Содержание
- 2. Plan The essence and the basic aspects of globalization. The driving forces of globalization and its
- 3. Definitions of globalization: "the compression of the world and the intensification of the consciousness of the
- 4. Globalization - a process of strengthening the relationship of the national economies of the world, which
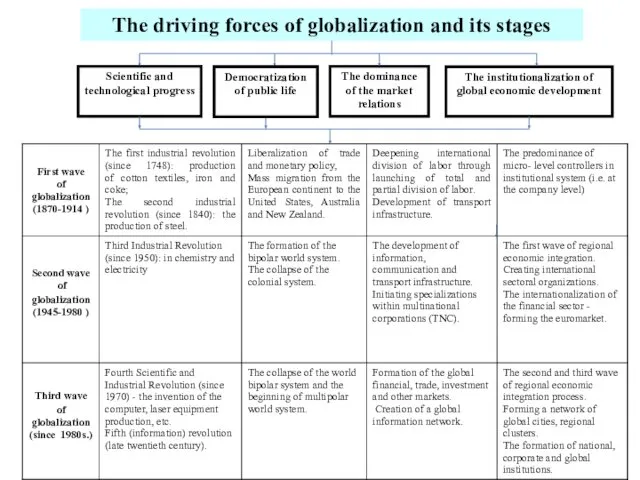
- 5. Scientific and technological progress The dominance of the market relations The institutionalization of global economic development
- 6. The impact of globalization on the development of national economies Formation of global regulatory system Globalization
- 7. Scholars separately defined economic, technological, political, cultural and social globalization: economic globalization - the institutionalization of
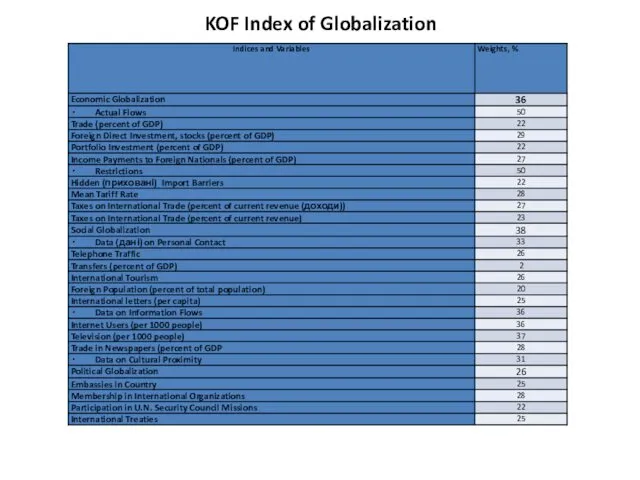
- 8. The KOF Index of Globalization measures the three main dimensions of globalization: economic globalization is characterized
- 9. KOF Index of Globalization
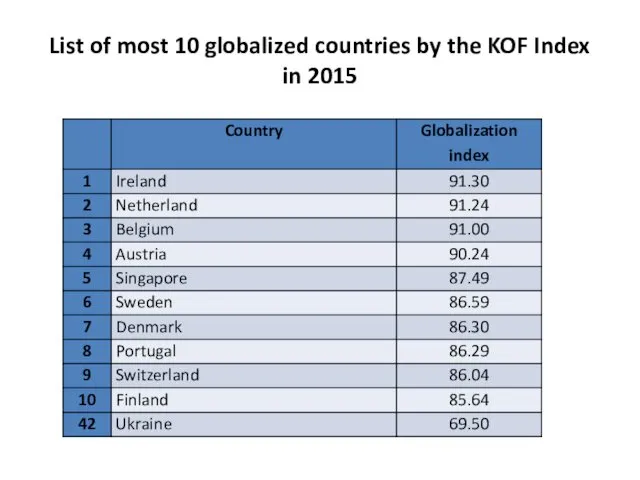
- 10. List of most 10 globalized countries by the KOF Index in 2015
- 11. Economies by size of merchandise trade in 2013
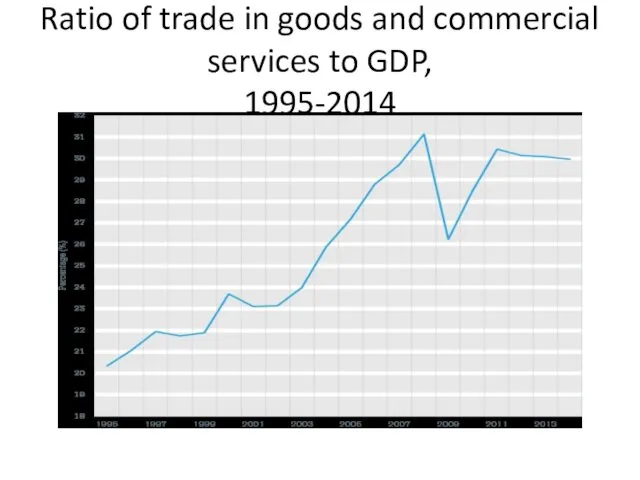
- 13. Ratio of trade in goods and commercial services to GDP, 1995-2014
- 14. China has become the world’s leading exporter China overtook Japan as the leading Asian exporter in
- 15. China, United States and Germany are top three merchandise traders China became the world’s biggest merchandise
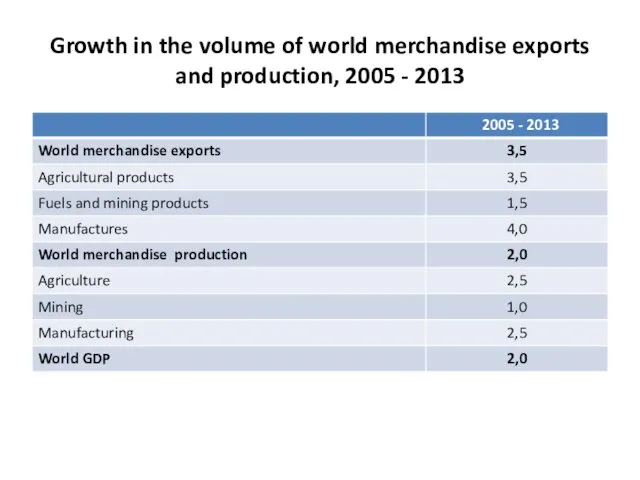
- 16. Growth in the volume of world merchandise exports and production, 2005 - 2013
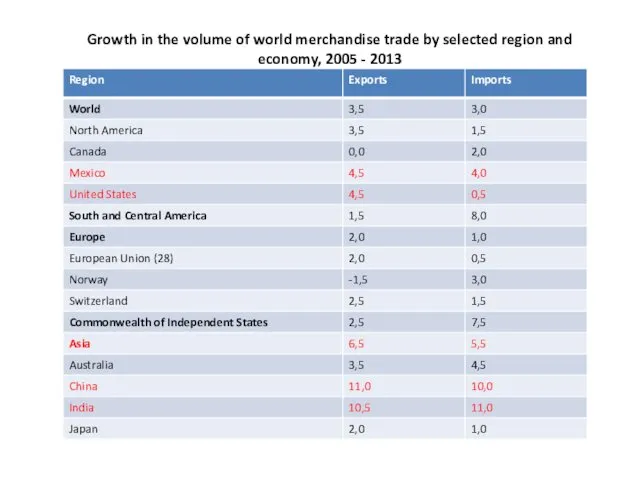
- 17. Growth in the volume of world merchandise trade by selected region and economy, 2005 - 2013
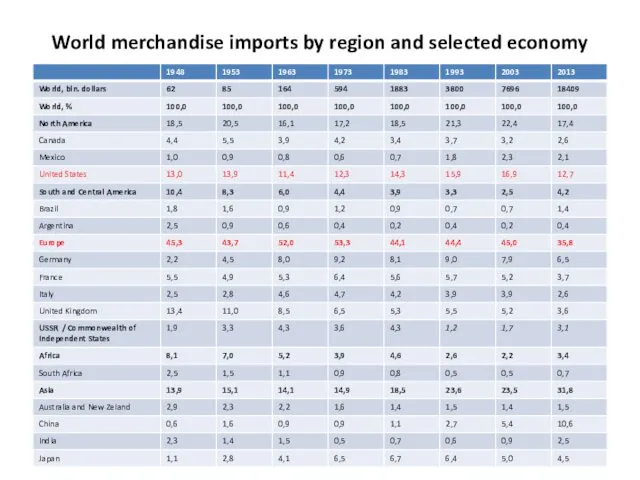
- 18. World merchandise imports by region and selected economy
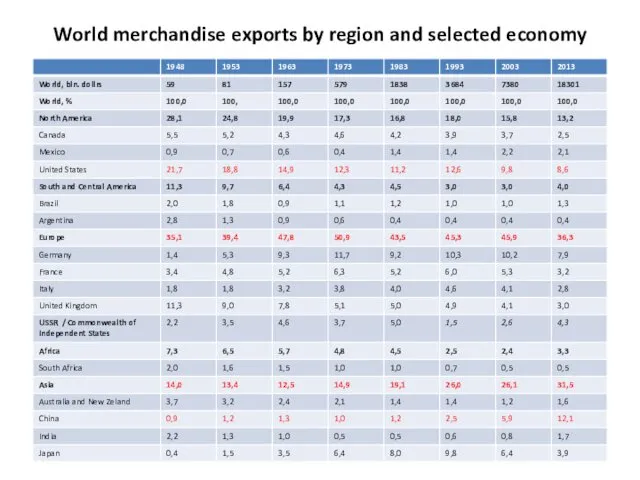
- 19. World merchandise exports by region and selected economy
- 20. Real GDP of leading countries and Ukraine in 2013
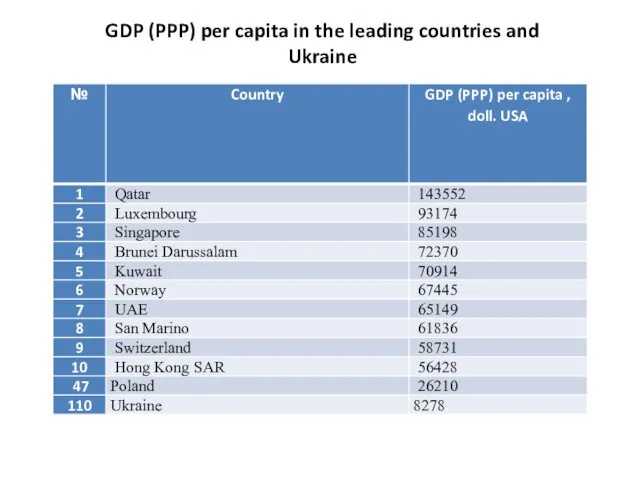
- 21. GDP (PPP) per capita in the leading countries and Ukraine
- 22. Structure of world GDP by region of the world
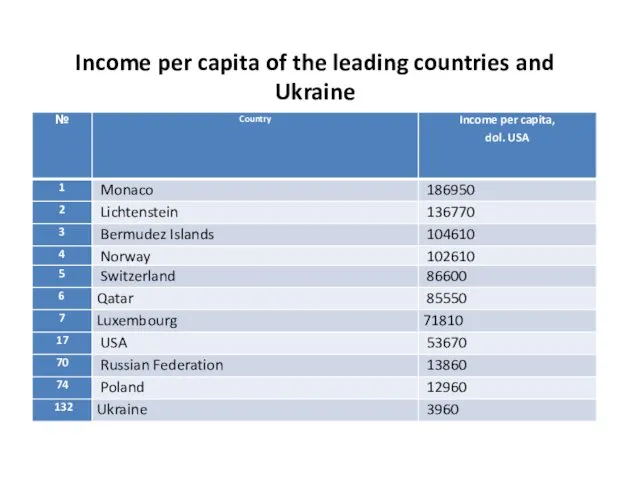
- 23. Income per capita of the leading countries and Ukraine
- 24. Human development index (HDI) is a composite statistic of life expectancy, education, and per capita income
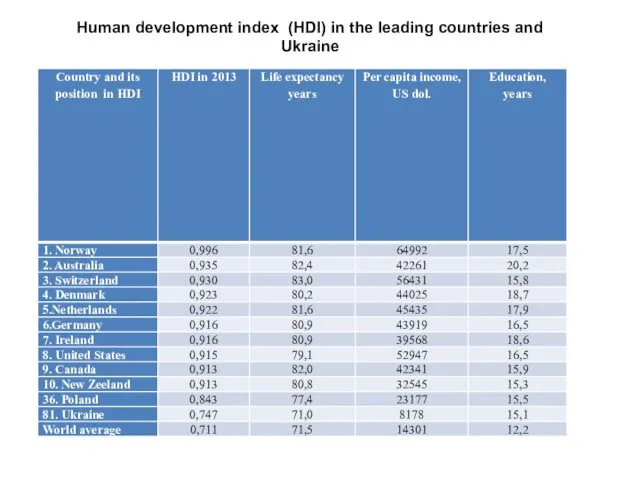
- 25. Human development index (HDI) in the leading countries and Ukraine
- 26. “Institutions are the “rules of the game” in society or, more formally, are the humanly devised
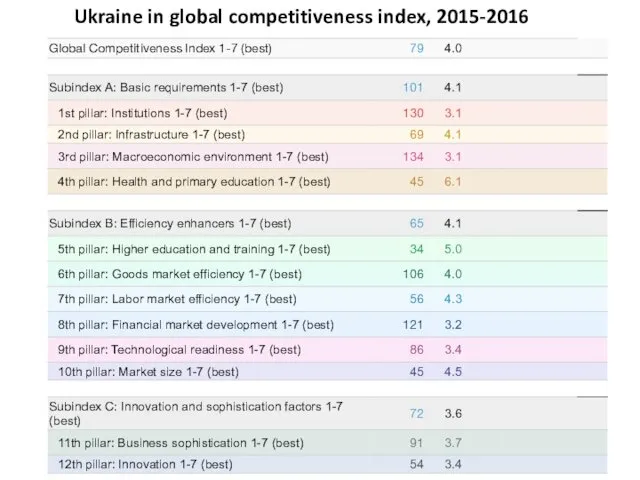
- 27. Ukraine in global competitiveness index, 2015-2016
- 28. Сurrent global economic problems Trade protectionism in advanced countries in a rapidly globalizing world. Excessive fluctuations
- 29. International economic integration is a process where the economic barriers between two or more economies are
- 30. Forms of international economic integration
- 32. Скачать презентацию

















 Система национальных счетов (СНС) и макроэкономические показатели
Система национальных счетов (СНС) и макроэкономические показатели Основы институционально-экономической теории. (Лекция 6)
Основы институционально-экономической теории. (Лекция 6) Информатизация экономического пространства ЕАЭС
Информатизация экономического пространства ЕАЭС Макроэкономические аспекты международной энергетики
Макроэкономические аспекты международной энергетики механизмы рынка. Тема 3-4
механизмы рынка. Тема 3-4 Макроэкономикалық көрсеткіш
Макроэкономикалық көрсеткіш Статус территории опережающего социально-экономического развития
Статус территории опережающего социально-экономического развития Особенности потребительского рынка Росии
Особенности потребительского рынка Росии Экономические циклы
Экономические циклы Теория предельных предельных продуктов и микроэкономическая модель предприятия. Издержки производства и прибыль
Теория предельных предельных продуктов и микроэкономическая модель предприятия. Издержки производства и прибыль Формы интеграционных объединений
Формы интеграционных объединений Национальный проект Производительность труда
Национальный проект Производительность труда Анализ социально-экономических показателей тверской области
Анализ социально-экономических показателей тверской области Закон убывающей предельной полезности
Закон убывающей предельной полезности Дальневосточный федеральный округ
Дальневосточный федеральный округ Государственное регулирование деятельности российских энергетических предприятий
Государственное регулирование деятельности российских энергетических предприятий Платежи при недропользовании в РФ
Платежи при недропользовании в РФ Региональная экономика
Региональная экономика Движение мирового капитала
Движение мирового капитала Региональная политика США
Региональная политика США Развитие РФ. Прогноз развития отраслей реального сектора экономики
Развитие РФ. Прогноз развития отраслей реального сектора экономики Підприємство в соціально-орієнтованій ринковій економіці
Підприємство в соціально-орієнтованій ринковій економіці Инфляция: причины и измерение. Виды инфляции
Инфляция: причины и измерение. Виды инфляции Деятельность в области стандартизации
Деятельность в области стандартизации ОСНОВНЫЕ ПРОИЗВОДСТВЕННЫЕ ФОНДЫ
ОСНОВНЫЕ ПРОИЗВОДСТВЕННЫЕ ФОНДЫ Экономика отраслевых рынков
Экономика отраслевых рынков Внешне-экономические отношения России и Австралии
Внешне-экономические отношения России и Австралии Единое экономическое пространство
Единое экономическое пространство