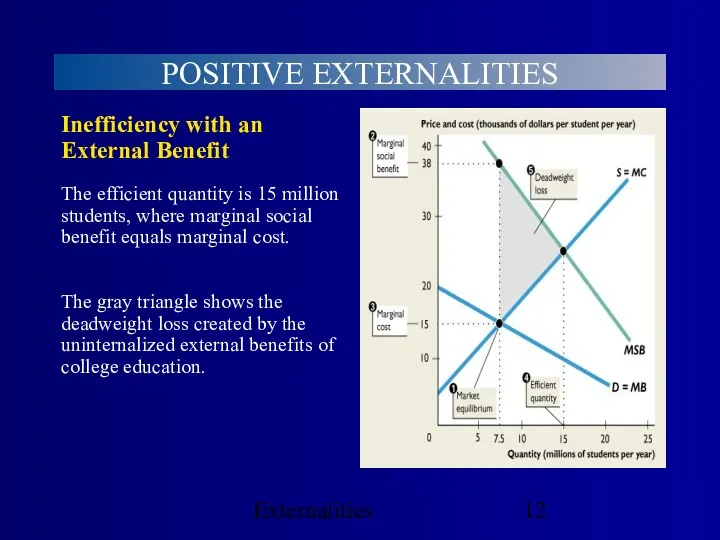
- 12. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES The gray triangle shows the deadweight loss created by the uninternalized external benefits
- 13. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Policy and External Benefits Internalizing an external benefit Internalizing an external benefit
- 14. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Policy and External Benefits Education is an example of a positive externality
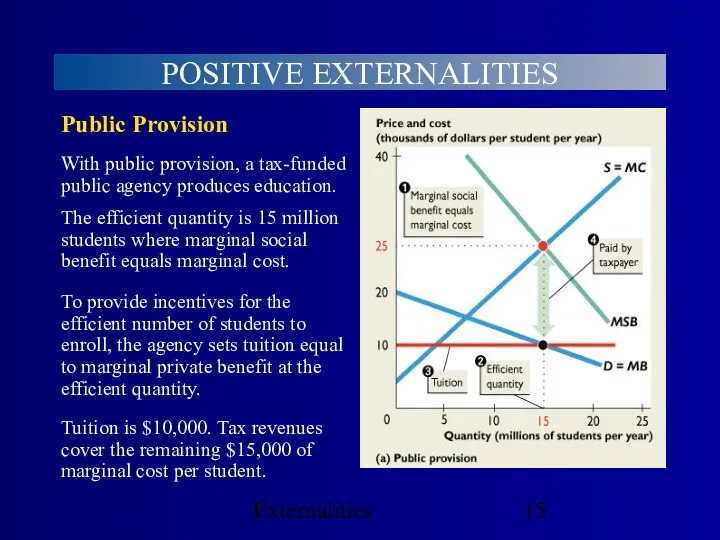
- 15. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Provision To provide incentives for the efficient number of students to enroll,
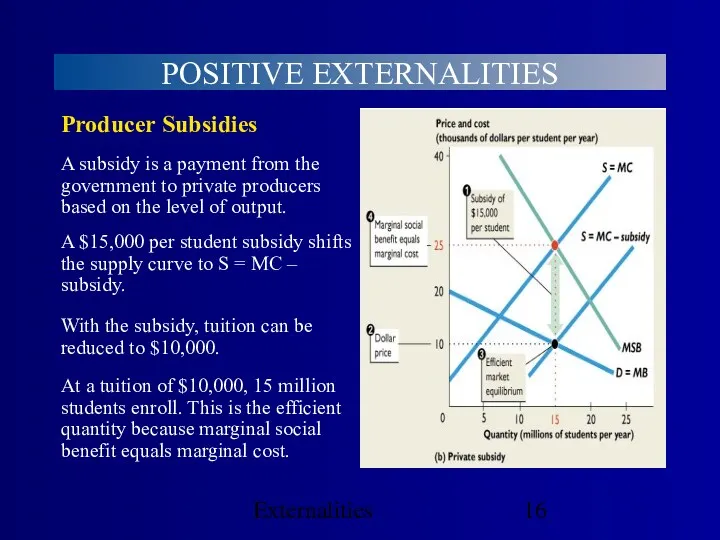
- 16. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES At a tuition of $10,000, 15 million students enroll. This is the efficient
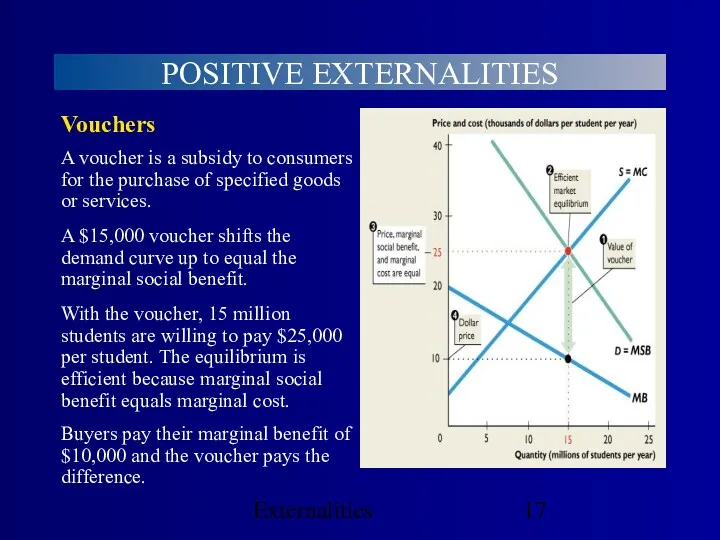
- 17. Externalities POSITIVE EXTERNALITIES Buyers pay their marginal benefit of $10,000 and the voucher pays the difference.
- 18. Externalities Negative Externalities
- 19. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Private Costs and Social Costs Marginal private cost The cost of producing an
- 20. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Private Costs and Social Costs Marginal social cost The marginal cost incurred by
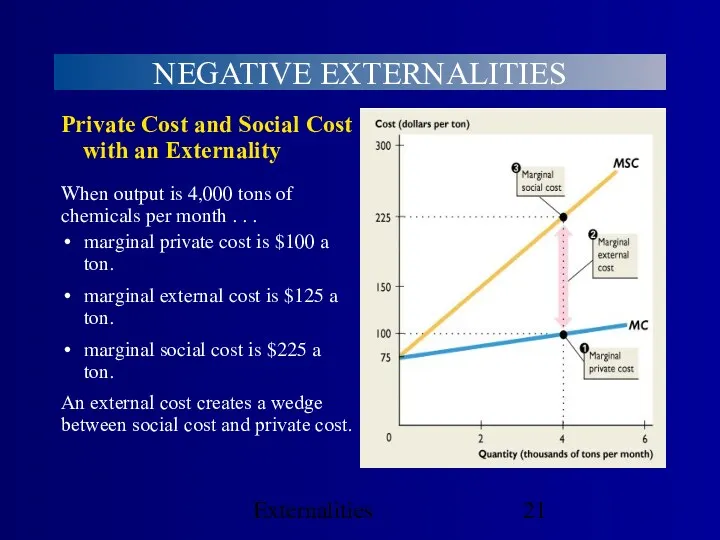
- 21. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Private Cost and Social Cost with an Externality When output is 4,000 tons
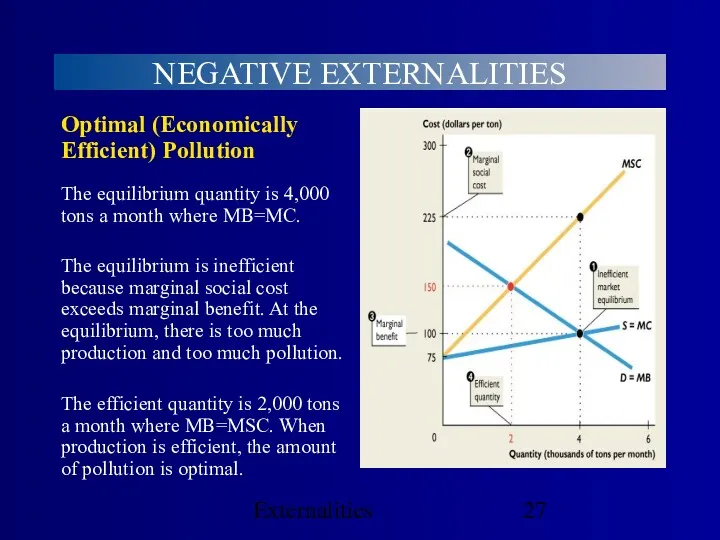
- 22. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Economic Efficiency with a Negative Externality Market equilibrium is inefficient with a negative
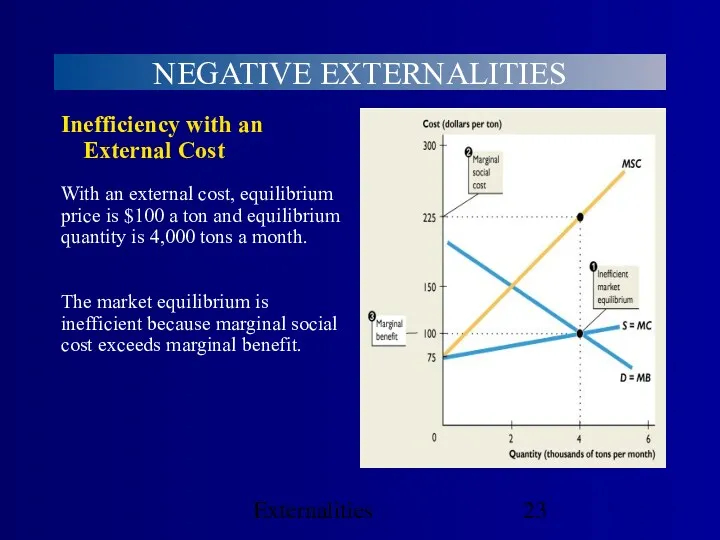
- 23. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES With an external cost, equilibrium price is $100 a ton and equilibrium quantity
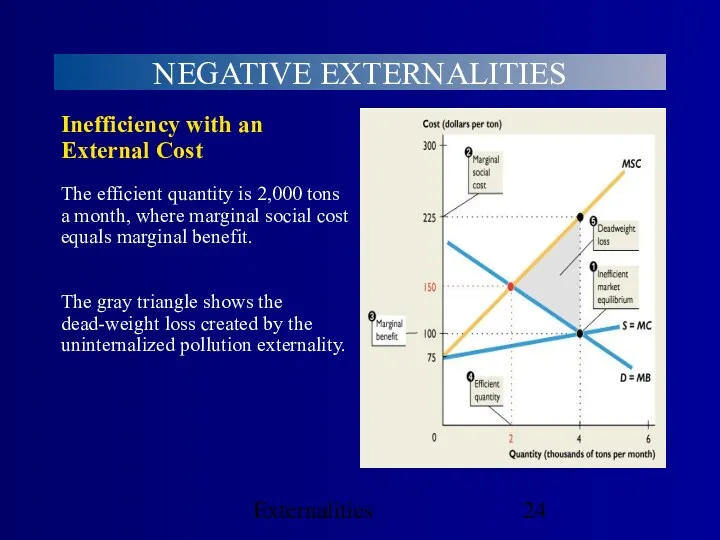
- 24. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES The gray triangle shows the dead-weight loss created by the uninternalized pollution externality.
- 25. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Policy and External Costs Internalizing an external cost Internalizing an external cost
- 26. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Policy and External Costs Pollution is an example of a negative externality
- 27. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES The efficient quantity is 2,000 tons a month where MB=MSC. When production is
- 28. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Policy and External Costs Quasi-market policies to achieve optimal pollution Economists favor
- 29. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Policy and External Costs Marketable permits The optimal amount of pollution in
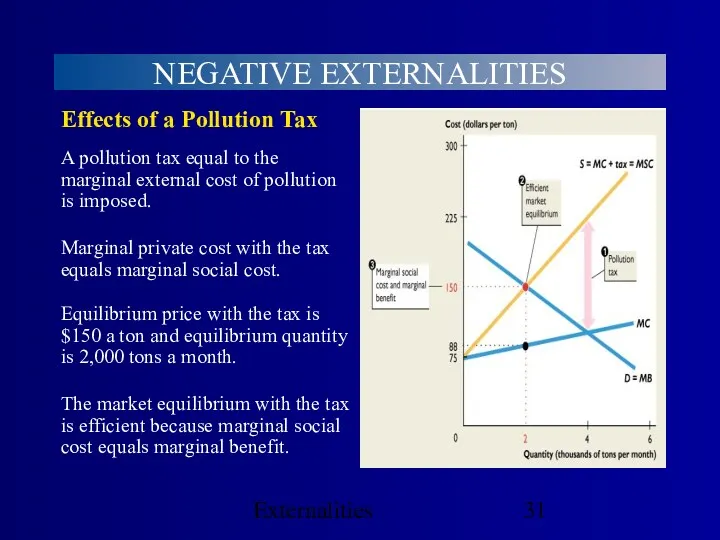
- 30. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Policy and External Costs Emission charges A price charged to polluters per
- 31. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Equilibrium price with the tax is $150 a ton and equilibrium quantity is
- 32. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Policy and External Costs Advantages of quasi-market policies Quasi-market policies are more
- 33. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Public Policy and External Costs Regulation is costly and often inefficient because it
- 34. Externalities NEGATIVE EXTERNALITIES Private Action to Internalize an Externality Private action is an alternative to public
- 35. Externalities Final Observation Not every externality problem is worth solving An uninternalized externality imposes an opportunity
- 36. Externalities Application: Resource Conservation
- 37. Externalities Property Rights and Conservation Private property encourages optimal conservation Many people mistakenly believe that resources
- 38. Externalities Common Property Resources Definition A resource for which rights are held in common by a
- 39. Externalities Common Property Resources Common property rights create uninternalized externalities An individual who refrains from consuming
- 40. Externalities Common Property Resources With common property rights, the benefits from future consumption may be enjoyed
- 41. Externalities APPLICATION: RESOURCE CONSERVATION Externalities and Property Rights Externalities arise when private property rights are absent
- 42. Externalities Externalities and Property Rights Example: Property rights and pollution Suppose polluting factories own a river
- 43. Externalities Externalities and Property Rights Either way, regardless of who owns the river, so long as
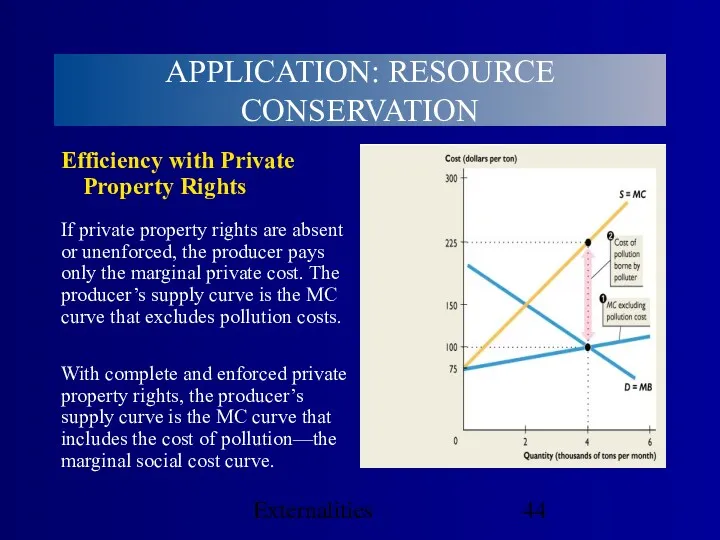
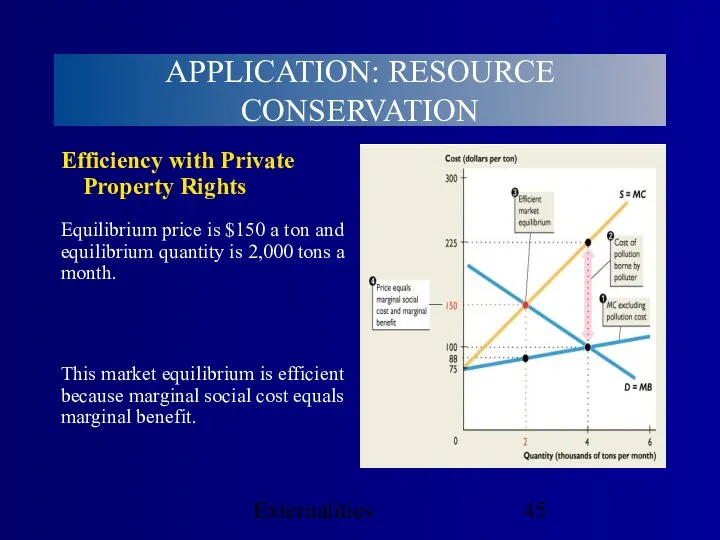
- 44. Externalities Efficiency with Private Property Rights With complete and enforced private property rights, the producer’s supply
- 45. Externalities Efficiency with Private Property Rights Equilibrium price is $150 a ton and equilibrium quantity is
- 46. Externalities Private Property and Optimal Conservation Prices determine the timing of resource consumption The expected future
- 47. Externalities Private Property and Optimal Conservation Prices reflect marginal benefits and marginal costs The value of
- 48. Externalities Private Property and Optimal Conservation Prices provide incentives for optimal conservation Resource owners will conserve
- 49. Externalities Private Property and Optimal Conservation Competitive markets and efficient conservation In competitive markets with private
- 50. Externalities APPLICATION: RESOURCE CONSERVATION Private Property and Resource Depletion Private property rights prevent too rapid depletion
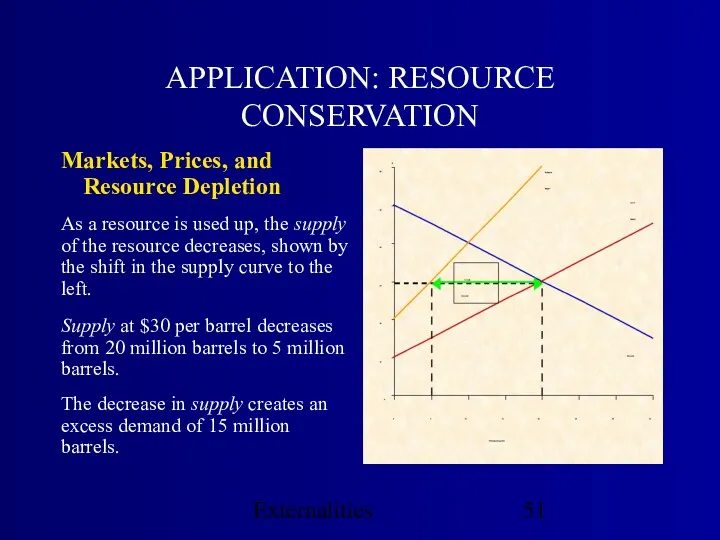
- 51. Externalities APPLICATION: RESOURCE CONSERVATION Markets, Prices, and Resource Depletion As a resource is used up, the
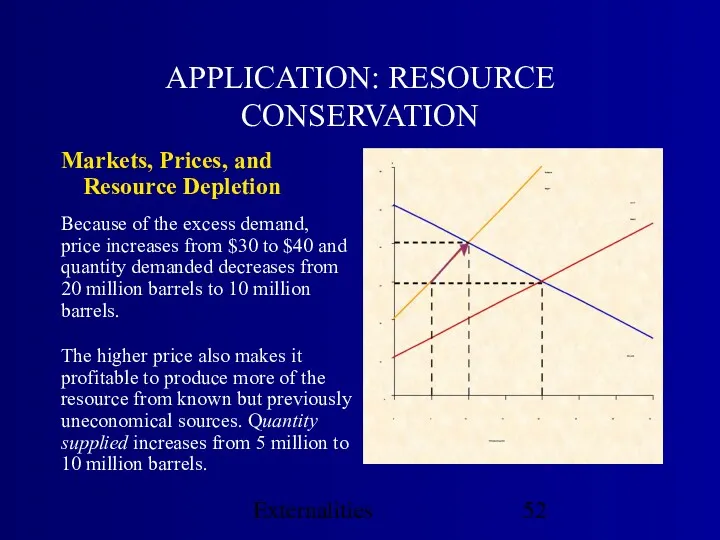
- 52. Externalities APPLICATION: RESOURCE CONSERVATION Markets, Prices, and Resource Depletion The higher price also makes it profitable
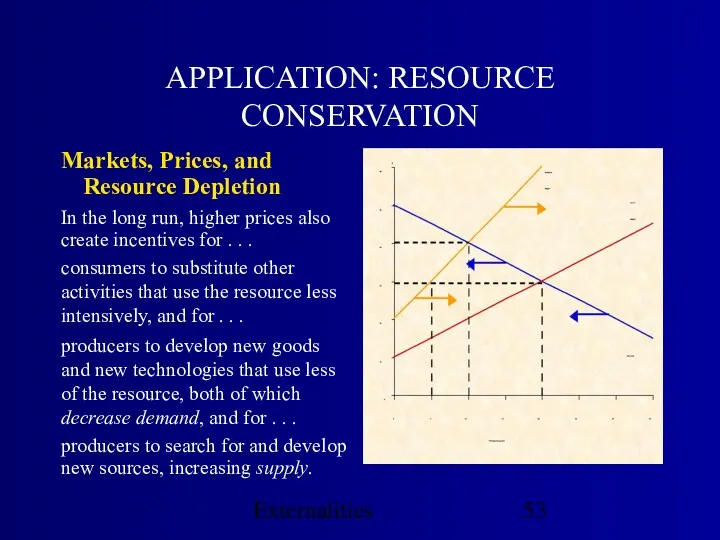
- 53. Externalities APPLICATION: RESOURCE CONSERVATION Markets, Prices, and Resource Depletion In the long run, higher prices also
- 55. Скачать презентацию




































 Сущность денег
Сущность денег Аппаратура для построения и развития мультисервисной транспортной сети связи
Аппаратура для построения и развития мультисервисной транспортной сети связи Основные макроэкономические показатели
Основные макроэкономические показатели Внешние эффекты (экстерналии)
Внешние эффекты (экстерналии) Теории международной торговли
Теории международной торговли Персонал предприятия и оплата труда
Персонал предприятия и оплата труда Инвестиционные процессы в регионе
Инвестиционные процессы в регионе Статистика цен. Задачи статистики цен
Статистика цен. Задачи статистики цен Европейский Союз
Европейский Союз Поведение фирмы на рынке совершенной конкуренции
Поведение фирмы на рынке совершенной конкуренции Прогноз научно-технологического развития России
Прогноз научно-технологического развития России Мировое хозяйство и российская экономика. Мир в постиндустриальной стадии
Мировое хозяйство и российская экономика. Мир в постиндустриальной стадии Алматы облысы Байсерке Агро оқу ғылыми-өндірістік орталығы жағдайында арпа өсіру технологиясының элементтерін жетідіру
Алматы облысы Байсерке Агро оқу ғылыми-өндірістік орталығы жағдайында арпа өсіру технологиясының элементтерін жетідіру Национальная экономика. Система национальных счетов
Национальная экономика. Система национальных счетов Підприємство і підприємництво
Підприємство і підприємництво Географія побуту
Географія побуту Общие черты социально-экономического развития стран Юго-Восточной Азии и их место в мировом хозяйстве
Общие черты социально-экономического развития стран Юго-Восточной Азии и их место в мировом хозяйстве Есть идея!
Есть идея! Специфика и следствия российского монополизма
Специфика и следствия российского монополизма Распределение доходов
Распределение доходов Трудовые ресурсы и оплата труда работников
Трудовые ресурсы и оплата труда работников Сущность, формы проявления и причины инфляции, ее социально-экономические последствия
Сущность, формы проявления и причины инфляции, ее социально-экономические последствия Глобальные проблемы современности
Глобальные проблемы современности О реализации региональных проектов национальной программы Цифровая экономика Российской Федерации в Ульяновской области
О реализации региональных проектов национальной программы Цифровая экономика Российской Федерации в Ульяновской области Экономика Республики Беларусь. Общая характеристика
Экономика Республики Беларусь. Общая характеристика Экономика предприятия
Экономика предприятия Сферы деятельности и приоритеты Европейского союза
Сферы деятельности и приоритеты Европейского союза Що таке трипартизм?
Що таке трипартизм?