Содержание
- 2. Topics in Macroeconomics WIUT Teaching Week 11 Presenter: Bilol Buzurukov MODULE
- 3. Seminar 10 The Financial System: Opportunities and Dangers
- 4. Financial Crisis: Case 1 Mexican Financial Crisis 1994-1995
- 5. Discussion 1 1994 – 1 peso = 30 cents 1995 – 1 peso = 16 cents
- 6. Discussion 2 Luis Donaldo Colosio’s Assassination (March 1994) Chiapas Conflict 1994 Zapatista Uprising Mexican political future
- 7. Discussion 3 What do you think? Why the risk premium did not effect the value of
- 8. Discussion 5 Mexico’s foreign-currency reserves were too small to maintain its fixed exchange rate; At the
- 9. Discussion 6 How was Mexican government able to recover from 1994-1995 Financial Crisis? What were the
- 10. Financial Crisis: Case 2 Asian Financial Crisis 1997-1998
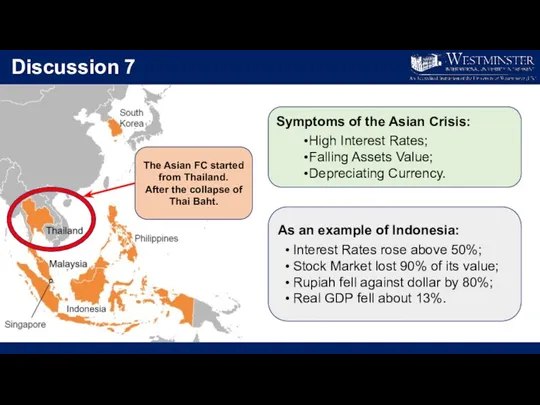
- 11. Discussion 7 Symptoms of the Asian Crisis: High Interest Rates; Falling Assets Value; Depreciating Currency. As
- 12. Discussion 8 What sparked the Asian Financial Crisis? The problem began in the Asian banking system:
- 13. Discussion 9 Asian banks extended loans to those with the most political clout rather than to
- 14. Discussion 10 How were Asian countries able to overcome the crisis? The IMF and the US
- 15. Discussion 11 Watch the video! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nZccen3yMxE How robust was the economy of Argentina in the last
- 16. Financial Crisis: Case 3 Great Depression 1930’s
- 17. Discussion 12 The Great depression was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th
- 18. Discussion 13 The Great Depression had devastating effects in countries both rich and poor. Personal income,
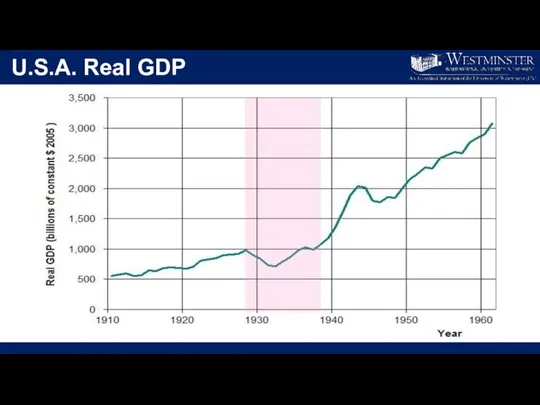
- 19. U.S.A. Real GDP
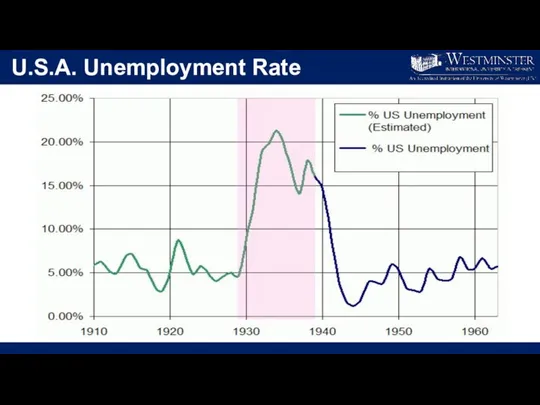
- 20. U.S.A. Unemployment Rate
- 21. Financial Crisis: Case 4 Great Recession 2008-2009
- 22. Discussion 14 How did everything start? Federal Reserve lowered interest rates to historically low levels in
- 23. Discussion 15 What is MORTGAGE? It is a form of debt created to finance investment in
- 24. Discussion 16 What was the reason behind encouraging high-risk lending by the government? Make homeownership more
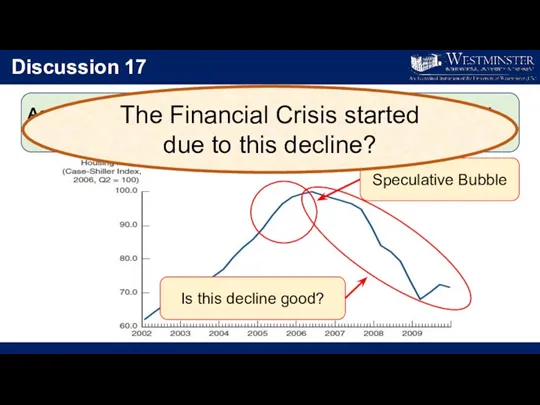
- 25. Discussion 17 As a result of the government’s support, housing demand and housing prices dramatically increased.
- 26. Discussion 18 When housing prices declined, the homeowners were underwater; The homeowners owed more on their
- 27. Discussion 19 How was the US government able to unfold the financial crisis problem? In September
- 28. Discussion 20 Asset-Price Booms and Bursts ANATOMY OF A CRISIS Insolvencies at Financial Institutions Falling Confidence
- 29. Practice Exercise 1
- 30. Practice Exercise 2
- 31. References Mankiw, G. (2013). Macroeconomics. 8th edition. Houndmills: Palgrave Macmillan. Pages: 567-587; 373-374; 374-375; 346-347. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Depression
- 33. Скачать презентацию


























 Стратегия развития информационного общества
Стратегия развития информационного общества Экономика отрасли
Экономика отрасли Стратегиялық жоспардың иерархиялық құрылымы
Стратегиялық жоспардың иерархиялық құрылымы Циклический характер экономического развития
Циклический характер экономического развития История экономической мысли
История экономической мысли Научно-техническая революция. Гуманитарные аспекты общественно-политического развития
Научно-техническая революция. Гуманитарные аспекты общественно-политического развития Экономикалық теория пәні және әдісі
Экономикалық теория пәні және әдісі The main directions of economic policy
The main directions of economic policy Классификация инвестиций по разным признакам. Структура инвестиционного рынка России. (Тема 2)
Классификация инвестиций по разным признакам. Структура инвестиционного рынка России. (Тема 2) Электронные финансовые и фондовые рынки
Электронные финансовые и фондовые рынки Определение оптимального объема производства: микроэкономический аспект
Определение оптимального объема производства: микроэкономический аспект Разрешение споров в ВТО
Разрешение споров в ВТО Макроэкономическая нестабильность: безработица и инфляция
Макроэкономическая нестабильность: безработица и инфляция Альтернативные источники энергии
Альтернативные источники энергии Основные сферы жизни общества
Основные сферы жизни общества Виды конкуренции и их роль
Виды конкуренции и их роль Державне регулювання економіки та зовнішньоекономічна діяльність
Державне регулювання економіки та зовнішньоекономічна діяльність Макроэкономическое равновесие в Модель AD – AS
Макроэкономическое равновесие в Модель AD – AS Droit de l’union europeene
Droit de l’union europeene Методы экономического анализа
Методы экономического анализа Семинар на тему Дж.М. Кейнс и его работа Общая теория занятости, процента и денег
Семинар на тему Дж.М. Кейнс и его работа Общая теория занятости, процента и денег Методические указания по выполнению курсовой работы по дисциплине экономика отрасли
Методические указания по выполнению курсовой работы по дисциплине экономика отрасли Система національних рахунків (СНР), як інструмент оцінки та аналізу економічних явищ і процесів. (Тема 3)
Система національних рахунків (СНР), як інструмент оцінки та аналізу економічних явищ і процесів. (Тема 3) Сучасні принципи розвитку міст та учасницькі практики
Сучасні принципи розвитку міст та учасницькі практики Development economics (market economy formation models)
Development economics (market economy formation models) Государственное регулирование предпринимательства
Государственное регулирование предпринимательства Инфляция в России. Причины, социально-экономические последствия, методы снижения
Инфляция в России. Причины, социально-экономические последствия, методы снижения Предмет и метод микроэкономики. Принципы и законы экономики
Предмет и метод микроэкономики. Принципы и законы экономики